Anastrozole
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION RECENT MAJOR CHANGESContraindications – Premenopausal Women and Pregnancy ( 4.1, 8.1) 01/2010Warnings and Precautions- Ischemic Cardiovascular Events ( 5.1, 6.1) 01/2010INDICATIONS AND USAGEAnastrozole tablets are an aromatase inhibitor indicated for:• Adjuvant treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer ( 1.1)• First-line treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive or hormone receptor unknown locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer ( 1.2)• Treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women with disease progression following tamoxifen therapy. Patients with ER-negative disease and patients who did not respond to previous tamoxifen therapy rarely responded to anastrozole tablets ( 1.3)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONOne 1 mg tablet taken once daily ( 2.1)DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS1 mg tablets ( 3)CONTRAINDICATIONS• Women of premenopausal endocrine status, including pregnant women ( 4.1, 8.1)• Patients with demonstrated hypersensitivity to anastrozole tablets or any excipient ( 4.2)WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS• In women with pre-existing ischemic heart disease, an increased incidence of ischemic cardiovascular events occurred with anastrozole tablets use compared to tamoxifen use. Consider risks and benefits. ( 5.1, 6.1)• Decreases in bone mineral density may occur. Consider bone mineral density monitoring. ( 5.2, 6.1)• Increases in total cholesterol may occur. Consider cholesterol monitoring. ( 5.3, 6.1)Side Effects To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. In the early breast cancer (ATAC) study, the most common (occurring with an incidence of >10%) side effects occurring in women taking anastrozole tablets included: hot flashes, asthenia, arthritis, pain, arthralgia, pharyngitis, hypertension, depression, nausea and vomiting, rash, osteoporosis, fractures, back pain, insomnia, headache, peripheral edema and lymphedema, regardless of causality. ( 6.1)In the advanced breast cancer studies, the most common (occurring with an incidence of >10%) side effects occurring in women taking anastrozole tablets included: hot flashes, nausea, asthenia, pain, headache, back pain, bone pain, increased cough, dyspnea, pharyngitis and peripheral edema. ( 6.1)DRUG INTERACTIONS• Tamoxifen: Do not use in combination with anastrozole tablets. No additional benefit seen over tamoxifen monotherapy ( 7.1, 14.1).• Estrogen-containing products: Combination use may diminish activity of anastrozole tablets ( 7.2).USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS• Pediatric patients: Efficacy has not been demonstrated for pubertal boys of adolescent age with gynecomastia or girls with McCune-Albright Syndrome and progressive precocious puberty. ( 8.4)See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA approved Patient Labeling.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
_________________________________________________________________________________
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Adjuvant Treatment
1.2 First-Line Treatment
1.3 Second-Line Treatment
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dose
2.2 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Pregnancy and Premenopausal Women
4.2 Hypersensitivity
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Ischemic Cardiovascular Events
5.2 Bone Effects
5.3 Cholesterol
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Adjuvant Therapy
First-Line Therapy
Second-Line Therapy
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Tamoxifen
7.2 Estrogen
7.3 Warfarin
7.4 Cytochrome P450
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10
OVERDOSAGE
11
DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Pharmacology and/or Toxicology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer in Postmenopausal Women
14.2 First-Line Therapy in Postmenopausal Women with Advanced Breast Cancer
14.3 Second-Line Therapy in Postmenopausal Women with Advanced Breast Cancer who had Disease Progression following Tamoxifen Therapy
16
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Storage:
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Pregnancy
17.2 Allergic (Hypersensitivity) Reactions
17.3 Ischemic Cardiovascular Events
17.4 Bone Effects
17.5 Cholesterol
17.6 Tamoxifen
17.7 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
* Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed
_________________________________________________________________________________
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1. INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1. Adjuvant Treatment
Anastrozole tablets are indicated for adjuvant treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer.
1.2. First-Line Treatment
Anastrozole tablets are indicated for the first-line treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive or hormone receptor unknown locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
1.3. Second-Line Treatment
Anastrozole tablets are indicated for the treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women with disease progression following tamoxifen therapy. Patients with ER-negative disease and patients who did not respond to previous tamoxifen therapy rarely responded to anastrozole tablets.
2. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1. Recommended Dose
The dose of anastrozole tablets are one 1 mg tablet taken once a day. For patients with advanced breast cancer, anastrozole tablets should be continued until tumor progression. Anastrozole tablets can be taken with or without food.
For adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer in postmenopausal women, the optimal duration of therapy is unknown. In the ATAC trial anastrozole tablets were administered for five years. [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]
No dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with renal impairment or for elderly patients. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]
2.2. Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No changes in dose are recommended for patients with mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment. Anastrozole tablets have not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)]
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
The tablets are white, biconvex, film-coated containing 1 mg of anastrozole. The tablets are debossed with “AN” and “1” on one side and plain surface on the other side.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1. Pregnancy and Premenopausal Women
Anastrozole tablets may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman and offers no clinical benefit to premenopausal women with breast cancer. Anastrozole tablets are contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. There are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women using anastrozole tablets. If anastrozole tablets are used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to a fetus or potential risk for loss of the pregnancy. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
4.2. Hypersensitivity
Anastrozole tablets are contraindicated in any patient who has shown a hypersensitivity reaction to the drug or to any of the excipients. Observed reactions include anaphylaxis, angioedema, and urticaria. [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1. Ischemic Cardiovascular Events
In women with pre-existing ischemic heart disease, an increased incidence of ischemic cardiovascular events was observed with anastrozole tablets in the ATAC trial (17% of patients on anastrozole tablets and 10% of patients on tamoxifen). Consider risk and benefits of anastrozole tablets therapy in patients with pre-existing ischemic heart disease. [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
5.2. Bone Effects
Results from the ATAC trial bone substudy at 12 and 24 months demonstrated that patients receiving anastrozole tablets had a mean decrease in both lumbar spine and total hip bone mineral density (BMD) compared to baseline. Patients receiving tamoxifen had a mean increase in both lumbar spine and total hip BMD compared to baseline [see Adverse Reactions, (6.1)].
5.3. Cholesterol
During the ATAC trial, more patients receiving anastrozole tablets were reported to have elevated serum cholesterol compared to patients receiving tamoxifen (9% versus 3.5%, respectively) [see Adverse Reactions, (6.1)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Serious adverse reactions with anastrozole tablets occurring in less than 1 in 10,000 patients, are: 1) skin reactions such as lesions, ulcers, or blisters; 2) allergic reactions with swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and/or throat. This may cause difficulty in swallowing and/or breathing; and 3) changes in blood tests of the liver function, including inflammation of the liver with symptoms that may include a general feeling of not being well, with or without jaundice, liver pain or liver swelling [see Adverse Reactions, (6.2)].
