Afinitor
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION RECENT MAJOR CHANGESIndications and Usage (1.2) 11/2013Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7) 2/2014Warnings and Precautions, Infections (5.2) 2/2014Warnings and Precautions, Oral Ulceration (5.3) 2/2014Warnings and Precautions, Impaired Wound Healing (5.5) 2/2014Warnings and Precautions, Lab Tests and Monitoring (5.7) 2/2014Warnings and Precautions, Embryo-fetal Toxicity (5.11) 2/2014INDICATIONS AND USAGEAFINITOR is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of: postmenopausal women with advanced hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer (advanced HR+ BC) in combination with exemestane after failure of treatment with letrozole or anastrozole. (1.1) adults with progressive neuroendocrine tumors of pancreatic origin (PNET) that are unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic. AFINITOR is not indicated for the treatment of patients with functional carcinoid tumors. (1.2) adults with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) after failure of treatment with sunitinib or sorafenib. (1.3) adults with renal angiomyolipoma and tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), not requiring immediate surgery. The effectiveness of AFINITOR in the treatment of renal angiomyolipoma is based on an analysis of durable objective responses in patients treated for a median of 8.3 months. Further follow-up of patients is required to determine long-term outcomes. (1.4) AFINITOR and AFINITOR DISPERZ are kinase inhibitors indicated for the treatment of: pediatric and adult patients with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) who have subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) that requires therapeutic intervention but cannot be curatively resected. The effectiveness is based on demonstration of durable objective response, as evidenced by reduction in SEGA tumor volume. Improvement in disease-related symptoms and overall survival in patients with SEGA and TSC has not been demonstrated. (1.5) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONAdvanced HR+ BC, advanced PNET, advanced RCC, or renal angiomyolipoma with TSC: 10 mg once daily with or without food. (2.1) For patients with hepatic impairment, reduce the AFINITOR dose. (2.2) If moderate inhibitors of CYP3A4 /P-glycoprotein (PgP) are required, reduce the AFINITOR dose to 2.5 mg once daily; if tolerated, consider increasing to 5 mg once daily. (2.2) If strong inducers of CYP3A4 are required, consider doubling the daily dose of AFINITOR using increments of 5 mg or less. (2.2) SEGA with TSC: 4.5 mg/m2 once daily; adjust dose to attain trough concentrations of 5-15 ng/mL. (2.3) Assess trough concentrations approximately 2 weeks after initiation of treatment, a change in dose, a change in co-administration of CYP3A4/PgP inducers or inhibitors, a change in hepatic function, or a change in dosage form between AFINITOR Tablets and AFINITOR DISPERZ. (2.3, 2.4) For patients with severe hepatic impairment reduce the starting dose of AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ. (2.3, 2.5) If concomitant use of moderate inhibitors of CYP3A4/PgP is required, reduce the dose of AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ by 50%. (2.3, 2.5) If concomitant use of strong inducers of CYP3A4/PgP is required, double the dose of AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ. (2.3, 2.5) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSAFINITOR Tablets: 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, and 10 mg tablets with no score (3.1)AFINITOR DISPERZ (everolimus tablets for oral suspension): 2 mg, 3 mg, and 5 mg tablets for oral suspension with no score (3.2)CONTRAINDICATIONSHypersensitivity to everolimus, to other rapamycin derivatives, or to any of the excipients (4)WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Non-infectious pneumonitis: Monitor for clinical symptoms or radiological changes; fatal cases have occurred. Manage by dose reduction or discontinuation until symptoms resolve, and consider use of corticosteroids. (5.1) Infections: Increased risk of infections, some fatal. Monitor for signs and symptoms, and treat promptly. (5.2) Oral ulceration: Mouth ulcers, stomatitis, and oral mucositis are common. Management includes mouthwashes and topical treatments. (5.3) Renal failure: Cases of renal failure (including acute renal failure), some with a fatal outcome, have been observed. (5.4) Impaired wound healing: Increased risk of wound-related complications. Monitor signs and symptoms. Exercise caution in the peri-surgical period. (5.5) Laboratory test alterations: Elevations of serum creatinine, urinary protein, blood glucose, and lipids may occur. Decreases in hemoglobin, neutrophils, and platelets may also occur. Monitor renal function, blood glucose, lipids, and hematologic parameters prior to treatment and periodically thereafter. (5.7) Vaccinations: Avoid live vaccines and close contact with those who have received live vaccines. (5.10) Embryo-fetal toxicity: Fetal harm can occur when administered to a pregnant woman. Apprise women of potential harm to the fetus. (5.11, 8.1) Side EffectsAdvanced HR+ BC, advanced PNET, advanced RCC: Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥30%) include stomatitis, infections, rash, fatigue, diarrhea, edema, abdominal pain, nausea, fever, asthenia, cough, headache and decreased appetite. (6.1, 6.2, 6.3)Renal angiomyolipoma with TSC: Most common adverse reaction (incidence ≥ 30%) is stomatitis. (6.4)SEGA with TSC: Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 30%) are stomatitis and respiratory tract infection. (6.5) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS Strong CYP3A4/PgP inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use. (2.2, 2.5, 5.8, 7.1) Moderate CYP3A4/PgP inhibitors: If combination is required, use caution and reduce dose of AFINITOR. (2.2, 2.3, 2.5, 5.8, 7.1) Strong CYP3A4/PgP inducers: Avoid concomitant use. If combination cannot be avoided, increase dose of AFINITOR. (2.2, 2.3, 2.5, 5.8, 7.2) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Nursing mothers: Discontinue drug or nursing, taking into consideration the importance of drug to the mother. (8.3) Hepatic impairment: For advanced HR+ BC, advanced PNET, advanced RCC, or renal angiomyolipoma with TSC patients with hepatic impairment, reduce AFINITOR dose. For SEGA patients with severe hepatic impairment, reduce the starting dose of AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ. (2.2, 2.3, 2.5, 5.9, 8.8)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 AFINITOR INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 1.1 Advanced Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer (Advanced HR+ BC)
- 1.2 Advanced Neuroendocrine Tumors of Pancreatic Origin (PNET)
- 1.3 Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
- 1.4 Renal Angiomyolipoma with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)
- 1.5 Subependymal Giant Cell Astrocytoma (SEGA) with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)
- 2 AFINITOR DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 2.1 Recommended Dose in Advanced Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer, Advanced PNET, Advanced RCC, and Renal Angiomyolipoma with TSC
- 2.2 Dose Modifications in Advanced Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer, Advanced PNET, Advanced RCC, and Renal Angiomyolipoma with TSC
- 2.3 Recommended Dose in SEGA with TSC
- 2.4 Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in SEGA with TSC
- 2.5 Dose Modifications in SEGA with TSC
- 2.6 Administration of AFINITOR Tablets in SEGA with TSC
- 2.7 Administration and Preparation of AFINITOR DISPERZ in SEGA with TSC
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 AFINITOR CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 AFINITOR ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 6.1 Clinical Study Experience in Advanced Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer
- 6.2 Clinical Study Experience in Advanced Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
- 6.3 Clinical Study Experience in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
- 6.4 Clinical Study Experience in Renal Angiomyolipoma with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
- 6.5 Clinical Study Experience in Subependymal Giant Cell Astrocytoma with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
- 6.6 Postmarketing Experience
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 AFINITOR DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 15 REFERENCES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Advanced Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer (Advanced HR+ BC)
AFINITOR® is indicated for the treatment of postmenopausal women with advanced hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer (advanced HR+ BC) in combination with exemestane, after failure of treatment with letrozole or anastrozole.
1.2 Advanced Neuroendocrine Tumors of Pancreatic Origin (PNET)
AFINITOR® is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with progressive neuroendocrine tumors of pancreatic origin (PNET) with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic disease.
AFINITOR® is not indicated for the treatment of patients with functional carcinoid tumors.
1.3 Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
AFINITOR® is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) after failure of treatment with sunitinib or sorafenib.
1.4 Renal Angiomyolipoma with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)
AFINITOR® is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with renal angiomyolipoma and tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), not requiring immediate surgery.
The effectiveness of AFINITOR in the treatment of renal angiomyolipoma is based on an analysis of durable objective responses in patients treated for a median of 8.3 months. Further follow-up of patients is required to determine long-term outcomes.
1.5 Subependymal Giant Cell Astrocytoma (SEGA) with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)
AFINITOR® Tablets and AFINITOR® DISPERZ are indicated in pediatric and adult patients with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) for the treatment of subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) that requires therapeutic intervention but cannot be curatively resected.
The effectiveness of AFINITOR Tablets and AFINITOR DISPERZ is based on demonstration of durable objective response, as evidenced by reduction in SEGA tumor volume. Improvement in disease-related symptoms and overall survival in patients with SEGA and TSC have not been demonstrated [see Clinical Studies (14.5)].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
AFINITOR is available in two dosage forms: tablets (AFINITOR Tablets) and tablets for oral suspension (AFINITOR DISPERZ).
- AFINITOR Tablets may be used for all approved indications.
- AFINITOR DISPERZ is approved for the treatment of patients with subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) and tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC).
2.1 Recommended Dose in Advanced Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer, Advanced PNET, Advanced RCC, and Renal Angiomyolipoma with TSC
The recommended dose of AFINITOR Tablets is 10 mg, to be taken once daily at the same time every day. Administer either consistently with food or consistently without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. AFINITOR Tablets should be swallowed whole with a glass of water. Do not break or crush tablets.
Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
2.2 Dose Modifications in Advanced Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer, Advanced PNET, Advanced RCC, and Renal Angiomyolipoma with TSC
Adverse Reactions
Management of severe or intolerable adverse reactions may require temporary dose interruption (with or without a dose reduction of AFINITOR therapy) or discontinuation. If dose reduction is required, the suggested dose is approximately 50% lower than the daily dose previously administered [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
Table 1 summarizes recommendations for dose reduction, interruption or discontinuation of AFINITOR in the management of adverse reactions. General management recommendations are also provided as applicable. Clinical judgment of the treating physician should guide the management plan of each patient based on individual benefit/risk assessment.
| a Severity grade description: 1 = mild symptoms; 2 = moderate symptoms; 3 = severe symptoms; 4 = life-threatening symptoms. | ||
| b If dose reduction is required, the suggested dose is approximately 50% lower than the dose previously administered. | ||
| c Activities of daily living (ADL) | ||
| d Avoid using agents containing alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, iodine, and thyme derivatives in management of stomatitis as they may worsen mouth ulcers. | ||
| Adverse Reaction | Severitya | AFINITOR Dose Adjustmentb and Management Recommendations |
| Non-infectious pneumonitis | Grade 1 Asymptomatic, radiographic findings only |
No dose adjustment required. Initiate appropriate monitoring. |
| Grade 2 Symptomatic, not interfering with ADLc |
Consider interruption of therapy, rule out infection and consider treatment with corticosteroids until symptoms improve to ≤ Grade 1. Re-initiate AFINITOR at a lower dose. Discontinue treatment if failure to recover within 4 weeks. |
|
| Grade 3 Symptomatic, interfering with ADLc; O2 indicated |
Interrupt AFINITOR until symptoms resolve to ≤ Grade 1. Rule out infection, and consider treatment with corticosteroids. Consider re-initiating AFINITOR at a lower dose. If toxicity recurs at Grade 3, consider discontinuation. |
|
| Grade 4 Life-threatening, ventilatory support indicated |
Discontinue AFINITOR, rule out infection, and consider treatment with corticosteroids. | |
| Stomatitis | Grade 1 Minimal symptoms, normal diet |
No dose adjustment required. Manage with non-alcoholic or salt water (0.9%) mouth wash several times a day. |
| Grade 2 Symptomatic but can eat and swallow modified diet |
Temporary dose interruption until recovery to Grade ≤1. Re-initiate AFINITOR at the same dose. If stomatitis recurs at Grade 2, interrupt dose until recovery to Grade ≤1. Re-initiate AFINITOR at a lower dose. Manage with topical analgesic mouth treatments (e.g., benzocaine, butyl aminobenzoate, tetracaine hydrochloride, menthol or phenol) with or without topical corticosteroids (i.e., triamcinolone oral paste).d |
|
| Grade 3 Symptomatic and unable to adequately aliment or hydrate orally |
Temporary dose interruption until recovery to Grade ≤1. Re-initiate AFINITOR at a lower dose. Manage with topical analgesic mouth treatments (i.e., benzocaine, butyl aminobenzoate, tetracaine hydrochloride, menthol or phenol) with or without topical corticosteroids (i.e., triamcinolone oral paste).d |
|
| Grade 4 Symptoms associated with life-threatening consequences |
Discontinue AFINITOR and treat with appropriate medical therapy. | |
| Other non-hematologic toxicities (excluding metabolic events) |
Grade 1 | If toxicity is tolerable, no dose adjustment required. Initiate appropriate medical therapy and monitor. |
| Grade 2 | If toxicity is tolerable, no dose adjustment required. Initiate appropriate medical therapy and monitor. If toxicity becomes intolerable, temporary dose interruption until recovery to Grade ≤1. Reinitiate AFINITOR at the same dose. If toxicity recurs at Grade 2, interrupt AFINITOR until recovery to Grade ≤1. Reinitiate AFINITOR at a lower dose. |
|
| Grade 3 | Temporary dose interruption until recovery to Grade ≤1. Initiate appropriate medical therapy and monitor. Consider reinitiating AFINITOR at a lower dose. If toxicity recurs at Grade 3, consider discontinuation. |
|
| Grade 4 | Discontinue AFINITOR and treat with appropriate medical therapy. | |
| Metabolic events (e.g. hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia) |
Grade 1 | No dose adjustment required. Initiate appropriate medical therapy and monitor. |
| Grade 2 | No dose adjustment required. Manage with appropriate medical therapy and monitor. |
|
| Grade 3 | Temporary dose interruption. Reinitiate AFINITOR at a lower dose. Manage with appropriate medical therapy and monitor. |
|
| Grade 4 | Discontinue AFINITOR and treat with appropriate medical therapy. | |
Hepatic Impairment
Hepatic impairment will increase the exposure to everolimus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Use in Specific Populations (8.8)]. Dose adjustments are recommended:
- Mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A) – The recommended dose is 7.5 mg daily; the dose may be decreased to 5 mg if not well tolerated.
- Moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B) – The recommended dose is 5 mg daily; the dose may be decreased to 2.5 mg if not well tolerated.
- Severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) – If the desired benefit outweighs the risk, a dose of 2.5 mg daily may be used but must not be exceeded.
Dose adjustments should be made if a patient’s hepatic (Child-Pugh) status changes during treatment.
CYP3A4/P-glycoprotein (PgP) Inhibitors
Avoid the use of strong CYP3A4/PgP inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, atazanavir, nefazodone, saquinavir, telithromycin, ritonavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, voriconazole) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Use caution when co-administered with moderate CYP3A4/PgP inhibitors (e.g., amprenavir, fosamprenavir, aprepitant, erythromycin, fluconazole, verapamil, diltiazem). If patients require co-administration of a moderate CYP3A4/PgP inhibitor, reduce the AFINITOR dose to 2.5 mg daily. The reduced dose of AFINITOR is predicted to adjust the area under the curve (AUC) to the range observed without inhibitors. An AFINITOR dose increase from 2.5 mg to 5 mg may be considered based on patient tolerance. If the moderate inhibitor is discontinued, a washout period of approximately 2 to 3 days should be allowed before the AFINITOR dose is increased. If the moderate inhibitor is discontinued, the AFINITOR dose should be returned to the dose used prior to initiation of the moderate CYP3A4/PgP inhibitor.
Grapefruit, grapefruit juice, and other foods that are known to inhibit cytochrome P450 and PgP activity may increase everolimus exposures and should be avoided during treatment.
Strong CYP3A4/PgP Inducers
Avoid the use of concomitant strong CYP3A4/PgP inducers (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentine, phenobarbital). If patients require co-administration of a strong CYP3A4/PgP inducer, consider doubling the daily dose of AFINITOR using increments of 5 mg or less. This dose of AFINITOR is predicted, based on pharmacokinetic data, to adjust the AUC to the range observed without inducers. However, there are no clinical data with this dose adjustment in patients receiving strong CYP3A4/PgP inducers. If the strong inducer is discontinued, consider a washout period of 3 to 5 days, before the AFINITOR dose is returned to the dose used prior to initiation of the strong CYP3A4/PgP inducer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum) may decrease everolimus exposure unpredictably and should be avoided.
2.3 Recommended Dose in SEGA with TSC
The recommended starting dose is 4.5 mg/m2, once daily. The recommended starting dose for patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) or requiring moderate CYP3A4/PgP inhibitors is 2.5 mg/m2, once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. The recommended starting dose for patients requiring a concomitant strong CYP3A4 inducer is 9 mg/m2, once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Round dose to the nearest strength of either AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ.
Do not combine AFINITOR Tablets and AFINITOR DISPERZ to achieve the desired total dose.
Use therapeutic drug monitoring to guide subsequent dosing [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. Adjust dose at 2 week intervals as needed to achieve and maintain trough concentrations of 5 to 15 ng/mL [see Dosage and Administration (2.4, 2.5)].
Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs. The optimal duration of therapy is unknown.
2.4 Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in SEGA with TSC
Monitor everolimus whole blood trough levels routinely in all patients. When possible, use the same assay and laboratory for therapeutic drug monitoring throughout treatment.
Assess trough concentrations approximately 2 weeks after initiation of treatment, a change in dose, a change in co-administration of CYP3A4/PgP inducers and/or inhibitors, a change in hepatic function, or a change in dosage form between AFINITOR Tablets and AFINITOR DISPERZ. Once a stable dose is attained, monitor trough concentrations every 3 to 6 months in patients with changing body surface area or every 6 to 12 months in patients with stable body surface area for the duration of treatment.
Titrate the dose to attain trough concentrations of 5 to 15 ng/mL.
- For trough concentrations less than 5 ng/mL, increase the daily dose by 2.5 mg (in patients taking AFINITOR Tablets) or 2 mg (in patients taking AFINITOR DISPERZ).
- For trough concentrations greater than 15 ng/mL, reduce the daily dose by 2.5 mg (in patients taking AFINITOR Tablets) or 2 mg (in patients taking AFINITOR DISPERZ).
- If dose reduction is required for patients receiving the lowest available strength, administer every other day.
2.5 Dose Modifications in SEGA with TSC
Adverse Reactions
Temporarily interrupt or permanently discontinue AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ for severe or intolerable adverse reactions. If dose reduction is required when reinitiating therapy, reduce the dose by approximately 50% [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5)]. If dose reduction is required for patients receiving the lowest available strength, administer every other day.
Hepatic Impairment
- Reduce the starting dose of AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ by approximately 50% in patients with SEGA who have severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Adjustment to the starting dose for patients with SEGA who have mild (Child-Pugh class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh class B) hepatic impairment may not be needed. Subsequent dosing should be based on therapeutic drug monitoring.
- Assess everolimus trough concentrations approximately 2 weeks after commencing treatment, a change in dose, or any change in hepatic function [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
CYP3A4/P-glycoprotein (PgP) Inhibitors
Avoid the use of concomitant strong CYP3A4/PgP inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, atazanavir, nefazodone, saquinavir, telithromycin, ritonavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, voriconazole) in patients receiving AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Drug Interactions (7.1)].
For patients who require treatment with moderate CYP3A4/PgP inhibitors (e.g., amprenavir, fosamprenavir, aprepitant, erythromycin, fluconazole, verapamil, diltiazem):
- Reduce the AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ dose by approximately 50%. Administer every other day if dose reduction is required for patients receiving the lowest available strength and maintain trough concentrations of 5 to 15 ng/mL [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
- Assess everolimus trough concentrations approximately 2 weeks after dose reduction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
- Resume the dose that was used prior to initiating the CYP3A4/PgP inhibitor 2 to 3 days after discontinuation of a moderate inhibitor. Assess the everolimus trough concentration approximately 2 weeks later [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
Do not ingest foods or nutritional supplements (e.g., grapefruit, grapefruit juice) that are known to inhibit cytochrome P450 or PgP activity.
Strong CYP3A4/PgP Inducers
Avoid the use of concomitant strong CYP3A4/PgP inducers (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentine, phenobarbital) if alternative therapy is available [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Drug Interactions (7.2)]. For patients who require treatment with a strong CYP3A4/PgP inducer:
- Double the dose of AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ and assess tolerability [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Assess the everolimus trough concentration 2 weeks after doubling the dose and adjust the dose if necessary to maintain a trough concentration of 5 to 15 ng/mL [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
- Return the AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ dose to that used prior to initiating the strong CYP3A4/PgP inducer if the strong inducer is discontinued, and assess the everolimus trough concentrations approximately 2 weeks later [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
Do not ingest foods or nutritional supplements (e.g., St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum)) that are known to induce cytochrome P450 activity.
2.6 Administration of AFINITOR Tablets in SEGA with TSC
Do not combine the 2 dosage forms (AFINITOR Tablets and AFINITOR DISPERZ) to achieve the desired total dose. Use one dosage form or the other.
Administer AFINITOR Tablets orally once daily at the same time every day. Administer either consistently with food or consistently without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
AFINITOR Tablets should be swallowed whole with a glass of water. Do not break or crush tablets.
2.7 Administration and Preparation of AFINITOR DISPERZ in SEGA with TSC
Wear gloves to avoid possible contact with everolimus when preparing suspensions of AFINITOR DISPERZ for another person.
Do not combine the 2 dosage forms (AFINITOR Tablets and AFINITOR DISPERZ) to achieve the desired total dose. Use one dosage form or the other.
Administer AFINITOR DISPERZ (everolimus tablets for oral suspension) as a suspension only.
Administer AFINITOR DISPERZ orally once daily at the same time every day. Administer either consistently with food or consistently without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Administer suspension immediately after preparation. Discard suspension if not administered within 60 minutes after preparation.
Prepare suspension in water only.
Using an oral syringe:
- Place the prescribed dose of AFINITOR DISPERZ into a 10-mL syringe. Do not exceed a total of 10 mg per syringe. If higher doses are required, prepare an additional syringe. Do not break or crush tablets.
- Draw approximately 5 mL of water and 4 mL of air into the syringe.
- Place the filled syringe into a container (tip up) for 3 minutes, until the AFINITOR DISPERZ tablets are in suspension.
- Gently invert the syringe 5 times immediately prior to administration.
- After administration of the prepared suspension, draw approximately 5 mL of water and 4 mL of air into the same syringe, and swirl the contents to suspend remaining particles. Administer the entire contents of the syringe.
Using a small drinking glass:
- Place the prescribed dose of AFINITOR DISPERZ into a small drinking glass (maximum size 100 mL) containing approximately 25 mL of water. Do not exceed a total of 10 mg of AFINITOR DISPERZ per glass. If higher doses are required, prepare an additional glass. Do not break or crush tablets.
- Allow 3 minutes for suspension to occur.
- Stir the contents gently with a spoon, immediately prior to drinking.
