Seroquel
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- SPL INDEXING DATA ELEMENTS
- BOXED WARNING
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
- SEROQUEL CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- SEROQUEL ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- SEROQUEL DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- CLINICAL STUDIES
- HOW SUPPLIED
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- SPL MEDGUIDE
- INACTIVE INGREDIENT
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
SPL INDEXING DATA ELEMENTS
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SEROQUEL XR safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SEROQUEL XR.SEROQUEL XRfumarate) Extended-Release Tablets
Initial U.S. Approval: 1997
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
-
● Antipsychotic drugs are associated with an increased risk of death. (5.1)
-
● Quetiapine is not approved for elderly patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis. (5.1)
-
● Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents and young adults taking antidepressants for major depressive disorder and other psychiatric disorders. (5.2)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
*
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
-
●
-
● Suicidality and Antidepressant Drugs: Increased the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents and young adults taking antidepressants for major depressive disorder and other psychiatric disorders. (5.2)
-
● Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS): Manage with immediate discontinuation and close monitoring. (5.3)
-
● Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus (DM): Ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar coma and death have been reported in patients treated with atypical antipsychotics, including quetiapine. Any patient treated with atypical antipsychotics should be monitored for symptoms of hyperglycemia including polydipsia, polyuria, polyphagia, and weakness. When starting treatment, patients with diabetes or risk factors for diabetes should undergo blood glucose testing before and during treatment. (5.4)
-
● Hyperlipidemia: Undesirable alterations in lipids have been observed. Increases in total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and decreases in HDL-cholesterol have been reported in clinical trials. Appropriate clinical monitoring is recommended, including fasting blood lipid testing at the beginning of, and periodically, during treatment. (5.5)
-
● Weight Gain: Patients should receive regular monitoring of weight. (5.6)
-
● Tardive Dyskinesia: Discontinue if clinically appropriate. (5.7)
-
● Orthostatic Hypotension: Associated dizziness, tachycardia and syncope may occur especially during the initial dose titration period. Use in caution in patients with known cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease. (5.8)
-
● Increased Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents: Blood pressure should be measured at the beginning of, and periodically during treatment in children and adolescents. SEROQUEL XR has not been evaluated in pediatric patients. (5.9)
-
● Leukopenia, Neutropenia and Agranulocytosis: have been reported with atypical antipsychotics including SEROQUEL XR. Patients with a pre-existing low white cell count (WBC) or a history of leukopenia/neutropenia should have complete blood count (CBC) monitored frequently during the first few months of treatment and should discontinue SEROQUEL XR at the first sign of a decline in WBC in absence of other causative factors. (5.10)
-
● Cataracts: Lens changes have been observed in patients during long-term quetiapine treatment. Lens examination is recommended when starting treatment and at 6-month intervals during chronic treatment. (5.11)
-
● Suicide: The possibility of a suicide attempt is inherent in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression, and close supervision of high risk patients should accompany drug therapy. (5.20)
-
● See Full Prescribing Information for additional WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
● P450 3A Inhibitors: May decrease the clearance of quetiapine. Lower doses of quetiapine may be required. (7.1)
-
● Hepatic Enzyme Inducers: May increase the clearance of quetiapine. Higher doses of quetiapine may be required with phenytoin or other inducers. (7.1)
-
● Centrally Acting Drugs: Caution should be used when quetiapine is used in combination with other CNS acting drugs. (7)
-
● Antihypertensive Agents: Quetiapine may add to the hypotensive effects of these agents. (7)
-
