Advocin
ADVOCIN™(danofloxacin mesylate)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- CAUTION
- ADVOCIN DESCRIPTION
- INDICATIONS
- ADVOCIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- WARNINGS
- ANTIBACTERIAL WARNINGS
- HUMAN WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- ADVOCIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- EFFECTIVENESS
- ANIMAL SAFETY
- TOXICOLOGY
- STORAGE INFORMATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- CONTACT INFORMATION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mL Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 250 mL Bottle Label
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Sterile Injectable Solution
180 mg of danofloxacin as the mesylate salt/mL
For subcutaneous use in cattle for treatment of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida.
Not for use in cattle intended for dairy production or in calves to be processed for veal.
CAUTION
Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Federal law prohibits the extra-label use of this drug in food-producing animals.
ADVOCIN DESCRIPTION
ADVOCIN is a sterile injectable solution containing danofloxacin mesylate, a synthetic fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agent. Danofloxacin mesylate is the non-proprietary designation for (1S)-1cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-(5-methyl-2,5-diazabicyclo [2.2.1]hept-2-yl)-4-oxo-3-quinolone carboxylic acid monomethanesulfonate. The empirical formula is C19H20FN3O3 • CH3SO3H and the molecular weight is 453.49.
Figure 1. The chemical structure of danofloxacin mesylate.
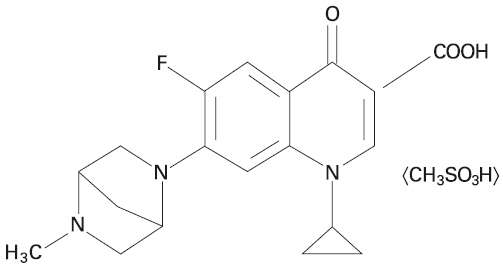
Each mL contains 180 mg of danofloxacin as the mesylate salt, 200 mg 2-pyrrolidone, 50 mg polyvinyl pyrrolidone, 20.3 mg heavy magnesium oxide, 2.5 mg phenol, 5 mg monothioglycerol, hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide as needed to adjust pH, nitrogen headspace and water for injection, q.s.
INDICATIONS
ADVOCIN (danofloxacin) injectable solution is indicated for the treatment of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida.
ADVOCIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
ADVOCIN is administered subcutaneously at either 8 mg/kg of body weight (2 mL/100 lb) as a one time injection, or at 6 mg/kg of body weight (1.5 mL/100 lb) with this treatment repeated once approximately 48 hours following the first injection. Care should be taken to dose accurately. Administered dose volume should not exceed 15 mL per injection site.
| Dose Volume (mL) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cattle Weight (lb) |
6 mg/kg, given twice, 48 hours apart |
8 mg/kg given once |
| 50 | 0.75 | 1 |
| 100 | 1.5 | 2 |
| 150 | 2.25 | 3 |
| 200 | 3 | 4 |
| 250 | 3.75 | 5 |
| 300 | 4.5 | 6 |
| 400 | 6 | 8 |
| 500 | 7.5 | 10 |
| 600 | 9 | 12 |
| 700 | 10.5 | 14 |
| 800 | 12 | 16 |
| 900 | 13.5 | 18 |
| 1000 | 15 | 20 |
WARNINGS
Animals intended for human consumption must not be slaughtered within 4 days from the last treatment. Do not use in cattle intended for dairy production. A withdrawal period has not been established for this product in preruminating calves. Do not use in calves to be processed for veal.
ANTIBACTERIAL WARNINGS
Use of antibacterial drugs in the absence of a susceptible bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to treated animals and may increase the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
HUMAN WARNINGS
For use in animals only. Keep out of reach of children. Avoid contact with eyes. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with copious amounts of water for 15 minutes. In case of dermal contact, wash skin with soap and water. Consult a physician if irritation persists following ocular or dermal exposures. Individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to quinolones should avoid this product. In humans, there is a risk of user photosensitization within a few hours after excessive exposure to quinolones. If excessive accidental exposure occurs, avoid direct sunlight. To report adverse reactions or to obtain a copy of the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), call 1-800-366-5288.
PRECAUTIONS
The effects of danofloxacin on bovine reproductive performance, pregnancy, and lactation have not been determined.