- After administration of the prepared suspension, add 25 mL of water and stir with the same spoon to re-suspend remaining particles. Administer the entire contents of the glass.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
3.1 AFINITOR (everolimus) Tablets
2.5 mg tablet
White to slightly yellow, elongated tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “LCL” on one side and “NVR” on the other.
5 mg tablet
White to slightly yellow, elongated tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “5” on one side and “NVR” on the other.
7.5 mg tablet
White to slightly yellow, elongated tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “7P5” on one side and “NVR” on the other.
10 mg tablet
White to slightly yellow, elongated tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “UHE” on one side and “NVR” on the other.
3.2 AFINITOR DISPERZ (everolimus tablets for oral suspension)
2 mg tablet for oral suspension
White to slightly yellowish, round, flat tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “D2” on one side and “NVR” on the other.
3 mg tablet for oral suspension
White to slightly yellowish, round, flat tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “D3” on one side and “NVR” on the other.
5 mg tablet for oral suspension
White to slightly yellowish, round, flat tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “D5” on one side and “NVR” on the other.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
AFINITOR is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to the active substance, to other rapamycin derivatives, or to any of the excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions manifested by symptoms including, but not limited to, anaphylaxis, dyspnea, flushing, chest pain, or angioedema (e.g., swelling of the airways or tongue, with or without respiratory impairment) have been observed with everolimus and other rapamycin derivatives.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Non-infectious Pneumonitis
Non-infectious pneumonitis is a class effect of rapamycin derivatives, including AFINITOR. Non-infectious pneumonitis was reported in up to 19% of patients treated with AFINITOR in clinical trials. The incidence of Common Terminology Criteria (CTC) Grade 3 and 4 non-infectious pneumonitis was up to 4.0% and up to 0.2%, respectively [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5)]. Fatal outcomes have been observed.
Consider a diagnosis of non-infectious pneumonitis in patients presenting with non-specific respiratory signs and symptoms such as hypoxia, pleural effusion, cough, or dyspnea, and in whom infectious, neoplastic, and other causes have been excluded by means of appropriate investigations. Advise patients to report promptly any new or worsening respiratory symptoms.
Patients who develop radiological changes suggestive of non-infectious pneumonitis and have few or no symptoms may continue AFINITOR therapy without dose alteration. Imaging appears to overestimate the incidence of clinical pneumonitis.
If symptoms are moderate, consider interrupting therapy until symptoms improve. The use of corticosteroids may be indicated. AFINITOR may be reintroduced at a daily dose approximately 50% lower than the dose previously administered [see Table 1 in Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
For cases of Grade 3 non-infectious pneumonitis interrupt AFINITOR until resolution to less than or equal to Grade 1. AFINITOR may be re-introduced at a daily dose approximately 50% lower than the dose previously administered depending on the individual clinical circumstances [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. If toxicity recurs at Grade 3, consider discontinuation of AFINITOR. For cases of Grade 4 non-infectious pneumonitis, discontinue AFINITOR. Corticosteroids may be indicated until clinical symptoms resolve. The development of pneumonitis has been reported even at a reduced dose.
5.2 Infections
AFINITOR has immunosuppressive properties and may predispose patients to bacterial, fungal, viral, or protozoal infections, including infections with opportunistic pathogens [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5)]. Localized and systemic infections, including pneumonia, mycobacterial infections, other bacterial infections, invasive fungal infections, such as aspergillosis or candidiasis, and viral infections including reactivation of hepatitis B virus have occurred in patients taking AFINITOR. Some of these infections have been severe (e.g., leading to sepsis, respiratory or hepatic failure) or fatal. Physicians and patients should be aware of the increased risk of infection with AFINITOR. Complete treatment of pre-existing invasive fungal infections prior to starting treatment with AFINITOR. While taking AFINITOR, be vigilant for signs and symptoms of infection; if a diagnosis of an infection is made, institute appropriate treatment promptly and consider interruption or discontinuation of AFINITOR. If a diagnosis of invasive systemic fungal infection is made, discontinue AFINITOR and treat with appropriate antifungal therapy.
5.3 Oral Ulceration
Mouth ulcers, stomatitis, and oral mucositis have occurred in patients treated with AFINITOR at an incidence ranging from 44%-78% across the clinical trial experience. Grade 3 or 4 stomatitis was reported in 4%-9% of patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5)]. In such cases, topical treatments are recommended, but alcohol-, hydrogen peroxide-, iodine-, or thyme- containing mouthwashes should be avoided as they may exacerbate the condition. Antifungal agents should not be used unless fungal infection has been diagnosed [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.4 Renal Failure
Cases of renal failure (including acute renal failure), some with a fatal outcome, have been observed in patients treated with AFINITOR [see Laboratory Tests and Monitoring (5.7)].
5.5 Impaired Wound Healing
Everolimus delays wound healing and increases the occurrence of wound-related complications like wound dehiscence, wound infection, incisional hernia, lymphocele, and seroma. These wound-related complications may require surgical intervention. Exercise caution with the use of AFINITOR in the peri-surgical period.
5.6 Geriatric Patients
In the randomized advanced hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer study, the incidence of deaths due to any cause within 28 days of the last AFINITOR dose was 6% in patients ≥ 65 years of age compared to 2% in patients < 65 years of age. Adverse reactions leading to permanent treatment discontinuation occurred in 33% of patients ≥ 65 years of age compared to 17% in patients < 65 years of age. Careful monitoring and appropriate dose adjustments for adverse reactions are recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
5.7 Laboratory Tests and Monitoring
Renal Function
Elevations of serum creatinine and proteinuria have been reported in patients taking AFINITOR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5)]. Monitoring of renal function, including measurement of blood urea nitrogen (BUN), urinary protein, or serum creatinine, is recommended prior to the start of AFINITOR therapy and periodically thereafter. Renal function of patients should be monitored particularly where patients have additional risk factors that may further impair renal function.
Blood Glucose and Lipids
Hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and hypertriglyceridemia have been reported in patients taking AFINITOR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5)]. Monitoring of fasting serum glucose and lipid profile is recommended prior to the start of AFINITOR therapy and periodically thereafter as well as management with appropriate medical therapy. More frequent monitoring is recommended when AFINITOR is co-administered with other drugs that may induce hyperglycemia. When possible, optimal glucose and lipid control should be achieved before starting a patient on AFINITOR.
Hematologic Parameters
Decreased hemoglobin, lymphocytes, neutrophils, and platelets have been reported in patients taking AFINITOR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5)]. Monitoring of complete blood count is recommended prior to the start of AFINITOR therapy and periodically thereafter.
5.8 Drug-drug Interactions
Due to significant increases in exposure of everolimus, co-administration with strong CYP3A4/PgP inhibitors should be avoided [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.5) and Drug Interactions (7.1)].
A reduction of the AFINITOR dose is recommended when co-administered with a moderate CYP3A4/PgP inhibitor [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.5) and Drug Interactions (7.1)].
An increase in the AFINITOR dose is recommended when co-administered with a strong CYP3A4/PgP inducer [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.5) and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
5.9 Hepatic Impairment
Exposure to everolimus was increased in patients with hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
For advanced HR+ BC, advanced PNET, advanced RCC, and renal angiomyolipoma with TSC patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C), AFINITOR may be used at a reduced dose if the desired benefit outweighs the risk. For patients with mild (Child-Pugh class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh class B) hepatic impairment, a dose reduction is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
For patients with SEGA and mild or moderate hepatic impairment, adjust the dose of AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ based on therapeutic drug monitoring. For patients with SEGA and severe hepatic impairment, reduce the starting dose of AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ by approximately 50% and adjust subsequent doses based on therapeutic drug monitoring [see Dosage and Administration (2.4, 2.5)].
5.10 Vaccinations
During AFINITOR treatment, avoid the use of live vaccines and avoid close contact with individuals who have received live vaccines (e.g., intranasal influenza, measles, mumps, rubella, oral polio, BCG, yellow fever, varicella, and TY21a typhoid vaccines).
For pediatric patients with SEGA that do not require immediate treatment, complete the recommended childhood series of live virus vaccinations according to American Council on Immunization Practices (ACIP) guidelines prior to the start of therapy. An accelerated vaccination schedule may be appropriate.
5.11 Embryo-fetal Toxicity
Based on the mechanism of action, AFINITOR can cause fetal harm. Everolimus caused embryo-fetal toxicities in animals at maternal exposures that were lower than human exposures. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to a fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise female patients of reproductive potential to avoid becoming pregnant and to use highly effective contraception while using AFINITOR and for up to 8 weeks after ending treatment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in another section of the label [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]:
- Non-infectious pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Oral ulceration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Renal failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Impaired wound healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed cannot be directly compared to rates in other trials and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
6.1 Clinical Study Experience in Advanced Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer
The efficacy and safety of AFINITOR (10 mg/day) plus exemestane (25 mg/day) (n=485) versus placebo plus exemestane (25 mg/day) (n=239) was evaluated in a randomized, controlled trial in patients with advanced or metastatic hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. The median age of patients was 61 years (range 28-93 years), and 75% were Caucasian. Safety results are based on a median follow-up of approximately 13 months.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 30%) were stomatitis, infections, rash, fatigue, diarrhea, and decreased appetite. The most common Grade 3/4 adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 2%) were stomatitis, infections, hyperglycemia, fatigue, dyspnea, pneumonitis, and diarrhea. The most common laboratory abnormalities (incidence ≥ 50%) were hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, increased aspartate transaminase (AST), anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, increased alanine transaminase (ALT), and hypertriglyceridemia. The most common Grade 3/4 laboratory abnormalities (incidence ≥ 3%) were lymphopenia, hyperglycemia, anemia, decreased potassium, increased AST, increased ALT, and thrombocytopenia.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred more frequently in patients who received AFINITOR plus exemestane (2%) compared to patients on the placebo plus exemestane arm (0.4%). The rates of treatment-emergent adverse events resulting in permanent discontinuation were 24% and 5% for the AFINITOR plus exemestane and placebo plus exemestane treatment groups, respectively. Dose adjustments (interruptions or reductions) were more frequent among patients in the AFINITOR plus exemestane arm than in the placebo plus exemestane arm (63% versus 14%).
Table 2 compares the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse reactions reported with an incidence of ≥10% for patients receiving AFINITOR 10 mg daily versus placebo.
| Grading according to CTCAE Version 3.0 * 160 patients (33.2%) were exposed to AFINITOR therapy for a period of ≥ 32 weeks) a Exemestane (25 mg/day) b Includes stomatitis, mouth ulceration, aphthous stomatitis, glossodynia, gingival pain, glossitis and lip ulceration c Includes all preferred terms within the ‘infections and infestations’ system organ class, the most common being nasopharyngitis (10%), urinary tract infection (10%), upper respiratory tract infection (5%), pneumonia (4%), bronchitis (4%), cystitis (3%), sinusitis (3%), and also including candidiasis (<1%), and sepsis (<1%), and hepatitis C (<1%). d Includes pneumonitis, interstitial lung disease, lung infiltration, and pulmonary fibrosis e Exposure to AFINITOR or placebo |
||||||
|
AFINITOR (10 mg/day)
+ exemestanea N=482 |
Placebo
+ exemestanea N=238 |
|||||
| All grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | All grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Any adverse reaction | 100 | 41 | 9 | 90 | 22 | 5 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||||
| Stomatitisb | 67 | 8 | 0 | 11 | 0.8 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 33 | 2 | 0.2 | 18 | 0.8 | 0 |
| Nausea | 29 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 28 | 1 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 17 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 12 | 0.8 | 0 |
| Constipation | 14 | 0.4 | 0 | 13 | 0.4 | 0 |
| Dry mouth | 11 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||||
| Fatigue | 36 | 4 | 0.4 | 27 | 1 | 0 |
| Edema peripheral | 19 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0.4 | 0 |
| Pyrexia | 15 | 0.2 | 0 | 7 | 0.4 | 0 |
| Asthenia | 13 | 2 | 0.2 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||||
| Infectionsc | 50 | 4 | 1 | 25 | 2 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||||||
| Weight decreased | 25 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||||
| Decreased appetite | 30 | 1 | 0 | 12 | 0.4 | 0 |
| Hyperglycemia | 14 | 5 | 0.4 | 2 | 0.4 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||||
| Arthralgia | 20 | 0.8 | 0 | 17 | 0 | 0 |
| Back pain | 14 | 0.2 | 0 | 10 | 0.8 | 0 |
| Pain in extremity | 9 | 0.4 | 0 | 11 | 2 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||||
| Dysgeusia | 22 | 0.2 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Headache | 21 | 0.4 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 0 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||||||
| Insomnia | 13 | 0.2 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||||
| Cough | 24 | 0.6 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| Dyspnea | 21 | 4 | 0.2 | 11 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| Epistaxis | 17 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Pneumonitisd | 19 | 4 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||||
| Rash | 39 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 13 | 0.2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Alopecia | 10 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Vascular disorders | ||||||
| Hot flush | 6 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 0 |
| Median duration of treatmente | 23.9 weeks | 13.4 weeks | ||||
Key observed laboratory abnormalities are presented in Table 3.
| Grading according to CTCAE Version 3.0 a Exemestane (25 mg/day) b Reflects corresponding adverse drug reaction reports of anemia, leukopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia (collectively as pancytopenia), which occurred at lower frequency. |
||||||
| Laboratory parameter |
AFINITOR (10 mg/day)
+ exemestanea N=482 |
Placebo
+ exemestanea N=238 |
||||
| All grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | All grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Hematologyb | ||||||
| Hemoglobin decreased | 68 | 6 | 0.6 | 40 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| WBC decreased | 58 | 1 | 0 | 28 | 5 | 0.8 |
| Platelets decreased | 54 | 3 | 0.2 | 5 | 0 | 0.4 |
| Lymphocytes decreased | 54 | 11 | 0.6 | 37 | 5 | 0.8 |
| Neutrophils decreased | 31 | 2 | 0 | 11 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Clinical chemistry | ||||||
| Glucose increased | 69 | 9 | 0.4 | 44 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| Cholesterol increased | 70 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 38 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Aspartate transaminase (AST) increased | 69 | 4 | 0.2 | 45 | 3 | 0.4 |
| Alanine transaminase (ALT) increased | 51 | 4 | 0.2 | 29 | 5 | 0 |
| Triglycerides increased | 50 | 0.8 | 0 | 26 | 0 | 0 |
| Albumin decreased | 33 | 0.8 | 0 | 16 | 0.8 | 0 |
| Potassium decreased | 29 | 4 | 0.2 | 7 | 1 | 0 |
| Creatinine increased | 24 | 2 | 0.2 | 13 | 0 | 0 |
6.2 Clinical Study Experience in Advanced Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
In a randomized, controlled trial of AFINITOR (n=204) versus placebo (n=203) in patients with advanced PNET the median age of patients was 58 years (range 20-87), 79% were Caucasian, and 55% were male. Patients on the placebo arm could cross over to open-label AFINITOR upon disease progression.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 30%) were stomatitis, rash, diarrhea, fatigue, edema, abdominal pain, nausea, fever, and headache. The most common Grade 3-4 adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 5%) were stomatitis and diarrhea. The most common laboratory abnormalities (incidence ≥ 50%) were decreased hemoglobin, hyperglycemia, alkaline phosphatase increased, hypercholesterolemia, bicarbonate decreased, and increased aspartate transaminase (AST). The most common Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities (incidence ≥ 3%) were hyperglycemia, lymphopenia, decreased hemoglobin, hypophosphatemia, increased alkaline phosphatase, neutropenia, increased aspartate transaminase (AST), potassium decreased, and thrombocytopenia. Deaths during double-blind treatment where an adverse event was the primary cause occurred in seven patients on AFINITOR and one patient on placebo. Causes of death on the AFINITOR arm included one case of each of the following: acute renal failure, acute respiratory distress, cardiac arrest, death (cause unknown), hepatic failure, pneumonia, and sepsis. There was one death due to pulmonary embolism on the placebo arm. After cross-over to open-label AFINITOR, there were three additional deaths, one due to hypoglycemia and cardiac arrest in a patient with insulinoma, one due to myocardial infarction with congestive heart failure, and the other due to sudden death. The rates of treatment-emergent adverse events resulting in permanent discontinuation were 20% and 6% for the AFINITOR and placebo treatment groups, respectively. Dose delay or reduction was necessary in 61% of everolimus patients and 29% of placebo patients. Grade 3-4 renal failure occurred in six patients in the everolimus arm and three patients in the placebo arm. Thrombotic events included five patients with pulmonary embolus in the everolimus arm and one in the placebo arm as well as three patients with thrombosis in the everolimus arm and two in the placebo arm.
Table 4 compares the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse reactions reported with an incidence of ≥ 10% for patients receiving AFINITOR 10 mg daily versus placebo.
| Grading according to CTCAE Version 3.0 a Includes stomatitis, aphthous stomatitis, gingival pain/swelling/ulceration, glossitis, glossodynia, lip ulceration, mouth ulceration, tongue ulceration, and mucosal inflammation. b Includes diarrhea, enteritis, enterocolitis, colitis, defecation urgency, and steatorrhea. c Includes pneumonitis, interstitial lung disease, pulmonary fibrosis and restrictive pulmonary disease. |
||||||
|
AFINITOR
N=204 |
Placebo
N=203 |
|||||
| All grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | All grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Any adverse reaction | 100 | 49 | 13 | 98 | 32 | 8 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||||
| Stomatitisa | 70 | 7 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Diarrheab | 50 | 5 | 0.5 | 25 | 3 | 0 |
| Abdominal pain | 36 | 4 | 0 | 32 | 6 | 1 |
| Nausea | 32 | 2 | 0 | 33 | 2 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 29 | 1 | 0 | 21 | 2 | 0 |
| Constipation | 14 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 0.5 | 0 |
| Dry mouth | 11 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||||
| Fatigue/malaise | 45 | 3 | 0.5 | 27 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Edema (general and peripheral) | 39 | 1 | 0.5 | 12 | 1 | 0 |
| Fever | 31 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 13 | 0.5 | 0 |
| Asthenia | 19 | 3 | 0 | 20 | 3 | 0 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||||
| Nasopharyngitis/rhinitis/URI | 25 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 0 |
| Urinary tract infection | 16 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0.5 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||||||
| Weight decreased | 28 | 0.5 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||||
| Decreased appetite | 30 | 1 | 0 | 18 | 1 | 0 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 10 | 2 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||||
| Arthralgia | 15 | 1 | 0.5 | 7 | 0.5 | 0 |
| Back pain | 15 | 1 | 0 | 11 | 1 | 0 |
| Pain in extremity | 14 | 0.5 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 0 |
| Muscle spasms | 10 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||||
| Headache/migraine | 30 | 0.5 | 0 | 15 | 1 | 0 |
| Dysgeusia | 19 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Dizziness | 12 | 0.5 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||||||
| Insomnia | 14 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||||
| Cough/productive cough | 25 | 0.5 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 0 |
| Epistaxis | 22 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Dyspnea/dyspnea exertional | 20 | 2 | 0.5 | 7 | 0.5 | 0 |
| Pneumonitisc | 17 | 3 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Oropharyngeal pain | 11 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous disorders | ||||||
| Rash | 59 | 0.5 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| Nail disorders | 22 | 0.5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Pruritus/pruritus generalized | 21 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 0 |
| Dry skin/xeroderma | 13 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Vascular disorders | ||||||
| Hypertension | 13 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 0 |
| Median duration of treatment (wks) | 37 | 16 | ||||
In female patients aged 18 to 55 years, irregular menstruation occurred in 5 of 46 (11%) AFINITOR-treated females and none of the 33 females in the placebo group.
Key observed laboratory abnormalities are presented in Table 5.
| Grading according to CTCAE Version 3.0 | ||||
| Laboratory parameter |
AFINITOR
N=204 |
Placebo
N=203 |
||
| All grades | Grade 3-4 | All grades | Grade 3-4 | |
| % | % | % | % | |
| Hematology | ||||
| Hemoglobin decreased | 86 | 15 | 63 | 1 |
| Lymphocytes decreased | 45 | 16 | 22 | 4 |
| Platelets decreased | 45 | 3 | 11 | 0 |
| WBC decreased | 43 | 2 | 13 | 0 |
| Neutrophils decreased | 30 | 4 | 17 | 2 |
| Clinical chemistry | ||||
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 74 | 8 | 66 | 8 |
| Glucose (fasting) increased | 75 | 17 | 53 | 6 |
| Cholesterol increased | 66 | 0.5 | 22 | 0 |
| Bicarbonate decreased | 56 | 0 | 40 | 0 |
| Aspartate transaminase (AST) increased | 56 | 4 | 41 | 4 |
| Alanine transaminase (ALT) increased | 48 | 2 | 35 | 2 |
| Phosphate decreased | 40 | 10 | 14 | 3 |
| Triglycerides increased | 39 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Calcium decreased | 37 | 0.5 | 12 | 0 |
| Potassium decreased | 23 | 4 | 5 | 0 |
| Creatinine increased | 19 | 2 | 14 | 0 |
| Sodium decreased | 16 | 1 | 16 | 1 |
| Albumin decreased | 13 | 1 | 8 | 0 |
| Bilirubin increased | 10 | 1 | 14 | 2 |
| Potassium increased | 7 | 0 | 10 | 0.5 |
6.3 Clinical Study Experience in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
The data described below reflect exposure to AFINITOR (n=274) and placebo (n=137) in a randomized, controlled trial in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received prior treatment with sunitinib and/or sorafenib. The median age of patients was 61 years (range 27-85), 88% were Caucasian, and 78% were male. The median duration of blinded study treatment was 141 days (range 19-451 days) for patients receiving AFINITOR and 60 days (range 21-295 days) for those receiving placebo.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 30%) were stomatitis, infections, asthenia, fatigue, cough, and diarrhea. The most common Grade 3-4 adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 3%) were infections, dyspnea, fatigue, stomatitis, dehydration, pneumonitis, abdominal pain, and asthenia. The most common laboratory abnormalities (incidence ≥ 50%) were anemia, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hyperglycemia, lymphopenia, and increased creatinine. The most common Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities (incidence ≥ 3%) were lymphopenia, hyperglycemia, anemia, hypophosphatemia, and hypercholesterolemia. Deaths due to acute respiratory failure (0.7%), infection (0.7%), and acute renal failure (0.4%) were observed on the AFINITOR arm but none on the placebo arm. The rates of treatment-emergent adverse events (irrespective of causality) resulting in permanent discontinuation were 14% and 3% for the AFINITOR and placebo treatment groups, respectively. The most common adverse reactions (irrespective of causality) leading to treatment discontinuation were pneumonitis and dyspnea. Infections, stomatitis, and pneumonitis were the most common reasons for treatment delay or dose reduction. The most common medical interventions required during AFINITOR treatment were for infections, anemia, and stomatitis.
Table 6 compares the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse reactions reported with an incidence of ≥ 10% for patients receiving AFINITOR 10 mg daily versus placebo. Within each MedDRA system organ class, the adverse reactions are presented in order of decreasing frequency.
