ALENDRONATE SODIUM
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Alendronate Sodium Tablets safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for alendronate sodium tablets, USP. Alendronate Sodium Tablets USP, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1995 INDICATIONS AND USAGEAlendronate sodium is a bisphosphonate indicated for: Treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women (1.1, 1.2) Treatment to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis (1.3) Treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (1.4) Treatment of Paget's disease of bone (1.5) Important limitations of use: The optimal duration of use has not been determined. The need for continued therapy should be re-evaluated on a periodic basis. (1.6)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Must be taken with 6-8 oz plain water at least 30 minutes before the first food, drink, or medication of the day; do not lie down for at least 30 minutes after taking alendronate sodium tablets and until after food. (2.6) Treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and in men: 10 mg daily or 70 mg tablet once weekly. (2.1, 2.3) Prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: 5 mg daily or 35 mg once weekly. (2.2) Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: 5 mg daily; or 10 mg daily in postmenopausal women not receiving estrogen. (2.4) Paget's disease: 40 mg daily for six months. (2.5) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSTablets: 5 mg, 10 mg, 35 mg and 70 mg (3)CONTRAINDICATIONS Abnormalities of the esophagus which delay emptying such as stricture or achalasia (4, 5.1) Inability to stand/sit upright for at least 30 minutes (2, 4, 5.1) Hypocalcemia (4, 5.2) Hypersensitivity to any component of this product (4, 6.2) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Severe irritation of upper gastrointestinal (GI) mucosa can occur. Follow dosing instructions. Use caution in patients with active upper GI disease. Discontinue if new or worsening symptoms occur. (5.1) Hypocalcemia can worsen and must be corrected prior to use. (5.2) Severe bone, joint, muscle pain may occur. Discontinue use if severe symptoms develop. (5.3) Osteonecrosis of the jaw has been reported. (5.4) Atypical femur fractures have been reported. Evaluate new thigh or groin pain to rule out an incomplete femoral fracture. (5.5) Side EffectsMost common adverse reactions (≥3%) are abdominal pain, acid regurgitation, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, musculoskeletal pain, nausea. (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AustarPharma, LLC at 1-732-346-6655 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS Calcium supplements, antacids, or oral medications containing multivalent cations interfere with absorption of alendronate. (2.6, 7.1) Aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use may worsen GI irritation; use caution. (7.2, 7.3) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Alendronate sodium is not indicated for use in pediatric patients. (8.4) Alendronate sodium is not recommended in patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 ALENDRONATE SODIUM INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 ALENDRONATE SODIUM DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 ALENDRONATE SODIUM CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 ALENDRONATE SODIUM ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 ALENDRONATE SODIUM DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
_______________________________________________________________________________
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
1.2 Prevention of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
1.3 Treatment to Increase Bone Mass in Men with Osteoporosis
1.4 Treatment of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
1.5 Treatment of Paget's Disease of Bone
1.6 Important Limitations of Use
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
2.2 Prevention of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
2.3 Treatment to Increase Bone Mass in Men with Osteoporosis
2.4 Treatment of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
2.5 Treatment of Paget's Disease of Bone
2.6 Dosing Instructions
2.7 Recommendations for Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation
2.8 Dosing in Severe Renal Impairment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Upper Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
5.2 Mineral Metabolism
5.3 Musculoskeletal Pain
5.4 Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
5.5 Atypical Subtrochanteric and Diaphyseal Femoral Fractures
5.6 Renal Impairment
5.7 Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Calcium Supplements/Antacids
7.2 Aspirin
7.3 Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
14.2 Prevention of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
14.3 Treatment to Increase Bone Mass in Men with Osteoporosis
14.4 Treatment of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
14.5 Treatment of Paget's Disease of Bone
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Osteoporosis Recommendations, Including Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation
17.2 Dosing Instructions
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Uses
1.1 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women[See Clinical Studies (14.1).]
