Risperidone
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- SPL INDEXING DATA ELEMENTS
- BOXED WARNING
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
- RISPERIDONE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- RISPERIDONE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- RISPERIDONE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- CLINICAL STUDIES
- HOW SUPPLIED
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- INACTIVE INGREDIENT
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
SPL INDEXING DATA ELEMENTS
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use RISPERIDONE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for RISPERIDONE.Initial U.S. Approval: 1993
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS
WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
5.1
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
● Treatment of schizophrenia in adults (1.1)
-
● Alone, or in combination with lithium or valproate, for the short-term treatment of acute manic or mixed episodes associated with Bipolar I Disorder in adults. (1.2)
-
● Due to Janssen Pharmaceuticals Corporation's marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled for use in pediatric patients with schizophrenia, or bipolar mania (1.1,1.2)
-
● Treatment of irritability associated with autistic disorder in children and adolescents aged 5-16 years (1.3)
2.12.22.3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
● Tablets: 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg and 4 mg (3)
-
● Known hypersensitivity to the product (4)
-
● Cerebrovascular events, including stroke, in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis. RISPERIDONE is not approved for use in patients with dementia-related psychosis (5.2)
-
● Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (5.3)
-
● Tardive dyskinesia (5.4)
-
● Hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus (5.5)
-
● Hyperprolactinemia (5.6)
-
● Orthostatic hypotension (5.7)
-
● Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis: has been reported with antipsychotics, including RISPERIDONE. Patients with a history of a clinically significant low white blood cell count (WBC) or a drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia should have their complete blood count (CBC) monitored frequently during the first few months of therapy and discontinuation of RISPERIDONEshould be considered at the first sign of a clinically significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors. (5.8)
-
● Potential for cognitive and motor impairment (5.9)
-
● Seizures (5.10)
-
● Dysphagia (5.11)
-
● Priapism (5.12)
-
● Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) (5.13)
-
● Disruption of body temperature regulation (5.14)
-
● Antiemetic Effect (5.15)
-
● Suicide (5.16)
-
● Increased sensitivity in patients with Parkinson's disease or those with dementia with Lewy bodies (5.17)
-
● Diseases or conditions that could affect metabolism or hemodynamic responses (5.17)
6
6
DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
● Due to CNS effects, use caution when administering with other centrally-acting drugs. Avoid alcohol. (7.1)
-
● Due to hypotensive effects, hypotensive effects of other drugs with this potential may be enhanced. (7.2)
-
● Effects of levodopa and dopamine agonists may be antagonized. (7.3)
-
● Cimetidine and ranitidine increase the bioavailability of risperidone. (7.5)
-
● Clozapine may decrease clearance of risperidone. (7.6)
-
● Fluoxetine and paroxetine increase plasma concentrations of risperidone. (7.10)
-
● Carbamazepine and other enzyme inducers decrease plasma concentrations of risperidone. (7.11)
-
● Nursing Mothers: should not breast feed. (8.3)
-
● Pediatric Use: safety and effectiveness not established for schizophrenia less than 13 years of age, for bipolar mania less than 10 years of age, and for autistic disorder less than 5 years of age. (8.4)
-
● Elderly or debilitated; severe renal or hepatic impairment; predisposition to hypotension or for whom hypotension poses a risk: Lower initial dose (0.5 mg twice daily), followed by increases in dose in increments of no more than 0.5 mg twice daily. Increases to dosages above 1.5 mg twice daily should occur at intervals of at least 1 week. (8.5,2.4)
See17for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
*
1. INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Schizophrenia
1.2 Bipolar Mania
1.3 Irritability Associated with Autistic Disorder
2. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Schizophrenia
2.2 Bipolar Mania
2.3 Irritability Associated with Autistic DisorderPediatrics (Children and Adolescents)
2.4 Dosage in Special Populations
2.5 Co-Administration of RISPERIDONE with Certain Other Medications
3. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4. CONTRAINDICATIONS
5. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
5.2 Cerebrovascular Adverse Events, Including Stroke, in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
