Amino Acids
15% Amino Acids Injection
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- AMINO ACIDS DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- AMINO ACIDS INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- AMINO ACIDS CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- AMINO ACIDS ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- AMINO ACIDS DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- Directions for Use of Pharmacy Bulk Package in B. Braun Glass Containers with Solid Stoppers
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1000 mL Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1000 mL Bottle Carton
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Package Insert
PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE
NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION
Protect from light until use.
AMINO ACIDS DESCRIPTION
15% Amino Acids Injection in a Pharmacy Bulk Package is a sterile, clear, nonpyrogenic solution of essential and nonessential amino acids for intravenous infusion in parenteral nutrition following appropriate dilution.
15% Amino Acids Injection in a Pharmacy Bulk Package is not for direct infusion. It is a sterile dosage form which contains several single doses for use in a pharmacy admixture program in the preparation of intravenous parenteral fluids.
Each 100 mL contains:
| Essential Amino Acids | ||
| Lysine (from Lysine Acetate, USP) | 1.18 | g |
| Leucine, USP | 1.04 | g |
| Phenylalanine, USP | 1.04 | g |
| Valine, USP | 960 | mg |
| Isoleucine, USP | 749 | mg |
| Methionine, USP | 749 | mg |
| Threonine, USP | 749 | mg |
| Tryptophan, USP | 250 | mg |
| Nonessential Amino Acids | ||
| Alanine, USP | 2.17 | g |
| Arginine, USP | 1.47 | g |
| Glycine, USP | 1.04 | g |
| Histidine, USP | 894 | mg |
| Proline, USP | 894 | mg |
| Glutamic Acid | 749 | mg |
| Serine, USP | 592 | mg |
| Aspartic Acid, USP | 434 | mg |
| Tyrosine, USP | 39 | mg |
| Sodium Metabisulfite, NF added | 30 | mg |
| Water for Injection, USP | qs | |
| Essential Amino Acids | 6.7 | g |
| Nonessential Amino Acids | 8.3 | g |
| Total Amino Acids | 15.0 | g |
| Total Nitrogen | 2.37 | g |
Acetate |
151 | mEq/L |
| Osmolarity (calculated) | 1383 | mOsmol/L |
| pH 5.6 (5.2–6.0) |
The formulas for the individual amino acids are as follows:
| Essential Amino Acids | |
| Lysine Acetate | H2N(CH2)4CH(NH2)COOH•CH3COOH |
| Leucine | (CH3)2CHCH2CH(NH2)COOH |
| Phenylalanine | 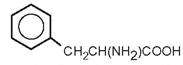
|
| Valine | (CH3)2CHCH(NH2)COOH |
| Isoleucine | CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH(NH2)COOH |
| Methionine | CH3S(CH2)2CH(NH2)COOH |
| Threonine | CH3CH(OH)CH(NH2)COOH |
| Tryptophan | 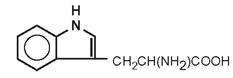
|
| Nonessential Amino Acids | |
| Alanine | CH3CH(NH2)COOH |
| Arginine | H2NC(NH)NH(CH2)3CH(NH2)COOH |
| Glycine | H2NCH2COOH |
| Histidine | 
|
| Proline | 
|
| Glutamic Acid | HOOC(CH2)2CH(NH2)COOH |
| Serine | HOCH2CH(NH2)COOH |
| Aspartic Acid | HOOCCH2CH(NH2)COOH |
| Tyrosine | 
|
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
15% Amino Acids Injection provides seventeen crystalline amino acids. This completely utilizable substrate promotes protein synthesis and wound healing and reduces the rate of protein catabolism.
A. Total Parenteral Nutrition (Central Infusion)
When enteral feeding is inadvisable, 15% Amino Acids Injection given by central venous infusion in combination with energy sources, vitamins, trace elements and electrolytes, will completely satisfy the requirements for weight maintenance or weight gain, depending upon the dose selected. The energy component in parenteral nutrition by central infusion may be derived solely from dextrose or may be provided by a combination of dextrose and intravenous fat emulsion. The addition of intravenous fat emulsion provides essential fatty acids and permits a dietary balance of fat and carbohydrate, at the same time offering the option of reducing the dextrose load and/or increasing the total caloric input. An adequate energy supply is essential for optimal utilization of amino acids.