Uses
1.2 Prevention of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women[see Clinical Studies (14.2)]
Uses
1.3 Treatment to Increase Bone Mass in Men with Osteoporosis[see Clinical Studies (14.3)]
Uses
1.4 Treatment of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis[see Clinical Studies (14.4)]
Uses
1.5 Treatment of Paget's Disease of Bone[See Clinical Studies (14.5).]
Uses
1.6 Important Limitations of Use2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
2.2 Prevention of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
2.3 Treatment to Increase Bone Mass in Men with Osteoporosis
The recommended dosage is:
2.4 Treatment of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
2.5 Treatment of Paget's Disease of Bone
Re-treatment of Paget’s Disease
2.6 Dosing Instructions
[see Patient Counseling Information (17.2)][see Drug Interactions (7.1)]
and[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Patient Counseling Information (17.2)]2.7 Recommendations for Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
2.8 Dosing in Severe Renal Impairment
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 5 mg (alendronate) tablets are round, flat face beveled edged, white to off-white tablets; one side debossed “AP209”, the other side blank.
- 10 mg (alendronate) tablets are modified oval, white to off-white tablets; one side debossed “AP208”, the other side blank.
- 35 mg (alendronate) tablets are modified oval, white to off white tablets; one side debossed “AP207”, the other side blank.
- 70 mg (alendronate) tablets are modified oval, white to off –white tablets; one side debossed “AP205”, the other side blank.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Abnormalities of the esophagus which delay esophageal emptying such as stricture or achalasia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Inability to stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes [see Dosage and Administration (2.6); Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypocalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this product. Hypersensitivity reactions including urticaria and angioedema have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Upper Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
[see Dosage and Administration (2.6)]
[see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]5.2 Mineral Metabolism
[see Contraindications (4)]
5.3 Musculoskeletal Pain
[see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
5.4 Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
5.5 Atypical Subtrochanteric and Diaphyseal Femoral Fractures
5.6 Renal Impairment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.8)]5.7 Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
[see Indications and Usage (1.4)]
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
Daily Dosing
Table 1. Osteoporosis Treatment Studies in Postmenopausal Women
Adverse Reactions Considered Possibly, Probably, or Definitely Drug Related by the Investigators and Reported in ≥ 1% of Patients
| * 10 mg/day for three years ** 5 mg/day for 2 years and 10 mg/day for either 1 or 2 additional years. |
||||
|
|
United States/Multinational Studes | Fracture Intervention Trail | ||
|
|
Alendronate sodium * % (n=196) | Placebo % (n=397) | Alendronate sodium** % (n=3236) | Placebo % (n=3223) |
| Gastrointestinal |
|
|||
| abdominal pain | 6.6 | 4.8 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| nausea | 3.6 | 4.0 | 1.1 | 1.5 |
| dyspepsia | 3.6 | 3.5 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| constipation | 3.1 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| diarrhea | 3.1 | 1.8 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| flatulence | 2.6 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| acid regurgitation | 2.0 | 4.3 | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| esophageal ulcer | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| vomiting | 1.0 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| dysphagia | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| abdominal distention | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| gastritis | 0.5 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
| Musculoskeletal |
|
|||
| Musculoskeletal (bone, muscle or joint) pain | 4.1 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| muscle cramp | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Nervous System/Psychiatric |
|
|||
| headache | 2.6 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| dizziness | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| Special Senses |
|
|||
| taste perversion | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions: [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1).]