● Levodopa and Dopamine Agents: Quetiapine may antagonize the effect of these drugs. (7)
-
● Drugs known to cause electrolyte imbalance or increase QT interval: Caution should be used when quetiapine is used concomitantly with these drugs. (7)
-
● Interference with Urine Drug Screens: False positive urine drug screens for methadone or tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) in patients taking quetiapine have been reported. (7)
-
● Geriatric Use: Consider a lower starting dose (50 mg/day), slower titration, and careful monitoring during the initial dosing period in the elderly. (2.3and8.5)
-
● Hepatic Impairment: Lower starting dose (50 mg/day) and slower titration may be needed. (2.3,8.7,12.3)
-
● Pregnancy: Limited human data. Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. (8.1)
-
● Nursing Mothers: Caution should be exercised when administered to a nursing woman. (8.3)
-
● Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness have not been established. (8.4)
See17for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and the FDA-approved Medication Guide
*
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
Recent Major Changes
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Schizophrenia
1.2 Bipolar Disorder
1.3 Adjunctive Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Schizophrenia
2.2 Bipolar Disorder
2.3 Major Depressive Disorder, Adjunctive Therapy with Antidepressants
2.4 Dosing in Special Populations
2.5 Re-initiation of Treatment in Patients Previously Discontinued
2.6 Switching Patients from SEROQUEL Tablets to SEROQUEL XR Tablets
2.7 Switching from Antipsychotics
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
5.2 Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
5.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
5.4 Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus
5.5 Hyperlipidemia
5.6 Weight Gain
5.7 Tardive Dyskinesia
5.8 Orthostatic Hypotension
5.9 Increases in Blood Pressure (Children and Adolescents)
5.10 Leukopenia, Neutropenia and Agranulocytosis
5.11 Cataracts
5.12 Seizures
5.13 Hypothyroidism
5.14 Hyperprolactinemia
5.15 Transaminase Elevations
5.16 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
5.17 Priapism
5.18 Body Temperature Regulation
5.19 Dysphagia
5.20 Suicide
5.21 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
5.22 Withdrawal
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
6.2 Vital Signs and Laboratory Values
6.3 Post Marketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 The Effect of Other Drugs on Quetiapine
7.2 Effect of Quetiapine on Other Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
9.2 Abuse
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Human Experience
10.2 Management of Overdosage
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Schizophrenia
14.2 Bipolar Disorder
14.3 Major Depressive Disorder, Adjunctive Therapy to Antidepressants
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Information for Patients
17.2 MEDICATION GUIDE
PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL
*
INDICATIONS & USAGE
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE1.1 Schizophrenia
1.2 Bipolar Disorder
1.3 Adjunctive Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
12.3
2.1 Schizophrenia
2.2 Bipolar Disorder
2.3 Major Depressive Disorder, Adjunctive Therapy with Antidepressants
2.4 Dosing in Special Populations
2.5 Re-initiation of Treatment in Patients Previously Discontinued
2.6 Switching Patients from SEROQUEL Tablets to SEROQUEL XR Tablets
2.7 Switching from Antipsychotics
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSSEROQUEL CONTRAINDICATIONS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis5.2 Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
AgeDrug-Placebo Difference in Number of Cases of SuicidalityRangeper 1000 Patients TreatedIncreases Compared to PlaceboDecreases Compared to Placebo
5.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
5.4 Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus
LaboratoryCategory Change (At Least Once) fromTreatmentNPatientsAnalyteBaselineArmn (%)
Laboratory AnalyteTreatment ArmNPatients n (%)
5.5 Hyperlipidemia
Laboratory AnalyteIndicationTreatmentNPatientsArmn (%)*****
Laboratory AnalyteTreatment Arm*NPatients n (%)*
Laboratory AnalyteIndicationTreatment ArmNPatientsn (%)* ****
5.6 Weight Gain
Vital signIndicationTreatmentNPatientsArmn (%)Weight Gain7% of*Body Weight*
Vital signTreatment ArmNPatientsn (%)Weight GainofBody Weight in MDDAdjunctive Therapy
Vital SignIndicationTreatment ArmNPatientsn (%)* *
5.7 Tardive Dyskinesia
5.8 Orthostatic Hypotension
5.9 Increases in Blood Pressure (Children and Adolescents)