Subcutaneous injection can cause a transient local tissue reaction that may result in trim loss of edible tissue at slaughter.
Quinolone-class drugs should be used with caution in animals with known or suspected central nervous system (CNS) disorders. In such animals, quinolones have, in rare instances, been associated with CNS stimulation, which may lead to convulsive seizures.
Quinolone-class drugs have been shown to produce erosions of cartilage of weight-bearing joints and other signs of arthropathy in immature, rapidly growing animals of various species. Refer to Animal Safety for information specific to danofloxacin.
ADVOCIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
A hypersensitivity reaction was noted in 2 healthy calves treated with ADVOCIN in a laboratory study. In one location of a multi-site field trial, one out of the 41 calves treated with 6 mg/kg q 48 hours showed lameness on Day 6 only. In this same field trial location one of 38 calves treated with 8 mg/kg once became lame 4 days after treatment and remained lame on the last day of the study (Day 10). Another calf in the same treatment group developed lameness on the last day of the study.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
(a) Pharmacokinetics
Danofloxacin distributes extensively throughout the body, as evidenced by a steady state volume of distribution (VDss) in cattle exceeding 1 L/kg. Danofloxacin concentrations in the lung homogenates markedly exceed those observed in plasma, further suggesting extensive distribution to the indicated site of infection. Danofloxacin is rapidly eliminated from the body (apparent terminal elimination T½ ranging from 3–6 hours), and negligible accumulation was observed when animals were dosed twice, 48 hours apart.
Danofloxacin is rapidly absorbed and is highly bioavailable when administered as a subcutaneous injection in the neck. Linear pharmacokinetics has been demonstrated when danofloxacin is administered to cattle by subcutaneous injection at doses between 1.25 to 10 mg/kg. No statistically significant gender difference was observed in peak or total systemic exposure following a single subcutaneous administration of danofloxacin to heifers and steers at a dose of 6 mg/kg body weight (Table 1).
| Steers | Heifers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | %CV |
Mean | %CV | ||
 |
µg × hr/mL | 9.4 | 10 | 8.8 | 9 |
|
|
92 | 5 | 87 | 3 | |
 |
µg/mL | 1.25 | 16 | 1.27 | 13 |
 |
hr | 3.2 | 42 | 1.7 | 31 |
 |
L/hr | 0.54 | 12 | 0.62 | 9 |
 |
L/kg | 2.7 | 7 | 2.6 | 4 |
 |
hr | 4.8 | 18 | 4.2 | 7 |
(b) Microbiology
Danofloxacin exerts its activity by inhibiting the bacterial DNA gyrase enzyme, thereby blocking DNA replication. Inhibition of DNA gyrase is lethal to bacteria and danofloxacin has been shown to be rapidly bactericidal. Danofloxacin is active against gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.
The Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC) of danofloxacin for pathogens isolated in natural infections from various clinical studies in North America, 1996–1997, were determined using the standardized microdilution technique (SENSITITRE/ALAMAR, Accumed International), and are shown in Table 2.
| Indicated Pathogen | Number of Isolates | MIC50
 |
MIC90
 |
MIC Range (μg/ mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mannheimia haemolytica | 106 | 0.06 | 0.06 | ≤0.015 to 0.12 |
| Pasteurella multocida | 94 | ≤0.015 | 0.06 | ≤0.015 to 0.12 |
EFFECTIVENESS
The effectiveness of 8 mg/kg administered once and the 6 mg/kg BW alternate day regimen was confirmed in 4 well-controlled studies of naturally acquired bacterial respiratory infections in feedlot age cattle. These studies were conducted under commercial conditions at 4 locations in North America. Bacterial pathogens isolated in the clinical field trial are provided in the Microbiology section.