Laboratory Test Findings:
Weekly Dosing
Table 2: Osteoporosis Treatment Studies in Postmenopausal Women
Adverse Reactions Considered Possibly, Probably, or Definitely Drug Related by the Investigators and Reported in ≥ 1% of Patients
|
|
Once Weekly Alendronate 70 mg % (n=519) |
Alendronate 10 mg/day % (n=370) |
| Gastrointestinal |
|
|
| abdominal pain | 3.7 | 3.0 |
| dyspepsia | 2.7 | 2.2 |
| acid regurgitation | 1.9 | 2.4 |
| nausea | 1.9 | 2.4 |
| abdominal distention | 1.0 | 1.4 |
| constipation | 0.8 | 1.6 |
| flatulence | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| gastritis | 0.2 | 1.1 |
| gastric ulcer | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| Musculoskeletal |
|
|
| musculoskeletal (bone, muscle or joint) pain | 2.9 | 3.2 |
| muscle cramp | 0.2 | 1.1 |
Daily Dosing
Weekly Dosing
Table 3. Osteoporosis Prevention Studies in Postmenopausal Women
Adverse Reactions Considered Possibly, Probably, or Definitely Drug Related by the Investigators and Reported in ≥ 1% of Patients
|
|
Two/Three-Year Studies | Fracture Intervention Trail | ||
|
|
Alendronate 5 mg/day % (n=642) | Placebo % (n=648) | Alendronate 5 mg/day % (n=361) | Once Weekly Alendronate 35 mg % (n=362) |
| Gastrointestinal |
|
|||
| dyspepsia | 1.9 | 1.4 | 2.2 | 1.7 |
| abdominal pain | 1.7 | 3.4 | 4.2 | 4.7 |
| acid regurgitation | 1.4 | 2.5 | 4.2 | 4.7 |
| nausea | 1.4 | 1.4 | 2.5 | 1.4 |
| diarrhea | 1.1 | 1.7 | 1.1 | 0.6 |
| constipation | 0.9 | 0.5 | 1.7 | 0.3 |
| abdominal distention | 0.2 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 1.1 |
| Musculoskeletal |
|
|||
| musculoskeletal (bone, muscle or joint) pain | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.9 | 2.2 |
Osteoporosis in Men
Table 4. Osteoporosis Studies in Men
Adverse Reactions Considered Possibly, Probably, or Definitely Drug Related by the Investigators and Reported in ≥ 2% of Patients
|
|
Two-Year Study | One-Year Study | ||
|
|
Alendronate 10 mg/day % (n=146) | Placebo % (n=95) | Once Weekly Alendronate 70 mg % (n=109) | Placebo % (n=58) |
| Gastrointestinal |
|
|||
| acid regurgitation | 4.1 | 3.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| flatulence | 4.1 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| gastroesophageal reflux disease | 0.7 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 0.0 |
| dyspepsia | 3.4 | 0.0 | 2.8 | 1.7 |
| diarrhea | 1.4 | 1.1 | 2.8 | 0.0 |
| abdominal pain | 2.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 3.4 |