Common adverse reactions (occurring with an incidence of >10%) in women taking anastrozole tablets included: hot flashes, asthenia, arthritis, pain, arthralgia, pharyngitis, hypertension, depression, nausea and vomiting, rash, osteoporosis, fractures, back pain, insomnia, pain, headache, bone pain, peripheral edema, increased cough, dyspnea, pharyngitis and lymphedema.
In the ATAC trial, the most common reported adverse reaction (>0.1%) leading to discontinuation of therapy for both treatment groups was hot flashes, although there were fewer patients who discontinued therapy as a result of hot flashes in the anastrozole tablets group.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Adjuvant Therapy
Adverse reaction data for adjuvant therapy are based on the ATAC trial [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The median duration of adjuvant treatment for safety evaluation was 59.8 months and 59.6 months for patients receiving anastrozole tablets 1 mg and tamoxifen 20 mg, respectively.
Adverse reactions occurring with an incidence of at least 5% in either treatment group during treatment or within 14 days of the end of treatment are presented in Table 1.
| Body system and adverse reactions by COSTART† preferred term ‡ |
Anastrozole tablets 1mg (N § = 3092) |
Tamoxifen 20mg (N § = 3094) |
| Body as a whole
Asthenia Pain Back pain Headache Abdominal pain Infection Accidental injury Flu syndrome Chest pain Neoplasm Cyst Cardiovascular Vasodilatation Hypertension Digestive Nausea Constipation Diarrhea Dyspepsia Gastrointestinal disorder Hemic and lymphatic Lymphedema Anemia Metabolic and nutritional Peripheral edema Weight gain Hypercholesterolemia Musculoskeletal Arthritis Arthralgia Osteoporosis Fracture Bone pain Arthrosis Joint Disorder Myalgia Nervous system Depression Insomnia Dizziness Anxiety Paresthesia Respiratory Pharyngitis Cough increased Dyspnea Sinusitis Bronchitis Skin and appendages Rash Sweating Special Senses Cataract Specified Urogenital Leukorrhea Urinary tract infection Breast pain Breast Neoplasm Vulvovaginitis Vaginal Hemorrhage¶ Vaginitis |
575 (19) 533 (17) 321 (10) 314 (10) 271 (9) 285 (9) 311 (10) 175 (6) 200 (7) 162 (5) 138 (5) 1104 (36) 402 (13) 343 (11) 249 (8) 265 (9) 206 (7) 210 (7) 304 (10) 113 (4) 311 (10) 285 (9) 278 (9) 512 (17) 467 (15) 325 (11) 315 (10) 201 (7) 207 (7) 184 (6) 179 (6) 413 (13) 309 (10) 236 (8) 195 (6) 215 (7) 443 (14) 261 (8) 234 (8) 184 (6) 167 (5) 333 (11) 145 (5) 182 (6) 86 (3) 244 (8) 251 (8) 164 (5) 194 (6) 122 (4) 125 (4) |
544 (18) 485 (16) 309 (10) 249 (8) 276 (9) 276 (9) 303 (10) 195 (6) 150 (5) 144 (5) 162 (5) 1264 (41) 349 (11) 335 (11) 252 (8) 216 (7) 169 (6) 158 (5) 341 (11) 159 (5) 343 (11) 274 (9) 108 (3.5) 445 (14) 344 (11) 226 (7) 209 (7) 185 (6) 156 (5) 160 (5) 160 (5) 382 (12) 281 (9) 234 (8) 180 (6) 145 (5) 422 (14) 287 (9) 237 (8) 159 (5) 153 (5) 387 (13) 177 (6) 213 (7) 286 (9) 313 (10) 169 (6) 139 (5) 150 (5) 180 (6) 158 (5) |
Certain adverse reactions and combinations of adverse reactions were prospectively specified for analysis, based on the known pharmacologic properties and side effect profiles of the two drugs (see Table 2).
| |
Anastrozole tablets N=3092 (%) |
Tamoxifen N=3094(%) |
Odds-ratio
|
95% CI
|
| Hot Flashes Musculoskeletal Events† Fatigue/Asthenia Mood Disturbances Nausea and Vomiting All Fractures Fractures of Spine, Hip, or Wrist Wrist/Colles’ fractures Spine fractures Hip fractures Cataracts Vaginal Bleeding Ischemic Cardiovascular Disease Vaginal Discharge Venous Thromboembolic events Deep Venous Thromboembolic Events Ischemic Cerebrovascular Event Endometrial Cancer‡ |
1104 (36) 1100 (36) 575 (19) 597 (19) 393 (13) 315 (10) 133 (4) 67 (2) 43 (1) 28 (1) 182 (6) 167 (5) 127 (4) 109 (4) 87 (3) 48 (2) 62 (2) 4 (0.2) |
1264(41) 911 (29) 544 (18) 554 (18) 384 (12) 209 (7) 91 (3) 50 (2) 22 (1) 26 (1) 213 (7) 317 (10) 104 (3) 408 (13) 140 (5) 74 (2) 88 (3) 13 (0.6) |
0.80 1.32 1.07 1.10 1.03 1.57 1.48 0.85 0.50 1.23 0.24 0.61 0.64 0.70 0.31 |
0.73 - 0.89 1.19 - 1.47 0.94 - 1.22 0.97 - 1.25 0.88 - 1.19 1.30 - 1.88 1.13 - 1.95 0.69 - 1.04 0.41 - 0.61 0.95 - 1.60 0.19 - 0.30 0.47 - 0.80 0.45 - 0.93 0.50 - 0.97 0.10 - 0.94 |
Ischemic Cardiovascular Events
Bone Mineral Density Findings
Cholesterol
Other Adverse Reactions
First-Line Therapy
| Body system Adverse Reaction* |
Number (%) of subjects Anastrozole tablets(n=506) |
Number (%) of subjects Tamoxifen(n=511) |
| Whole body
Asthenia Pain Back pain Headache Abdominal pain Chest pain Flu syndrome Pelvic pain Cardiovascular Vasodilation Hypertension Digestive Nausea Constipation Diarrhea Vomiting Anorexia Metabolic and Nutritional Peripheral edema Muscoloskeletal Bone pain Nervous Dizziness Insomnia Depression Hypertonia Respiratory Cough increased Dyspnea Pharyngitis Skin and appendages Rash Urogenital Leukorrhea |