| Grading according to CTCAE Version 3.0 a Stomatitis (including aphthous stomatitis), and mouth and tongue ulceration. b Includes all preferred terms within the ‘infections and infestations’ system organ class, the most common being nasopharyngitis (6%), pneumonia (6%), urinary tract infection (5%), bronchitis (4%), and sinusitis (3%), and also including aspergillosis (<1%), candidiasis (<1%), and sepsis (<1%). c Includes pneumonitis, interstitial lung disease, lung infiltration, pulmonary alveolar hemorrhage, pulmonary toxicity, and alveolitis. |
||||||
|
AFINITOR
10 mg/day
N=274 |
Placebo
N=137 |
|||||
| All grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | All grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Any a dverse r eaction | 97 | 52 | 13 | 93 | 23 | 5 |
| Gastrointestinal d isorders | ||||||
| Stomatitisa | 44 | 4 | <1 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 30 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Nausea | 26 | 1 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 20 | 2 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| Infections and i nfestations b | 37 | 7 | 3 | 18 | 1 | 0 |
| General d isorders and a dministration s ite c onditions | ||||||
| Asthenia | 33 | 3 | <1 | 23 | 4 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 31 | 5 | 0 | 27 | 3 | <1 |
| Edema peripheral | 25 | <1 | 0 | 8 | <1 | 0 |
| Pyrexia | 20 | <1 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| Mucosal inflammation | 19 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Respiratory, t horacic and m ediastinal d isorders | ||||||
| Cough | 30 | <1 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 0 |
| Dyspnea | 24 | 6 | 1 | 15 | 3 | 0 |
| Epistaxis | 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pneumonitisc | 14 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Skin and s ubcutaneous t issue d isorders | ||||||
| Rash | 29 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 14 | <1 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Dry skin | 13 | <1 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Metabolism and n utrition d isorders | ||||||
| Anorexia | 25 | 1 | 0 | 14 | <1 | 0 |
| Nervous s ystem d isorders | ||||||
| Headache | 19 | <1 | <1 | 9 | <1 | 0 |
| Dysgeusia | 10 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and c onnective t issue d isorders | ||||||
| Pain in extremity | 10 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Medi an d uration of t reatment (d) | 141 | 60 | ||||
Other notable adverse reactions occurring more frequently with AFINITOR than with placebo, but with an incidence of < 10% include:
Gastrointestinal disorders: Abdominal pain (9%), dry mouth (8%), hemorrhoids (5%), dysphagia (4%)
General disorders and administration site conditions: Weight decreased (9%), chest pain (5%), chills (4%), impaired wound healing (< 1%)
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Pleural effusion (7%), pharyngolaryngeal pain (4%), rhinorrhea (3%)
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Hand-foot syndrome (reported as palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome) (5%), nail disorder (5%), erythema (4%), onychoclasis (4%), skin lesion (4%), acneiform dermatitis (3%)
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Exacerbation of pre-existing diabetes mellitus (2%), new onset of diabetes mellitus (< 1%)
Psychiatric disorders: Insomnia (9%)
Nervous system disorders: Dizziness (7%), paresthesia (5%)
Eye disorders: Eyelid edema (4%), conjunctivitis (2%)
Vascular disorders: Hypertension (4%), deep vein thrombosis (< 1%)
Renal and urinary disorders: Renal failure (3%)
Cardiac disorders: Tachycardia (3%), congestive cardiac failure (1%)
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Jaw pain (3%)
Hematologic disorders: Hemorrhage (3%)
Key laboratory abnormalities are presented in Table 7.
| Grading according to CTCAE Version 3.0 a Reflects corresponding adverse drug reaction reports of anemia, leukopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia (collectively pancytopenia), which occurred at lower frequency. |
||||||
| Laboratory p arameter |
AFINITOR
10 mg/day
N=274 |
Placebo
N=137 |
||||
| All grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | All grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Hematology a | ||||||
| Hemoglobin decreased | 92 | 12 | 1 | 79 | 5 | <1 |
| Lymphocytes decreased | 51 | 16 | 2 | 28 | 5 | 0 |
| Platelets decreased | 23 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | <1 |
| Neutrophils decreased | 14 | 0 | <1 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Clinical c hemistry | ||||||
| Cholesterol increased | 77 | 4 | 0 | 35 | 0 | 0 |
| Triglycerides increased | 73 | <1 | 0 | 34 | 0 | 0 |
| Glucose increased | 57 | 15 | <1 | 25 | 1 | 0 |
| Creatinine increased | 50 | 1 | 0 | 34 | 0 | 0 |
| Phosphate decreased | 37 | 6 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Aspartate transaminase (AST) increased | 25 | <1 | <1 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Alanine transaminase (ALT) increased | 21 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Bilirubin increased | 3 | <1 | <1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
6.4 Clinical Study Experience in Renal Angiomyolipoma with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
The data described below are based on a randomized (2:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of AFINITOR in 118 patients with renal angiomyolipoma as a feature of TSC (n=113) or sporadic lymphangioleiomyomatosis (n=5). The median age of patients was 31 years (range 18 to 61 years), 89% were Caucasian, and 34% were male. The median duration of blinded study treatment was 48 weeks (range 2 to 115 weeks) for patients receiving AFINITOR and 45 weeks (range 9 to 115 weeks) for those receiving placebo.
The most common adverse reaction reported for AFINITOR (incidence ≥ 30%) was stomatitis. The most common Grade 3-4 adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 2%) were stomatitis and amenorrhea. The most common laboratory abnormalities (incidence ≥ 50%) were hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and anemia. The most common Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormality (incidence ≥ 3%) was hypophosphatemia.
The rate of adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation was 3.8% in the AFINITOR-treated patients. Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation in the AFINITOR arm were hypersensitivity/angioedema/bronchospasm, convulsion, and hypophosphatemia. Dose adjustments (interruptions or reductions) due to adverse reactions occurred in 52% of AFINITOR-treated patients. The most common adverse reaction leading to AFINITOR dose adjustment was stomatitis.
Table 8 compares the incidence of adverse reactions reported with an incidence of ≥ 10% for patients receiving AFINITOR and occurring more frequently with AFINITOR than with placebo. Laboratory abnormalities are described separately in Table 9.
| Grading according to CTCAE Version 3.0 a Includes stomatitis, aphthous stomatitis, mouth ulceration, gingival pain, glossitis, and glossodynia. |
||||||
|
AFINITOR
N=79 |
Placebo
N=39 |
|||||
|
All grades
% |
Grade 3
% |
Grade 4
% |
All grades
% |
Grade 3
% |
Grade 4
% |
|
| Any adverse reaction | 100 | 25 | 5 | 97 | 8 | 5 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||||
| Stomatitisa | 78 | 6 | 0 | 23 | 0 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 15 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 14 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||||
| Peripheral edema | 13 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||||
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 11 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||||
| Arthralgia | 13 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||||
| Cough | 20 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||||
| Acne | 22 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
Amenorrhea occurred in 15% of AFINITOR-treated females (8 of 52) and 4% (1 of 26) of females in the placebo group. Other adverse reactions involving the female reproductive system were menorrhagia (10%), menstrual irregularities (10%), and vaginal hemorrhage (8%).
The following additional adverse reactions occurred in less than 10% of Afinitor-treated patients: epistaxis (9%), decreased appetite (6%), otitis media (6%), depression (5%), abnormal taste (5%), increased blood luteinizing hormone (LH) levels (4%), increased blood follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) levels (3%), hypersensitivity (3%), and pneumonitis (1%).
| Grading according to CTCAE Version 3.0 | ||||||
|
AFINITOR
N=79 |
Placebo
N=39 |
|||||
|
All grades
% |
Grade 3
% |
Grade 4
% |
All grades
% |
Grade 3
% |
Grade 4
% |
|
| Hematology | ||||||
| Anemia | 61 | 0 | 0 | 49 | 0 | 0 |
| Leucopenia | 37 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 0 | 0 |
| Neutropenia | 25 | 0 | 1 | 26 | 0 | 0 |
| Lymphopenia | 20 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 19 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Clinical chemistry | ||||||
| Hypercholesterolemia | 85 | 1 | 0 | 46 | 0 | 0 |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 52 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 49 | 5 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 32 | 1 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| Elevated aspartate transaminase (AST) | 23 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Elevated alanine transaminase (ALT) | 20 | 1 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| Fasting hyperglycemia | 14 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
6.5 Clinical Study Experience in Subependymal Giant Cell Astrocytoma with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
The data described below are based on a randomized (2:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (Study 1) of AFINITOR in 117 patients with subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) and tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC). The median age of patients was 9.5 years (range 0.8 to 26 years), 93% were Caucasian, and 57% were male. The median duration of blinded study treatment was 52 weeks (range 24 to 89 weeks) for patients receiving AFINITOR and 47 weeks (range 14 to 88 weeks) for those receiving placebo.
The most common adverse reactions reported for AFINITOR (incidence ≥ 30%) were stomatitis and respiratory tract infection. The most common Grade 3-4 adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 2%) were stomatitis, pyrexia, pneumonia, gastroenteritis, aggression, agitation, and amenorrhea. The most common key laboratory abnormalities (incidence ≥ 50%) were hypercholesterolemia and elevated partial thromboplastin time. The most common Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormality (incidence ≥ 3%) was neutropenia.
There were no adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation. Dose adjustments (interruptions or reductions) due to adverse reactions occurred in 55% of AFINITOR-treated patients. The most common adverse reaction leading to AFINITOR dose adjustment was stomatitis.
Table 10 compares the incidence of adverse reactions reported with an incidence of ≥ 10% for patients receiving AFINITOR and occurring more frequently with AFINITOR than with placebo. Laboratory abnormalities are described separately in Table 11.
| Grading according to CTCAE Version 3.0 a Includes mouth ulceration, stomatitis, and lip ulceration b Includes respiratory tract infection, upper respiratory tract infection, and respiratory tract infection viral c Includes gastroenteritis, gastroenteritis viral, and gastrointestinal infection d Includes agitation, anxiety, panic attack, aggression, abnormal behavior, and obsessive compulsive disorder e Includes rash, rash generalized, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash papular, dermatitis allergic, and urticaria |
||||||
|
AFINITOR
N=78 |
Placebo
N=39 |
|||||
|
All grades
% |
Grade 3
% |
Grade 4
% |
All grades
% |
Grade 3
% |
Grade 4
% |
|
| Any adverse reaction | 97 | 36 | 3 | 92 | 23 | 3 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||||
| Stomatitisa | 62 | 9 | 0 | 26 | 3 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 22 | 1 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 17 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Constipation | 10 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||||
| Respiratory tract infectionb | 31 | 1 | 1 | 23 | 0 | 0 |
| Gastroenteritisc | 10 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Pharyngitis streptococcal | 10 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||||
| Pyrexia | 23 | 6 | 0 | 18 | 3 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 14 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||||||
| Anxiety, aggression or other behavioral disturbanced | 21 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||||
| Rashe | 21 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Acne | 10 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
Amenorrhea occurred in 17% of AFINITOR-treated females aged 10 to 55 years (3 of 18) and none of the females in the placebo group. For this same group of AFINITOR-treated females, the following menstrual abnormalities were reported: dysmenorrhea (6%), menorrhagia (6%), metrorrhagia (6%), and unspecified menstrual irregularity (6%).
The following additional adverse reactions occurred in less than 10% of AFINITOR-treated patients: nausea (8%), pain in extremity (8%), insomnia (6%), pneumonia (6%), epistaxis (5%), hypersensitivity (3%), increased blood luteinizing hormone (LH) levels (1%) and pneumonitis (1%).
| Grading according to CTCAE Version 3.0 | ||||||
|
AFINITOR
N=78 |
Placebo
N=39 |
|||||
|
All grades
% |
Grade 3
% |
Grade 4
% |
All grades
% |
Grade 3
% |
Grade 4
% |
|
| Hematology | ||||||
| Elevated partial thromboplastin time | 72 | 3 | 0 | 44 | 5 | 0 |
| Neutropenia | 46 | 9 | 0 | 41 | 3 | 0 |
| Anemia | 41 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 0 | 0 |
| Clinical chemistry | ||||||
| Hypercholesterolemia | 81 | 0 | 0 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| Elevated aspartate transaminase (AST) | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 27 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| Elevated alanine transaminase (ALT) | 18 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 9 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
Longer-term follow-up of 34.2 months (range 4.7 to 47.1 months) from a non-randomized, open-label, 28-patient trial resulted in the following additional notable adverse reactions and key laboratory abnormalities: cellulitis (29%), hyperglycemia (25%), and elevated creatinine (14%).
6.6 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of AFINITOR. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure: acute pancreatitis.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Everolimus is a substrate of CYP3A4, and also a substrate and moderate inhibitor of the multidrug efflux pump PgP. In vitro, everolimus is a competitive inhibitor of CYP3A4 and a mixed inhibitor of CYP2D6.
7.1 Agents That May Increase Everolimus Blood Concentrations
CYP3A4 Inhibitors and PgP Inhibitors
In healthy subjects, compared to AFINITOR treatment alone there were significant increases in everolimus exposure when AFINITOR was coadministered with:
- ketoconazole (a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor and a PgP inhibitor) - Cmax and AUC increased by 3.9- and 15.0-fold, respectively.
- erythromycin (a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor and a PgP inhibitor) - Cmax and AUC increased by 2.0- and 4.4-fold, respectively.
- verapamil (a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor and a PgP inhibitor) - Cmax and AUC increased by 2.3- and 3.5-fold, respectively.
Concomitant strong inhibitors of CYP3A4/PgP should not be used [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Use caution when AFINITOR is used in combination with moderate CYP3A4/PgP inhibitors. If alternative treatment cannot be administered reduce the AFINITOR dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
7.2 Agents That May Decrease Everolimus Blood Concentrations
CYP3A4/PgP Inducers
In healthy subjects, co-administration of AFINITOR with rifampin, a strong inducer of CYP3A4 and an inducer of PgP, decreased everolimus AUC and Cmax by 63% and 58% respectively, compared to everolimus treatment alone. Consider a dose increase of AFINITOR when co-administered with strong CYP3A4/PgP inducers if alternative treatment cannot be administered. St. John’s Wort may decrease everolimus exposure unpredictably and should be avoided [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.5)].
7.3 Drugs That May Have Their Plasma Concentrations Altered by Everolimus
Studies in healthy subjects indicate that there are no clinically significant pharmacokinetic interactions between AFINITOR and the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors atorvastatin (a CYP3A4 substrate) and pravastatin (a non-CYP3A4 substrate) and population pharmacokinetic analyses also detected no influence of simvastatin (a CYP3A4 substrate) on the clearance of AFINITOR.
A study in healthy subjects demonstrated that co-administration of an oral dose of midazolam (sensitive CYP3A4 substrate) with everolimus resulted in a 25% increase in midazolam Cmax and a 30% increase in midazolam AUC(0-inf).
Coadministration of everolimus and exemestane increased exemestane Cmin by 45% and C2h by 64%. However, the corresponding estradiol levels at steady state (4 weeks) were not different between the 2 treatment arms. No increase in adverse events related to exemestane was observed in patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer receiving the combination.
Coadministration of everolimus and depot octreotide increased octreotide Cmin by approximately 50%.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D
Risk Summary
Based on the mechanism of action, AFINITOR can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Everolimus caused embryo-fetal toxicities in animals at maternal exposures that were lower than human exposures. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking the drug, apprise the patient of the potential hazard to the fetus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Animal Data
In animal reproductive studies, oral administration of everolimus to female rats before mating and through organogenesis induced embryo-fetal toxicities, including increased resorption, pre-implantation and post-implantation loss, decreased numbers of live fetuses, malformation (e.g., sternal cleft), and retarded skeletal development. These effects occurred in the absence of maternal toxicities. Embryo-fetal toxicities in rats occurred at doses ≥ 0.1 mg/kg (0.6 mg/m2) with resulting exposures of approximately 4% of the exposure (AUC0-24h) achieved in patients receiving the 10 mg daily dose of everolimus. In rabbits, embryotoxicity evident as an increase in resorptions occurred at an oral dose of 0.8 mg/kg (9.6 mg/m2), approximately 1.6 times either the 10 mg daily dose or the median dose administered to SEGA patients on a body surface area basis. The effect in rabbits occurred in the presence of maternal toxicities.
In a pre- and post-natal development study in rats, animals were dosed from implantation through lactation. At the dose of 0.1 mg/kg (0.6 mg/m2), there were no adverse effects on delivery and lactation or signs of maternal toxicity; however, there were reductions in body weight (up to 9% reduction from the control) and in survival of offspring (~5% died or missing). There were no drug-related effects on the developmental parameters (morphological development, motor activity, learning, or fertility assessment) in the offspring.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether everolimus is excreted in human milk. Everolimus and/or its metabolites passed into the milk of lactating rats at a concentration 3.5 times higher than in maternal serum. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from everolimus, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Pediatric use of AFINITOR Tablets and AFINITOR DISPERZ is recommended for patients 1 year of age and older with TSC for the treatment of SEGA that requires therapeutic intervention but cannot be curatively resected. The safety and effectiveness of AFINITOR Tablets and AFINITOR DISPERZ have not been established in pediatric patients with renal angiomyolipoma with TSC in the absence of SEGA.
The effectiveness of AFINITOR in pediatric patients with SEGA was demonstrated in two clinical trials based on demonstration of durable objective response, as evidenced by reduction in SEGA tumor volume [see Clinical Studies (14.5)]. Improvement in disease-related symptoms and overall survival in pediatric patients with SEGA has not been demonstrated. The long term effects of AFINITOR on growth and pubertal development are unknown.
Study 1 was a randomized, double-blind, multicenter trial comparing AFINITOR (n=78) to placebo (n=39) in pediatric and adult patients. The median age was 9.5 years (range 0.8 to 26 years). At the time of randomization, a total of 20 patients were < 3 years of age, 54 patients were 3 to < 12 years of age, 27 patients were 12 to < 18 years of age, and 16 patients were ≥ 18 years of age. The overall nature, type, and frequency of adverse reactions across the age groups evaluated were similar, with the exception of a higher per patient incidence of infectious serious adverse events in patients < 3 years of age. A total of 6 of 13 patients (46%) < 3 years of age had at least 1 serious adverse event due to infection, compared to 2 of 7 patients (29%) treated with placebo. No patient in any age group discontinued AFINITOR due to infection [see Adverse Reactions (6.5)]. Subgroup analyses showed reduction in SEGA volume with AFINITOR treatment in all pediatric age subgroups.
Study 2 was an open-label, single-arm, single-center trial of AFINITOR (N=28) in patients aged ≥ 3 years; median age was 11 years (range 3 to 34 years). A total of 16 patients were 3 to < 12 years, 6 patients were 12 to < 18 years, and 6 patients were ≥ 18 years. The frequency of adverse reactions across the age groups was generally similar [see Adverse Reactions (6.5)]. Subgroup analyses showed reductions in SEGA volume with AFINITOR treatment in all pediatric age subgroups.
Everolimus clearance normalized to body surface area was higher in pediatric patients than in adults with SEGA [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].The recommended starting dose and subsequent requirement for therapeutic drug monitoring to achieve and maintain trough concentrations of 5 to 15 ng/mL are the same for adult and pediatric patients with SEGA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the randomized advanced hormone receptor positive, HER2-negative breast cancer study, 40% of AFINITOR-treated patients were ≥ 65 years of age, while 15% were 75 years and over. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between elderly and younger patients. The incidence of deaths due to any cause within 28 days of the last AFINITOR dose was 6% in patients ≥ 65 years of age compared to 2% in patients < 65 years of age. Adverse reactions leading to permanent treatment discontinuation occurred in 33% of patients ≥ 65 years of age compared to 17% in patients < 65 years of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
In two other randomized trials (advanced renal cell carcinoma and advanced neuroendocrine tumors of pancreatic origin), no overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between elderly and younger patients. In the randomized advanced RCC study, 41% of AFINITOR treated patients were ≥ 65 years of age, while 7% were 75 years and over. In the randomized advanced PNET study, 30% of AFINITOR-treated patients were ≥ 65 years of age, while 7% were 75 years and over.
Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in response between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
No dosage adjustment in initial dosing is required in elderly patients, but close monitoring and appropriate dose adjustments for adverse reactions is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Females
AFINITOR can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use highly effective contraception while receiving AFINITOR and for up to 8 weeks after ending treatment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Infertility
Females
Menstrual irregularities, secondary amenorrhea, and increases in luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) occurred in female patients taking AFINITOR. Based on these clinical findings and findings in animals, female fertility may be compromised by treatment with AFINITOR [see Adverse Reactions (6.2, 6.4, 6.5) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Males
AFINITOR treatment may impair fertility in male patients based on animal findings [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
No clinical studies were conducted with AFINITOR in patients with decreased renal function. Renal impairment is not expected to influence drug exposure and no dosage adjustment of everolimus is recommended in patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.8 Hepatic Impairment
The safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of AFINITOR were evaluated in a 34 subject single oral dose study of everolimus in subjects with impaired hepatic function relative to subjects with normal hepatic function. Exposure was increased in patients with mild (Child-Pugh class A), moderate (Child-Pugh class B), and severe (Child-Pugh class C) hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
For advanced HR+ BC, advanced PNET, advanced RCC, and renal angiomyolipoma with TSC patients with severe hepatic impairment, AFINITOR may be used at a reduced dose if the desired benefit outweighs the risk. For patients with mild (Child-Pugh class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh class B) hepatic impairment, a dose reduction is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
For patients with SEGA who have severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C), reduce the starting dose of AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ by approximately 50%. For patients with SEGA who have mild (Child-Pugh class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh class B) hepatic impairment, adjustment to the starting dose may not be needed. Subsequent dosing should be based on therapeutic drug monitoring [ see Dosage and Administration (2.4, 2.5)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
In animal studies, everolimus showed a low acute toxic potential. No lethality or severe toxicity was observed in either mice or rats given single oral doses of 2000 mg/kg (limit test).
Reported experience with overdose in humans is very limited. Single doses of up to 70 mg have been administered. The acute toxicity profile observed with the 70 mg dose was consistent with that for the 10 mg dose.
11 DESCRIPTION
AFINITOR (everolimus), an inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), is an antineoplastic agent.
The chemical name of everolimus is (1R,9S,12S,15R,16E,18R,19R,21R,23S,24E,26E,28E,30S,32S,35R)-1,18- dihydroxy-12-{(1R)-2-[(1S,3R,4R)-4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3-methoxycyclohexyl]-1-methylethyl}-19,30-dimethoxy-15,17,21,23,29,35-hexamethyl-11,36-dioxa-4-aza-tricyclo[30.3.1.04,9]hexatriaconta-16,24,26,28-tetraene-2,3,10,14,20-pentaone.
The molecular formula is C53H83NO14 and the molecular weight is 958.2. The structural formula is:

