Simvastatin
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use simvastatin safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for simvastatin tablets. Simvastatin Tablets, USP Initial U.S. Approval: 1991
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- SPL INDEXING DATA ELEMENTS
- SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
- SIMVASTATIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- SIMVASTATIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- SIMVASTATIN DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- PHARMACODYNAMICS
- PHARMACOKINETICS
- NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
SPL INDEXING DATA ELEMENTS
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use simvastatin safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for simvastatin tablets.Simvastatin Tablets, USP
Initial U.S. Approval: 1991
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
(2.5)
(2.6)
(5.1)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
● Reduce the risk of total mortality by reducing CHD deaths and reduce the risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction, stroke, and the need for revascularization procedures in patients at high risk of coronary events.(1.1)
-
● Reduce elevated total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, TG and increase HDL-C in patients with primary hyperlipidemia (heterozygous familial and nonfamilial) and mixed dyslipidemia.(1.2)
-
● Reduce elevated TG in patients with hypertriglyceridemia and reduce TG and VLDL-C in patients with primary dysbeta(1.2)
-
● Reduce total-C and LDL-C in adult patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.(1.2)
-
● Reduce elevated total-C, LDL-C, and Apo B in boys and postmenarchal girls, 10 to 17 years of age with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia after failing an adequate trial of diet therapy.(1.2,1.3)
-
●
(1.4)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
(2.1)
-
● Recommended usual starting dose is 20 to 40 mg once a day in the evening.(2.1)
-
● Recommended starting dose for patients at high risk of CHD is 40 mg/day.(2.1)
-
● Adolescents (10 to 17 years of age) with HeFH: starting dose is 10 mg/day; maximum recommended dose is 40 mg/day.(2.3)
-
● DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
(46.2)
-
● Active liver disease, which may include unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase levels.(4,5.2)
-
● Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant.(4,8.1)
-
● Nursing mothers.(4,8.3)
-
● WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
-
● Patients should be advised to report promptly any symptoms of myopathy. Simvastatin therapy should be discontinued immediately if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected. See Drug Interaction table.(5.1)
-
● Liver enzyme abnormalities and monitoring: Persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase can occur. Monitor liver enzymes before and during treatment. Patients titrated to the 80 mg dose should receive more frequent liver function tests than patients on lower doses.(5.2)
-
● ADVERSE REACTIONS
(6.1)
DRUG INTERACTIONS
2.65.17.17.27.37.4)
Interacting AgentsPrescribing Recommendations(7.7)
-
● USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
(2.48.6)
See17for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
*1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Reductions in Risk of CHD Mortality and Cardiovascular Events
1.2 Hyperlipidemia
1.3 Adolescent Patients with Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HeFH)
1.4 Limitations of Use
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
2.2 Patients with Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
2.3 Adolescents (10 to 17 years of age) with Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
2.4 Patients with Renal Impairment
2.5 Chinese Patients Taking Lipid-Modifying Doses (g/day Niacin) of Niacin-Containing Products
2.6 Coadministration with Other Drugs
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis
5.2 Liver Dysfunction
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP3A4 Interactions
7.2 Lipid-Lowering Drugs That Can Cause Myopathy When Given Alone
7.3 Cyclosporine or Danazol
7.4 Amiodarone, Verapamil, or Diltiazem
7.5 Niacin
7.6 Digoxin
7.7 Coumarin Anticoagulants
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Clinical Studies in Adults
14.2 Clinical Studies in Adolescents
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Muscle Pain
17.2 Liver Enzymes
17.3 Pregnancy
17.4 Breastfeeding
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg (30 Tablet Bottle)
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg Bulk Tablet Label
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg (30 Tablet Bottle)
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Bulk Tablet Label
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mg (30 Tablet Bottle)
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mg Bulk Tablet Label
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 40 mg (30 Tablet Bottle)
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 40 mg Bulk Tablet Label
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 80 mg (30 Tablet Bottle)
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 80 mg Bulk Tablet Label
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed
INDICATIONS & USAGE
1.1 Reductions in Risk of CHD Mortality and Cardiovascular Events
-
● Reduce the risk of total mortality by reducing CHD deaths.
-
● Reduce the risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction and stroke.
-
● Reduce the need for coronary and non-coronary revascularization procedures.
-
●
-
● Reduce elevated TG in patients with hypertriglyceridemia (Fredrickson type IV hyperlipidemia).
-
● Reduce elevated TG and VLDL-C in patients with primary dysbetalipoproteinemia (Fredrickson type III hyperlipidemia).