5.10 Leukopenia, Neutropenia and Agranulocytosis
5.11 Cataracts
5.12 Seizures
5.13 Hypothyroidism
*
*
5.14 Hyperprolactinemia
5.15 Transaminase Elevations
5.16 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
5.17 Priapism
5.18 Body Temperature Regulation
5.19 Dysphagia
5.20 Suicide
5.21 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
5.22 Withdrawal
SEROQUEL ADVERSE REACTIONS
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
*
Body System/Preferred TermPLACEBOSEROQUEL XR(n=319)(n=951)Cardiac DisordersEye DisordersGastrointestinal DisordersGeneral Disorders and Administration Site ConditionsInvestigationsMetabolism and Nutrition DisordersMusculoskeletal and Connective Tissue DisordersNervous System DisordersPsychiatric DisordersVascular Disorders*
*
Body System/Preferred TermPLACEBOSEROQUEL XR(n=160)(n=151)Cardiac DisordersGastrointestinal DisordersGeneral Disorders and Administration Site ConditionsInvestigationsInjury, Poisoning And Procedural ComplicationsMetabolism And Nutrition DisordersNervous System DisordersMusculoskeletal And Connective Tissue DisordersRespiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal DisordersVascular Disorders*
*
Body System/Preferred TermPlaceboSEROQUEL XR(n=140)(n=137)Ear And Labyrinth DisordersGastrointestinal DisordersGeneral Disorders and Administration Site ConditionsImmune System DisordersInfections And InfestationsInvestigationsMetabolism and Nutrition DisorderMusculoskeletal And Connective Tissue DisordersNervous System DisordersPsychiatric DisordersRenal And Urinary DisordersRespiratory, Thoracic And Mediastinal DisordersSkin And Subcutaneous Tissue DisordersVascular Disorders*
*
Body System/PlaceboSEROQUEL XR 150 mgSEROQUELPreferred Term(n = 309)(n = 315)XR 300mg(n= 312)Ear And Labyrinth DisordersEye DisordersGastrointestinal DisordersGeneral Disorders and Administration Site ConditionsInfections And InfestationsInjury, Poisoning And Procedural ComplicationsInvestigationsMetabolism And Nutrition DisordersMusculoskeletal And Connective Tissue DisordersNervous System DisordersPsychiatric Disorders*
**
In a placebo-controlled clinical trial for the treatment of bipolar mania, utilizing the dose range of 400-800 mg/day of SEROQUEL XR, the incidence of any adverse reactions potentially related to EPS was 6.6% for SEROQUEL XR and 3.8% in the placebo group. In this study, the incidence of the individual adverse reactions (akathisia, extrapyramidal disorder, tremor, dystonia, restlessness, and cogwheel rigidity) did not exceed 2.0% for any adverse reaction.
Table 16: Adverse Experiences Associated with Extrapyramidal Symptoms in a Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial for Bipolar Mania
Preferred term*Placebo (N=160)SEROQUEL XR (N=151)n%n%Dystonic event00.010.7Parkinsonism31.942.7Akathisia10.621.3Other21.332.0extrapyramidal event *There were no adverse experiences with the preferred term of dyskinetic event.
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: nuchal rigidity, hypertonia, dystonia, muscle rigidity, oculogyration
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: cogwheel rigidity, tremor, drooling, hypokinesia
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: akathisia, psychomotor agitation
In a placebo-controlled clinical trial for the treatment of bipolar depression utilizing 300 mg of SEROQUEL XR, the incidence of any adverse reactions potentially related to EPS was 4.4% for SEROQUEL XR and 0.7% in the placebo group. In this study, the incidence of the individual adverse reactions (akathisia, extrapyramidal disorder, tremor, dystonia, hypertonia) did not exceed 1.5% for any individual adverse reaction.
Table 17: Adverse Experiences Associated with Extrapyramidal Symptoms in a Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial for Bipolar Depression
Preferred term*Placebo (N=140)SEROQUEL XR (N=137)n%n%Dystonic event00.021.5Parkinsonism10.710.7Akathisia00.021.5Other00.010.7extrapyramidal event *There were no adverse experiences with the preferred term of dyskinetic event.
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: nuchal rigidity, hypertonia, dystonia, muscle rigidity, oculogyration
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: cogwheel rigidity, tremor, drooling, hypokinesia
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: akathisia, psychomotor agitation
In two placebo-controlled short-term adjunctive therapy clinical trials for the treatment of MDD utilizing between 150 mg and 300 mg of SEROQUEL XR, the incidence of any adverse reactions potentially related to EPS was 5.1% for SEROQUEL XR and 4.2% for the placebo group.