AFINITOR Tablets are supplied for oral administration and contain 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, or 10 mg of everolimus. The tablets also contain anhydrous lactose, butylated hydroxytoluene, crospovidone, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, and magnesium stearate as inactive ingredients.
AFINITOR DISPERZ (everolimus tablets for oral suspension) is supplied for oral administration and contains 2 mg, 3 mg, or 5 mg of everolimus. The tablets for oral suspension also contain butylated hydroxytoluene, colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and microcrystalline cellulose as inactive ingredients.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Everolimus is an inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), a serine-threonine kinase, downstream of the PI3K/AKT pathway. The mTOR pathway is dysregulated in several human cancers. Everolimus binds to an intracellular protein, FKBP-12, resulting in an inhibitory complex formation with mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and thus inhibition of mTOR kinase activity. Everolimus reduced the activity of S6 ribosomal protein kinase (S6K1) and eukaryotic elongation factor 4E-binding protein (4E-BP1), downstream effectors of mTOR, involved in protein synthesis. S6K1 is a substrate of mTORC1 and phosphorylates the activation domain 1 of the estrogen receptor which results in ligand-independent activation of the receptor. In addition, everolimus inhibited the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (e.g., HIF-1) and reduced the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Inhibition of mTOR by everolimus has been shown to reduce cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and glucose uptake in in vitro and/or in vivo studies.
Constitutive activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway can contribute to endocrine resistance in breast cancer. In vitro studies show that estrogen-dependent and HER2+ breast cancer cells are sensitive to the inhibitory effects of everolimus, and that combination treatment with everolimus and Akt, HER2, or aromatase inhibitors enhances the anti-tumor activity of everolimus in a synergistic manner.
Two regulators of mTORC1 signaling are the oncogene suppressors tuberin-sclerosis complexes 1 and 2 (TSC1, TSC2). Loss or inactivation of either TSC1 or TSC2 leads to activation of downstream signaling. In TSC, a genetic disorder, inactivating mutations in either the TSC1 or the TSC2 gene lead to hamartoma formation throughout the body.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Exposure Response R elationships
Markers of protein synthesis show that inhibition of mTOR is complete after a 10 mg daily dose.
In patients with SEGA, higher everolimus trough concentrations appear to be associated with larger reductions in SEGA volume. However, as responses have been observed at trough concentrations as low as 5 ng/mL, once acceptable efficacy has been achieved, additional dose increase may not be necessary.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After administration of AFINITOR tablets in patients with advanced solid tumors, peak everolimus concentrations are reached 1 to 2 hours after administration of oral doses ranging from 5 mg to 70 mg. Following single doses, Cmax is dose-proportional with daily dosing between 5 mg and 10 mg. With single doses of 20 mg and higher, the increase in Cmax is less than dose-proportional, however AUC shows dose-proportionality over the 5 mg to 70 mg dose range. Steady-state was achieved within 2 weeks following once-daily dosing.
Dose Proportionality in Patients with SEGA and TSC: In patients with SEGA and TSC, everolimus Cmin was approximately dose-proportional within the dose range from 1.35 mg/m2 to 14.4 mg/m2.
Food effect: In healthy subjects, high-fat meals reduced systemic exposure to AFINITOR 10 mg tablet (as measured by AUC) by 22% and the peak blood concentration Cmax by 54%. Light-fat meals reduced AUC by 32% and Cmax by 42%. Food, however, had no apparent effect on the post absorption phase concentration-time profile.
Relative bioavailability of AFINITOR DISPERZ (everolimus tablets for oral suspension): The AUC0-∞ of AFINITOR DISPERZ was equivalent to that of AFINITOR Tablets; the Cmax of this dosage form was 20%-36% lower than that of AFINITOR Tablets. The predicted trough concentrations at steady-state were similar after daily administration.
Distribution
The blood-to-plasma ratio of everolimus, which is concentration-dependent over the range of 5 to 5000 ng/mL, is 17% to 73%. The amount of everolimus confined to the plasma is approximately 20% at blood concentrations observed in cancer patients given AFINITOR 10 mg/day. Plasma protein binding is approximately 74% both in healthy subjects and in patients with moderate hepatic impairment.
Metabolism
Everolimus is a substrate of CYP3A4 and PgP. Following oral administration, everolimus is the main circulating component in human blood. Six main metabolites of everolimus have been detected in human blood, including three monohydroxylated metabolites, two hydrolytic ring-opened products, and a phosphatidylcholine conjugate of everolimus. These metabolites were also identified in animal species used in toxicity studies, and showed approximately 100-times less activity than everolimus itself.
In vitro, everolimus competitively inhibited the metabolism of CYP3A4 and was a mixed inhibitor of the CYP2D6 substrate dextromethorphan.
Elimination
No specific elimination studies have been undertaken in cancer patients. Following the administration of a 3 mg single dose of radiolabeled everolimus in patients who were receiving cyclosporine, 80% of the radioactivity was recovered from the feces, while 5% was excreted in the urine. The parent substance was not detected in urine or feces. The mean elimination half-life of everolimus is approximately 30 hours.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Approximately 5% of total radioactivity was excreted in the urine following a 3 mg dose of [14C]-labeled everolimus. In a population pharmacokinetic analysis which included 170 patients with advanced cancer, no significant influence of creatinine clearance (25–178 mL/min) was detected on oral clearance (CL/F) of everolimus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of AFINITOR were evaluated in a single oral dose study of everolimus in subjects with impaired hepatic function relative to subjects with normal hepatic function. Compared to normal subjects (N=13), there was a 1.8-fold, 3.2-fold, and 3.6-fold increase in exposure (i.e. AUC) for subjects with mild (Child-Pugh class A, n=6), moderate (Child-Pugh class B, n=9), and severe (Child-Pugh class C, n=6) hepatic impairment, respectively. In another study, the average AUC of everolimus in eight subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B) was twice that found in eight subjects with normal hepatic function.
For advanced HR+ BC, advanced PNET, advanced RCC, and renal angiomyolipoma with TSC patients with severe hepatic impairment, AFINITOR may be used at a reduced dose if the desired benefit outweighs the risk. For patients with moderate or mild hepatic impairment, a dose reduction is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
For patients with SEGA and mild or moderate hepatic impairment, adjust the dose of AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ based on therapeutic drug monitoring. For patients with SEGA and severe hepatic impairment, reduce the starting dose of AFINITOR Tablets or AFINITOR DISPERZ by approximately 50% and adjust subsequent doses based on therapeutic drug monitoring [see Dosage and Administration (2.4, 2.5)].
Effects of A ge and G ender
In a population pharmacokinetic evaluation in cancer patients, no relationship was apparent between oral clearance and patient age or gender.
In patients with SEGA, the geometric mean Cmin values normalized to mg/m2 dose in patients aged < 10 years and 10 to 18 years were lower by 54% and 40%, respectively, than those observed in adults (> 18 years of age), suggesting that everolimus clearance normalized to body surface area was higher in pediatric patients as compared to adults.
Ethnicity
Based on a cross-study comparison, Japanese patients (n=6) had on average exposures that were higher than non-Japanese patients receiving the same dose.
Based on analysis of population pharmacokinetics, oral clearance (CL/F) is on average 20% higher in black patients than in Caucasians.
The significance of these differences on the safety and efficacy of everolimus in Japanese or black patients has not been established.
12.6 QT/QTc Prolongation Potential
In a randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over study, 59 healthy subjects were administered a single oral dose of AFINITOR (20 mg and 50 mg) and placebo. There is no indication of a QT/QTc prolonging effect of AFINITOR in single doses up to 50 mg.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Administration of everolimus for up to 2 years did not indicate oncogenic potential in mice and rats up to the highest doses tested (0.9 mg/kg) corresponding respectively to 3.9 and 0.2 times the estimated clinical exposure (AUC0-24h) at the 10 mg daily human dose.
Everolimus was not genotoxic in a battery of in vitro assays (Ames mutation test in Salmonella, mutation test in L5178Y mouse lymphoma cells, and chromosome aberration assay in V79 Chinese hamster cells). Everolimus was not genotoxic in an in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus test at doses up to 500 mg/kg/day (1500 mg/m2/day, approximately 255-fold the 10 mg daily human dose, and 103-fold the maximum dose administered to patients with SEGA, based on the body surface area), administered as 2 doses, 24 hours apart.
Based on non-clinical findings, male fertility may be compromised by treatment with AFINITOR. In a 13-week male fertility study in rats, testicular morphology was affected at 0.5 mg/kg and above. Sperm motility, sperm count, and plasma testosterone levels were diminished in rats treated with 5 mg/kg. These doses result in exposures which are within the range of therapeutic exposure (52 ng•hr/mL and 414 ng•hr/mL respectively compared to 560 ng•hr/mL human exposure at 10 mg/day), and resulted in infertility in the rats at 5 mg/kg. Effects on male fertility occurred at the AUC0-24h values below that of therapeutic exposure (approximately 10%-81% of the AUC0-24h in patients receiving the 10 mg daily dose). After a 10-13 week non-treatment period, the fertility index increased from zero (infertility) to 60% (12/20 mated females were pregnant).
Oral doses of everolimus in female rats at ≥0.1 mg/kg (approximately 4% the AUC0-24h in patients receiving the 10 mg daily dose) resulted in increased incidence of pre-implantation loss, suggesting that the drug may reduce female fertility.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In juvenile rat toxicity studies, dose-related delayed attainment of developmental landmarks including delayed eye-opening, delayed reproductive development in males and females and increased latency time during the learning and memory phases were observed at doses as low as 0.15 mg/kg/day.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Advanced Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer
A randomized, double-blind, multicenter study of AFINITOR plus exemestane versus placebo plus exemestane was conducted in 724 postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive, HER 2/neu-negative advanced breast cancer with recurrence or progression following prior therapy with letrozole or anastrozole. Randomization was stratified by documented sensitivity to prior hormonal therapy (yes versus no) and by the presence of visceral metastasis (yes versus no). Sensitivity to prior hormonal therapy was defined as either (1) documented clinical benefit (complete response [CR], partial response [PR], stable disease ≥ 24 weeks) to at least one prior hormonal therapy in the advanced setting or (2) at least 24 months of adjuvant hormonal therapy prior to recurrence. Patients were permitted to have received 0-1 prior lines of chemotherapy for advanced disease.
The primary endpoint for the trial was progression-free survival (PFS) evaluated by Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST), based on investigator (local radiology) assessment. Other endpoints included overall survival (OS), objective response rate (ORR), and safety.
Patients were randomly allocated in a 2:1 ratio to AFINITOR 10 mg/day plus exemestane 25 mg/day (n = 485) or to placebo plus exemestane 25 mg/day (n = 239). The two treatment groups were generally balanced with respect to baseline demographics and disease characteristics. Patients were not permitted to cross over to AFINITOR at the time of disease progression.
The median progression-free survival by investigator assessment at the time of the final PFS analysis was 7.8 and 3.2 months in the AFINITOR and placebo arms, respectively [HR = 0.45 (95% CI: 0.38, 0.54), one-sided log-rank p < 0.0001] (see Table 12 and Figure 1). The results of the PFS analysis based on independent central radiological assessment were consistent with the investigator assessment. PFS results were also consistent across the subgroups of age, race, presence and extent of visceral metastases, and sensitivity to prior hormonal therapy.
Objective response rate was 12.6% (95% CI: 9.8, 15.9) in the AFINITOR plus exemestane arm versus 1.7% (95% CI: 0.5, 4.2) in the placebo plus exemestane arm. There were 3 complete responses (0.6%) and 58 partial responses (12.0%) in the AFINITOR plus exemestane arm. There were no complete responses and 4 partial responses (1.7%) in the placebo plus exemestane arm.
The overall survival results were not mature at the time of the interim analysis, and no statistically significant treatment-related difference in OS was noted [HR=0.77 (95% CI: 0.57, 1.04)].
|
a Exemestane (25 mg/day) b Hazard ratio is obtained from the stratified Cox proportional-hazards model by sensitivity to prior hormonal therapy and presence of visceral metastasis c p-value is obtained from the one-sided log-rank test stratified by sensitivity to prior hormonal therapy and presence of visceral metastasis d Objective response rate = proportion of patients with CR or PR e not applicable |
|||||
| Analysis |
AFINITOR
+ exemestanea N = 485 |
Placebo
+ exemestanea N = 239 |
Hazard ratio | P-value | |
| Median progression-free survival (months, 95% CI) | |||||
| Investigator radiological review | 7.8 (6.9 to 8.5) |
3.2 (2.8 to 4.1) |
0.45b
(0.38 to 0.54) |
<0.0001c | |
| Independent radiological review | 11.0 (9.7 to 15.0) |
4.1 (2.9 to 5.6) |
0.38b
(0.3 to 0.5) |
<0.0001c
|
|
| Best overall response (%, 95% CI) | |||||
| Objective response rate (ORR)d | 12.6% (9.8 to 15.9) |
1.7% (0.5 to 4.2) |
n/ae | ||

