AMOXICILLIN
AMOXICILLIN 250MG CAPSULES USP AMOXICILLIN 500MG CAPSULES USP Rx Only
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- AMOXICILLIN DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- AMOXICILLIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- AMOXICILLIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- Information for Patients
- AMOXICILLIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- AMOXICILLIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- Storage and Dispensing
- CLINICAL STUDIES
- REFERENCES
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 500 mg (30 Capsule Bottle)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
AMOXICILLIN DESCRIPTION
SRRRp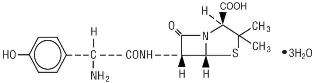
1619352
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Amoxicillin is stable in the presence of gastric acid and is rapidly absorbed after oral administration. Amoxicillin diffuses readily into most body tissues and fluids, with the exception of brain and spinal fluid, except when meninges are inflamed. The half-life of amoxicillin is 61.3 minutes. Most of the amoxicillin is excreted unchanged in the urine; its excretion can be delayed by concurrent administration of probenecid. In blood serum, amoxicillin is approximately 20% protein-bound.
Orally administered doses of 250 mg and 500 mg amoxicillin capsules result in average peak blood levels 1 to 2 hours after administration in the range of 3.5 mcg/mL to 5 mcg/mL and 5.5 mcg/mL to 7.5 mcg/mL, respectively.
Microbiology
in vitroINDICATIONS AND USAGEEnterococcus faecalis
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Proteus mirabilis
Helicobacter pylori
Susceptibility Tests
1ampicillinS. pneumoniaeS. pneumoniae
Enterococcus
| MIC
(mcg/mL)
|
Interpretation
|
| ≤8
|
Susceptible (S)
|
| ≥16
|
Resistant (R)
|
Staphylococcusa
| MIC
(mcg/mL)
|
Interpretation
|
| ≤0.25
|
Susceptible (S)
|
| ≥0.5
|
Resistant (R)
|
Streptococcus S. pneumoniae
| MIC
(mcg/mL)
|
Interpretation
|
| ≤0.25
|
Susceptible (S)
|
| 0.5 to 4
|
Intermediate (I)
|
| ≥8 |
Resistant
(R) |
S. pneumoniaeb
Amoxicillin
| MIC
(mcg/mL)
|
Interpretation
|
| ≤2
|
Susceptible (S)
|
| 4
|
Intermediate (I)
|
| ≥8 |
Resistant
(R) |
NOTE:
| MIC
(mcg/mL)
|
Interpretation
|
| ≤8
|
Susceptible (S)
|
| 16
|
Intermediate (I)
|
| ≥32 |
Resistant
(R) |
H. influenzaec
| MIC
(mcg/mL)
|
Interpretation
|
| ≤1
|
Susceptible (S)
|
| 2
|
Intermediate (I)
|
| ≥4 |
Resistant
(R) |
H. influenzae Haemophilus1
ampicillin
|
Microorganism
|
MIC Range
(mcg/mL)
|
|
E.
coli ATCC 25922
|
2 to 8 |
|
E. faecalis
ATCC 29212
|
0.5 to 2 |
|
H. influenzae
ATCC 49247d
|
2 to 8 |
|
S.
aureus ATCC 29213
|
0.25 to
1 |
amoxicillin
|
Microorganism
|
MIC Range
(mcg/mL)
|
|
S. pneumoniae
ATCC 49619e
|
0.03 to
0.12 |
H. influenzae1
S. pneumoniae
2S. pneumoniaeampicillin
Enterococcus
| Zone
Diameter (mm)
|
Interpretation
|
| ≥17 |
Susceptible (S) |
| ≤16 |
Resistant
(R) |
Staphylococcusf
| Zone
Diameter (mm)
|
Interpretation
|
| ≥29 |
Susceptible (S) |
| ≤28 |
Resistant
(R) |
-
|
Zone Diameter
(mm)
|
Interpretation
|
| ≥26 |
Susceptible (S) |
| 19 to 25 |
Intermediate (I) |
| ≤18 |
Resistant (R) |
NOTE:Spneumoniae
S. pneumoniae
S. pneumoniaeS. pneumoniae
Enterobacteriaceae
| Zone
Diameter (mm)
|
Interpretation
|
| ≥17 |
Susceptible (S) |
| 14 to 16 |
Intermediate (I) |
| ≤13 |
Resistant
(R) |
H. influenzaeg
| Zone
Diameter (mm)
|
Interpretation
|
| ≥22 |
Susceptible (S) |
| 19 to 21 |
Intermediate (I) |
| ≤18 |
Resistant
(R) |
H. influenzaeHaemophilus2
ampicillin
|
Microorganism
|
Zone Diameter
(mm)
|
|
E.