B. Total Parenteral Nutrition (Peripheral Infusion)
15% Amino Acids Injection can also be administered as part of a total parenteral nutrition program by peripheral vein when the enteral route is inadvisable and use of the central venous catheter is contraindicated.
Reduction of protein loss can be achieved by use of diluted 15% Amino Acids Injection in combination with dextrose or with dextrose and intravenous fat emulsion by peripheral infusion. Complete peripheral intravenous nutrition can be achieved in patients with low caloric requirements by a 15% Amino Acids Injection-dextrose-fat regimen.
AMINO ACIDS INDICATIONS AND USAGE
15% Amino Acids Injection is indicated as an amino acid (nitrogen) source in parenteral nutrition regimens. This use is appropriate when the enteral route is inadvisable, inadequate or not possible, as when:
— Gastrointestinal absorption is impaired by obstruction, inflammatory disease or its complications, or antineoplastic therapy;
— Bowel rest is needed because of gastrointestinal surgery or its complications such as ileus, fistulae or anastomotic leaks;
— Tube feeding methods alone cannot provide adequate nutrition.
AMINO ACIDS CONTRAINDICATIONS
This solution should not be used in patients in hepatic coma, severe renal failure, metabolic disorders involving impaired nitrogen utilization or hypersensitivity to one or more amino acids.
WARNINGS
Administration of amino acids solutions at excessive rates or to patients with hepatic insufficiency may result in plasma amino acid imbalances, hyperammonemia, prerenal azotemia, stupor and coma. Conservative doses of amino acids should be given to these patients, dictated by the nutritional status of the patient. Should symptoms of hyperammonemia develop, amino acid administration should be discontinued and the patient's clinical status re-evaluated.
Contains sodium metabisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown and probably low.
Sulfite sensitivity is seen more frequently in asthmatic than in nonasthmatic people.
WARNING: This product contains aluminum that may be toxic. Aluminum may reach toxic levels with prolonged parenteral administration if kidney function is impaired. Premature neonates are particularly at risk because their kidneys are immature, and they require large amounts of calcium and phosphate solutions, which contain aluminum.
Research indicates that patients with impaired kidney function, including premature neonates, who receive parenteral levels of aluminum at greater than 4 to 5 mcg/kg/day accumulate aluminum at levels associated with central nervous system and bone toxicity. Tissue loading may occur at even lower rates of administration.
PRECAUTIONS
A. General
It is essential to provide adequate calories concurrently if parenterally administered amino acids are to be retained by the body and utilized for protein synthesis.
The administration of 15% Amino Acids Injection as part of total parenteral nutrition (TPN) with large volumes of hyperosmotic fluids requires periodic monitoring of the patient for signs of hyperosmolarity, hyperglycemia, glycosuria and hypertriglyceridemia.
During parenteral nutrition with concentrated dextrose and amino acids solutions, essential fatty acid deficiency syndrome may develop but may not be clinically apparent. Early demonstration of this condition can only be accomplished by gas liquid chromatographic analysis of plasma lipids. The syndrome may be prevented or corrected by appropriate treatment with intravenous fat emulsions.
For complete nutritional support, TPN regimens must also include multiple vitamins and trace elements. Potentially incompatible ions such as calcium and phosphate may be added to alternate infusate bottles to avoid precipitation. Although the metabolizable acetate ion in 15% Amino Acids Injection diminishes the risk of acidosis, the physician must be alert to the potential appearance of this disorder.
Initiation and termination of infusions of TPN fluids must be gradual to permit adjustment of endogenous insulin release.
Undiluted 15% Amino Acids Injection should not be administered peripherally. When administered centrally, it should be diluted with appropriate diluents, e.g., dextrose, electrolytes and other nutrient components, to at least half strength. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Caution against volume overload should be exercised.