14.2 Advanced Neuroendocrine Tumors
Locally Advanced or Metastatic Advanced Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (PNET)
A randomized, double-blind, multi-center trial of AFINITOR plus best supportive care (BSC) versus placebo plus BSC was conducted in patients with locally advanced or metastatic advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNET) and disease progression within the prior 12 months. Patients were stratified by prior cytotoxic chemotherapy (yes versus no) and by WHO performance status (0 versus 1 and 2). Treatment with somatostatin analogs was allowed as part of BSC. The primary endpoint for the trial was progression-free survival (PFS) evaluated by RECIST (Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors). After documented radiological progression, patients could be unblinded by the investigator; those randomized to placebo were then able to receive open-label AFINITOR. Other endpoints included safety, objective response rate [ORR (complete response (CR) or partial response (PR)], response duration, and overall survival.
Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either AFINITOR 10 mg/day (n=207) or placebo (n=203). Demographics were well balanced (median age 58 years, 55% male, 79% Caucasian). Cross-over from placebo to open-label AFINITOR occurred in 73% (148/203) of patients.
The trial demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in PFS (median 11.0 months versus 4.6 months), resulting in a 65% risk reduction in investigator-determined PFS (HR 0.35; 95%CI: 0.27 to 0.45; p<0.001) (see Table 13 and Figure 2). PFS improvement was observed across all patient subgroups, irrespective of prior somatostatin analog use. The PFS results by investigator radiological review, central radiological review and adjudicated radiological review are shown below in Table 13.
| a includes adjudication for discrepant assessments between investigator radiological review and central radiological review | |||||
| Analysis |
N
|
AFINITOR
N=207 |
Placebo
N=203 |
Hazard Ratio (95%CI) | p-value |
| 410 | Median progression-free survival (months) (95% CI) | ||||
| Investigator radiological review | 11.0 (8.4 to 13.9) |
4.6 (3.1 to 5.4) |
0.35 (0.27 to 0.45) |
<0.001 | |
| Central radiological review | 13.7 (11.2 to 18.8) |
5.7 (5.4 to 8.3) |
0.38 (0.28 to 0.51) |
<0.001 |
|
| Adjudicated radiological reviewa | 11.4 (10.8 to 14.8) |
5.4 (4.3 to 5.6) |
0.34 (0.26 to 0.44) |
<0.001 | |