| nausea | 2.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
Table 5. One-Year Studies in Glucocorticoid -Treated Patients
Adverse Reactions Considered Possibly, Probably, or Definitely Drug Related by the Investigators and Reported in ≥ 1% of Patients
|
|
Alendronate 10 mg/day % (n=157) |
Alendronate 5 mg/day % (n=161) |
Placebo % (n=159) |
| Gastrointestinal |
|
||
| abdominal pain | 3.2 | 1.9 | 0.0 |
| acid regurgitation | 2.5 | 1.9 | 1.3 |
| constipation | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.0 |
| melena | 1.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| nausea | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.6 |
| diarrhea | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.3 |
| Nervous System/Psychiatric |
|
||
| headache | 0.6 | 0.0 | 1.3 |
Paget's Disease of Bone
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
Body as a Whole:
Gastrointestinal:[see Dosage and Administration (2); Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Musculoskeletal:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)][see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
Nervous System:
Skin:
Special Senses:
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Calcium Supplements/Antacids
7.2 Aspirin
7.3 Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C:
28.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
[See Adverse Reactions (6.2).]8.5 Geriatric Use
[see Clinical Studies (14.1), (14.3), (14.4), (14.5)]8.6 Renal Impairment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.8) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]8.7 Hepatic Impairment
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
10 OVERDOSAGE
22211 DESCRIPTION
412722
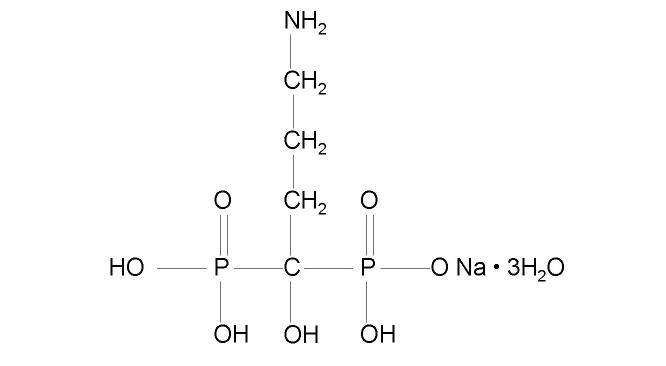
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
3312.2 Pharmacodynamics
Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
Osteoporosis in Men
Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
Paget's Disease of Bone
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
14
Specific Populations
Gender:
Geriatric:
Race:
Renal Impairment:
Drug Interactions
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
2
2
in vitroin vitroin vitroin vivoin vitro
213.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
Daily Dosing
Effect on Fracture Incidence
Fracture Intervention Trial: Three-Year Study (patients with at least one baseline radiographic vertebral fracture)