Table 18 shows the percentage of patients experiencing adverse reactions potentially associated with EPS in adjunct clinical trials for MDD by dose:
Table 18: Adverse Reactions Potentially Associated with EPS in MDD Trials by Dose, Adjunctive Therapy Clinical Trials (6 weeks duration)
Preferred termPlaceboSEROQUEL XRSEROQUEL XRAll Doses(N = 309)150 mg/ day300 mg/ day(N = 627)(N = 315)(N = 312)n%n%n%n%Dystonic event*00.010.300.010.2Parkinsonism51.631.041.371.1Akathisia31.051.682.6132.1Dyskinetic event00.000.010.310.2Other51.651.672.2121.9extrapyramidal event *Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: nuchal rigidity, hypertonia, dystonia, muscle rigidity, oculogyration
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: cogwheel rigidity, tremor, drooling, hypokinesia
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: akathisia, psychomotor agitation
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: tardive dyskinesia, dyskinesia, choreoathetosis
Children and Adolescents: Safety and effectiveness of SEROQUEL XR have not been established in pediatric patients and SEROQUEL XR is not approved for patients under the age of 18 years. In a short-term placebo-controlled monotherapy trial in adolescent patients with schizophrenia (6-week duration), the aggregated incidence of extrapyramidal symptoms was 12.9% for SEROQUEL and 5.3% for placebo, though the incidence of the individual adverse events (eg, akathisia, tremor, extrapyramidal disorder, hypokinesia, restlessness, psychomotor hyperactivity, muscle rigidity, dyskinesia) did not exceed 4.1% in any treatment group. In a short-term placebo-controlled monotherapy trial in children and adolescent patients with bipolar mania (3-week duration), the aggregated incidence of extrapyramidal symptoms was 3.6% for SEROQUEL and 1.1% for placebo.
Table 19 below presents a listing of patients with adverse experiences potentially associated with EPS in the short-term placebo-controlled monotherapy trial in adolescent patients with schizophrenia (6-week duration).
Table 19 Adverse experiences potentially associated with EPS in the short-term placebo-controlled monotherapy trial in adolescent patients with schizophrenia (6-week duration).
Preferred termPlaceboSEROQUEL XRSEROQUEL XRAll Doses(N = 75)400 mg/ day800 mg/ day(N = 147)(N = 73)(N = 74)n:%n%n%n%Dystonic event*00.022.700.021.4Parkinsonism22.745.545.485.4Akathisia34.034.145.474.8Dyskinetic event00.022.700.021.4Other00.022.722.742.7extrapyramidal event *Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: nuchal rigidity, hypertonia, dystonia, muscle rigidity
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: cogwheel rigidity, tremor
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: akathisia
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: tardive dyskinesia, dyskinesia, choreoathetosis
Table 20 below presents a listing of patients with Adverse Experiences potentially associated with EPS in a short-term placebo-controlled monotherapy trial in children and adolescent patients with bipolar mania (3-week duration)
Table 20: Adverse experiences potentially associated with EPS in a short-term placebo-controlled monotherapy trial in children and adolescent patients with bipolar mania (3-week duration)
Preferred term*PlaceboSEROQUELSEROQUELALL SEROQUEL(n=90)400 mg/day600 mg/day(N= 193)(N=95)(N=98)en%n%n%n%Parkinsonism11.122.111.031.6Akathisia00.011.011.021.0Other00.011.111.021.0extrapyramidal event *There were no adverse experiences with the preferred term of dystonic or dyskinetic events.
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: cogwheel rigidity, tremor
Patients with the following terms were counted in this category: akathisia
Children and Adolescents: Safety and effectiveness of SEROQUEL XR have not been established in pediatric patients and SEROQUEL XR is not approved for patients under the age of 18 years. In acute placebo-controlled trials in children and adolescent patients with schizophrenia (6-week duration) or bipolar mania (3-week duration), the incidence of increased appetite was 7.6% for SEROQUEL compared to 2.4% for placebo. In a 26-week open-label study that enrolled patients from the above two pediatric trials, the incidence of increased appetite was 7% for SEROQUEL.
6.2 Vital Signs and Laboratory Values
Hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, weight gain, orthostatic hypotension and changes in thyroid hormone levels have been reported with quetiapine. Increases in blood pressure have also been reported with quetiapine in children and adolescents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.8, 5.9 and 5.13)].
Laboratory Changes:
Neutrophil Counts
In three-arm SEROQUEL XR placebo-controlled monotherapy clinical trials, among patients with a baseline neutrophil count1.5 x 109/L, the incidence of at least one occurrence of neutrophil count <1.5 x 109/L was 1.5% in patients treated with SEROQUEL XR and 1.5% for SEROQUEL, compared to 0.8% in placebo-treated patients.