5.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
5.4 Tardive Dyskinesia
5.5 Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus
5.6 Hyperprolactinemia
5.7 Orthostatic Hypotension
5.8 Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis
5.9 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
5.10 Seizures
5.11 Dysphagia
5.12 Priapism
5.13 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
5.14 Body Temperature Regulation
5.15 Antiemetic Effect
5.16 Suicide
5.17 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
5.18 Monitoring: Laboratory Tests
6. ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Commonly-Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials - Schizophrenia
6.2 Commonly-Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical TrialsBipolar Mania
6.3 Commonly-Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials - Autistic Disorder
6.4 Other Adverse Reactions Observed During the Premarketing Evaluation of RISPERIDONE
6.5 Discontinuations Due to Adverse Reactions
6.6 Dose Dependency of Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials
6.7 Changes in Body Weight
6.8 Changes in ECG
6.9 Postmarketing Experience
7. DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Centrally-Acting Drugs and Alcohol
7.2 Drugs with Hypotensive Effects
7.3 Levodopa and Dopamine Agonists
7.4 Amitriptyline
7.5 Cimetidine and Ranitidine
7.6 Clozapine
7.7 Lithium
7.8 Valproate
7.9 Digoxin
7.10 Drugs That Inhibit CYP 2D6 and Other CYP Isozymes
7.11 Carbamazepine and Other Enzyme Inducers
7.12 Drugs Metabolized by CYP 2D6
8. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
9. DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
9.2 Abuse
9.3 Dependence
10. OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Human Experience
10.2 Management of Overdosage
11. DESCRIPTION
12. CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13. NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
14. CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Schizophrenia
14.2 Bipolar Mania - Monotherapy
14.3 Bipolar ManiaCombination Therapy
14.4 Irritability Associated with Autistic Disorder
16. HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17. PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Orthostatic Hypotension
17.2 Interference with Cognitive and Motor Performance
17.3 Pregnancy
17.4 Nursing
17.5 Concomitant Medication
17.6 Alcohol
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
*
INDICATIONS & USAGE
1.1 SchizophreniaClinical Studies14.1
1.2 Bipolar Mania
Clinical Studies14.2
Clinical Studies14.3
1.3 Irritability Associated with Autistic Disorder
14.4
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Schizophrenia14.1
14.1
2.2 Bipolar Mania
14.214.3
2.3 Irritability Associated with Autistic DisorderPediatrics (Children and Adolescents)
14.4
2.4 Dosage in Special Populations
12.35.25.75.17
2.5 Co-Administration of RISPERIDONE with Certain Other Medications
7.11
Drug Interactions7.10
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
RISPERIDONE CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis5.2 Cerebrovascular Adverse Events, Including Stroke, in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
5.1
5.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
5.4 Tardive Dyskinesia
5.5 Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus
5.6 Hyperprolactinemia
13.1
5.7 Orthostatic Hypotension
RISPERIDONE may induce orthostatic hypotension associated with dizziness, tachycardia, and in some patients, syncope, especially during the initial dose-titration period, probably reflecting its alpha-adrenergic antagonistic properties. Syncope was reported in 0.2% (6/2607) of RISPERIDONE-treated patients in Phase 2 and 3 studies in adults with schizophrenia. The risk of orthostatic hypotension and syncope may be minimized by limiting the initial dose to 2 mg total (either once daily or 1 mg twice daily) in normal adults and 0.5 mg twice daily in the elderly and patients with renal or hepatic impairment [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.1,2.4)]. Monitoring of orthostatic vital signs should be considered in patients for whom this is of concern. A dose reduction should be considered if hypotension occurs. RISPERIDONE should be used with particular caution in patients with known cardiovascular disease (history of myocardial infarction or ischemia, heart failure, or conduction abnormalities), cerebrovascular disease, and conditions which would predispose patients to hypotension, e.g., dehydration and hypovolemia. Clinically significant hypotension has been observed with concomitant use of RISPERIDONE and antihypertensive medication.
5.8 Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis
Class Effect
In clinical trial and/or postmarketing experience, events of leukopenia/neutropenia have been reported temporally related to antipsychotic agents, including RISPERIDONE. Agranulocytosis has also been reported.
