benzonatate
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- BENZONATATE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- BENZONATATE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- BENZONATATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- Information for patients:
- Usage in Pregnancy:
- Nursing Mothers:
- Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility:
- Pediatric Use:
- BENZONATATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- BENZONATATE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- Principal Display Panel
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Rx only
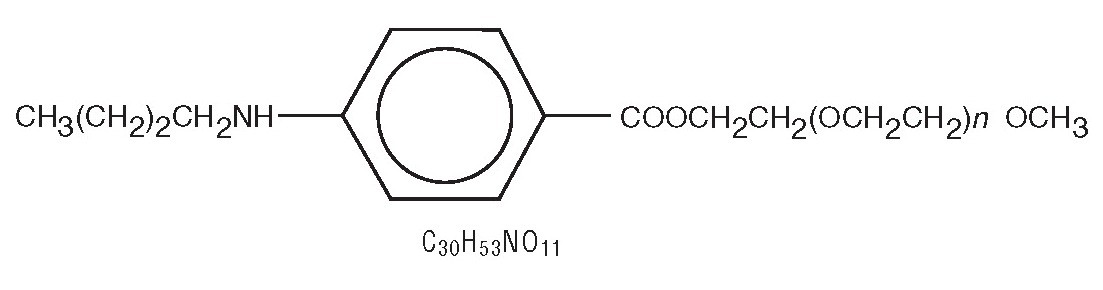
BENZONATATE DESCRIPTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Benzonatate acts peripherally by anesthetizing the stretch receptors located in the respiratory passages, lungs, and pleura by dampening their activity and thereby reducing the cough reflex at its source. It begins to act within 15 to 20 minutes and its effect lasts for 3 to 8 hours. Benzonatate has no inhibitory effect on the respiratory center in recommended dosage.
BENZONATATE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Benzonatate is indicated for the symptomatic relief of cough.
BENZONATATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to benzonatate or related compounds.
WARNINGS
Severe hypersensitivity reactions (including bronchospasm, laryngospasm and cardiovascular collapse) have been reported which are possibly related to local anesthesia from sucking or chewing the capsule instead of swallowing it. Severe reactions have required intervention with vasopressor agents and supportive measures.
Isolated instances of bizarre behavior, including mental confusion and visual hallucinations, have also been reported in patients taking benzonatate in combination with other prescribed drugs.
PRECAUTIONS
Benzonatate is chemically related to anesthetic agents of the para-aminobenzoic acid class (e.g. procaine; tetracaine) and has been associated with adverse CNS effects possibly related to a prior sensitivity to related agents or interaction with concomitant medication.
Information for patients:
Release of benzonatate from the capsule in the mouth can produce a temporary local anesthesia of the oral mucosa and choking could occur. Therefore, the capsules should be swallowed without chewing.
Usage in Pregnancy:
Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with benzonatate. It is also not known whether benzonatate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Benzonatate should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers:
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility:
Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, and reproduction studies have not been conducted with benzonatate.
Pediatric Use:
Safety and effectiveness in children below the age of 10 have not been established.
BENZONATATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Potential Adverse Reactions to benzonatate may include:
Hypersensitivity reactions including bronchospasm, laryngospasm, cardiovascular collapse possibly related to local anesthesia from chewing or sucking the capsule.
CNS: sedation; headache; dizziness; mental confusion; visual hallucinations.
GI: constipation; nausea; GI upset.
Dermatologic: pruritus; skin eruptions.
Other: nasal congestion; sensation of burning in the eyes; vague “chilly” sensation; numbness of the chest; hypersensitivity.
Rare instances of deliberate or accidental overdose have resulted in death.
OVERDOSAGE
Overdose may result in death.
The drug is chemically related to tetracaine and other topical anesthetics and shares various aspects of their pharmacology and toxicology. Drugs of this type are generally well absorbed after ingestion.
Signs and Symptoms:
If capsules are chewed or dissolved in the mouth, oropharyngeal anesthesia will develop rapidly. CNS stimulation may cause restlessness and tremors which may proceed to clonic convulsions followed by profound CNS depression.
Treatment:
Evacuate gastric contents and administer copious amounts of activated charcoal slurry. Even in the conscious patient, cough and gag reflexes may be so depressed as to necessitate special attention to protection against aspiration of gastric contents and orally administered materials. Convulsions should be treated with a short-acting barbiturate given intravenously and carefully titrated for the smallest effective dosage. Intensive support of respiration and cardiovascular - renal function is an essential feature of the treatment of severe intoxication from overdosage.
Do not use CNS stimulants.
BENZONATATE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adults and Children over 10 years of age: Usual dose is one 100 mg or 200 mg capsule t.i.d. as required. If necessary, up to 600 mg daily may be given.
HOW SUPPLIED
Principal Display Panel
NDC 0904-5904-60
Benzonatate
Capsules, USP
100 mg
Rx only
100 Capsules
MAJOR


benzonatatebenzonatate CAPSULE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
benzonatatebenzonatate CAPSULE
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||