In placebo-controlled monotherapy clinical trials involving 3368 patients on quetiapine fumarate and 1515 on placebo, the incidence of at least one occurrence of neutrophil count <1.0 x 109/L among patients with a normal baseline neutrophil count and at least one available follow up laboratory measurement was 0.3% (10/2967) in patients treated with quetiapine, compared to 0.1% (2/1349) in patients treated with placebo. Patients with a pre-existing low WBC or a history of drug induced leukopenia/neutropenia should have their complete blood count (CBC) monitored frequently during the first few months of therapy and should discontinue SEROQUEL XR at the first sign of a decline in WBC in absence of other causative factors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Decreased Hemoglobin
In short-term placebo-controlled trials, decreases in hemoglobin to13 g/dL males,12 g/dL females on at least one occasion occurred in 8.3% (594/7155) of quetiapine-treated patients compared to 6.2% (219/3536) of patients treated with placebo. In a database of controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials, decreases in hemoglobin to13 g/dL males,12 g/dL females on at least one occasion occurred in 11% (2277/20729) of quetiapine-treated patients.
ECG Changes:
2.5% of SEROQUEL XR patients, and 2.3% of placebo patients, had tachycardia (>120 bpm) at any time during the trials. SEROQUEL XR was associated with a mean increase in heart rate, assessed by ECG, of 6.3 beats per minute compared to a mean increase of 0.4 beats per minute for placebo. This is consistent with the rates for SEROQUEL. The incidence of adverse reactions of tachycardia was 1.9% for SEROQUEL XR compared to 0.5% for placebo. SEROQUEL use was associated with a mean increase in heart rate, assessed by ECG, of 7 beats per minute compared to a mean increase of 1 beat per minute among placebo patients. The slight tendency for tachycardia may be related to quetiapine's potential for inducing orthostatic changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Children and Adolescents: Safety and effectiveness of SEROQUEL XR have not been established in pediatric patients. In the acute (6-week) schizophrenia trial in adolescents, potentially clinically significant increases in heart rate (> 110 bpm) occurred in 5.2% of patients receiving SEROQUEL 400 mg and 8.5% of patients receiving SEROQUEL 800 mg compared to 0% of patients receiving placebo. Mean increases in heart rate were 3.8 bpm and 11.2 bpm for SEROQUEL 400 mg and 800 mg groups, respectively, compared to a decrease of 3.3 bpm in the placebo group [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
In the acute (3-week) bipolar mania trial in children and adolescents, potentially clinically significant increases in heart rate (> 110 bpm) occurred in 1.1% of patients receiving SEROQUEL 400 mg and 2.4% of patients receiving SEROQUEL 600 mg compared to 0% of patients receiving placebo. Mean increases in heart rate were 12.8 bpm and 13.4 bpm for SEROQUEL 400 mg and 600 mg groups, respectively, compared to a decrease of 1.7 bpm in the placebo group [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
6.3 Post Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions were identified during post approval use of SEROQUEL. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse reactions reported since market introduction which were temporally related to SEROQUEL therapy include anaphylactic reaction and galactorrhea.
Other adverse reactions reported since market introduction, which were temporally related to SEROQUEL therapy, but not necessarily causally related, include the following: agranulocytosis, cardiomyopathy, hyponatremia, myocarditis, rhabdomyolysis, syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH), Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and decreased platelets.