Table 6: Effect of Alendronate Sodium on Fracture Incidence in the Three-Year Study of FIT
(patients with vertebral fracture at baseline)
| § Number evaluable for vertebral fractures: Alendronate sodium, n=984; placebo, n=966 *p<0.001, **p=0.007, ***p<0.01, +p<0.05 |
||||
|
|
Percent of Patients | |||
|
|
Alendronate Sodium (n=1022) |
Placebo (n=1005) |
Absolute Reduction in Fracture Incidence |
Relative Reduction in Fracture Risk % |
| Patients with: | ||||
| Vertebral fracture (diagnosed by X-ray)§ | ||||
| ≥1 new vertebral fracture | 7.9 | 15.0 | 7.1 | 47* |
| ≥2 new vertebral fractures | 0.5 | 4.9 | 4.4 | 90* |
| Clinical (symptomatic) fractures | ||||
| Any clinical (symptomatic) fracture | 13.8 | 18.1 | 4.3 | 26** |
| ≥1 clinical (symptomatic) vertebral fracture | 2.3 | 5.0 | 2.7 | 54*** |
| Hip fracture | 1.1 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 51+ |
| Wrist (forearm) fracture | 2.2 | 4.1 | 1.9 | 48+ |
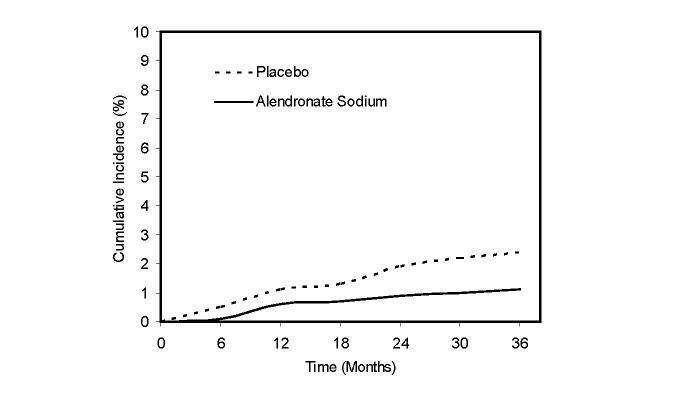
Figure 1: Cumulative Incidence of Hip Fractures in the Three-Year Study of FIT
(patients with radiographic vertebral fracture at baseline)
|
Table 7: Effect of Alendronate Sodium on Fracture Incidence in Osteoporotic+ Patients in the Four-Year Study of FIT
(patients without vertebral fracture baseline)
|
+Baseline femoral neck BMD at least 2 SD below the mean for young adult women ++ Number evaluable for vertebral fractures: Alendronate sodium, n=1426; placebo, n=1428 *p<0.001, **p=0.035, *** p=0.01, +++ Not significant. This study was not powered to detect differences at these sites. |
||||
|
|
Percent of Patients | |||
|
|
Alendronate Sodium (n=1545) |
Placebo (n=1521) |
Absolute Reduction in Fracture Incidence |
Relative Reduction in Fracture Risk % |
| Patients with: | ||||
| Vertebral fracture (diagnosed by X-ray)++ | ||||
| ≥1 new vertebral fracture | 2.5 | 4.8 | 2.3 | 48* |
| ≥2 new vertebral fractures | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 78** |
| Clinical (symptomatic) fractures | ||||
| Any clinical (symptomatic) fracture | 12.9 | 16.2 | 3.3 | 22*** |
| ≥1 clinical (symptomatic) vertebral fracture | 1.0 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 41 (NS)+++ |
| Hip fracture | 1.0 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 29 (NS)+++ |
| Wrist (forearm) fracture | 3.9 | 3.8 | -0.1 | NS+++ |
Effect on Bone Mineral Density
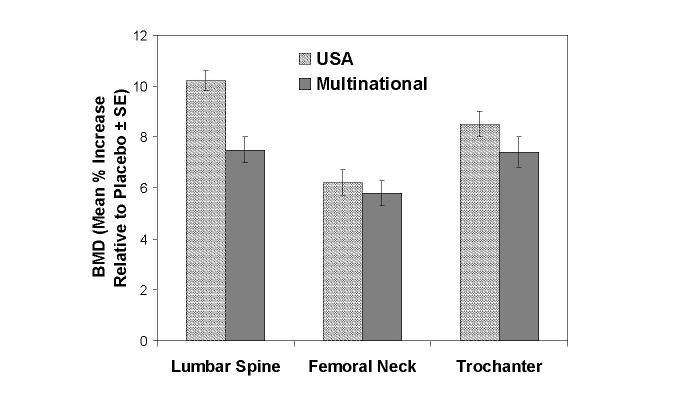
Figure 2: Osteoporosis Treatment Studies in Postmenopausal Women
Increase in BMD