Investigator-determined response rate was low (4.8%) in the AFINITOR arm and there were no complete responses. The overall survival results are not yet mature and no statistically significant treatment-related difference in OS was noted [HR=1.05 (95% CI: 0.71 to 1.55)].
Lack of Efficacy in Locally Advanced or Metastatic Functional Carcinoid Tumors
The safety and effectiveness of AFINITOR in patients with locally advanced or metastatic functional carcinoid tumors have not been demonstrated. In a randomized (1:1), double-blind, multi-center trial in 429 patients with carcinoid tumors, AFINITOR plus depot octreotide (Sandostatin LAR®) was compared to placebo plus depot octreotide. After documented radiological progression, patients on the placebo arm could receive AFINITOR; of those randomized to placebo, 143 (67%) patients received open-label AFINITOR plus depot octreotide. The study did not meet its primary efficacy endpoint of a statistically significant improvement in PFS and the final analysis of OS favored the placebo plus depot octreotide arm.
14.3 Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
An international, multi-center, randomized, double-blind trial comparing AFINITOR 10 mg daily and placebo, both in conjunction with best supportive care, was conducted in patients with metastatic RCC whose disease had progressed despite prior treatment with sunitinib, sorafenib, or both sequentially. Prior therapy with bevacizumab, interleukin 2, or interferon-α was also permitted. Randomization was stratified according to prognostic score1 and prior anticancer therapy.
Progression-free survival (PFS), documented using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) was assessed via a blinded, independent, central radiologic review. After documented radiological progression, patients could be unblinded by the investigator: those randomized to placebo were then able to receive open-label AFINITOR 10 mg daily.
In total, 416 patients were randomized 2:1 to receive AFINITOR (n=277) or placebo (n=139). Demographics were well balanced between the 2 arms (median age 61 years; 77% male, 88% Caucasian, 74% received prior sunitinib or sorafenib, and 26% received both sequentially).
AFINITOR was superior to placebo for PFS (see Table 14 and Figure 3). The treatment effect was similar across prognostic scores and prior sorafenib and/or sunitinib. Final overall survival (OS) results yield a hazard ratio of 0.90 (95% CI: 0.71 to 1.14), with no statistically significant difference between the 2 treatment groups. Planned cross-over from placebo due to disease progression to open label AFINITOR occurred in 111 of the 139 patients (79.9%) and may have confounded the OS benefit.
|
a Log-rank test stratified by prognostic score. b Not applicable. |
||||
|
AFINITOR
N=277 |
Placebo
N=139 |
Hazard
R
atio
(95% CI) |
p-value a | |
|
Median P
rogression-
free S
urvival
(95% CI) |
4.9 months (4.0 to 5.5) |
1.9 months (1.8 to 1.9) |
0.33 (0.25 to 0.43) |
<0.0001 |
| Objective R esponse R ate | 2% | 0% | n/a b | n/a b |