Drug product contains no more than 25 mcg/L of aluminum.
B. Laboratory Tests
Infusion of 15% Amino Acids Injection without concomitant infusion of an adequate number of non-protein calories may result in elevated BUN. Monitoring of BUN is required and the balance between 15% Amino Acids Injection and the calorie source may require adjustment. Frequent clinical evaluations and laboratory determinations are required to prevent the complications which may occur during the administration of solutions used in TPN. Laboratory tests should include blood glucose, serum electrolytes, liver and kidney function, serum osmolarity, blood ammonia, serum protein, pH, hematocrit, WBC and urinary glucose. When 15% Amino Acids Injection is combined with electrolytes, care should be used in administering this solution to patients with congestive heart failure, renal failure, edema, adrenal hyperactivity, acid-base imbalance and those receiving diuretics or antihypertensive therapy. Total volume infused should be closely monitored. Serum electrolytes should be monitored daily in these patients.
C. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies with 15% Amino Acids Injection have not been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential, or effects on fertility.
D. Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with 15% Amino Acids Injection. It is also not known whether 15% Amino Acids Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. 15% Amino Acids Injection should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
E. Nursing Mothers
Caution should be exercised when 15% Amino Acids Injection is administered to a nursing woman.
F. Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of 15% Amino Acids Injection in pediatric patients have not been established by adequate and well-controlled studies. However, the use of amino acids injections in pediatric patients as an adjunct in the offsetting of nitrogen loss or in the treatment of negative nitrogen balance is referenced in the medical literature.
G. Special Precautions for Central Infusion
TPN delivered by indwelling catheter through a central or large peripheral vein is a special technique requiring a team effort by physician, nurse and pharmacist. The responsibility for administering this therapy should be confined to those trained in the procedures and alert to signs of complications. Complications known to occur from the placement of central venous catheter are pneumothorax, hemothorax, hydrothorax, artery puncture and transection, injury to the brachial plexus, malposition of the catheter, formation of arteriovenous fistula, phlebitis, thrombosis, and air/catheter emboli. The risk of sepsis is present during intravenous therapy, especially when using central venous catheters for prolonged periods. It is imperative that the preparation of admixtures and the placement and care of the catheters be accomplished under controlled aseptic conditions.
H. Admixtures
Admixtures should be prepared under a laminar flow hood using aseptic technique.
Admixtures should be stored under refrigeration and must be administered within 24 hours after removal from refrigerator.
Filters of less than 1.2 micron pore size must not be used with admixtures containing fat emulsion.
I. Use only if bottle and seal are undamaged and solution is clear with vacuum present.
IT IS ESSENTIAL THAT A CAREFULLY PREPARED PROTOCOL, BASED ON CURRENT MEDICAL PRACTICES, BE FOLLOWED, PREFERABLY BY AN EXPERIENCED TEAM.
AMINO ACIDS ADVERSE REACTIONS
(See WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS and Special Precautions for Central Infusion .)
OVERDOSAGE
In the event of overhydration or solute overload, re-evaluate the patient and institute appropriate corrective measures. (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS .)
AMINO ACIDS DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The appropriate daily dose of amino acids to be used with dextrose or with dextrose and intravenous fat emulsion will depend upon the metabolic status and clinical response of the patient as therapy proceeds. Doses which achieve nitrogen equilibrium or positive balance are the most desirable. The dosage on the first day should be approximately half the anticipated optimal dosage and should be increased gradually to minimize glycosuria; similarly, withdrawal should be accomplished gradually to avoid rebound hypoglycemia.
Fat emulsion coadministration should be considered when prolonged (more than 5 days) parenteral nutrition is required in order to prevent essential fatty acid deficiency (EFAD). Serum lipids should be monitored for evidence of EFAD in patients maintained on fat free TPN.
The amount administered is dosed on the basis of amino acids/kg of body weight/day. In general, two to three g/kg of body weight for neonates and infants with adequate calories are sufficient to satisfy protein needs and promote positive nitrogen balance. In pediatric patients, the final solution should not exceed twice normal serum osmolarity (718 mOsmol/L).