coli ATCC 25922
|
16 to 22 |
|
H. influenzae
ATCC 49247h
|
13 to 21 |
|
S.
aureus ATCC 25923 |
27 to
35 |
oxacillin
|
Microorganism
|
Zone Diameter
(mm)
|
|
S. pneumoniae
ATCC 49619i
|
8 to
12 |
H. influenzae2
S. pneumoniae2
In vitroH. pylori
AMOXICILLIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Infections of the ear, nose, and throatStreptococcusS. pneumoniaeStaphylococcusH. influenzae
Infections of the genitourinary tractE. coli, P. mirabilisE. faecalis
Infections of the skin and skin structureStreptococcusStaphylococcusE. coli
Infections of the lower respiratory tractStreptococcusS. pneumoniae, StaphylococcusH. influenzae
Gonorrhea, acute uncomplicated (ano-genital and urethral infections)N. gonorrhoeae
H. pyloriH. pyloriH. pylori(See CLINICAL STUDIES and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
H. pyloriwho are either allergic or intolerant to clarithromycin or in whom resistance to clarithromycin is known or suspected.H. pylori(See CLINICAL STUDIES and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
AMOXICILLIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
SERIOUS ANAPHYLACTIC REACTIONS REQUIRE IMMEDIATE EMERGENCY TREATMENT WITH EPINEPHRINE. OXYGEN, INTRAVENOUS STEROIDS, AND AIRWAY MANAGEMENT, INCLUDING INTUBATION, SHOULD ALSO BE ADMINISTERED AS INDICATED.Clostridium difficile C. difficile.
C. difficile C. difficile
C. difficileC. difficile
PRECAUTIONS
GeneralLaboratory Tests
Drug Interactions
in vitro
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
®®Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
2Pregnancy
Labor and Delivery
Nursing Mothers
Pediatric Use
(See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Neonates and Infants.)Geriatric Use
An analysis of clinical studies of amoxicillin was conducted to determine whether subjects aged 65 and over respond differently from younger subjects. Of the 1,811 subjects treated with capsules of amoxicillin, 85 percent were younger than 60 years old, 15 percent were older than 61 years old and 7 percent were over 71 years old. This analysis and other reported clinical experience have not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but a greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because eldery patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Information for Patients
AMOXICILLIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
As with other penicillins, it may be expected that untoward reactions will be essentially limited to sensitivity phenomena. They are more likely to occur in individuals who have previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to penicillins and in those with a history of allergy, asthma, hay fever, or urticaria. The following adverse reactions have been reported as associated with the use of penicillins:
Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and hemorrhagic / pseudomembranous colitis.
Onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibiotic treatment. (See WARNINGS.)
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serum sickness–like reactions, erythematous maculopapular rashes, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, hypersensitivity vasculitis and urticaria have been reported.
NOTE: These hypersensitivity reactions may be controlled with antihistamines and, if necessary, systemic corticosteroids. Whenever such reactions occur, amoxicillin should be discontinued unless, in the opinion of the physician, the condition being treated is life-threatening and amenable only to amoxicillin therapy.
Liver: A moderate rise in AST (SGOT) and/or ALT (SGPT) has been noted, but the significance of this finding is unknown. Hepatic dysfunction including cholestatic jaundice, hepatic cholestasis and acute cytolytic hepatitis have been reported.
Renal: Crystalluria has also been reported (see OVERDOSAGE)
Hemic and Lymphatic Systems: Anemia, including hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, eosinophilia, leukopenia, and agranulocytosis have been reported during therapy with penicillins. These reactions are usually reversible on discontinuation of therapy and are believed to be hypersensitivity phenomena.
Central Nervous System: Reversible hyperactivity, agitation, anxiety, insomnia, confusion, convulsions, behavioral changes, and/or dizziness have been reported rarely.
Miscellaneous: Tooth discoloration (brown, yellow, or gray staining) has been rarely reported. Most reports occurred in pediatric patients. Discoloration was reduced or eliminated with brushing or dental cleaning in most cases.
Combination therapy with clarithromycin
and lansoprazole:
In clinical trials using combination therapy
with amoxicillin plus clarithromycin and lansoprazole, and amoxicillin plus
lansoprazole, no adverse reactions peculiar to these drug combinations were
observed. Adverse reactions that have occurred have been limited to those that
had been previously reported with amoxicillin, clarithromycin, or
lansoprazole.