Alendronate 10mg/day at Three Years
|
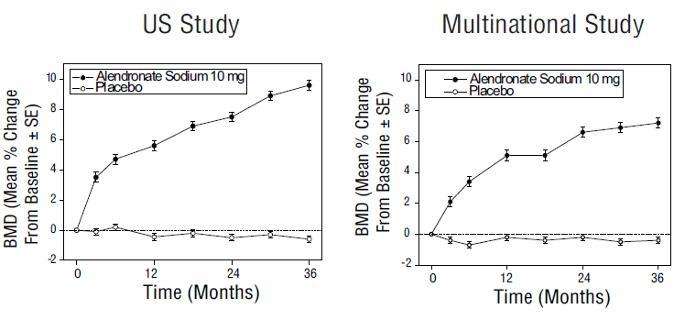
Figure 3: Osteoporosis Treatment Studies in Postmenopausal Women
Time Course of Effect of Alendronate 10 mg/day Versus Placebo:
Lumbar Spine BMD Percent Change From Baseline
|
Bone Histology
Effect on Height
Weekly Dosing
Concomitant Use with Estrogen/Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
14.2 Prevention of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
Daily Dosing
Figure 4: Osteoporosis Prevention Studies in Postmenopausal Women
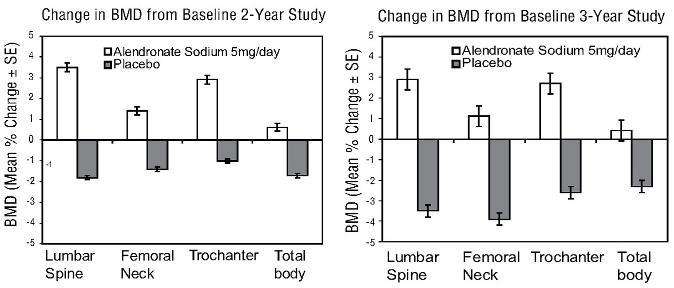
|
Weekly Dosing
14.3 Treatment to Increase Bone Mass in Men with Osteoporosis
Daily Dosing
Weekly Dosing
14.4 Treatment of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
Figure 5: Studies in Glucocorticoid - Treated Patients
Increase in BMD
Alendronate 5mg/day at One Year
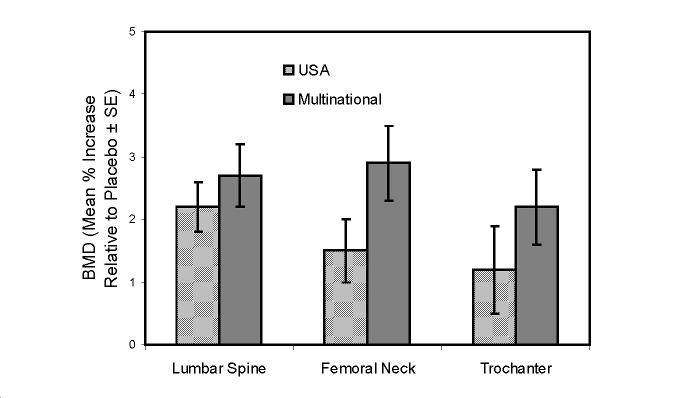
|
14.5 Treatment of Paget's Disease of Bone
Figure 6: Studies in Paget's Disease of Bone
Effect on Serum Alkaline Phosphatase of Alendronate 40 mg/day
Versus Placebo or Etidronate 400 mg/day
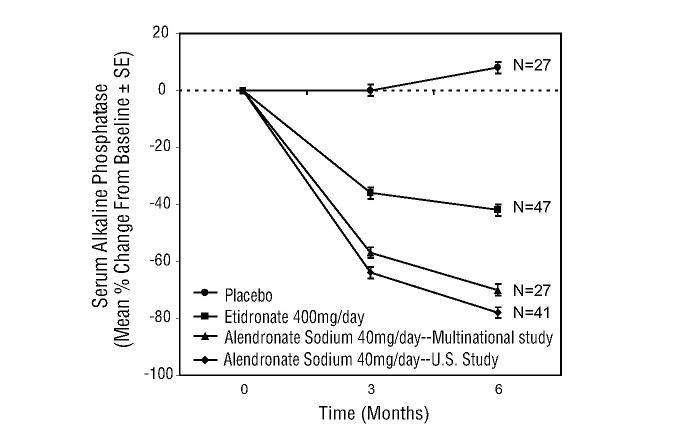
|
[see Clinical Studies (14.1)]
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How SuppliedStorage
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Medication Guide17.1 Osteoporosis Recommendations, Including Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation
17.2 Dosing Instructions
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
Medication Guide
Alendronate Sodium Tablets, USP
What is the most important information I should know about alendronate sodium tablets?
Alendronate sodium tablets can cause serious side effects including:
- Esophagus problems
- Low calcium levels in your blood (hypocalcemia)
- Bone, joint, or muscle pain
- Severe jaw bone problems (osteonecrosis)
- Unusual thigh bone fractures
1.Esophagus problems.
Some people who take alendronate sodium tablets may develop problems in the esophagus (the tube that connects the mouth and the stomach). These problems include irritation, inflammation, or ulcers of the esophagus which may sometimes bleed.
• It is important that you take alendronate sodium tablets exactly as prescribed to help lower your chance of getting esophagus problems. (See the section “How should I take alendronate sodium tablets?”)
• Stop taking alendronate sodium tablets and call your doctor right away if you get chest pain, new or worsening heartburn, or have trouble or pain when you swallow.