DIRECTIONS FOR PROPER USE OF PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE
15% Amino Acids Injection in a Pharmacy Bulk Package is not intended for direct infusion. The container closure may be penetrated only once using a suitable sterile transfer device or dispensing set which allows measured dispensing of the contents. The Pharmacy Bulk Package is to be used only in a suitable work area such as a laminar flow hood (or an equivalent clean air compounding area). Once the closure is penetrated, the contents should be dispensed as soon as possible; the transfer of contents must be completed within 4 hours of closure entry. The bottle may be stored at room temperature (25°C) after the closure has been entered. Date and time of container entry should be noted in the area designated on the container label.
When using 15% Amino Acids Injection in patients with a need for fluid volume restriction, it can be diluted as follows:
| Volume | Amount | Final Concentration | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15% Amino Acids Injection | 500 mL | 75 g | 7.5% |
| Dextrose 70% | 250 mL | 175 g | 17.5% |
| Intralipid® 20% | 250 mL | 50 g | 5.0% |
This will provide 1395 kilocalories (kcal) per 1000 mL of admixture with a ratio of 118 non-protein calories per gram of nitrogen and an osmolarity of 1561 mOsmol/L.
In patients where the need for fluid restriction is not so marked, either of the following regimens may be used dependent upon the energy needs of the patient.
| Volume | Amount | Final Concentration | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15% Amino Acids Injection | 500 mL | 75 g | 3.75% |
| Dextrose 50% | 1000 mL | 500 g | 25% |
| Intralipid® 20% | 500 mL | 100 g | 5% |
This will provide 1500 kcal per 1000 mL of admixture with a ratio of 228 non-protein calories per gram of nitrogen and an osmolarity of 1633 mOsmol/L.
| Volume | Amount | Final Concentration | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15% Amino Acids Injection | 500 mL | 75 g | 3.75% |
| Dextrose 30% | 1000 mL | 300 g | 15% |
| Intralipid® 10% | 500 mL | 50 g | 2.5% |
This will provide 935 kcal per 1000 mL of admixture with a ratio of 158 non-protein calories per gram of nitrogen and an osmolarity of 1128.5 mOsmol/L.
A. Total Parenteral Nutrition (Central Infusion)
In unstressed adult patients with no unusual nitrogen losses, a minimum dosage of 0.1 gram nitrogen (4.2 mL of 15% Amino Acids Injection) plus 4.4 grams (15 calories) of dextrose per kilogram of body weight per day are required to achieve nitrogen balance and weight stability. Intravenous fat emulsion may be used as a partial substitute for dextrose. This regimen provides a ratio of 150 non-protein calories per gram of nitrogen.
For patients stressed by surgery, trauma or sepsis, and those with unusual nitrogen losses, the dosage required for maintenance may be as high as 0.3 to 0.4 grams of nitrogen (13 to 17 mL 15% Amino Acids Injection) per kilogram of body weight per day, with proportionate increases in non-protein calories. Periodic assessment of nitrogen balance of the individual patient is the best indicator of proper dosage. Volume overload and glycosuria may be encountered at high dosage, and nitrogen balance may not be achieved in extremely hypermetabolic patients under these constraints. Concomitant insulin administration may be required to minimize glycosuria. Daily laboratory monitoring is essential.
Use of an infusion pump is advisable to maintain a steady infusion rate during central venous infusion.
B. Peripheral Nutrition
In patients for whom central venous catheterization is not advisable, protein catabolism can be reduced by peripheral use of diluted 15% Amino Acids Injection plus non-protein calorie sources. Dilution of 250 mL 15% Amino Acids Injection in 750 mL of 10% dextrose will reduce the osmolarity to a level (724 mOsmol/L) which is more favorable to the maintenance of the integrity of the walls of the veins. Intravenous fat emulsion can be infused separately or simultaneously; if infused simultaneously the fat emulsion will provide a dilution effect upon the osmolarity while increasing the energy supply.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
To reduce the risk of bacterial contamination, all intravenous administration sets should be replaced at least every 24 hours. Usage of admixtures must be initiated within 24 hours after mixing. If storage is necessary during this 24 hour period, admixtures must be refrigerated and completely used within 24 hours of beginning administration.