In post-marketing clinical trials, elevations in total cholesterol (predominantly LDL cholesterol), dyspnea, palpitations and somnambulism (and other related events) have been reported.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS7.1 The Effect of Other Drugs on Quetiapine
7.2 Effect of Quetiapine on Other Drugs
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
12.3
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE9.1 Controlled Substance
9.2 Abuse
OVERDOSAGE
10 OVERDOSAGE10.1 Human Experience
10.2 Management of Overdosage
SEROQUEL DESCRIPTION
11 DESCRIPTION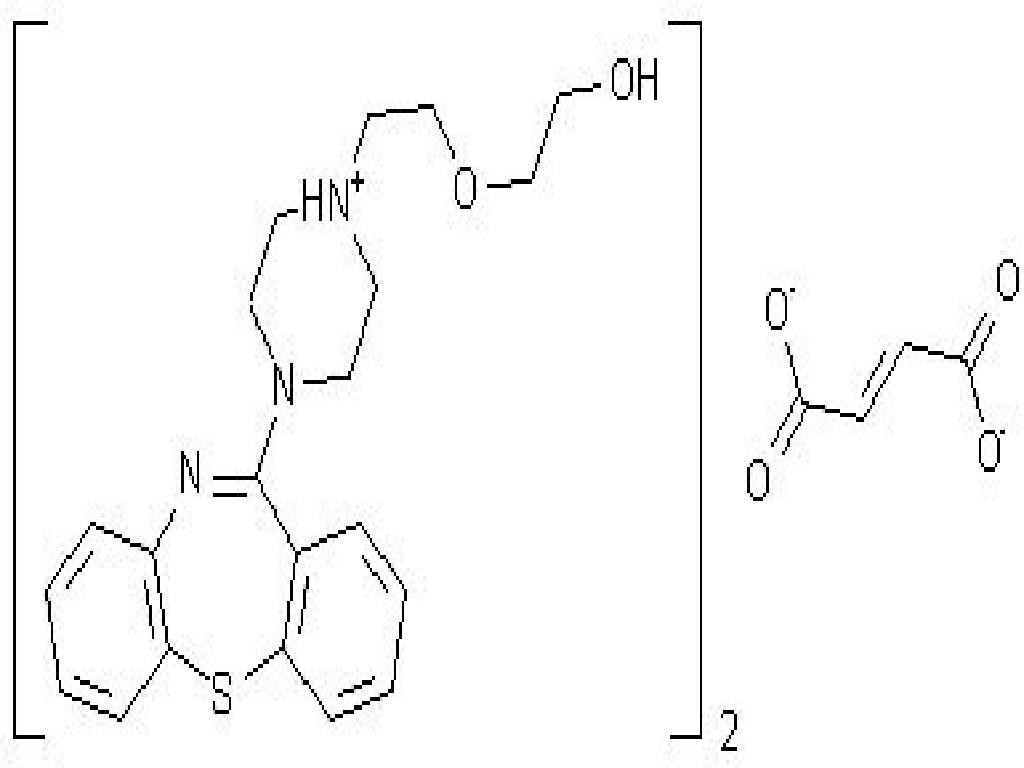
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
ReceptorQuetiapineNorquetiapine
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
7.2
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
CLINICAL STUDIES
14 CLINICAL STUDIES14.1 Schizophrenia
14.2 Bipolar Disorder
14.3 Major Depressive Disorder, Adjunctive Therapy to Antidepressants
HOW SUPPLIED
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING-
● 50 mg Tablets (NDC 0310-0280) peach, film coated, capsule-shaped, biconvex, intagliated tablet withXR 50on one side and plain on the other are supplied in bottles of 60 tablets and hospital unit dose packages of 100 tablets.
-
● 150 mg Tablets (NDC 0310-0281) white, film-coated, capsule-shaped, biconvex, intagliated tablet withXR 150'on one side and plain on the other are supplied in bottles of 60 tablets and hospital unit dose packages of 100 tablets.
-
● 200 mg Tablets (NDC 0310-0282) yellow, film coated, capsule-shaped, biconvex, intagliated tablet withXR 200on one side and plain on the other are supplied in bottles of 60 tablets and hospital unit dose packages of 100 tablets.
-
● 300 mg Tablets (NDC 0310-0283) pale yellow, film coated, capsule-shaped, biconvex, intagliated tablet withXR 300on one side and plain on the other are supplied in bottles of 60 tablets and hospital unit dose packages of 100 tablets.
-
● 400 mg Tablets (NDC 0310-0284) white, film coated, capsule-shaped, biconvex, intagliated tablet withXR 400on one side and plain on the other are supplied in bottles of 60 tablets and hospital unit dose packages of 100 tablets.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION17.1 Information for Patients
SPL MEDGUIDE
17.2 MEDICATION GUIDE-
● Risk of death in the elderly with dementia: Medicines like SEROQUEL XR can raise the risk of death in elderly people who have lost touch with reality due to confusion and memory loss (dementia). SEROQUEL XR is not approved for treating psychosis in the elderly with dementia.
-
● Risk of suicidal thoughts or actions: Antidepressant medicines, depression and other serious mental illnesses, and suicidal thoughts or actions:
-
● Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is started or when the dose is changed.