83 (16) 70 (14) 60 (12) 47 (9) 40 (8) 37 (7) 35 (7) 23 (5) 128 (25) 25 (5) 94 (19) 47 (9) 40 (8) 38 (8) 26 (5) 51 (10) 54 (11) 30 (6) 30 (6) 23 (5) 16 (3) 55 (11) 51 (10) 49 (10) 38 (8) 9 (2) |
81 (16) 73 (14) 68 (13) 40 (8) 38 (7) 37 (7) 30 (6) 30 (6) 106 (21) 36 (7) 106 (21) 66 (13) 33 (6) 36 (7) 46 (9) 41 (8) 52 (10) 22 (4) 38 (7) 32 (6) 26 (5) 52 (10) 47 (9) 68 (13) 34 (8) 31 (6) |
| Adverse Reaction*
|
Number (n) and Percentage of Patients Anastrozole tablets 1 mg (n=506) n (%) |
Number (n) and Percentage of Patients NOLVADEX 20 mg (n=511) n (%) |
| Depression Tumor Flare Thromboembolic Disease† Venous† Coronary and Cerebral‡ Gastrointestinal Disturbance Hot Flushes Vaginal Dryness Lethargy Vaginal Bleeding Weight Gain |
23 (5) 15 (3) 18 (4) 5 13 170 (34) 134 (26) 9 (2) 6 (1) 5 (1) 11 (2) |
32 (6) 18 (4) 33 (6) 15 19 196 (38) 118 (23) 3 (1) 15 (3) 11 (2) 8 (2) |
Second-Line Therapy
| Adverse Reaction*
|
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg (N=262) n (%) |
Anastrozole tablets 10 mg (N=246) n (%) |
Megestrol Acetate 160 mg (N=253) n (%) |
| Asthenia Nausea Headache Hot Flashes Pain Back Pain Dyspnea Vomiting Cough Increased Diarrhea Constipation Abdominal Pain Anorexia Bone Pain Pharyngitis Dizziness Rash Dry Mouth Peripheral Edema Pelvic Pain Depression Chest Pain Paresthesia Vaginal Hemorrhage Weight Gain Sweating Increased Appetite |
42 (16) 41 (16) 34 (13) 32 (12) 28 (11) 28 (11) 24 (9) 24 (9) 22 (8) 22 (8) 18 (7) 18 (7) 18 (7) 17 (6) 16 (6) 16 (6) 15 (6) 15 (6) 14 (5) 14 (5) 14 (5) 13 (5) 12 (5) 6 (2) 4 (2) 4 (2) 0 (0) |
33 (13) 48 (20) 44 (18) 29 (11) 38 (15) 26 (11) 27 (11) 26 (11) 18 (7) 18 (7) 18 (7) 14 (6) 19 (8) 26 (12) 23 (9) 12 (5) 15 (6) 11 (4) 21 (9) 17 (7) 6 (2) 18 (7) 15 (6) 4 (2) 9 (4) 3 (1) 1 (0) |
47 (19) 28 (11) 24 (9) 21 (8) 29 (11) 19 (8) 53 (21) 16 (6) 19 (8) 7 (3) 21 (8) 18 (7) 11 (4) 19 (8) 15 (6) 15 (6) 19 (8) 13 (5) 28 (11) 13 (5) 5 (2) 13 (5) 9 (4) 13 (5) 30 (12) 16 (6) 13 (5) |
Body as a Whole:
Cardiovascular:
Hepatic:
Hematologic:
Metabolic and Nutritional:
Musculoskeletal:
Nervous:
Respiratory:
Skin and Appendages:
Urogenital:
| Adverse Event Group
|
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg (N=262) n (%) |
Anastrozole tablets 10 mg (N=246) n (%) |
Megestrol Acetate 160 mg (N=253) n (%) |
| Gastrointestinal Disturbance Hot Flushes Edema Thromboembolic Disease Vaginal Dryness Weight Gain |
77 (29) 33 (13) 19 (7) 9 (3) 5 (2) 4 (2) |
81 (33) 29 (12) 28 (11) 4 (2) 3 (1) 10 (4) |
54 (21) 35 (14) 35 (14) 12 (5) 2 (1) 30 (12) |
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
[see Contraindications (4.2)]
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Tamoxifen
Co-administration of anastrozole and tamoxifen in breast cancer patients reduced anastrozole plasma concentration by 27%. However, the coadministration of anastrozole and tamoxifen did not affect the pharmacokinetics of tamoxifen or Ndesmethyltamoxifen. At a median follow-up of 33 months, the combination of anastrozole tablets and tamoxifen did not demonstrate any efficacy benefit when compared with tamoxifen in all patients as well as in the hormone receptor-positive subpopulation. This treatment arm was discontinued from the trial. [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Based on clinical and pharmacokinetic results from the ATAC trial, tamoxifen should not be administered with anastrozole.
7.2 Estrogen
Estrogen-containing therapies should not be used with anastrozole tablets as they may diminish its pharmacological action.
7.3 Warfarin
In a study conducted in 16 male volunteers, anastrozole did not alter the exposure (as measured by Cmax and AUC) and anticoagulant activity (as measured by prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and thrombin time) of both R- and S-warfarin.
7.4 Cytochrome P450
Based on in vitro and in vivo results, it is unlikely that co-administration of anastrozole tablets 1 mg will affect other drugs as a result inhibition of cytochrome P450 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
PREGNANCY CATEGORY X [see Contraindications (4.1)]
Anastrozole tablets may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman and offers no clinical benefit to premenopausal women with breast cancer. Anastrozole tablets are contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. In animal studies, anastrozole caused pregnancy failure, increased pregnancy loss, and signs of delayed fetal development. There are no studies of anastrozole tablets use in pregnant women. If anastrozole tablets are used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while receiving this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus and potential risk for pregnancy loss.