HOW SUPPLIED
15% Amino Acids Injection is supplied sterile and nonpyrogenic in glass containers, Pharmacy Bulk Packages, packaged 6 per case.
| NDC | REF | Size |
|---|---|---|
| 0264-3200-55 | S3200-SS | 1000 mL |
| 0264-3205-55 | S3205-SS | 2000 mL |
Storage
Store in the closed carton; do not expose solution to light until ready for use. Exposure of pharmaceutical products to heat should be minimized. Avoid excessive heat. It is recommended that the product be stored at 20 to 25°C (68 to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Brief exposure to temperatures above 25°C during transport and storage will not adversely affect the product. Solution that has been frozen must not be used.
Rx only
Revised: November 2013
Intralipid is a registered trademark of Fresenius Kabi AB.
Directions for Use of Pharmacy Bulk Package in B. Braun Glass Containers with Solid Stoppers
Warning: Not for direct infusion. For preparation of admixtures for intravenous infusion.
The pharmacy bulk package is for use in a Pharmacy Admixture Service only. Use of this product is restricted to a suitable work area, such as a laminar flow hood (or an equivalent clean air compounding area).
Additives should not be made to Pharmacy Bulk Packages.
Designed for use with a vented sterile dispensing set.
Before use, perform the following checks:
- Inspect each container. Read the label. Ensure solution is the one ordered and is within the expiration date.
- Invert container and carefully inspect the solution in good light for cloudiness, haze, or particulate matter; check the bottle for cracks or other damage. In checking for cracks, do not be confused by normal surface marks and seams on the bottom and sides of the bottle. These are not flaws. Look for bright reflections that have depth and penetrate into the wall of the bottle. Reject any such bottle.
- To remove the outer closure, lift the tear tab and pull up, over, and down until it is below the stopper (see Figure 1). Use a circular pulling motion on the tab until it breaks away.

- Grasp and remove the metal disk, exercising caution not to touch the exposed sterile stopper surface.
- Check for vacuum at first puncture of the stopper. Insert the spike fully into the target area of the rubber stopper (See Figure 2) and promptly invert the bottle. Verify vacuum by observing rising air bubbles. Do not use the bottle if vacuum is not present. Refer to Directions for Use of set to be used.

- If set insertion is not performed immediately following removal of protective metal disk, swab stopper with a suitable disinfectant.
The container closure may be penetrated only one time, utilizing a suitable sterile dispensing set which allows measured dispensing of the contents.
Transfer individual dose(s) to appropriate intravenous infusion solutions. Use of a syringe with needle is not recommended. Multiple entries increase the potential of the microbial and particulate contamination.
The withdrawal of container contents should be accomplished without delay using aseptic technique. Discard container no later than 4 hours after initial closure puncture.
The bottle may be stored under laminar flow hood at room temperature (25°C) after the closure has been entered. Date and time of container entry should be noted in the area designated on the container label.
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Irvine, CA 92614-5895 USA
1-800-227-2862
www.bbraun.com
Made in USA
LD-242-2 Y36-002-851
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1000 mL Bottle Label
15% Amino Acids Injection
NDC 0264-3200-55
REF S3200-SS
1000 mL
PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE - NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION
Protect from light until use.
For Intravenous Use
Store at 20 to 25°C (68 to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Solution that has been frozen must not be used. Do not expose to light
before using. Once closure is penetrated, transfer contents promptly, total
time not to exceed 4 hours. See package insert for proper use of Pharmacy
Bulk Package.