-
● Call the healthcare provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings.
-
● Keep all follow-up visits with the healthcare provider as scheduled. Call the healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you have concerns about symptoms.
-
● thoughts about suicide or dying
-
● attempts to commit suicide
-
● new or worse depression
-
● new or worse anxiety
-
● feeling very agitated or restless
-
● panic attacks
-
● trouble sleeping (insomnia)
-
● new or worse irritability
-
● acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
-
● acting on dangerous impulses
-
● an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
-
● other unusual changes in behavior or mood
-
● Never stop an antidepressant medicine without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping an antidepressant medicine suddenly can cause other symptoms.
-
● Antidepressants are medicines used to treat depression and other illnesses. It is important to discuss all the risks of treating depression and also the risks of not treating it. Patients and their families or other caregivers should discuss all treatment choices with the healthcare provider, not just the use of antidepressants.
-
● Antidepressant medicines have other side effects. Talk to the healthcare provider about the side effects of the medicine prescribed for you or your family member.
-
● Antidepressant medicines can interact with other medicines. Know all of the medicines that you or your family member take. Keep a list of all medicines to show the healthcare provider. Do not start new medicines without first checking with your healthcare provider.
-
● Not all antidepressant medicines prescribed for children are FDA approved for use in children. Talk to your child's healthcare provider for more information.
-
● SEROQUEL XR is a prescription medicine used to treat schizophrenia in adults.
-
● SEROQUEL XR is a prescription medicine used to treat bipolar disorder in adults, including:
-
● manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder alone or with lithium or divalproex.
-
● depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder.
-
● long-term treatment of bipolar I disorder with lithium or divalproex.
-
● SEROQUEL XR is a prescription medicine used to treat major depressive disorder as add-on treatment with antidepressant medicines when your doctor determines that one antidepressant alone is not enough to treat your depression.
-
● diabetes or high blood sugar in you or your family: your healthcare provider should check your blood sugar before you start SEROQUEL XR and also during therapy.
-
● high levels of total cholesterol, triglycerides or LDL-cholesterol or low levels of HDL- cholesterol
-
● low or high blood pressure
-
● low white blood cell count
-
● cataracts
-
● seizures
-
● abnormal thyroid tests
-
● high prolactin levels
-
● heart problems
-
● liver problems
-
● any other medical condition
-
● pregnancy or plans to become pregnant. It is not known if SEROQUEL XR will harm your unborn baby.
-
● breast-feeding or plans to breast-feed. It is not known if SEROQUEL XR will pass into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take SEROQUEL XR or breast-feed. You should not do both.
-
● depression
-
● high blood pressure
-
● Parkinson's disease
-
● trouble sleeping
-
● phenytoin, divalproex or carbamazepine (for epilepsy)
-
● barbiturates (to help you sleep)
-
● rifampin (for tuberculosis)
-
● glucocorticoids (steroids for inflammation)
-
● thioridazine (an antipsychotic)
-
● ketoconazole, fluconazole or itraconazole (for fungal infections)
-
● erythromycin (an antibiotic)
-
● protease inhibitors (for HIV)
-
● Take SEROQUEL XR exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it. Do not change the dose yourself.
-
● Take SEROQUEL XR by mouth, with a light meal or without food.
-
● SEROQUEL XR should be swallowed whole and not split, chewed or crushed.
-
● If you feel you need to stop SEROQUEL XR, talk with your healthcare provider first.
-
● If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is close to the next dose, skip the missed dose. Just take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take 2 doses at the same time unless your healthcare provider tells you to. If you are not sure about your dosing, call your healthcare provider.
-
● If you take too much SEROQUEL XR, call your healthcare provider or poison control center at 1-800-222-1222 right away or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
-
● Avoid getting over-heated or dehydrated.
-
● Do not over-exercise.
-
● In hot weather, stay inside in a cool place if possible.
-
● Stay out of the sun. Do not wear too much or heavy clothing.
-
● Drink plenty of water.
-
● Do not drink alcohol while taking SEROQUEL XR. It may make some side effects of SEROQUEL XR worse.