Possible risk factors for leukopenia/neutropenia include pre-existing low white blood cell count (WBC) and history of drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia. Patients with a history of a clinically significant low WBC or a drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia should have their complete blood count (CBC) monitored frequently during the first few months of therapy and discontinuation of RISPERIDONEshould be considered at the first sign of a clinically significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors.
Patients with clinically significant neutropenia should be carefully monitored for fever or other symptoms or signs of infection and treated promptly if such symptoms or signs occur. Patients with severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count <1000/mm3) should discontinue RISPERIDONEand have their WBC followed until recovery.
5.9 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
Somnolence was a commonly reported adverse event associated with RISPERIDONE treatment, especially when ascertained by direct questioning of patients. This adverse event is dose-related, and in a study utilizing a checklist to detect adverse events, 41% of the high-dose patients (RISPERIDONE 16 mg/day) reported somnolence compared to 16% of placebo patients. Direct questioning is more sensitive for detecting adverse events than spontaneous reporting, by which 8% of RISPERIDONE 16 mg/day patients and 1% of placebo patients reported somnolence as an adverse event. Since RISPERIDONE has the potential to impair judgment, thinking, or motor skills, patients should be cautioned about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain that RISPERIDONE therapy does not affect them adversely.
5.10 Seizures
During premarketing testing in adult patients with schizophrenia, seizures occurred in 0.3% (9/2607) of RISPERIDONE-treated patients, two in association with hyponatremia. RISPERIDONE should be used cautiously in patients with a history of seizures.
5.11 Dysphagia
Esophageal dysmotility and aspiration have been associated with antipsychotic drug use. Aspiration pneumonia is a common cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with advanced Alzheimer's dementia. RISPERIDONE and other antipsychotic drugs should be used cautiously in patients at risk for aspiration pneumonia [see alsoBOXED WARNINGand WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)].
5.12 Priapism
Priapism has been reported during postmarketing surveillance [see ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.9)]. Severe priapism may require surgical intervention.
5.13 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
A single case of TTP was reported in a 28 year-old female patient receiving RISPERIDONE in a large, open premarketing experience (approximately 1300 patients). She experienced jaundice, fever, and bruising, but eventually recovered after receiving plasmapheresis. The relationship to RISPERIDONE therapy is unknown.
5.14 Body Temperature Regulation
Disruption of body temperature regulation has been attributed to antipsychotic agents. Both hyperthermia and hypothermia have been reported in association with oral RISPERIDONE use. Caution is advised when prescribing for patients who will be exposed to temperature extremes.
5.15 Antiemetic Effect
's syndrome, and brain tumor.
5.16 Suicide
The possibility of a suicide attempt is inherent in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar mania, including children and adolescent patients, and close supervision of high-risk patients should accompany drug therapy. Prescriptions for RISPERIDONE should be written for the smallest quantity of tablets, consistent with good patient management, in order to reduce the risk of overdose.
5.17 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
Clinical experience with RISPERIDONE in patients with certain concomitant systemic illnesses is limited. Patients with Parkinson's Disease or Dementia with Lewy Bodies who receive antipsychotics, including RISPERIDONE, are reported to have an increased sensitivity to antipsychotic medications. Manifestations of this increased sensitivity have been reported to include confusion, obtundation, postural instability with frequent falls, extrapyramidal symptoms, and clinical features consistent with the neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
Caution is advisable in using RISPERIDONE in patients with diseases or conditions that could affect metabolism or hemodynamic responses. RISPERIDONE has not been evaluated or used to any appreciable extent in patients with a recent history of myocardial infarction or unstable heart disease. Patients with these diagnoses were excluded from clinical studies during the product's premarket testing.
Increased plasma concentrations of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone occur in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min/1.73 m2), and an increase in the free fraction of risperidone is seen in patients with severe hepatic impairment. A lower starting dose should be used in such patients [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.4)].
5.18 Monitoring: Laboratory Tests
No specific laboratory tests are recommended.