14.4 Renal Angiomyolipoma with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
A randomized (2:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of AFINITOR was conducted in 118 patients with renal angiomyolipoma as a feature of TSC (n=113) or sporadic lymphangioleiomyomatosis (n=5).
The key eligibility requirements for this trial were at least one angiomyolipoma of ≥ 3 cm in longest diameter on CT/MRI based on local radiology assessment, no immediate indication for surgery, and age ≥ 18 years. Patients received daily oral AFINITOR 10 mg or matching placebo until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. CT or MRI scans for disease assessment were obtained at baseline, 12, 24, and 48 weeks and annually thereafter. Clinical and photographic assessment of skin lesions were conducted at baseline and every 12 weeks thereafter until treatment discontinuation. The major efficacy outcome measure was angiomyolipoma response rate based on independent central radiology review, which was defined as a ≥ 50% reduction in angiomyolipoma volume, absence of new angiomyolipoma lesion ≥ 1 cm, absence of kidney volume increase ≥ 20%, and no angiomyolipoma related bleeding of ≥ Grade 2. Key supportive efficacy outcome measures were time to angiomyolipoma progression and skin lesion response rate. Analyses of efficacy outcome measures were limited to the blinded treatment period which ended 6 months after the last patient was randomized. The comparative angiomyolipoma response rate analysis was stratified by use of enzyme-inducing antiepileptic drugs (EIAEDs) at randomization (yes versus no).
Of the 118 patients enrolled, 79 were randomized to AFINITOR and 39 to placebo. The median age was 31 years (range 18 to 61 years), 34% were male, and 89% were Caucasian. At baseline, 17% of patients were receiving EIAEDs. On central radiology review at baseline, 92% of patients had at least 1 angiomyolipoma of ≥ 3 cm in longest diameter, 29% had angiomyolipomas ≥ 8 cm, 78% had bilateral angiomyolipomas, and 97% had skin lesions. The median values for the sum of all target renal angiomyolipoma lesions at baseline were 85 cm3 (range 9 to 1612 cm3) and 120 cm3 (range 3 to 4520 cm3) in the AFINITOR and placebo arms respectively. Forty-six (39%) patients had prior renal embolization or nephrectomy. The median duration of follow-up was 8.3 months (range 0.7 to 24.8 months).
The renal angiomyolipoma response rate was statistically significantly higher in AFINITOR-treated patients; there were 33 (41.8%) patients with angiomyolipoma responses in the AFINITOR arm as compared to none in the placebo arm. Results are displayed in Table 15. The median response duration was 5.3+ months (range 2.3+ to 19.6+ months).
| a Per independent central radiology review | |||
| AFINITOR | Placebo | p-value | |
| N=79 | N=39 | ||
| Primary analysis | |||
| Angiomyolipoma response ratea - % | 41.8 | 0 | <0.0001 |
| 95% CI | (30.8, 53.4) | (0.0, 9.0) | |
There were 3 patients in the AFINITOR arm and 8 patients in the placebo arm with documented angiomyolipoma progression by central radiologic review. The time to angiomyolipoma progression was statistically significantly longer in the AFINITOR arm (HR 0.08 [95% CI: 0.02, 0.37]; p <0.0001).
Skin lesion response rates were assessed by local investigators in 77 patients in the AFINITOR arm and 37 patients in the placebo arm with skin lesions at study entry. The skin lesion response rate was statistically significantly higher in the AFINITOR arm (26% versus 0, p=0.0011); all skin lesion responses were partial responses, defined as visual improvement in 50%-99% skin lesions, considering all skin lesions, durable for at least 8 weeks (Physician's Global Assessment of Clinical Condition).
14.5 Subependymal Giant Cell Astrocytoma with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
Study 1 was a randomized (2:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of AFINITOR Tablets conducted in 117 pediatric and adult patients with subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) and tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC). Eligible patients had at least one SEGA lesion ≥ 1.0 cm in longest diameter on MRI based on local radiology assessment and one or more of the following: serial radiological evidence of SEGA growth, a new SEGA lesion ≥ 1 cm in longest diameter, or new or worsening hydrocephalus. Patients randomized to the treatment arm received AFINITOR Tablets at a starting dose of 4.5 mg/m2 daily, with subsequent dose adjustments as needed to achieve and maintain everolimus trough concentrations of 5 to 15 ng/mL as tolerated. AFINITOR/matched placebo treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. MRI scans for disease assessment were obtained at baseline, 12, 24, and 48 weeks, and annually thereafter.
The main efficacy outcome measure was SEGA response rate based on independent central radiology review. SEGA response was defined as a ≥ 50% reduction in the sum of SEGA volume relative to baseline, in the absence of unequivocal worsening of non-target SEGA lesions, a new SEGA lesion ≥ 1 cm, and new or worsening hydrocephalus. Analysis of SEGA response rate was limited to the blinded treatment period which ended 6 months after the last patient was randomized. The analysis of SEGA response rate was stratified by use of enzyme-inducing antiepileptic drugs (EIAEDs) at randomization (yes versus no).
Of the 117 patients enrolled, 78 were randomized to AFINITOR and 39 to placebo. The median age was 9.5 years (range 0.8 to 26 years; 69% were 3 to < 18 years at enrollment; 17% were < 3 years at enrollment), 57% were male, and 93% were Caucasian. At baseline, 18% of patients were receiving EIAEDs. Based on central radiology review at baseline, 98% of patients had at least one SEGA lesion ≥ 1.0 cm in longest diameter, 79% had bilateral SEGAs, 43% had ≥ 2 target SEGA lesions, 26% had growth in or into the inferior surface of the ventricle, 9% had evidence of growth beyond the subependymal tissue adjacent to the ventricle, and 7% had radiographic evidence of hydrocephalus. The median values for the sum of all target SEGA lesions at baseline were 1.63 cm3 (range 0.18 to 25.15 cm3) and 1.30 cm3 (range 0.32 to 9.75 cm3) in the AFINITOR and placebo arms respectively. Eight (7%) patients had prior SEGA-related surgery. The median duration of follow-up was 8.4 months (range 4.6 to 17.2 months).
The SEGA response rate was statistically significantly higher in AFINITOR-treated patients. There were 27 (35%) patients with SEGA responses in the AFINITOR arm and no SEGA responses in the placebo arm. Results are displayed in Table 16. At the time of the final analysis, all SEGA responses were ongoing and the median duration of response was 5.3 months (range 2.1 to 8.4 months). No patient in either treatment arm required surgical intervention during the course of Study 1.
| a Per independent central radiology review | |||
| AFINITOR | Placebo | p-value | |
| N=78 | N=39 | ||
| Final analysis | |||
| SEGA response ratea - (%) | 35 | 0 | <0.0001 |
| 95% CI | 24, 46 | 0, 9 | |
With a median follow-up of 8.4 months, SEGA progression was detected in 6 of 39 (15.4%) patients randomized to receive placebo and none of the 78 patients randomized to receive AFINITOR.
Study 2 was an open-label, single-arm trial conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of AFINITOR in patients with SEGA and TSC. Serial radiological evidence of SEGA growth was required for entry. Change in SEGA volume at the end of the core 6-month treatment phase was assessed via independent central radiology review. In total, 28 patients received treatment with AFINITOR; median age was 11 years (range 3-34), 61% male, 86% Caucasian. Four patients had surgical resection of their SEGA lesions with subsequent re-growth prior to receiving AFINITOR treatment. After the core treatment phase, patients could continue to receive AFINITOR treatment as part of an extension treatment phase where SEGA volume was assessed every 6 months. The median duration of treatment was 34.2 months (range 4.7-47.1 months).
At 6 months, nine of 28 patients (32%, 95% CI: 16% to 52%) had a ≥ 50% reduction in the tumor volume of their largest SEGA lesion. The median duration of response for these nine patients was 11.8 months (range 3.2 to 39.1 months). Seven of these nine patients had an ongoing volumetric reduction of ≥ 50% at the data cutoff.
Three of four patients who had prior surgery experienced a ≥ 50% reduction in the tumor volume of their largest SEGA lesion. One of these three patients responded by month 6. No patient developed new lesions.
15 REFERENCES
- Motzer RJ, Bacik J, Schwartz LH, et al. Prognostic factors for survival in previously treated patients with metastatic renal cell cancer. J Clin Oncol (2004) 22:454-63.
- OSHA Hazardous Drugs. OSHA. http://www.osha.gov/SLTC/hazardousdrugs/index.html.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
AFINITOR (everolimus) Tablets
2.5 mg tablets
White to slightly yellow, elongated tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “LCL” on one side and “NVR” on the other; available in:
Blisters of 28 tablets………………………………………………………………………………NDC 0078-0594-51
Each carton contains 4 blister cards of 7 tablets each
5 mg tablets
White to slightly yellow, elongated tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “5” on one side and “NVR” on the other; available in:
Blisters of 28 tablets………………………………………………………………………………NDC 0078-0566-51
Each carton contains 4 blister cards of 7 tablets each
7.5 mg tablets
White to slightly yellow, elongated tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “7P5” on one side and “NVR” on the other; available in:
Blisters of 28 tablets………………………………………………………………………………NDC 0078-0620-51
Each carton contains 4 blister cards of 7 tablets each
10 mg tablets
White to slightly yellow, elongated tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “UHE” on one side and “NVR” on the other; available in:
Blisters of 28 tablets………………………………………………………………………………NDC 0078-0567-51
Each carton contains 4 blister cards of 7 tablets each
AFINITOR DISPERZ (everolimus tablets for oral suspension)
2 mg tablets for oral suspension
White to slightly yellowish, round, flat tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “D2” on one side and “NVR” on the other; available in:
Blisters of 28 tablets………………………………………………………………………………NDC 0078-0626-51
Each carton contains 4 blister cards of 7 tablets each
3 mg tablets for oral suspension
White to slightly yellowish, round, flat tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “D3” on one side and “NVR” on the other; available in:
Blisters of 28 tablets………………………………………………………………………………NDC 0078-0627-51
Each carton contains 4 blister cards of 7 tablets each
5 mg tablets for oral suspension
White to slightly yellowish, round, flat tablets with a bevelled edge and no score, engraved with “D5” on one side and “NVR” on the other; available in:
Blisters of 28 tablets………………………………………………………………………………NDC 0078-0628-51
Each carton contains 4 blister cards of 7 tablets each
Store AFINITOR (everolimus) Tablets and AFINITOR DISPERZ (everolimus tablets for oral suspension) at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted between 15°–30°C (59°–86°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature. Store in the original container, protect from light and moisture. Keep this and all drugs out of the reach of children.
Follow special handling and disposal procedures for anticancer pharmaceuticals.2
AFINITOR Tablets and AFINITOR DISPERZ should not be crushed. Do not take tablets which are crushed or broken.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use)
Non-infectious Pneumonitis
Warn patients of the possibility of developing non-infectious pneumonitis. In clinical studies, some non-infectious pneumonitis cases have been severe and occasionally fatal. Advise patients to report promptly any new or worsening respiratory symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Infections
Inform patients that they are more susceptible to infections while being treated with AFINITOR and that cases of hepatitis B reactivation have been associated with AFINITOR treatment. In clinical studies, some of these infections have been severe (e.g., leading to sepsis, respiratory or hepatic failure) and occasionally fatal. Patients should be aware of the signs and symptoms of infection and should report any such signs or symptoms promptly to their physician [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Oral Ulceration
Inform patients of the possibility of developing mouth ulcers, stomatitis, and oral mucositis. In such cases, mouthwashes and/or topical treatments are recommended, but these should not contain alcohol, peroxide, iodine, or thyme [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Renal Failure
Inform patients of the possibility of developing kidney failure. In some cases kidney failure has been severe and occasionally fatal. Inform patients of the need for the healthcare provider to monitor kidney function, especially in patients with risk factors that may impair kidney function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Impaired Wound Healing
Inform patients of the possibility of impaired wound healing or dehiscence while being treated with AFINITOR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Laboratory Tests and Monitoring
Inform patients of the need to monitor blood chemistry and hematology prior to the start of AFINITOR therapy and periodically thereafter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Drug-drug Interactions
Advise patients to inform their healthcare providers of all concomitant medications, including over-the-counter medications and dietary supplements. Inform the patients to avoid concomitant administration of strong CYP3A4/PgP inhibitors or inducers while on AFINITOR treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.8), and Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)].
Vaccinations
Advise patients to avoid the use of live vaccines and close contact with those who have received live vaccines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Embryo-fetal Toxicity
Advise female patients of childbearing potential that AFINITOR may cause fetal harm and that a highly effective method of contraception should be used during therapy with AFINITOR and for up to 8 weeks after ending treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Safe Handling Practices for AFINITOR DISPERZ
Advise patients and their caregivers to read and carefully follow the FDA approved AFINITOR DISPERZ “Instructions for Use”.
Dosing Instructions
Inform patients to take AFINITOR Tablets orally once daily at the same time every day, either consistently with food or consistently without food. Inform patients that AFINITOR Tablets should be swallowed whole with a glass of water.
Inform patients to take AFINITOR DISPERZ orally once daily at the same time every day as a suspension. Refer patients to the “Instructions for Use” pamphlet for additional information regarding these procedures.
Instruct patients that if they miss a dose of AFINITOR, they may still take it up to 6 hours after the time they would normally take it. If more than 6 hours have elapsed, they should be instructed to skip the dose for that day. The next day, they should take AFINITOR at the usual time. Warn patients to not take 2 doses to make up for the one that they missed.
Manufactured by:
Novartis Pharma Stein AG
Stein, Switzerland
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
T2014-16
February 2014
PATIENT INFORMATION
AFINITOR® (a-fin-it-or)
(everolimus)
Tablets
AFINITOR® DISPERZ (a-fin-it-or dis-perz)
(everolimus tablets for oral suspension)
Read this Patient Information leaflet that comes with AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about AFINITOR and AFINITOR DISPERZ?
AFINITOR and AFINITOR DISPERZ can cause serious side effects. These serious side effects include:
1.
You may develop lung or breathing problems. In some people lung or breathing problems may be severe, and can even lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms:
• New or worsening cough
• Shortness of breath
• Chest pain
• Difficulty breathing or wheezing
2. You may be more likely to develop an infection, such as pneumonia, or a bacterial, fungal or viral infection. Viral infections may include active hepatitis B in people who have had hepatitis B in the past (reactivation). In some people these infections may be severe, and can even lead to death. You may need to be treated as soon as possible.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have a temperature of 100.5˚F or above, chills, or do not feel well.
Symptoms of hepatitis B or infection may include the following:
- Fever
- Chills
- Skin rash
- Joint pain and inflammation
- Tiredness
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Pale stools or dark urine
- Yellowing of the skin
- Pain in the upper right side of the stomach
3. You may develop kidney failure. In some people this may be severe and can even lead to death. Your healthcare provider should do tests to check your kidney function before and during your treatment with AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ.
If you have any of the serious side effects listed above, you may need to stop taking AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ for a while or use a lower dose. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions.
What is AFINITOR?
AFINITOR is a prescription medicine used to treat:
- advanced hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, along with the medicine exemestane, in postmenopausal women who have already received certain other medicines for their cancer.
- adults with a type of pancreatic cancer known as pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (PNET), that has progressed and cannot be treated with surgery.
AFINITOR is not for use in people with carcinoid tumors that actively produce hormones.
- adults with advanced kidney cancer (renal cell carcinoma or RCC) when certain other medicines have not worked.
- people with the following types of tumors that are seen with a genetic condition called tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC):
- adults with a kidney tumor called angiomyolipoma, when their kidney tumor does not require surgery right away.
- adults and children with a brain tumor called subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) when the tumor cannot be removed completely by surgery.
What is AFINITOR DISPERZ?
AFINITOR DISPERZ is a prescription medicine used to treat:
- adults and children with a genetic condition called tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) who have a brain tumor called subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) when the tumor cannot be removed completely by surgery.
Who should not take AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ?
Do not take AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ if you are allergic to everolimus or to any of the ingredients in AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in AFINITOR and AFINITOR DISPERZ.
Talk to your healthcare provider before taking this medicine if you are allergic to:
- sirolimus (Rapamune®)
- temsirolimus (Torisel®)
Ask your healthcare provider if you do not know.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ?
Before taking AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- Have or have had kidney problems
- Have or have had liver problems
- Have diabetes or high blood sugar
- Have high blood cholesterol levels
- Have any infections
- Previously had hepatitis B
- Are scheduled to receive any vaccinations. You should not receive a “live vaccine” or be around people who have recently received a “live vaccine” during your treatment with AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ. If you are not sure about the type of immunization or vaccine, ask your healthcare provider.
- Have other medical conditions
- Are pregnant, or could become pregnant. AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ can cause harm to your unborn baby. You should use effective birth control while using AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ and for 8 weeks after stopping treatment. Talk to your healthcare provider about birth control options while taking AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ.
- Are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ, or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines can affect how AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ work. Using AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ with other medicines can cause serious side effects.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum)
- Medicine for:
- Fungal infections
- Bacterial infections
- Tuberculosis
- Seizures
- HIV-AIDS
- Heart conditions or high blood pressure
- Fungal infections
- Medicines that weaken your immune system (your body’s ability to fight infections and other problems)
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if your medicine is one of those taken for the conditions listed above. If you are taking any medicines for the conditions listed above, your healthcare provider might need to prescribe a different medicine or your dose of AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ may need to be changed. You should also tell your healthcare provider before you start taking any new medicine.
How should I take AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ?
- Your healthcare provider will prescribe the dose of AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ that is right for you.
- Take AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose of AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ or tell you to temporarily interrupt dosing, if needed.
- Use scissors to open the blister pack.
AFINITOR:
- Swallow AFINITOR tablets whole with a glass of water. Do not take any tablet that is broken or crushed.
AFINITOR DISPERZ:
- If your healthcare provider prescribes AFINITOR DISPERZ for you, see the “Instructions for Use” that come with your medicine for instructions on how to prepare and take your dose.
- Each dose of AFINITOR DISPERZ must be prepared as a suspension before it is given.
- AFINITOR DISPERZ can cause harm to an unborn baby. When possible, the suspension should be prepared by an adult who is not pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
- Anyone who prepares suspensions of AFINITOR DISPERZ for another person should wear gloves to avoid possible contact with the medicine.
• Take AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ 1 time each day at about the same time.
• Take AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ the same way each time, either with food or without food.
• If you take too much AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ contact your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away. Take the pack of AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ with you.
• If you miss a dose of AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ, you may still take it up to 6 hours after the time you normally take it. If it is more than 6 hours after you normally take your AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ, skip the dose for that day. The next day, take AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ at your usual time. Do not take 2 doses to make up for a missed dose. If you are not sure about what to do, call your healthcare provider.
• You should have blood tests before you start AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ and as needed during your treatment. These will include tests to check your blood cell count, kidney and liver function, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
• If you take AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ to treat SEGA, you will also need to have blood tests regularly to measure how much medicine is in your blood. This will help your healthcare provider decide how much AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ you need to take.
What should I avoid while taking AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ?
You should not drink grapefruit juice or eat grapefruit during your treatment with AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ. It may make the amount of AFINITOR in your blood increase to a harmful level.
What are the possible side effects of AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ?
AFINITOR and AFINITOR DISPERZ can cause serious side effects.
- See “What is the most important information I should know about AFINITOR and AFINITOR DISPERZ?” for more information.
-
Delayed wound healing. AFINITOR can cause incisions to heal slowly or not heal well. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- your incision is red, warm or painful
- blood, fluid, or pus in your incision
- your incision opens up
- swelling of your incision
Common side effects of AFINITOR in people with advanced hormone receptor-positive, HER 2-negative breast cancer, advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, and advanced kidney cancer include:
- Mouth ulcers. AFINITOR can cause mouth ulcers and sores. Tell your healthcare provider if you have pain, discomfort, or open sores in your mouth. Your healthcare provider may tell you to use a special mouthwash or mouth gel that does not contain alcohol, peroxide, iodine, or thyme.
- Infections
- Feeling weak or tired
- Cough, shortness of breath
- Diarrhea and constipation
- Rash, dry skin, and itching
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Loss of appetite, weight loss
- Swelling of arms, hands, feet, ankles, face or other parts of the body
- Abnormal taste
- Dry mouth
- Inflammation of lining of the digestive system
- Headache
- Nose bleeds
- Pain in arms and legs, mouth and throat, back or joints
- High blood glucose
- High blood pressure
- Difficulty sleeping
- Hair loss
- Muscle spasms
- Feeling dizzy
- Nail disorders
Common side effects of AFINITOR and AFINITOR DISPERZ in people who have SEGA or renal angiomyolipoma with TSC include:
- Mouth ulcers. AFINITOR can cause mouth ulcers and sores. Tell your healthcare provider if you have pain, discomfort, or open sores in your mouth. Your healthcare provider may tell you to use a special mouthwash or mouth gel that does not contain alcohol, peroxide iodine, or thyme.
- Infections
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea and constipation
- Swelling of your hands, arms, legs, and feet
- Joint pain
- Cough
- Skin problems (such as rash, acne, or dry skin)
- Fever
- Feeling tired
- Anxiety, aggression, and other abnormal behaviors
- Absence of menstrual periods (menstruation). You may miss 1 or more menstrual periods. Tell your healthcare provider if this happens.
- Low red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets
- Increased blood cholesterol level and certain other blood tests
- Increased blood sugar levels
- Decreased blood phosphate levels
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of AFINITOR and AFINITOR DISPERZ. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ?
- Store AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ at room temperature, between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ in the pack it comes in.
- Open the blister pack just before taking AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ.
- Keep AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ dry and away from light.
- Do not use AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ that is out of date or no longer needed.
Keep AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about AFINITOR and AFINITOR DISPERZ
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give AFINITOR or AFINITOR DISPERZ to other people, even if they have the same problem you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about AFINITOR and AFINITOR DISPERZ. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information written for healthcare professionals.
For more information call 1-888-423-4648 or go to www.AFINITOR.com.
What are the ingredients in AFINITOR?
Active ingredient: everolimus.
Inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, butylated hydroxytoluene, crospovidone, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, and magnesium stearate.
What are the ingredients in AFINITOR DISPERZ?
Active ingredient: everolimus.
Inactive ingredients: butylated hydroxytoluene, colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and microcrystalline cellulose.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Novartis Pharma Stein AG
Stein, Switzerland
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
Revised Feb 2014
The brands listed are the trademarks or register marks of their respective owners and are not trademarks or register marks of Novartis.
© Novartis
T2014-17
February 2014
Instructions For Use
AFINITOR® (a-fin-it-or) DISPERZ™ (dis-perz)
(everolimus tablets for oral suspension)
Read these Instructions for Use for AFINITOR DISPERZ before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
Important Information:
- Take AFINITOR DISPERZ as a suspension only. AFINITOR DISPERZ is prepared as a suspension of un-dissolved medicine that is mixed with water, and then it is taken by mouth. Do not chew, crush, or swallow AFINITOR DISPERZ whole.
- AFINITOR DISPERZ can cause harm to an unborn baby. When possible, the suspension should be prepared by an adult who is not pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
- Keep AFINITOR DISPERZ and the prepared suspension out of the reach of children.
- Anyone who prepares suspensions of AFINITOR DISPERZ for another person should wear gloves to avoid possible contact with the drug.
- Only use water with AFINITOR DISPERZ to prepare the suspension. Do not prepare the suspension with juice or any other liquids.
- The suspension must be given right away. If you do not give the dose within 60 minutes after it has been prepared, throw away the dose and prepare a new dose of AFINITOR DISPERZ.
- Before starting to prepare the suspension, collect all of the supplies that you will need to prepare and take the suspension. Do not use any of these supplies for purposes other than preparing and taking the AFINITOR DISPERZ suspension.
Supplies needed to prepare the suspension in an oral syringe:
- Blister card with AFINITOR DISPERZ
- Scissors to open the blister card
- Disposable gloves (for one time use)
- 2 clean drinking glasses
- Approximately 30 mL of water
- 10 mL oral syringe (for one time use) (see Figure A)
- Paper towels