In animal reproduction studies, pregnant rats and rabbits received anastrozole during organogenesis at doses equal to or greater than 1 (rats) and 1/3 (rabbits) the recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis. In both species, anastrozole crossed the placenta, and there was increased pregnancy loss (increased pre- and/or post-implantation loss, increased resorption, and decreased numbers of live fetuses). In rats, these effects were dose related, and placental weights were significantly increased. Fetotoxicity, including delayed fetal development (i.e., incomplete ossification and depressed fetal body weights), occurred in rats at anastrozole doses that produced peak plasma levels 19 times higher than serum levels in humans at the therapeutic dose (AUC0-24hr 9 times higher). In rabbits, anastrozole caused pregnancy failure at doses equal to or greater than 16 times the recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis. [see Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology (13.2)]
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known if anastrozole is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the tumorigenicity shown for anastrozole in animal studies, or the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In studies 0030 and 0027 about 50% of patients were 65 or older. Patients ≥ 65 years of age had moderately better tumor response and time to tumor progression than patients < 65 years of age regardless of randomized treatment. In studies 0004 and 0005 50% of patients were 65 or older. Response rates and time to progression were similar for the over 65 and younger patients.
In the ATAC study 45% of patients were 65 years of age or older. The efficacy of anastrozole tablets compared to tamoxifen in patients who were 65 years or older (N=1413 for anastrozole tablets and N=1410 for tamoxifen, the hazard ratio for disease-free survival was 0.93 (95% CI: 0.80, 1.08)) was less than efficacy observed in patients who were less than 65 years of age (N=1712 for anastrozole tablets and N=1706 for tamoxifen, the hazard ratio for disease-free survival was 0.79 (95% CI: 0.67, 0.94)).
The pharmacokinetics of anastrozole are not affected by age.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Since only about 10% of anastrozole is excreted unchanged in the urine, the renal impairment does not influence the total body clearance. Dosage adjustment in patients with renal impairment is not necessary [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
The plasma anastrozole concentrations in the subjects with hepatic cirrhosis were within the range of concentrations seen in normal subjects across all clinical trials. Therefore, dosage adjustment is also not necessary in patients with stable hepatic cirrhosis. Anastrozole tablets have not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Clinical trials have been conducted with anastrozole tablets, up to 60 mg in a single dose given to healthy male volunteers and up to 10 mg daily given to postmenopausal women with advanced breast cancer; these dosages were tolerated. A single dose of anastrozole tablets that results in life-threatening symptoms has not been established. There is no specific antidote to overdosage and treatment must be symptomatic. In the management of an overdose, consider that multiple agents may have been taken. Vomiting may be induced if the patient is alert. Dialysis may be helpful because anastrozole tablets are not highly protein bound. General supportive care, including frequent monitoring of vital signs and close observation of the patient, is indicated.
11 DESCRIPTION
Anastrozole tablets for oral administration contain 1 mg of anastrozole, a non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor. It is chemically described as 1,3-Benzenediacetonitrile, a, a, a’, a’-tetramethyl-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl). Its molecular formula is C17H19N5 and its structural formula is:
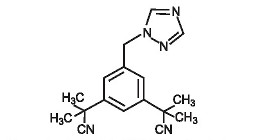
Anastrozole is an off-white powder with a molecular weight of 293.4. Anastrozole has moderate aqueous solubility (0.5 mg/mL at 25°C); solubility is independent of pH in the physiological range. Anastrozole is freely soluble in methanol, acetone, ethanol, and tetrahydrofuran, and very soluble in acetonitrile.
Each tablet contains as inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, sodium starch glycolate and titanium dioxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The growth of many cancers of the breast is stimulated or maintained by estrogens. Treatment of breast cancer thought to be hormonally responsive (i.e., estrogen and/or progesterone receptor positive or receptor unknown) has included a variety of efforts to decrease estrogen levels (ovariectomy, adrenalectomy, hypophysectomy) or inhibit estrogen effects (antiestrogens and progestational agents). These interventions lead to decreased tumor mass or delayed progression of tumor growth in some women.
In postmenopausal women, estrogens are mainly derived from the action of the aromatase enzyme, which converts adrenal androgens (primarily androstenedione and testosterone) to estrone and estradiol. The suppression of estrogen biosynthesis in peripheral tissues and in the cancer tissue itself can therefore be achieved by specifically inhibiting the aromatase enzyme.
Anastrozole is a potent and selective non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor. It significantly lowers serum estradiol concentrations and has no detectable effect on formation of adrenal corticosteroids or aldosterone.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Effect on Estradiol
Mean serum concentrations of estradiol were evaluated in multiple daily dosing trials with 0.5, 1, 3, 5, and 10 mg of anastrozole tablets in postmenopausal women with advanced breast cancer. Clinically significant suppression of serum estradiol was seen with all doses. Doses of 1 mg and higher resulted in suppression of mean serum concentrations of estradiol to the lower limit of detection (3.7 pmol/L). The recommended daily dose, anastrozole tablets 1 mg, reduced estradiol by approximately 70% within 24 hours and by approximately 80% after 14 days of daily dosing. Suppression of serum estradiol was maintained for up to 6 days after cessation of daily dosing with anastrozole tablets 1 mg.
The effect of anastrozole tablets in premenopausal women with early or advanced breast cancer has not been studied. Because aromatization of adrenal androgens is not a significant source of estradiol in premenopausal women, anastrozole tablets would not be expected to lower estradiol levels in premenopausal women.
Effect on Corticosteroids
In multiple daily dosing trials with 3, 5, and 10 mg, the selectivity of anastrozole was assessed by examining effects on corticosteroid synthesis. For all doses, anastrozole did not affect cortisol or aldosterone secretion at baseline or in response to ACTH. No glucocorticoid or mineralocorticoid replacement therapy is necessary with anastrozole.
Other Endocrine Effects
In multiple daily dosing trials with 5 and 10 mg, thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) was measured; there was no increase in TSH during the administration of anastrozole tablets. Anastrozole tablets does not possess direct progestogenic, androgenic, or estrogenic activity in animals, but does perturb the circulating levels of progesterone, androgens, and estrogens.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Inhibition of aromatase activity is primarily due to anastrozole, the parent drug. Absorption of anastrozole is rapid and maximum plasma concentrations typically occur within 2 hours of dosing under fasted conditions. Studies with radiolabeled drug have demonstrated that orally administered anastrozole is well absorbed into the systemic circulation. Food reduces the rate but not the overall extent of anastrozole absorption. The mean Cmax of anastrozole decreased by 16% and the median Tmax was delayed from 2 to 5 hours when anastrozole was administered 30 minutes after food. The pharmacokinetics of anastrozole are linear over the dose range of 1 to 20 mg, and do not change with repeated dosing. The pharmacokinetics of anastrozole were similar in patients and healthy volunteers.