RISPERIDONE ADVERSE REACTIONS
-
● Increased mortality in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis [see BOXED WARNING and WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
-
● Cerebrovascular adverse events, including stroke, in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2)]
-
● Neuroleptic malignant syndrome [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.3)]
-
● Tardive dyskinesia [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.4)]
-
● Hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.5)]
-
● Hyperprolactinemia [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.6)]
-
● Orthostatic hypotension [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.7)]
-
● Leukopenia, neutropenia, and agranulocytosis [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.8)]
-
● Potential for cognitive and motor impairment [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.9)]
-
● Seizures [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.10)]
-
● Dysphagia [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.11)]
-
● Priapism [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.12)]
-
● Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.13)]
-
● Disruption of body temperature regulation [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.14)]
-
● Antiemetic effect [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.15)]
-
● Suicide [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.16)]
-
● Increased sensitivity in patients with Parkinson's disease or those with dementia with Lewy bodies [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.17)]
-
● Diseases or conditions that could affect metabolism or hemodynamic responses [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.17)]
6.5
6.1 Commonly-Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials - Schizophrenia
Percentage of Patients Reporting EventRISPERIDONESystem/Organ Class2-8 mg per day>8-16 mg per dayPlacebo(N = 366)(N = 198)(N = 225)Blood and Lymphatic System DisordersCardiac DisordersEar and Labyrinth DisordersDisordersGastrointestinal DisordersGeneral DisordersImmune System DisordersInfections and InfestationsInvestigationsMetabolism and Nutrition DisordersMusculoskeletal and ConnectiveTissue DisordersNervous System DisordersPsychiatric DisordersRenal and Urinary DisordersReproductive System and Breast DisordersRespiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal DisordersSkin and Subcutaneous Tissue DisordersVascular Disorders
Percentage of Patients Reporting EventRISPERIDONESystem/Organ Class1-3 mg per day4-6 mg per dayPlacebo(N = 55)(N = 51)(N = 54)Gastrointestinal DisordersNervous System DisordersPsychiatric Disorders
6.2 Commonly-Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical TrialsBipolar Mania
Percentage of Patients Reporting EventSystem/Organ ClassRISPERIDONEPlacebo1-6 mg per day(N = 448)(N = 424)Cardiac DisordersEye DisordersGastrointestinal DisordersGeneral DisordersInfections and InfestationsNervous System DisordersReproductive System and Breast DisordersSkin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Table 4Adverse Reactions inof RISPERIDONE -Treated Adult Patients with Bipolar Mania in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Adjuvant Therapy Trials