ANIMAL SAFETY
Safety studies were conducted in feeder calves using single doses of 10, 20, or 30 mg/kg for 6 consecutive days and 18, 24, or 60 mg/kg for 3 consecutive days. No clinical signs of toxicity were observed at doses of 10 and 20 mg/kg when administered for 6 days, nor at doses of 18 and 24 mg/kg when administered for 3 days. Articular cartilage lesions, consistent with fluoroquinolone chondropathy, were observed after examination of joints from animals as follows: one of 5 animals administered 18 mg/kg for 3 days; one of 6 animals administered 20 mg/kg for 6 days; 5 of 6 animals administered 30 mg/kg for 6 days; and in all 4 animals administered 60 mg/kg for 3 days. Clinical signs of inappetence, transient lameness (2/6), ataxia (2/6), tremors (2/6), nystagmus (1/6), exophthalmos (1/6), and recumbency (2/6) were observed when a dose of 30 mg/kg was administered for 6 consecutive days. Recumbency and depression were seen in one out of 4 animals administered 60 mg/kg for 3 days. Swelling at the injection site was noted at each dose level.
Safety was also evaluated in 21-day-old calves. In one group, these immature animals were given injections of 6 mg/kg on study days 0, 2, 3, 5, 6, and 8. A second group of animals received injections of 18 mg/kg for a total of 2 injections 48 hours apart. The only treatmentrelated sign was erythema of the nasal pad in 3 of 6 calves that received 18 mg/kg. One calf in the 6 mg/kg group had pre-treatment scleral erythema, and developed nasal erythema after treatment that may or may not have been treatment-related. No changes in clinical pathology parameters were observed. No articular cartilage lesions were observed in the joints at any dosage.
An injection site study conducted in feeder calves demonstrated that the product can induce a transient local reaction in the subcutaneous tissue and underlying tissue.
TOXICOLOGY
Ninety-day oral toxicity studies in dogs and rats established a no observable effect level (NOEL) of 2.5 mg/kg bw/day and 2.4 mg/kg bw/day, respectively. Higher doses in juvenile dogs produced arthropathy, a typical quinolone-associated side effect. In chronic rodent bioassays, no evidence of carcinogenicity was associated with long-term danofloxacin administration in rats and mice. No teratogenic effects were observed in rodents at doses up to 50 mg/kg bw/day (mice) or 100 mg/kg bw/day (rats) or in rabbits at the highest dose tested of 15 mg/kg bw/day. A three-generation rat reproductive toxicity study established a NOEL of 6.25 mg/kg bw/day. Microbial safety analyses indicate that danofloxacin residues present in edible tissues of treated animals under the current use conditions would most likely not cause adverse effects on the human intestinal microflora of the consumer.
STORAGE INFORMATION
Store at or below 30°C (86°F). Protect from light. Protect from freezing. The color is yellow to amber and does not affect potency.
HOW SUPPLIED
ADVOCIN (180 mg danofloxacin/mL) is supplied in 100- and 250-mL, amber-glass, sterile, multi-dose vials.
NADA #141-207, Approved by FDA
Distributed by:
Zoetis Inc.
Kalamazoo, MI 49007
Use Only as Directed
CONTACT INFORMATION
To report suspected adverse effects and/or obtain a copy of the MSDS or for technical assistance, call Zoetis Inc. at 1-888-963-8471.
For a complete listing of adverse reactions for ADVOCIN Sterile Injectable Solution reported to CVM see: http://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/SafetyHealth
| TAKE TIME |

|
OBSERVE LABEL DIRECTIONS |
Revised: January 2013
Made in France
8713831
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mL Bottle Label
ADVOCIN™
(danofloxacin mesylate)
Sterile Injectable Solution
180 mg of danofloxacin as the mesylate salt/mL
For subcutaneous use in cattle for treatment of
bovine respiratory disease (BRD) associated with
Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida.
Not for use in cattle intended for dairy production or
in calves to be processed for veal.
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by or
on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Federal law prohibits the extra-label use of this drug
in food-producing animals.
Net Contents: 100 mL
NADA #141-207,
Approved by FDA
zoetis

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 250 mL Bottle Label
ADVOCIN™
(danofloxacin mesylate)
Sterile Injectable Solution
180 mg of danofloxacin as the mesylate salt/mL
For subcutaneous use in cattle for treatment of
bovine respiratory disease (BRD) associated
with Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella
multocida.
Not for use in cattle intended for dairy production or
in calves to be processed for veal.
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by or
on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Federal law prohibits the extra-label use of this drug
in food-producing animals.
Net Contents: 250 mL
NADA #141-207,
Approved by FDA
zoetis

Advocindanofloxacin mesylate INJECTION, SOLUTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||