-
● Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS): Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have some or all of the following symptoms: high fever, stiff muscles, confusion, sweating, changes in pulse, heart rate, and blood pressure. These may be symptoms of a rare and serious condition that can lead to death. Stop SEROQUEL XR and call your healthcare provider right away.
-
● High blood sugar (hyperglycemia): Increases in blood sugar can happen in some people who take SEROQUEL XR. Extremely high blood sugar can lead to coma or death. If you have diabetes or risk factors for diabetes (such as being overweight or a family history of diabetes) your healthcare provider should check your blood sugar before you start SEROQUEL XR and during therapy.
-
● feel very thirsty
-
● need to urinate more than usual
-
● feel very hungry
-
● feel weak or tired
-
● feel sick to your stomach
-
● feel confused, or your breath smells fruity.
-
● High cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood (fat in the blood) Increases in total cholesterol, triglycerides and LDL (bad) cholesterol and decreases in HDL (good) cholesterol have been reported in clinical trials with SEROQUEL XR. You may not have any symptoms, so your healthcare provider should do blood tests to check your cholesterol and triglyceride levels before you start taking SEROQUEL XR and during therapy.
-
● Increase in weight (weight gain): Weight gain has been seen in patients who take SEROQUEL XR so you and your healthcare provider should check your weight regularly.
-
● Tardive dyskinesia: Tell your healthcare provider about any movements you cannot control in your face, tongue, or other body parts. These may be signs of a serious condition. Tardive dyskinesia may not go away, even if you stop taking SEROQUEL XR. Tardive dyskinesia may also start after you stop taking SEROQUEL XR.
-
● Orthostatic hypotension (decreased blood pressure): lightheadedness or fainting caused by a sudden change in heart rate and blood pressure when rising too quickly from a sitting or lying position.
-
● Increases in blood pressure: reported in children and teenagers. Your healthcare provider should check blood pressure in children and adolescents before starting SEROQUEL XR and during therapy. SEROQUEL XR is not approved for patients under 18 years of age.
-
● Low white blood cell count
-
● Cataracts
-
● Seizures
-
● Abnormal thyroid tests: Your healthcare provider may do blood tests to check your thyroid hormone level.
-
● Increases in prolactin levels: Your healthcare provider may do blood tests to check your prolactin levels.
-
● Increases in liver enzymes: Your healthcare provider may do blood tests to check your liver enzyme levels.
-
● Long lasting and painful erection
-
● Difficulty swallowing
-
● drowsiness
-
● dry mouth
-
● constipation
-
● dizziness
-
● increased appetite
-
● upset stomach
-
● weight gain
-
● fatigue
-
● disturbance in speech and language
-
● stuffy nose
-
● Store SEROQUEL XR at room temperature, between 59to 86(15to 30
-
● Keep SEROQUEL XR and all medicines out of the reach of children.
-
● Having lost touch with reality (psychosis)
-
● Seeing things that are not there or hearing voices (hallucinations)
-
● Believing things that are not true (delusions) and
-
● Being suspicious (paranoia).
-
● General symptoms of bipolar disorder include extreme mood swings, along with other specific symptoms and behaviors. These mood swings, or "episodes," include manic (highs) and depressive (lows)
-
● Common symptoms of a manic episode include feeling extremely happy, being very irritable, restless, talking too fast and too much, and having more energy and needing less sleep than usual
-
● Common symptoms of a depressive episode include feelings of sadness or emptiness, increased tearfulness, a loss of interest in activities you once enjoyed, loss of energy, difficulty concentrating or making decisions, feelings of worthlessness or guilt, changes in sleep or appetite.
-
● Thoughts of death or suicide.
-
● Feeling of sadness, emptiness and increased tearfulness
-
● Loss of interest in activities that you once enjoyed and loss of energy
-
● Problems focusing and making decisions
-
● Feeling of worthlessness or guilt
-
● Changes in sleep or eating patterns
-
● Thoughts of death or suicide
-
● MDD symptoms last most of the day, nearly every day for at least two weeks, and interfere with daily life at home and at work.
INACTIVE INGREDIENT
INACTIVE INGREDIENTLACTOSE MONOHYDRATE
CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE
SODIUM CITRATE
HYPROMELLOSES
MAGNESIUM STEARATE
POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 400
TITANIUM DIOXIDE
WATER
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION


SeroquelSeroquel TABLET, EXTENDED RELEASE
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!