Distribution
Steady-state plasma levels are approximately 3- to 4-fold higher than levels observed after a single dose of anastrozole tablets. Plasma concentrations approach steady-state levels at about 7 days of once daily dosing. Anastrozole is 40% bound to plasma proteins in the therapeutic range.
Metabolism
Metabolism of anastrozole occurs by N-dealkylation, hydroxylation and glucuronidation. Three metabolites of anastrozole (triazole, a glucuronide conjugate of hydroxy-anastrozole, and a glucuronide conjugate of anastrozole itself) have been identified in human plasma and urine. The major circulating metabolite of anastrozole, triazole, lacks pharmacologic activity.
Anastrozole inhibited reactions catalyzed by cytochrome P450 1A2, 2C8/9, and 3A4 in vitro with Ki values which were approximately 30 times higher than the mean steady-state Cmax values observed following a 1 mg daily dose. Anastrozole had no inhibitory effect on reactions catalyzed by cytochrome P450 2A6 or 2D6 in vitro. Administration of a single 30 mg/kg or multiple 10 mg/kg doses of anastrozole to healthy subjects had no effect on the clearance of antipyrine or urinary recovery of antipyrine metabolites.
Excretion
Eighty-five percent of radiolabeled anastrozole was recovered in feces and urine. Hepatic metabolism accounts for approximately 85% of anastrozole elimination. Renal elimination accounts for approximately 10% of total clearance. The mean elimination halflife of anastrozole is 50 hours.
Effect of Gender and Age
Anastrozole pharmacokinetics have been investigated in postmenopausal female volunteers and patients with breast cancer. No age related effects were seen over the range <50 to >80 years.
Effect of Race
Estradiol and estrone sulfate serum levels were similar between Japanese and Caucasian postmenopausal women who received 1 mg of anastrozole daily for 16 days. Anastrozole mean steady-state minimum plasma concentrations in Caucasian and Japanese postmenopausal women were 25.7 and 30.4 ng/mL, respectively.
Effect of Renal Impairment
Anastrozole pharmacokinetics have been investigated in subjects with renal impairment. Anastrozole renal clearance decreased proportionally with creatinine clearance and was approximately 50% lower in volunteers with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min/1.73m2) compared to controls. Total clearance was only reduced 10%. No dosage adjustment is needed for renal impairment. [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]
Effect of Hepatic Impairment
Anastrozole pharmacokinetics have been investigated in subjects with hepatic cirrhosis related to alcohol abuse. The apparent oral clearance (CL/F) of anastrozole was approximately 30% lower in subjects with stable hepatic cirrhosis than in control subjects with normal liver function. However, these plasma concentrations were still with the range of values observed in normal subjects. The effect of severe hepatic impairment was not studied. No dose adjustment is necessary for stable hepatic cirrhosis. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7)]
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A conventional carcinogenesis study in rats at doses of 1.0 to 25 mg/kg/day (about 10 to 243 times the daily maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis) administered by oral gavage for up to 2 years revealed an increase in the incidence of hepatocellular adenoma and carcinoma and uterine stromal polyps in females and thyroid adenoma in males at the high dose. A dose related increase was observed in the incidence of ovarian and uterine hyperplasia in females. At 25 mg/kg/day, plasma AUC0-24 hr levels in rats were 110 to 125 times higher than the level exhibited in postmenopausal volunteers at the recommended dose. A separate carcinogenicity study in mice at oral doses of 5 to 50 mg/kg/day (about 24 to 243 times the daily maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis) for up to 2 years produced an increase in the incidence of benign ovarian stromal, epithelial and granulosa cell tumors at all dose levels. A dose related increase in the incidence of ovarian hyperplasia was also observed in female mice. These ovarian changes are considered to be rodent-specific effects of aromatase inhibition and are of questionable significance to humans. The incidence of lymphosarcoma was increased in males and females at the high dose. At 50mg/kg/day, plasma AUC levels in mice were 35 to 40 times higher than the level exhibited in postmenopausal volunteers at the recommended dose.
Anastrozole tablets have not been shown to be mutagenic in in vitro tests (Ames and E. coli bacterial tests, CHO-K1 gene mutation assay) or clastogenic either in vitro (chromosome aberrations in human lymphocytes) or in vivo (micronucleus test in rats).
Oral administration of anastrozole to female rats (from 2 weeks before mating to pregnancy day 7) produced significant incidence of infertility and reduced numbers of viable pregnancies at 1 mg/kg/day (about 10 times the recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis and 9 times higher than the AUC0-24 hr found in postmenopausal volunteers at the recommended dose). Preimplantation loss of ova or fetus was increased at doses equal to or greater than 0.02 mg/kg/day (about one-fifth the recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis). Recovery of fertility was observed following a 5-week non-dosing period which followed 3 weeks of dosing. It is not known whether these effects observed in female rats are indicative of impaired fertility in humans.
Multiple-dose studies in rats administered anastrozole for 6 months at doses equal to or greater than 1 mg/kg/day (which produced plasma anastrozole Cssmax and AUC0-24 hr that were 19 and 9 times higher than the respective values found in postmenopausal volunteers at the recommended dose) resulted in hypertrophy of the ovaries and the presence of follicular cysts. In addition, hyperplastic uteri were observed in 6-month studies in female dogs administered doses equal to or greater than 1 mg/kg/day (which produced plasma anastrozole Cssmax and AUC0-24 hr that were 22 times and 16 times higher than the respective values found in postmenopausal women at the recommended dose). It is not known whether these effects on the reproductive organs of animals are associated with impaired fertility in premenopausal women.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Reproductive Toxicology
Anastrozole has been found to cross the placenta following oral administration of 0.1 mg/kg in rats and rabbits (about 1 and 1.9 times the recommended human dose, respectively, on a mg/m2 basis). Studies in both rats and rabbits at doses equal to or greater than 0.1 and 0.02 mg/kg/day, respectively (about 1 and 1/3, respectively, the recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis), administered during the period of organogenesis showed that anastrozole increased pregnancy loss (increased pre- and/or postimplantation loss, increased resorption, and decreased numbers of live fetuses); effects were dose related in rats. Placental weights were significantly increased in rats at doses of 0.1 mg/kg/day or more.