-
● Reduce total-C and LDL-C in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering treatments (e.g., LDL apheresis) or if such treatments are unavailable.
-
●
-
● Two or more other CVD risk factors are present in the adolescent patient.
-
● The minimum goal of treatment in pediatric and adolescent patients is to achieve a mean LDL-C <130 mg/dL. The optimal age at which to initiate lipid-lowering therapy to decrease the risk of symptomatic adulthood CAD has not been determined.
1.4 Limitations of Use
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing2.2 Patients with Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
2.3 Adolescents (10 to 17 years of age) with Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Clinical Studies (14.2)
2.4 Patients with Renal Impairment
Warnings and Precautions (5.1) Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
2.5 Chinese Patients Taking Lipid-Modifying Doses (g/day Niacin) of Niacin-Containing Products
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)
2.6 Coadministration with Other Drugs
-
● Simvastatin tablets may be used concomitantly with bile acid sequestrants.
-
● Combination therapy with gemfibrozil increases simvastatin exposure. Therefore, if simvastatin tablets are used in combination with gemfibrozil, the dose of simvastatin tablets should not exceed 10 mg/day [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.1),Drug Interactions (7.2), andClinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
●
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)Drug Interactions (7.3)
-
●
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)Drug Interactions (7.4)Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
-
● Patients taking Diltiazem
-
●
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
-
● Tablets simvastatin 5 mg are yellow colored, round shaped, biconvex, film coated tablets, debossed withA'on one side and15'on the other side.
-
● Tablets simvastatin 10 mg are light pink colored, round shaped, biconvex, film coated tablets, debossed withA'on one side and01'on the other side.
-
● Tablets simvastatin 20 mg are light pink colored, round shaped, biconvex, film coated tablets, debossed withA'on one side and02'on the other side.
-
● Tablets simvastatin 40 mg are pink colored, round shaped, biconvex, film coated tablets, debossed withA'on one side and03'on the other side.
-
● Tablets simvastatin 80 mg are pink colored, capsule shaped, biconvex, film coated tablets, debossed withA'on one side and04'on the other side.
-
●
SIMVASTATIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
● Hypersensitivity to any component of this medication [seeAdverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
● Active liver disease, which may include unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase levels [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
● Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant. Serum cholesterol and triglycerides increase during normal pregnancy, and cholesterol or cholesterol derivatives are essential for fetal development. Because HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) decrease cholesterol synthesis and possibly the synthesis of other biologically active substances derived from cholesterol, simvastatin tablets may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Atherosclerosis is a chronic process and the discontinuation of lipid-lowering drugs during pregnancy should have little impact on the outcome of long-term therapy of primary hypercholesterolemia. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of use with simvastatin tablets during pregnancy; however, in rare reports congenital anomalies were observed following intrauterine exposure to statins. In rat and rabbit animal reproduction studies, simvastatin revealed no evidence of teratogenicity. Simvastatin tablets should be administered to women of childbearing age only when such patients are highly unlikely to conceive. If the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, simvastatin tablets should be discontinued immediately and the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [seeUse in Specific Populations (8.1)].
-
● Nursing mothers. It is not known whether simvastatin is excreted into human milk; however, a small amount of another drug in this class does pass into breast milk. Because statins have the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women who require treatment with simvastatin tablets should not breastfeed their infants [seeUse in Specific Populations (8.3)].
-
●
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Myopathy/RhabdomyolysisDrug Interactions (7)
Dosage and Administration (2.6)Drug Interactions (7)Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
5.2 Liver Dysfunction
Clinical Studies (14.1)
In 2 controlled clinical studies in 1,105 patients, the 12-month incidence of persistent hepatic transaminase elevation without regard to drug relationship was 0.9% and 2.1% at the 40 and 80 mg dose, respectively. No patients developed persistent liver function abnormalities following the initial 6 months of treatment at a given dose.
It is recommended that liver function tests be performed before the initiation of treatment, and thereafter when clinically indicated. Patients titrated to the 80 mg dose should receive an additional test prior to titration, 3 months after titration to the 80 mg dose, and periodically thereafter (e.g., semiannually) for the first year of treatment. Patients who develop increased transaminase levels should be monitored with a second liver function evaluation to confirm the finding and be followed thereafter with frequent liver function tests until the abnormality(ies) return to normal. Should an increase in AST or ALT of 3X ULN or greater persist, withdrawal of therapy with simvastatin is recommended.
The drug should be used with caution in patients who consume substantial quantities of alcohol and/or have a past history of liver disease. Active liver diseases or unexplained transaminase elevations are contraindications to the use of simvastatin.