2.Low calcium levels in your blood (hypocalcemia).
3.Bone, joint, or muscle pain.
4.Severe jaw bone problems (osteonecrosis).
5.Unusual thigh bone fractures.
Call your doctor right away if you have any of these side effects.
What is alendronate sodium tablet?
- Treat or prevent osteoporosis in women after menopause. It helps reduce the chance of having a hip or spinal fracture (break).
- Increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis.
- Treat osteoporosis in either men or women who are taking corticosteroid medicines.
- Treat certain men and women who have Paget’s disease of the bone.
Who should not take alendronate sodium tablets?
Do not take alendronate sodium tablets if you:
- Have certain problems with your esophagus, the tube that connects your mouth with your stomach
- Cannot stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes
- Have low levels of calcium in your blood
- Are allergic to alendronate sodium tablet or any of its ingredients. A list of ingredients is at the end of this leaflet.
What should I tell my doctor before taking alendronate sodium tablets?
Before you start alendronate sodium tablets, be sure to talk to your doctor if you:
- Have problems with swallowing
- Have stomach or digestive problems
- Have low blood calcium
- Plan to have dental surgery or teeth removed
- Have kidney problems
- Have been told you have trouble absorbing minerals in your stomach or intestines (malabsorption syndrome)
- Are pregnant, or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if alendronate sodium tablets can harm your unborn baby.
- Are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. It is not known if alendronate sodium passes into your milk and may harm your baby.
- antacids
- aspirin
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory (NSAID) medicines
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take,
How should I take alendronate sodium tablets?
- Take alendronate sodium tablets exactly as your doctor tells you.
- Alendronate sodium tablet works only if taken on an empty stomach.
- Take alendronate sodium tablets, after you get up for the day and before taking your first food, drink, or other medicine.
- Take alendronate sodium tablets while you are sitting or standing.
- Do not chew or suck on a tablet of alendronate sodium.
- Swallow alendronate sodium tablet with a full glass (6-8 oz) of plain water only.
- Do not take alendronate sodium tablets with mineral water, coffee, tea, soda, or juice.
- If you take Alendronate Sodium Tablets Daily:
- Take 1 alendronate sodium tablet one time a day, every day after you get up for the day and before taking your first food, drink, or other medicine.
- If you take Once Weekly Alendronate Sodium Tablets:
- Choose the day of the week that best fits your schedule.
- Take 1 dose of alendronate sodium tablets every week on your chosen day after you get up for the day and before taking your first food, drink, or other medicine.
- Before you lie down. You may sit, stand or walk, and do normal activities like reading.
- Before you take your first food or drink except for plain water.
- Before you take other medicines, including antacids, calcium, and other supplements and vitamins.
What are the possible side effects of alendronate sodium tablets?
- See “What is the most important information I should know about alendronate sodium tablets?”
- Stomach area (abdominal) pain
- Heartburn
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Upset stomach
- Pain in your bones, joints, or muscles
- Nausea
How do I store alendronate sodium tablets?
- Store at 20° - 25°C (68° - 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° - 30°C (59° - 86°F).
- Keep alendronate sodium tablets in a tightly closed container.
General information about the safe and effective use of alendronate sodium tablets.
What are the ingredients in alendronate sodium tablets?
Rx only
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
ASCEND
Laboratories, LLC
NDC 67877-240-31
Once Weekly
Alendronate Sodium Tablets, USP 35 mg*
PHARMACIST: Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each Patient.
Rx only
4 Tablets

PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
ASCEND
Laboratories, LLC
NDC 67877-240-33
Once Weekly
Alendronate Sodium Tablets, USP 70 mg*
PHARMACIST: Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each Patient.
Rx only
20 (2x10) Unit-Dose Tablets

ALENDRONATE SODIUMALENDRONATE SODIUM TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ALENDRONATE SODIUMALENDRONATE SODIUM TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||