Evidence of fetotoxicity, including delayed fetal development (i.e., incomplete ossification and depressed fetal body weights), was observed in rats administered doses of 1 mg/kg/day (which produced plasma anastrozole Cssmax and AUC0-24 hr that were 19 times and 9 times higher than the respective values found in postmenopausal volunteers at the recommended dose). There was no evidence of teratogenicity in rats administered doses up to 1.0 mg/kg/day. In rabbits, anastrozole caused pregnancy failure at doses equal to or greater than 1.0 mg/kg/day (about 16 times the recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis); there was no evidence of teratogenicity in rabbits administered 0.2 mg/kg/day (about 3 times the recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer in Postmenopausal Women
[)]
| Demographic Characteristic |
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg (N*=3125) |
Tamoxifen 20 mg (N*=3116) |
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg plus Tamoxifen 20 mg (N*=3125) |
| Mean age (yrs.) Age Range (yrs.) Age Distribution (%) LT45 yrs. 45-60 yrs. GT60 LT70 yrs. GT70 yrs. Mean Weight (kg) Receptor Status(%) Positive‡ Negative§ Other¶ Other Treatment (%) prior to Randomization Mastectomy Breast conservation# Axillary surgery Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Neoadjuvant Tamoxifen Primary Tumor Size (%) T1 (LTE2 cm) T2 (GT2 cm and LTE5 cm) T3 (GT5 cm) Nodal Status (%) Node positive 1-3 (# of nodes) 4-9 GT9 Tumor Grade (%) Well-differentiated Moderately differentiated Poorly/undifferentiated Not assessed/recorded |
64.1 38.1 - 92.8 0.7 34.6 38.0 26.7 70.8 83.5 7.4 8.8 47.8 52.3 95.5 63.3 22.3 1.6 63.9 32.6 2.7 34.9 24.4 7.5 2.9 20.8 46.8 23.7 8.7 |
64.1 32.8 - 94.9 0.4 35.0 37.1 27.4 71.1 83.1 8.0 8.6 47.3 52.8 95.7 62.5 20.8 1.6 62.9 34.2 2.2 33.6 24.4 6.4 2.7 20.5 47.8 23.3 8.4 |
64.3 37.0 – 92.2 0.5 34.5 37.7 27.3 71.3 84.0 7.0 9.0 48.1 51.9 95.2 61.9 20.8 1.7 64.1 32.9 2.3 33.5 24.3 6.8 2.3 21.2 46.5 23.7 8.5 |
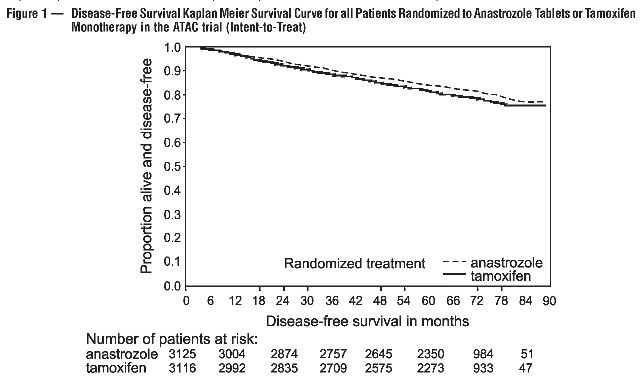
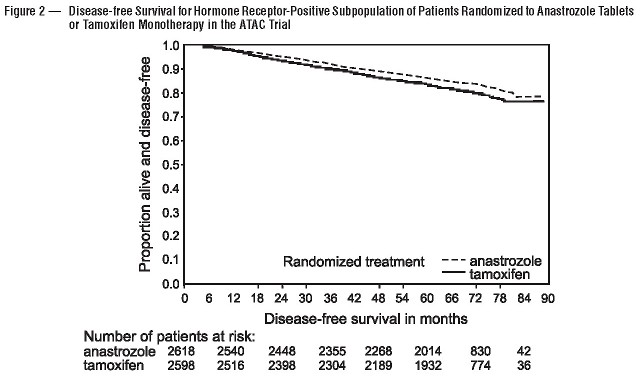
| |
Intent-To-Treat Population‡ | Hormone Receptor-Positive Subpopulation‡ |
| |
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg (N†=3125) |
Tamoxifen 20 mg (N†=3116) |
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg (N†=2618) |
Tamoxifen 20 mg (N†=2598) |
| Median Duration of Therapy (mo) Median Efficacy Follow-up (mo) Loco-regional recurrence Contralateral breast cancer Invasive Ductal carcinoma in situ Unknown Distant recurrence Death from Any Cause Death breast cancer Death other reason (including unknown) |
60 68 119 (3.8) 35 (1.1) 27 (0.9) 8 (0.3) 0 324 (10.4) 411 (13.2) 218 (7.0) 193 (6.2) |
60 68 149 (4.8) 59 (1.9) 52 (1.7) 6 (0.2) 1 (LT0.1) 375 (12.0) 420 (13.5) 248 (8.0) 172 (5.5) |
60 68 76 (2.9) 26 (1.0) 21 (0.8) 5 (0.2) 0 226 (8.6) 296 (11.3) 138 (5.3) 158 (6.0) |
60 68 101 (3.9) 54 (2.1) 48 (1.8) 5 (0.2) 1 (LT0.1) 265 (10.2) 301 (11.6) 160 (6.2) 141 (5.4) |
| |
Intent-To-Treat Population
|
Hormone Receptor-Positive Subpopulation |
| Anastrozole tablets 1 mg (N=3125) |
Tamoxifen 20 mg (N=3116) |
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg (N=2618) |
Tamoxifen 20 mg (N=2598) |
| |
Number of Events |
Number of Events |
| Disease free Survival
Hazard ratio 2-sided 95% CI p-value Distant Disease-free Survival Hazard ratio 2-sided 95% CI Overall Survival Hazard ratio 2-sided 95% CI |
575 500 411 |
0.87 0.78 to 0.97 0.0127 0.94 0.83 to 1.06 0.97 0.85 to 1.12 |
651 530 420 |
424 370 296 |
0.83 0.73 to 0.94 0.0049 0.93 0.80 to 1.07 0.97 0.83 to 1.14 |
497 394 301 |
14.2 First-Line Therapy in Postmenopausal Women with Advanced Breast Cancer
Two double-blind, controlled clinical studies of similar design (0030, a North American study and 0027, a predominately European study) were conducted to assess the efficacy of anastrozole tablets compared with tamoxifen as first-line therapy for hormone receptor positive or hormone receptor unknown locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women. A total of 1021 patients between the ages of 30 and 92 years old were randomized to receive trial treatment. Patients were randomized to receive 1 mg of anastrozole tablets once daily or 20 mg of tamoxifen once daily. The primary end points for both trials were time to tumor progression, objective tumor response rate, and safety.