The most frequently reported adverse events for patients who received triple therapy were diarrhea (7%), headache (6%), and taste perversion (5%). No treatment-emergent adverse events were observed at significantly higher rates with triple therapy than with any dual therapy regimen.
Dual therapy: Amoxicillin/lansoprazole:The most frequently reported adverse events for patients who received amoxicillin 3 times daily plus lansoprazole three times daily dual therapy were diarrhea (8%) and headache (7%). No treatment-emergent adverse events were observed at significantly higher rates with amoxicillin 3 times daily plus lansoprazole 3 times daily dual therapy than with lansoprazole alone.
For more information on adverse reactions with clarithromycin or lansoprazole, refer to their package inserts, ADVERSE REACTIONS.
OVERDOSAGE
In case of overdosage, discontinue medication, treat symptomatically, and institute supportive measures as required. If the overdosage is very recent and there is no contraindication, an attempt at emesis or other means of removal of drug from the stomach may be performed. A prospective study of 51 pediatric patients at a poison-control center suggested that overdosages of less than 250 mg/kg of amoxicillin are not associated with significant clinical symptoms and do not require gastric emptying.3
Interstitial nephritis resulting in oliguric renal failure has been reported in a small number of patients after over-dosage with amoxicillin.
Crystalluria, in some cases leading to renal failure, has also been reported after amoxicillin overdosage in adult and pediatric patients. In case of overdosage, adequate fluid intake and diuresis should be maintained to reduce the risk of amoxicillin crystalluria.
Renal impairment appears to be reversible with cessation of drug administration. High blood levels may occur more readily in patients with impaired renal function because of decreased renal clearance of amoxicillin. Amoxicillin may be removed from circulation by hemodialysis.
AMOXICILLIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Amoxicillin capsules, chewable tablets, and oral suspensions may be given without regard to meals. The 400 mg suspension, 400 mg chewable tablet and the 875 mg tablet have been studied only when administered at the start of a light meal. However, food effect studies have not been performed with the 200 mg and 500 mg formulations.
Amoxicillin tablets, chewable should be chewed before swallowing
Neonates and Infants aged ≤ 12 weeks (≤ 3 months): Due to incompletely developed renal function affecting elimination of amoxicillin in this age group, the recommended upper dose of amoxicillin is 30 mg/kg/day divided q12h.
Adults and Pediatric Patients > 3 months
| Infection | Severity‡ | Usual Adult Dose | Usual Dose for Children >3 months§ π |
| Ear/Nose/Throat | Mild/Moderate | 500 mg every12 hours or 250 mg every 8 hours | 25 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 20 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours |
| Severe | 875 mg every 12 hours or 500 mg every 8 hours | 45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours | |
| Lower Respiratory Tract | Mild/Moderate or Severe | 875 mg every 12 hours or 500 mg every 8 hours | 45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours |
| Skin/Skin Structure | Mild/Moderate | 500 mg every12 hours or 250 mg every 8 hours | 25 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 20 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours |
| Severe | 875 mg every12 hours or 500 mg every 8 hours | 45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours | |
| Genitourinary Tract | Mild/Moderate | 500 mg every12 hours or 250 mg every 8 hours | 25 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 20 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours |
| Severe | 875 mg every12 hours or 500 mg every 8 hours | 45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours | |
| Gonorrhea Acute, uncomplicated ano-genital and urethral infections in males and females | 3 grams as single oral dose | Prepubertal children: 50 mg/kg amoxicillin, combined with 25 mg/kg probenecid as a single dose. NOTE: SINCE PROBENECID IS CONTRAINDICATED IN CHILDREN UNDER 2 YEARS, DO NOT USE THIS REGIMEN IN THESE CASES. |
‡ Dosing for infections caused by less susceptible organisms should follow the recommendations for severe infections.
§ The children’s dosage is intended for individuals whose weight is less than 40 kg. Children weighing 40 kg or more should be dosed according to the adult recommendations.
π Each strength of the suspension of amoxicillin is available as a chewable tablet for use by older children.
After reconstitution, the required amount of suspension should be placed directly on the child’s tongue for swallowing. Alternate means of administration are to add the required amount of suspension to formula, milk, fruit juice, water, ginger ale, or cold drinks. These preparations should then be taken immediately. To be certain the child is receiving full dosage, such preparations should be consumed in entirety.