Entry Date: _______________ Time: _______________
Each 100 mL contains:
| Essential Amino Acids | |
| Lysine (from Lysine Acetate, USP) | 1.18 g |
| Leucine, USP | 1.04 g |
| Phenylalanine, USP | 1.04 g |
| Valine, USP | 960 mg |
| Isoleucine, USP | 749 mg |
| Methionine, USP | 749 mg |
| Threonine, USP | 749 mg |
| Tryptophan, USP | 250 mg |
| Nonessential Amino Acids | |
| Alanine, USP | 2.17 g |
| Arginine, USP | 1.47 g |
| Glycine, USP | 1.04 g |
| Histidine, USP | 894 mg |
| Proline, USP | 894 mg |
| Glutamic Acid | 749 mg |
| Serine, USP | 592 mg |
| Aspartic Acid, USP | 434 mg |
| Tyrosine, USP | 39 mg |
| Sodium Metabisulfite, NF added | 30 mg |
| Water for Injection USP | qs |
pH 5.6 (5.2-6.0), adjusted with acetic acid.
Acetate: 151 mEq/L, including quantity used
for pH adjustment.
Calculated Osmolarity:
1383 mOsmol/L
Contains no more than
25 mcg/L of aluminum.
Sterile, nonpyrogenic.
Single dose container.
Use only if bottle and seal
are undamaged and solution
is clear with vacuum
present.
Administer intravenously.
Rx only
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Irvine, CA 92614-5895 USA
1-800-227-2862
www.bbraun.com
Made in USA
LD-243-1 Y37-002-179
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1000 mL Bottle Carton
15% Amino Acids
Injection
NDC 0264-3200-55
REF S3200-SS
1000 mL
Protect from light until use.
PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE
NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION
Each 100 mL contains:
| Essential Amino Acids | |
| Lysine (from Lysine Acetate, USP) | 1.18 g |
| Leucine, USP | 1.04 g |
| Phenylalanine, USP | 1.04 g |
| Valine, USP | 960 mg |
| Isoleucine, USP | 749 mg |
| Methionine, USP | 749 mg |
| Threonine, USP | 749 mg |
| Tryptophan, USP | 250 mg |
| Nonessential Amino Acids | |
| Alanine, USP | 2.17 g |
| Arginine, USP | 1.47 g |
| Glycine, USP | 1.04 g |
| Histidine, USP | 894 mg |
| Proline, USP | 894 mg |
| Glutamic Acid | 749 mg |
| Serine, USP | 592 mg |
| Aspartic Acid, USP | 434 mg |
| Tyrosine, USP | 39 mg |
| Sodium Metabisulfite, NF added | 30 mg |
| Water for Injection USP qs |
See adjacent panel for further product information.
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Irvine, CA 92614-5895 USA
1-800-227-2862
www.bbraun.com
Made in USA
For Intravenous Use
pH 5.6 (5.2-6.0), adjusted with acetic acid.
Acetate: 151 mEq/L, including quantity used
for pH adjustment.
Calculated Osmolarity: 1383 mOsmol/L
Contains no more than 25 mcg/L of aluminum.
Sterile, nonpyrogenic. Single dose container.
Use only if bottle and seal are undamaged and
solution is clear with vacuum present.
Administer intravenously.
Store at 20 to 25°C (68 to 77°F). [See USP
Controlled Room Temperature.] Solution that
has been frozen must not be used. Do not
expose to light before using. Once closure is
penetrated, transfer contents promptly, total
time not to exceed 4 hours. See package
insert for proper use of Pharmacy Bulk
Package.
Rx only
LD-247-1 X12-002-444

Amino AcidsLYSINE ACETATE, LEUCINE, PHENYLALANINE, VALINE, ISOLEUCINE, METHIONINE, THREONINE, TRYPTOPHAN, ALANINE, ARGININE, GLYCINE, HISTIDINE, PROLINE, GLUTAMIC ACID, SERINE, ASPARTIC ACID, and TYROSINE SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino AcidsLYSINE ACETATE, LEUCINE, PHENYLALANINE, VALINE, ISOLEUCINE, METHIONINE, THREONINE, TRYPTOPHAN, ALANINE, ARGININE, GLYCINE, HISTIDINE, PROLINE, GLUTAMIC ACID, SERINE, ASPARTIC ACID, and TYROSINE SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||