Demographics and other baseline characteristics, including patients who had measurable and no measurable disease, patients who were given previous adjuvant therapy, the site of metastatic disease and ethnic origin were similar for the two treatment groups for both trials. The following table summarizes the hormone receptor status at entry for all randomized patients in trials 0030 and 0027.
| |
Number (%) of subjects
|
| |
Trial 0030
|
Trial 0027
|
| Receptor status
|
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg (n=171) |
Tamoxifen 20 mg (n=182) |
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg (n=340) |
Tamoxifen 20 mg (n=328) |
| ER* and/or PgR†
ER* unknown, PgR† Unknown |
151 (88.3) 19 (11.1) |
162 (89.0) 20 (11.0) |
154 (45.3) 185 (54.4) |
144 (43.9) 183 (55.8) |
* ER=Estrogen receptor
† PgR=Progesterone receptor
For the primary endpoints, trial 0030 showed that anastrozole tablets had a statistically significant advantage over tamoxifen (p=0.006) for time to tumor progression; objective tumor response rates were similar for anastrozole tablets and tamoxifen. Trial 0027 showed that anastrozole tablets and tamoxifen had similar objective tumor response rates and time to tumor progression (see Table 11 and Figure 3 and 4).
Table 11 below summarizes the results of trial 0030 and trial 0027 for the primary efficacy endpoints.
| Endpoint |
Trial 0030
|
Trial 0027
|
| |
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg (N=171) |
Tamoxifen 20 mg (N=182) |
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg (N=340) |
Tamoxifen 20 mg (N=328) |
| Time to progression (TTP) Median TTP (months) Number (%) of subjects who Progressed Hazard ratio (LCL*)† 2-sided 95% CI‡ p-value§ Best objective response rate Number (%) of subjects With CR¶ + PR# Odds Ratio (LCL*)♠ |
11.1 114 (67%) 36 (21.1%) |
1.42 (1.15) (1.11, 1.82) 0.006 1.30 (0.83) |
5.6 138 (76%) 31 (17.0%) |
|
8.2 249 (73%) 112 (32.9%) |
1.01 (0.87) 0.85, 1.20) 0.920 1.01 (0.77) |
8.3 247 (75%) 107 (32.6%) |
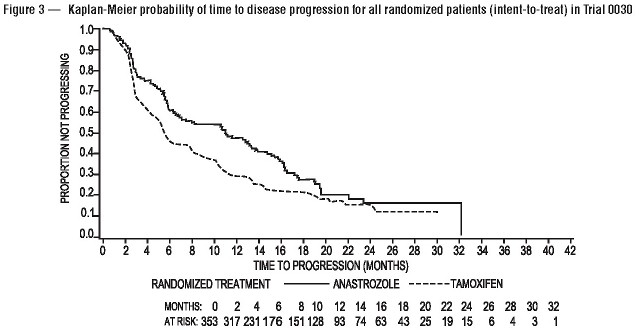
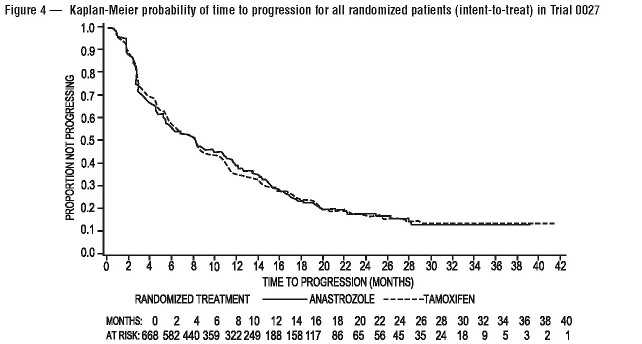
Results from the secondary endpoints were supportive of the results of the primary efficacy endpoints. There were too few deaths occurring across treatment groups of both trials to draw conclusions on overall survival differences.
14.3 Second-Line Therapy in Postmenopausal Women with Advanced Breast Cancer who had Disease Progression following Tamoxifen Therapy
| |
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg |
Anastrozole tablets 10 mg |
Megestrol Acetate 160 mg |
| Trial 0004 (N. America) Median Follow-up (months)* Median Time to Death (months) 2 Year Survival Probability (%) Median Time to Progression (months) Objective Response (all patients ) (%) Stable Disease for GT24 weeks (%) Progression (%) Trial 0005 (Europe, Australia, S. Africa) Median Follow-up (months)* Median Time to Death (months) 2 Year Survival Probability (%) Median Time to Progression (months) Objective Response (all patients) (%) Stable Disease for GT24 weeks (%) Progression (%) |
(N=128) 31.3 29.6 62.0 5.7 12.5 35.2 86.7 (N=135) 31.0 24.3 50.5 4.4 12.6 24.4 91.9 |
(N=130) 30.9 25.7 58.0 5.3 10.0 29.2 85.4 (N=118) 30.9 24.8 50.9 5.3 15.3 25.4 89.8 |
(N=128) 32.9 26.7 53.1 5.1 10.2 32.8 90.6 (N=125) 31.5 19.8 39.1 3.9 14.4 23.2 92.0 |
| Trials 0004 and 0005 (Pooled Data) |
Anastrozole tablets 1 mg N=263 |
Anastrozole tablets 10 mg N=248 |
Megestrol Acetate 160 mg N=253 |
| Median Time to Death (months) 2 Year Survival Probability (%) Median Time to Progression Objective Response (all patients) (%) |
26.7 56.1 4.8 12.5 |
25.5 54.6 5.3 12.5 |
22.5 46.3 4.6 12.3 |
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
These tablets are supplied in unit dose box of 100 tablets (NDC 0904-6229-61)
Storage
Store at controlled room temperature, 20-25°C (68-77°F) [see USP].
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Pregnancy
Patients should be advised that anastrozole tablets may cause fetal harm. They should also be advised that anastrozole tablets are not for use in premenopausal women; therefore, if they become pregnant they should stop taking anastrozole tablets and immediately contact their doctor.
17.2 Allergic (Hypersensitivity) Reactions
Patients should be informed of the possibility of serious allergic reactions with swelling of the face, lips, tongue and/or throat (angioedema) which may cause difficulty in swallowing and/or breathing and to immediately report this to their doctor.