Percentage of Patients Reporting EventSystem/Organ ClassRISPERIDONE + Mood StabilizerPlacebo + Mood Stabilizer(N=127)(N=126)Cardiac DisordersGastrointestinal DisordersGeneral DisordersInfections and InfestationsInvestigationsNervous System DisordersPsychiatric DisordersRespiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders
Percentage of Patients Reporting EventRISPERIDONESystem/Organ Class0.5-2.5 mgper day3-6 mg per dayPlacebo(N= 50)(N = 61)(N = 58)Eye DisordersGastrointestinal DisordersGeneral DisordersMetabolism and Nutrition DisordersNervous System DisordersPsychiatric DisordersRespiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal DisordersSkin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
6.3 Commonly-Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials - Autistic Disorder
Percentage of Patients Reporting EventSystem/Organ ClassRISPERIDONEPlacebo0.5-4.0 mg per day(N=80)(N=76)Cardiac DisordersGastrointestinal DisordersGeneral DisordersInfections and InfestationsInvestigationsMetabolism and Nutrition DisordersNervous System DisordersRespiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal DisordersSkin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
6.4 Other Adverse Reactions Observed During the Premarketing Evaluation of RISPERIDONE
6.5 Discontinuations Due to Adverse Reactions
RISPERIDONEAdverse Reaction2-8 mg/day (N=366)>8-16 mg/day (N=198)Placebo(N=225)
Adverse ReactionRISPERIDONEPlacebo1-6 mg/day (N=448)(N=424)
6.6 Dose Dependency of Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials
6.7 Changes in Body Weight
8.4
6.8 Changes in ECG
6.9 Postmarketing Experience
DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Centrally-Acting Drugs and Alcohol7.2 Drugs with Hypotensive Effects
7.3 Levodopa and Dopamine Agonists
7.4 Amitriptyline
7.5 Cimetidine and Ranitidine
7.6 Clozapine
7.7 Lithium
7.8 Valproate
7.9 Digoxin
7.10 Drugs That Inhibit CYP 2D6 and Other CYP Isozymes
12.3
7.11 Carbamazepine and Other Enzyme Inducers
7.12 Drugs Metabolized by CYP 2D6
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
1.36.314.4
5.4
6.7
6.16.26.32.12.22.3
5.6
8.5 Geriatric Use
12.32.42.55.7
2.4
5.1
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance9.2 Abuse
9.3 Dependence
OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Human Experience10.2 Management of Overdosage
RISPERIDONE DESCRIPTION
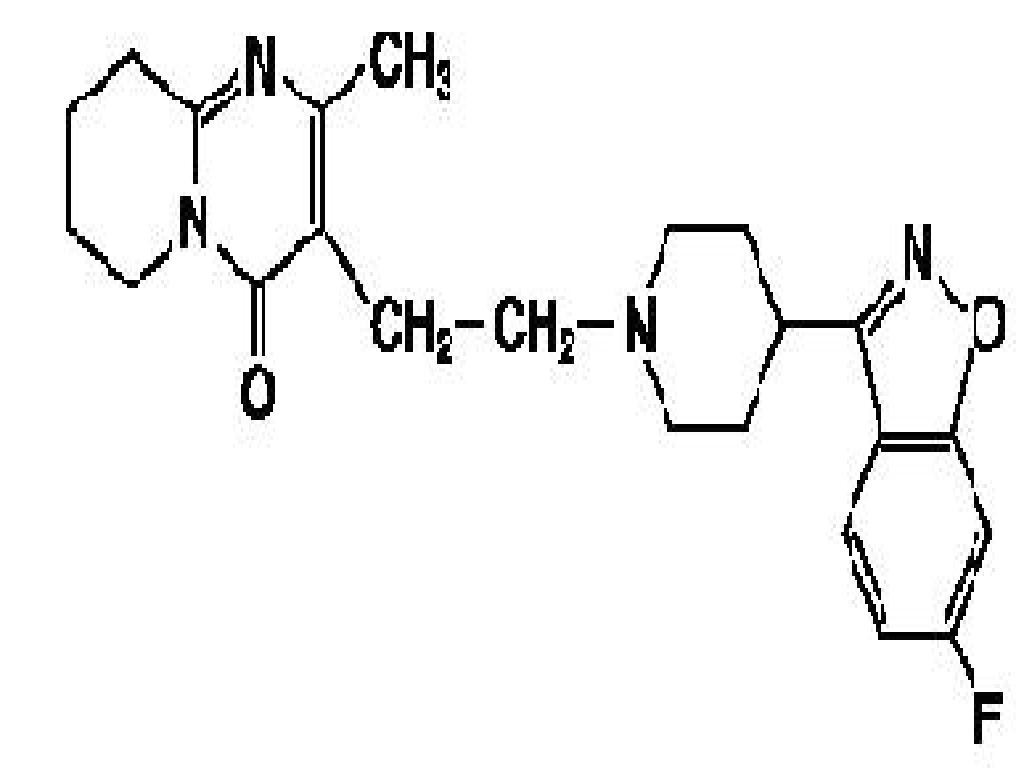
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.312.1
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
7.127.117.12
2.45.17
2.45.17
2.4
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility5.6
CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Schizophrenia14.2 Bipolar Mania - Monotherapy
14.3 Bipolar ManiaCombination Therapy
14.4 Irritability Associated with Autistic Disorder
HOW SUPPLIED
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
17.1 Orthostatic Hypotension
5.7
17.2 Interference with Cognitive and Motor Performance
5.9
17.3 Pregnancy
8.1
17.4 Nursing
8.3
17.5 Concomitant Medication
7
17.6 Alcohol
7.1
INACTIVE INGREDIENT
INACTIVE INGREDIENTS:STARCH, CORN
FERRIC OXIDE RED
FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW
HYPROMELLOSES
LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE
MAGNESIUM STEARATE
CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE
PROPYLENE GLYCOL
SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE
TITANIUM DIOXIDE
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

RisperidoneRisperidone TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!