As with other lipid-lowering agents, moderate (less than 3X ULN) elevations of serum transaminases have been reported following therapy with simvastatin. These changes appeared soon after initiation of therapy with simvastatin, were often transient, were not accompanied by any symptoms and did not require interruption of treatment.
SIMVASTATIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials ExperienceWarnings and Precautions (5.2)Warnings and Precautions (5.1)
Use in Specific Populations (8.4)Clinical Studies (14.2)
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP3A4 InteractionsWarnings and Precautions (5.1)Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
7.2 Lipid-Lowering Drugs That Can Cause Myopathy When Given Alone
Dosage and Administration (2.6)Warnings and Precautions (5.1)
7.3 Cyclosporine or Danazol
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
7.4 Amiodarone, Verapamil, or Diltiazem
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)
7.5 Niacin
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
7.6 Digoxin
Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
7.7 Coumarin Anticoagulants
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 PregnancyContraindications (4)
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Contraindications (4)
8.4 Pediatric Use
Dosage and Administration (2.3)Adverse Reactions (6.1)Clinical Studies (14.2)Contraindications (4)Use in Specific Populations (8.1)
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
Clinical Studies (14.1)
8.6 Renal Impairment
Caution should be exercised when simvastatin is administered to patients with severe renal impairment. [SeeDosage and Administration (2.4)
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Contraindications (4)Warnings and Precautions (5.2)
OVERDOSAGE
SIMVASTATIN DESCRIPTION
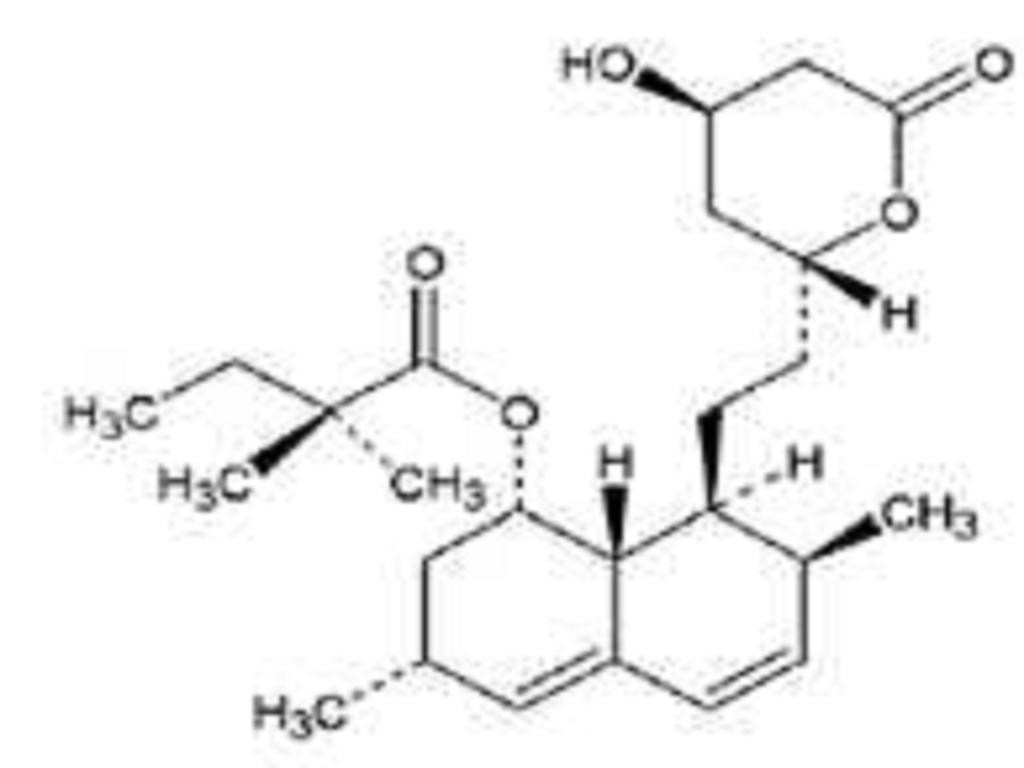
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of ActionPHARMACODYNAMICS
12.2 PharmacodynamicsPHARMACOKINETICS
12.3 PharmacokineticsUse in Specific Populations (8.5)
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)Drug Interactions (7.1)
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)Warnings and Precautions (5.1)Warnings and Precautions (5.1)Warnings and Precautions (5.1)Warnings and Precautions (5.1)
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)Drug Interactions (7.5)
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

SimvastatinSimvastatin TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!