17.3 Ischemic Cardiovascular Events
Patients with pre-existing ischemic heart disease should be informed that an increased incidence of cardiovascular events has been observed with anastrozole tablets use compared to tamoxifen use.
17.4 Bone Effects
Patients should be informed that anastrozole tablets lower the level of estrogen. This may lead to a loss of the mineral content of bones, which might decrease bone strength. A possible consequence of decreased mineral content of bones is an increase in the risk of fractures.
17.5 Cholesterol
Patients should be informed that an increased level of cholesterol might be seen while receiving anastrozole tablets.
17.6 Tamoxifen
Patients should be advised not to take anastrozole tablets with Tamoxifen.
17.7 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
PATIENT INFORMATION
ANASTROZOLE TABLETS
Read the information that comes with anastrozole tablets before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. The information may have changed. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or treatment. Talk with your doctor about anastrozole tablets when you start taking it and at regular checkups.
What are anastrozole tablets?
Anastrozole tablets are a prescription medicine used in women who have finished menopause (“the change of life”) for:
• treatment of early breast cancer
o after surgery, with or without radiation
o in women whose breast cancer is hormone receptor-positive
• first treatment of locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer, in women whose breast cancer is hormone receptor-positive or the hormone receptors are not known.
• treatment of advanced breast cancer, if the cancer has grown, or the disease has spread after tamoxifen therapy.
Anastrozole tablets do not work in women with breast cancer who have not finished menopause (premenopausal women).
Who should not take anastrozole tablets?
Do not take anastrozole tablets if you:
• are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or plan to get pregnant. Anastrozole tablets may harm your unborn child. If you become pregnant while taking anastrozole tablets, tell your doctor right away.
• have not finished menopause (are premenopausal)
• are allergic to any of the ingredients in anastrozole tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a list of the ingredients in anastrozole tablets.
• are a man or child
What is the most important information I should know about anastrozole tablets?
Anastrozole tablets may cause serious side effects including:
• Heart disease. Women with early breast cancer, who have a history of blockages in heart arteries (ischemic heart disease) and who take anastrozole tablets may have a slight increase in this type of heart disease compared to similar patients who take tamoxifen.
o Stop taking anastrozole tablets and call your doctor right away if you have chest pain or shortness of breath. These can be symptoms of heart disease.
• Osteoporosis (bone softening and weakening). Anastrozole tablets lower estrogen in your body, which may cause your bones to become softer and weaker. This can increase your chance of fractures, specifically of the spine, hip and wrist. Your doctor may order a test for you called a bone mineral density study before you start taking anastrozole tablets and during treatment with anastrozole tablets as needed.
What should I tell my doctor before taking anastrozole tablets?
Anastrozole tablets may not be right for you. Before taking anastrozole tablets, tell your doctor about all your medical conditions, including if you:
• have not finished menopause. Talk to your doctor if you are not sure. See “Who should not take anastrozole tablets?”
• have had a previous heart problem
• have a condition called osteoporosis
• have high cholesterol
• are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breast feeding. See “Who should not take anastrozole tablets?”
• are nursing a baby. It is not known if anastrozole tablets pass into breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take
anastrozole tablets or breast feed. You should not do both.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Especially tell your doctor if you take:
• Tamoxifen. You should not take anastrozole tablets with tamoxifen. Taking tamoxifen with anastrozole tablets may lower the amount of anastrozole tablets in your blood and may cause anastrozole tablets not to work as well.
• Medicines containing estrogen. Anastrozole tablets may not work if taken with one of these medicines:
o hormone replacement therapy
o birth control pills
o estrogen creams
o vaginal rings
o vaginal suppositories
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How should I take anastrozole tablets?
• Take anastrozole tablets exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Keep taking anastrozole tablets for as long as your doctor prescribes it for you.
• Take one anastrozole tablet each day.
• Anastrozole tablets can be taken with or without food.
• If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next regularly scheduled dose. Do not take two doses at the same time.
• If you have taken more anastrozole tablets than your doctor has prescribed, contact your doctor right away. Do not take any additional anastrozole tablets until instructed to do so by your doctor.
Talk with your doctor about any health changes you have while taking anastrozole tablets.
What are possible side effects of anastrozole tablets?
Anastrozole tablets can cause serious side effects including:
• See “What is the most important information I should know about anastrozole tablets?”
• increased blood cholesterol (fat in the blood). Your doctor may check your cholesterol while you take anastrozole tablets therapy.
• skin reactions. Stop taking anastrozole tablets and call your doctor right away if you get any skin lesions, ulcers, or blisters.
• severe allergic reactions. Get medical help right away if you have:
• swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
• trouble swallowing
• trouble breathing
• liver problems. Anastrozole tablets can cause inflammation of the liver and changes in blood tests of the liver function. Your doctor may monitor you for this. Stop taking anastrozole tablets and call your doctor right away if you have any of these signs or symptoms of a liver problem:
• a general feeling of not being well
• yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes
• pain on the right side of your abdomen
Common side effects in women taking anastrozole tablets include:
• hot flashes
• weakness
• joint pain
• carpal tunnel syndrome (tingling, pain, coldness, weakness in parts of the hand)
• pain
• sore throat
• mood changes
• high blood pressure
• depression
• nausea and vomiting
• thinning of the hair (hair loss)
• rash
• back pain
• sleep problems
• bone pain
• headache
• swelling
• increased cough
• shortness of breath
• lymphedema (build up of lymph fluid in the tissues of your affected arm)
• trigger finger (a condition in which one of your fingers or your thumb catches in a bent position)
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
HOW SHOULD I STORE ANASTROZOLE TABLETS?
• Store anastrozole tablets at 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
• Keep anastrozole tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about anastrozole tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not take anastrozole tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give anastrozole tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This patient information leaflet summarizes the most important information about anastrozole tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about anastrozole tablets that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in anastrozole tablets?
Active ingredient: anastrozole
Inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, sodium starch glycolate and titanium dioxide.
Manufactured by:
Natco Pharma Limited
Kothur – 509 228. A.P. India.
Mfd for:
Ascend Laboratories, LLC
Montvale, NJ 07645
346036
Rev: 00/Apr/2010
ASCEND
Laboratories, LLC
NDC 0904-6229-61
ANASTROZOLE TABLETS
1 mg
100 Unit Dose Tablets
Rx only
Mfd by: Natco Pharma Limited
Kothur - 509 228. A.P. India.

AnastrozoleAnastrozole TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||