Verapamil Hydrochloride
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- VERAPAMIL HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- PHARMACOKINETICS AND METABOLISM
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- VERAPAMIL HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- LABOR & DELIVERY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY & OR TOXICOLOGY
- VERAPAMIL HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
VERAPAMIL HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
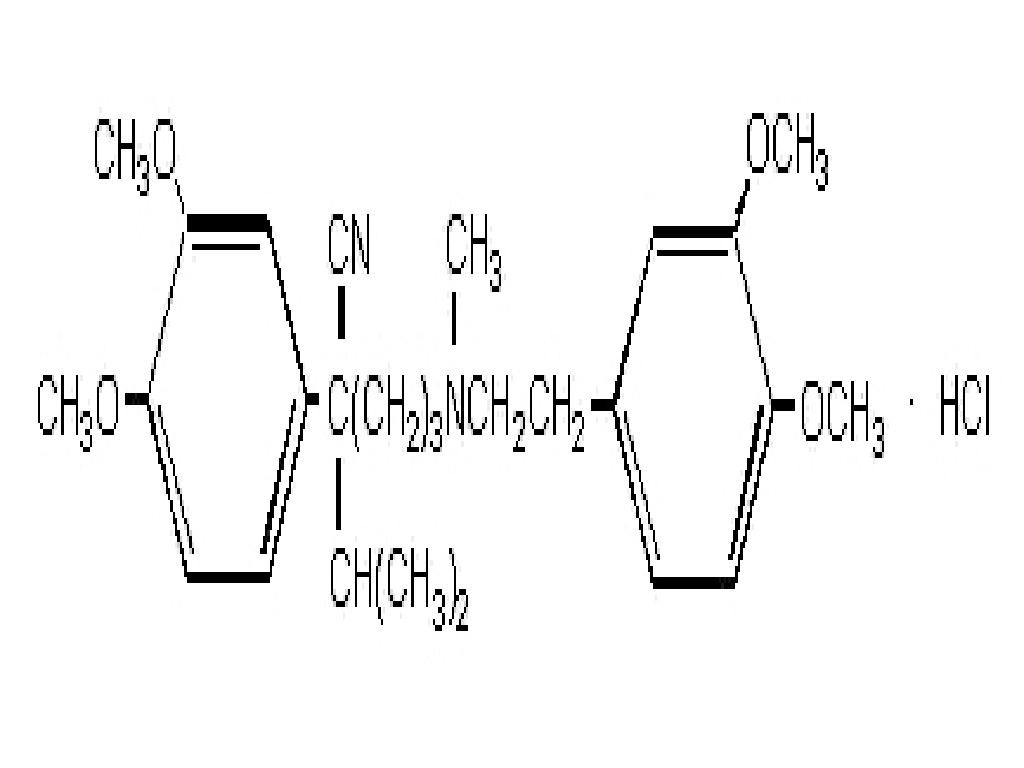
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of ActionEssential Hypertension
Other Pharmacologic Actions of Verapamil Hydrochloride Include The Following
WARNINGS
WARNINGS
PHARMACOKINETICS AND METABOLISM
PRECAUTIONS
After 4 weeks of oral dosing (120 mg q.i.d.), verapamil and norverapamil levels were noted in the cerebrospinal fluid with estimated partition coefficient of 0.06 for verapamil and 0.04 for norverapamil.
In ten healthy males, administration of oral verapamil (80 mg every 8 hours for 6 days) and a single oral dose of ethanol (0.8 g/kg) resulted in a 17% increase in mean peak ethanol concentrations (106.4521.40 to 124.2324.74 mghr/dL) compared to placebo. The area under the blood ethanol concentration versus time curve (AUC over 12 hours) increased by 30% (365.6793.52 to 475.0797.24 mghr/dL). Verapamil AUCs were positively correlated (r = 0.71) to increased ethanol blood AUC values (seePRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).
Hemodynamics and Myocardial Metabolism
Verapamil reduces afterload and myocardial contractility. Improved left ventricular diastolic function in patients with IHSS and those with coronary heart disease has also been observed with verapamil therapy. In most patients, including those with organic cardiac disease, the negative inotropic action of verapamil is countered by reduction of afterload and cardiac index is usually not reduced. However, in patients with severe left ventricular dysfunction (e.g., pulmonary wedge pressure above 20 mmHg or ejection fraction less than 30%), or in patients taking beta-adrenergic blocking agents or other cardiodepressant drugs, deterioration of ventricular function may occur (seePRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).
Pulmonary Function
Verapamil does not induce bronchoconstriction and hence, does not impair ventilatory function.
INDICATIONS & USAGE
VERAPAMIL HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
WARNINGS
WARNINGS
Heart FailurePRECAUTIONS: Drug InteractionsPRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions: Digitalis
Hypotension
Elevated Liver Enzymes
Accessory Bypass Tract (Wolff-Parkinson-White or Lown-Ganong-Levine)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Atrioventricular Block
Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (IHSS)
PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions
PRECAUTIONS
GeneralUse in Patients with Impaired Hepatic Functions
OVERDOSAGE
Use in Patients with Attenuated (Decreased) Neuromuscular Transmission
Use in Patients with Impaired Renal Function
OVERDOSAGE
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Clonidine
Cytochrome Inducers/Inhibitors
Aspirin
Grapefruit Juice
Beta-Blockers
Digitalis
Antihypertensive Agents
Antiarrhythmic Agents
Disopyramide
Flecainide
Quinidine
Nitrates
Other
Alcohol
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Cimetidine
Lithium
Carbamazepine
Verapamil may increase carbamazepine concentrations during combined therapy. This may produce carbamazepine side effects such as diplopia, headache, ataxia, or dizziness.
Rifampin
Therapy with rifampin may markedly reduce oral verapamil bioavailability.
Phenobarbital
Phenobarbital therapy may increase verapamil clearance.
Cyclosporine
Verapamil therapy may increase serum levels of cyclosporine.
Theophylline
Verapamil therapy may inhibit the clearance and increase the plasma levels of theophylline.
Inhalation Anesthetics
Animal experiments have shown that inhalation anesthetics depress cardiovascular activity by decreasing the inward movement of calcium ions. When used concomitantly, inhalation anesthetics and calcium antagonists, such as verapamil, should each be titrated carefully to avoid excessive cardiovascular depression.
Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
Clinical data and animal studies suggest that verapamil may potentiate the activity of neuromuscular blocking agents (curare-like and depolarizing). It may be necessary to decrease the dose of verapamil and/or the dose of the neuromuscular blocking agent when the drugs are used concomitantly.
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
PREGNANCY
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category CLABOR & DELIVERY
NURSING MOTHERS
PEDIATRIC USE
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY & OR TOXICOLOGY
VERAPAMIL HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
WARNINGSWARNINGS
Treatment of Acute Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions
OVERDOSAGE
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Essential HypertensionHOW SUPPLIED
STORAGE AND HANDLING
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

Verapamil HydrochlorideVerapamil Hydrochloride TABLET, EXTENDED RELEASE
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!