Supplies needed to prepare the suspension in a small drinking glass:
- Blister card with AFINITOR DISPERZ
- Scissors to open the blister card
- Disposable gloves (for one time use)
- 30 mL dose cup for measuring water (you can ask your pharmacist for this)
- 1 clean drinking glass (maximum size 100 mL)
- Water to prepare the suspension
- Spoon for stirring
- Paper towels
Preparing a dose of AFINITOR DISPERZ suspension using an oral syringe:
Step 1: Prepare a clean, flat work surface that is away from where you prepare and eat food. Place a clean paper towel on the work surface. Place the needed supplies on the paper towel.
Step 2: Wash and dry your hands well before preparing the medicine (see Figure B).

Step 3: If preparing the AFINITOR DISPERZ suspension for another person, put on disposable gloves (see Figure C).

Step 4: Take a 10 mL oral syringe and pull back on the plunger. Remove the plunger from the barrel of the syringe (see Figure D).

Step 5: Use scissors to open the blister card along the dotted line (see Figure E) and remove the prescribed number of AFINITOR DISPERZ tablets for oral suspension from the blister card. Place them into the barrel of the oral syringe (see Figure F).


- Doses of up to 10 mg can be prepared with the oral syringe. If your total prescribed dose is more than 10 mg, you will need to split the dose. Follow steps 4 through 17 for the first half of the dose. Then repeat steps 4 through 17 for the second half of the dose. Do not prepare a dose of more than 10 mg in one syringe. Ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider if you are not sure what to do.
Step 6: Re-insert the plunger into the barrel of the oral syringe (see Figure G) and push the plunger in until it comes into contact with the AFINITOR DISPERZ tablets for oral suspension (see Figure H).


Step 7: Fill a small drinking glass with about 30 mL of water. Insert the tip of the oral syringe into the water. Then slowly pull back on the plunger until the syringe is about half full of water and all the tablets are covered by water (see Figure I).

Step 8: Hold the oral syringe with the tip pointing up. Pull back on the plunger to draw back about 4 mL of air (see Figure J).

Step 9: Place the filled oral syringe in the clean, empty glass with the tip pointing up. Wait 3 minutes to allow AFINITOR DISPERZ to break apart (see Figure K).

Step 10: Slowly turn the oral syringe up and down five times just before giving the dose (see Figure L). Do not shake the syringe.

Step 11: Hold the oral syringe in an upright position (with the tip up). Carefully remove most of the air by pushing up gently on the plunger (see Figure M).

Step 12: Give the full contents of the oral syringe slowly and gently into the mouth right away, within 60 minutes of preparing it (see Figure N). Carefully remove the syringe from the mouth. Continue with steps 13 through 17 to make sure that the entire dose of medicine is given.

Step 13: Insert the tip of the oral syringe into the drinking glass that is filled with water, and pull up about 5 mL of water by slowly pulling back on the plunger (see Figure O).

Step 14: Hold the oral syringe with the tip pointing up and use the plunger to draw back about 4 mL of air (see Figure P).

Step 15: With the tip of the syringe still pointing up, swirl the contents by gently rotating the syringe in a circular motion (see Figure Q).

Step 16: Hold the oral syringe in an upright position (with the tip up). Carefully remove most of the air by pushing up gently on the plunger (see Figure R).

Step 17: Give the full contents of the oral syringe slowly and gently into the mouth by pushing on the plunger (see Figure S). Carefully remove the syringe from the mouth.

If the total prescribed dose is more than 10 mg, repeat steps 4 through 17 to finish giving the dose.
Step 18: Throw away the oral syringe, paper towel, and used gloves in your household trash.
Step 19: Wash your hands.
Preparing a dose of AFINITOR DISPERZ suspension using a small drinking glass:
Step 1: Prepare a clean, flat work surface that is away from where you prepare and eat food. Place a clean paper towel on the work surface. Place the needed supplies on the paper towel.
Step 2: Wash and dry your hands before preparing the medicine (See Figure T).

Step 3: If preparing the AFINITOR DISPERZ suspension for another person, put on disposable gloves (see Figure U).

Step 4: Add about 25 mL of water to the 30 mL dose cup. The amount of water added does not need to be exact (see Figure V).

Step 5: Pour the water from the dose cup into a small drinking glass (maximum size 100 mL) (see Figure W).

- Doses up to 10 mg can be prepared in the small drinking glass. If your total prescribed dose is more than 10 mg you will need to split the dose. Follow steps 4 through 10 for the first half of the dose. Then repeat steps 4 through 10 for the second half of the dose. Ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider if you are not sure what to do.
Step 6: Use scissors to open the blister card along the dotted line (see Figure X) and remove the prescribed number of AFINITOR DISPERZ tablets for oral suspension from the blister card.

Step 7: Add the prescribed number of AFINITOR DISPERZ tablets for oral suspension into the water (see Figure Y).
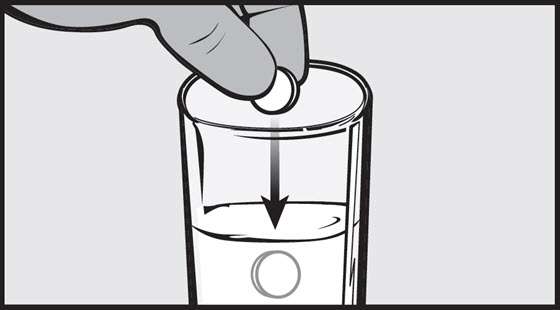
Step 8: Wait 3 minutes to allow AFINITOR DISPERZ tablets for oral suspension to break apart (see Figure Z).

Step 9: Gently stir the contents of the glass with a spoon and place the spoon back on the paper towel (see Figure AA). Drink the full amount of the suspension right away, within 60 minutes of preparing it (see Figure BB).


Step 10: Refill the glass with the same amount of water (about 25 mL). Stir the contents with the same spoon and place the spoon back on the paper towel (see Figure CC). Drink the full amount right away so that you take any remaining medicine (see Figure DD).
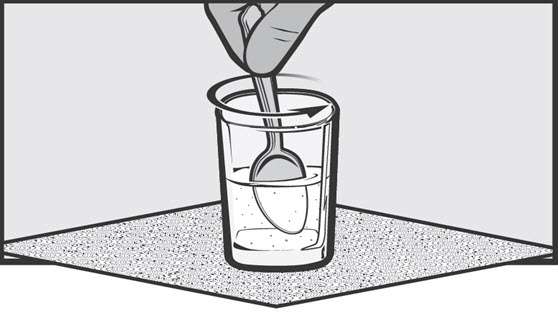

If your total prescribed dose is more than 10 mg, repeat steps 4 through 10 to finish taking your dose.
Step 11: Wash the glass and the spoon thoroughly with water. Wipe the glass and spoon with a clean paper towel and store them in a dry and clean place until your next dose of AFINITOR DISPERZ (see Figure EE).

Step 12: Throw away the used paper towel and gloves in your household trash.
Step 13: Wash your hands.
How should I store AFINITOR DISPERZ?
- Store AFINITOR at room temperature, between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep AFINITOR DISPERZ in the pack it comes in.
- Open the blister pack just before taking AFINITOR DISPERZ.
- Keep AFINITOR DISPERZ dry and away from light.
- Do not use AFINITOR DISPERZ that is out of date or no longer needed.
Keep AFINITOR DISPERZ and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Novartis Pharma Stein AG
Stein, Switzerland
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
T2012-157
August 2012
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 2.5 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0594-51
Afinitor® (everolimus) Tablets
Each tablet contains
2.5 mg everolimus
28 Tablets
Carton contains 4 individual blister cards of 7 tablets.

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 5 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0566-51
Afinitor® (everolimus) Tablets
Each tablet contains
5 mg everolimus
28 Tablets
Carton contains 4 individual blister cards of 7 tablets.

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 7.5 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0620-51
Afinitor® (everolimus) Tablets
Each tablet contains
7.5 mg everolimus
28 Tablets
Carton contains 4 individual blister cards of 7 tablets.

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 10 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0567-51
Afinitor® (everolimus) Tablets
Each tablet contains
10 mg everolimus
28 Tablets
Carton contains 4 individual blister cards of 7 tablets.

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 2 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0626-51
Afinitor® DISPERZTM
(everolimus tablets for oral suspension)
TABLETS MUST BE DISPERSED IN WATER.
TABLETS MUST NOT BE SWALLOWED WHOLE, CHEWED OR CRUSHED.
28 Tablets for Oral Suspension
Carton contains 4 individual blister cards of 7 tablets.

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 3 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0627-51
Afinitor® DISPERZTM
(everolimus tablets for oral suspension)
TABLETS MUST BE DISPERSED IN WATER.
TABLETS MUST NOT BE SWALLOWED WHOLE, CHEWED OR CRUSHED.
28 Tablets for Oral Suspension
Carton contains 4 individual blister cards of 7 tablets.

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 5 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0628-51
Afinitor® DISPERZTM
(everolimus tablets for oral suspension)
TABLETS MUST BE DISPERSED IN WATER.
TABLETS MUST NOT BE SWALLOWED WHOLE, CHEWED OR CRUSHED.
28 Tablets for Oral Suspension
Carton contains 4 individual blister cards of 7 tablets.

Afinitoreverolimus TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Afinitoreverolimus TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Afinitoreverolimus TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Afinitoreverolimus TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Afinitoreverolimus TABLET, FOR SUSPENSION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Afinitoreverolimus TABLET, FOR SUSPENSION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Afinitoreverolimus TABLET, FOR SUSPENSION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||