All patients with gonorrhea should be evaluated for syphilis. (See PRECAUTIONS – Laboratory Tests.)
Larger doses may be required for stubborn or severe infections.
General
Streptococcus pyogenesH. pylori Eradication to Reduce the Risk of Duodenal Ulcer Recurrence
(See INDICATIONS AND USAGE.)
(See INDICATIONS AND USAGE.)
Dosing Recommendations for Adults with Impaired Renal Function
There are currently no dosing recommendations for pediatric patients with impaired renal function.
HOW SUPPLIED
Amoxicillin Capsules, USP250 mg Capsule
- NDC 12634-183-91 Blister Pack UD
- NDC 12634-183-94 Bottle of 4
- NDC 12634-183-84 Bottle of 14
- NDC 12634-183-85 bottle of 15
- NDC 12634-183-81 Bottle of 21
- NDC 12634-183-71 Bottle of 30
- NDC 12634-183-60 Bottle of 60
- NDC 12634-183-01 Bottle of 100
500 mg Capsule
- NDC 12634-185-91 Blister Pack UD
- NDC 12634-185-94 Bottle of 4
- NDC 12634-185-96 Bottle of 6
- NDC 12634-185-99 Bottle of 9
- NDC 12634-185-84 Bottle of 14
- NDC 12634-185-85 Bottle of 15
- NDC 12634-185-81 Bottle of 21
- NDC 12634-185-71 Bottle of 30
- NDC 12634-185-60 Bottle of 60
- NDC 12634-185-01 Bottle of 100
Storage and Dispensing
CLINICAL STUDIES
H. pylori Eradication to Reduce the Risk of Duodenal Ulcer RecurrenceH. pyloriH. pylori
H. pylori
H. pylori
H. pylori Eradication Rates – Triple Therapy (amoxicillin/ clarithromycin /lansoprazole) Percent of Patients Cured [95% Confidence Interval] (Number of Patients)
| Study | Triple Therapy | Triple Therapy |
| Evaluable Analysis* | Intent-to-Treat Analysis† |
|
| Study 1 | 92‡ | 86‡ |
| [80 - 97.7] | [73.3 - 93.5] | |
| (n = 48) | (n = 55) | |
| Study 2 | 86§ | 83§ |
| [75.7 - 93.6] | [72 - 90.8] | |
| (n = 66) | (n = 70) |

H. pylori Eradication Rates – Dual Therapy (amoxicillin/lansoprazole) Percent of Patients Cured [95% Confidence Interval] (Number of Patients)
| Study | Dual Therapy | Dual Therapy |
| Evaluable Analysis* | Intent-to-Treat | |
| Analysis† | ||
| Study 1 | 77‡ | 70‡ |
| [62.5 - 87.2] | [56.8 - 81.2] | |
| (n = 51) | (n = 60) | |
| Study 2 | 66§ | 61§ |
| [51.9 - 77.5] | [48.5 - 72.9] | |
| (n = 58) | (n = 67) |

REFERENCES
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically – Fourth Edition; Approved Standard. NCCLS Document M7-A4, Vol. 17, No. 2. NCCLS, Wayne, PA, January 1997.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests – Sixth Edition; Approved Standard. NCCLS Document M2-A6, Vol. 17, No. 1. NCCLS, Wayne, PA, January 1997.
- Swanson-Biearman B, Dean BS, Lopez G, Krenzelok EP. The effects of penicillin and cephalosporin ingestions in children less than six years of age. Vet Hum Toxicol. 1988;30:66-67.
CLINITEST® is a registered trademark of
Miles, Inc.
CLINISTIX® is a registered trademark of
Bayer Corporation.
CLOtest® is a registered trademark
of Kimberly-Clark Corporation.
Manufactured by: Aurobindo Pharma Limited
Manufactured for: Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Repackaged by: Sandhills Packaging, Inc. for Apotheca, Inc..
Repackaged by: Apotheca, Inc.
Distributed by: Apotheca, Inc.
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 500 mg (30 Capsule Bottle)
NDC 12634-185-71Amoxicillin Capsules, USP
500 mg
Rx only 30 Capsules

NDC 12634-185-71
Amoxicillin Capsules, USP
500 mg
Rx only 30 Capsules

AMOXICILLINAMOXICILLIN CAPSULE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
AMOXICILLINAMOXICILLIN CAPSULE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||