Atenolol
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- BOXED WARNING
- ATENOLOL DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- PHARMACOKINETICS AND METABOLISM
- PHARMACODYNAMICS
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- ATENOLOL CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY & OR TOXICOLOGY
- PREGNANCY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- GERIATRIC USE
- ATENOLOL ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
BOXED WARNING
Cessation of Therapy with AtenololPatients with coronary artery disease, who are being treated with atenolol, should be advised against abrupt discontinuation of therapy. Severe exacerbation of angina and the occurrence of myocardial infarction and ventricular arrhythmias have been reported in angina patients following the abrupt discontinuation of therapy with beta-blockers. The last two complications may occur with or without preceding exacerbation of the angina pectoris. As with other beta-blockers, when discontinuation of atenolol is planned, the patients should be carefully observed and advised to limit physical activity to a minimum. If the angina worsens or acute coronary insufficiency develops, it is recommended that atenolol be promptly reinstituted, at least temporarily. Because coronary artery disease is common and may be unrecognized, it may be prudent not to discontinue atenolol therapy abruptly even in patients treated only for hypertension (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
ATENOLOL DESCRIPTION
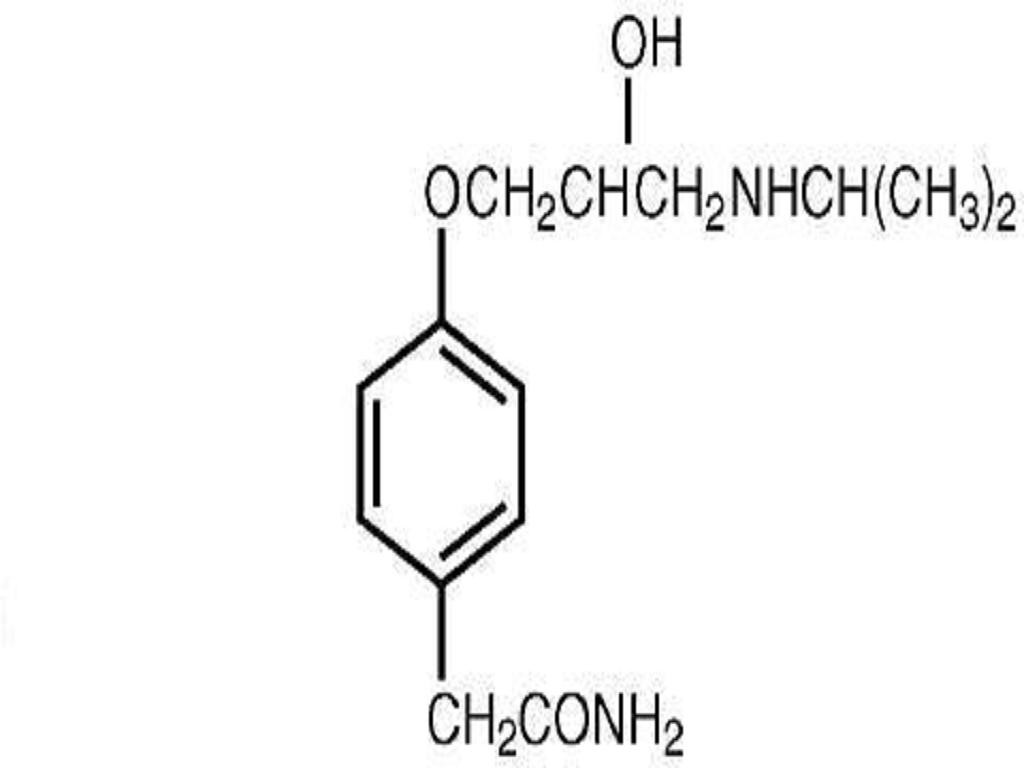
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
PHARMACOKINETICS AND METABOLISM
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PHARMACODYNAMICS
INDICATIONS & USAGE
HypertensionAngina Pectoris Due to Coronary Atherosclerosis
Acute Myocardial Infarction
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONCONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS
ATENOLOL CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGSWARNINGS
Cardiac FailureIn Patients Without a History of Cardiac Failure
DOSAGE AND ADMNISTRATION
Cessation of Therapy with Atenolol
Patients with coronary artery disease, who are being treated with atenolol, should be advised against abrupt discontinuation of therapy. Severe exacerbation of angina and the occurrence of myocardial infarction and ventricular arrhythmias have been reported in angina patients following the abrupt discontinuation of therapy with beta-blockers. The last two complications may occur with or without preceding exacerbation of the angina pectoris. As with other beta-blockers, when discontinuation of atenolol is planned, the patients should be carefully observed and advised to limit physical activity to a minimum. If the angina worsens or acute coronary insufficiency develops, it is recommended that atenolol be promptly reinstituted, at least temporarily. Because coronary artery disease is common and may be unrecognized, it may be prudent not to discontinue atenolol therapy abruptly even in patients treated only for hypertension (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Concomitant Use of Calcium Channel Blockers
PRECAUTIONS
Bronchospastic Diseases
PATIENTS WITH BRONCHOSPASTIC DISEASE SHOULD, IN GENERAL, NOT RECEIVE BETA-BLOCKERS. Because of its relative beta1 selectivity, however, atenolol may be used with caution in patients with bronchospastic disease who do not respond to, or cannot tolerate, other antihypertensive treatment. Since beta1 selectivity is not absolute, the lowest possible dose of atenolol should be used with therapy initiated at 50 mg and a beta2-stimulating agent (bronchodilator) should be made available. If dosage must be increased, dividing the dose should be considered in order to achieve lower peak blood levels.
Anesthesia and Major Surgery
OVERDOSAGE
Diabetes and Hypoglycemia
Thyrotoxicosis
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Untreated Pheochromocytoma
Pregnancy and Fetal Injury
PRECAUTIONS, Nursing Mothers
PRECAUTIONS
GeneralImpaired Renal Function
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DRUG INTERACTIONS
WARNINGS
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY & OR TOXICOLOGY
PREGNANCY
WARNINGS - Pregnancy and Fetal Injury
NURSING MOTHERS
WARNINGS, Pregnancy and Fetal Injury
PEDIATRIC USE
GERIATRIC USE
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYINDICATIONS AND USAGE).
In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. Evaluation of patients with hypertension or myocardial infarction should always include assessment of renal function.
ATENOLOL ADVERSE REACTIONS
WARNINGS
Acute Myocardial Infarction
POTENTIAL ADVERSE EFFECTS
Hematologic:
Allergic:
Central Nervous System:
Gastrointestinal:
Other:
Miscellaneous:INDICATIONS AND USAGE
OVERDOSAGE
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
HypertensionAngina Pectoris
Acute Myocardial Infarction
Elderly Patients or Patients with Renal Impairment
Cessation of Therapy in Patients with Angina Pectoris
HOW SUPPLIED
Atenolol Tablets, USPSTORAGE AND HANDLING
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

AtenololAtenolol TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!