Buprenorphine hydrochloride and naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONBuprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl dihydrate sublingual tabletsThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Buprenorphine hydrochloride and naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Buprenorphine hydrochloride and naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate. Buprenorphine hydrochloride and naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate (Buprenorphine hydrochloride and naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate) TABLET for SUBLINGUAL use.Initial U.S. Approval: 2002INDICATIONS AND USAGE Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are indicated for the maintenance treatment of opioid dependence. Prescription use of this product is limited under the Drug Addiction Treatment Act. (1)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Administer buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets sublingually as a single daily dose. (2) The recommended daily dose for maintenance is 16 mg/4 mg.DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Sublingual tablets: 2 mg buprenorphine with 0.5 mg naloxone and 8 mg buprenorphine with 2 mg naloxone (3)CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to buprenorphine or naloxone. (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Buprenorphine can be abused in a similar manner to other opioids. Clinical monitoring appropriate to the patient’s level of stability is essential. Multiple refills should not be prescribed early in treatment or without appropriate patient follow-up visits. (5.1) Significant respiratory depression and death have occurred in association with buprenorphine, particularly when taken by the intravenous (IV) route in combination with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants (including alcohol). (5.2) Consider dose reduction of CNS depressants, buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, or both in situations of concomitant prescription. (5.3) Store buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets safely out of the sight and reach of children. Buprenorphine can cause severe, possibly fatal, respiratory depression in children. (5.4) Chronic administration produces opioid-type physical dependence. Abrupt discontinuation or rapid dose taper may result in opioid withdrawal syndrome. (5.5) Monitor liver function tests prior to initiation and during treatment and evaluate suspected hepatic events. (5.6) Do not administer buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets to patients with known hypersensitivity to buprenorphine or naloxone. (5.7) A marked and intense opioid withdrawal syndrome is highly likely to occur with parenteral misuse of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets by individuals physically dependent on full opioid agonists or by sublingual administration before the agonist effects of other opioids have subsided. (5.8) Neonatal withdrawal has been reported following use of buprenorphine by the mother during pregnancy. (5.9) Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are not appropriate as an analgesic. There have been reported deaths of opioid naïve individuals who received a 2 mg sublingual dose. (5.10) Caution patients about the risk of driving or operating hazardous machinery. (5.11) Side Effects Adverse events commonly observed with the sublingual administration of the buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets during clinical trials and post-marketing experience are headache, nausea, vomiting, hyperhidrosis, constipation, signs and symptoms of withdrawal, insomnia, pain, and peripheral edema. (6.1 and 6.2) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Actavis at 1-800-432-8534 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS Monitor patients starting or ending CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers for potential over or under dosing. (7.1) Use caution in prescribing buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets for patients receiving benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants and warn patients against concomitant self administration/misuse. (7.3) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are not indicated for use during pregnancy unless potential benefit justifies potential risk. (8.1) Buprenorphine passes into the mother’s milk. Breast-feeding is not advised while taking buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets. (8.3) Safety and effectiveness of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets in patients below the age of 16 has not been established. (8.4) Administer buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets with caution to elderly or debilitated patients. (8.5) Administer buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets with caution to patients with liver dysfunction. (8.6)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are indicated for the maintenance treatment of opioid dependence and should be used as part of a complete treatment plan to include counseling and psychosocial support.
Under the Drug Addiction Treatment Act (DATA) codified at 21 U.S.C. 823(g), prescription use of this product in the treatment of opioid dependence is limited to physicians who meet certain qualifying requirements, and who have notified the Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS) of their intent to prescribe this product for the treatment of opioid dependence and have been assigned a unique identification number that must be included on every prescription.
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are administered sublingually as a single daily dose. Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets should be used in patients who have been initially inducted using buprenorphine HCl sublingual tablets.
Medication should be prescribed in consideration of the frequency of visits. Provision of multiple refills is not advised early in treatment or without appropriate patient follow-up visits
- Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are indicated for maintenance treatment. The recommended target dosage of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are 16 mg/4 mg buprenorphine/naloxone/day as a single daily dose
- The dosage of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets should be progressively adjusted in increments/decrements of 2 mg/0.5 mg or 4 mg/1 mg buprenorphine/naloxone to a level that holds the patient in treatment and suppresses opioid withdrawal signs and symptoms
- The maintenance dose of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are generally in the range of 4 mg/1 mg buprenorphine/naloxone to 24 mg/6 mg buprenorphine/naloxone per day depending on the individual patient. Dosages higher than this have not been demonstrated to provide any clinical advantage
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets should be placed under the tongue until it is dissolved. For doses requiring the use of more than two tablets, patients are advised to either place all the tablets at once or alternatively (if they cannot fit in more than two tablets comfortably), place two tablets at a time under the tongue. Either way, the patients should continue to hold the tablets under the tongue until they dissolve; swallowing the tablets reduces the bioavailability of the drug. To ensure consistency in bioavailability, patients should follow the same manner of dosing with continued use of the product.
Proper administration technique should be demonstrated to the patient.
Treatment should be initiated with supervised administration, progressing to unsupervised administration as the patient’s clinical stability permits. Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are subject to diversion and abuse. When determining the prescription quantity for unsupervised administration, consider the patient’s level of stability, the security of his or her home situation, and other factors likely to affect the ability to manage supplies of take-home medication.
Ideally patients should be seen at reasonable intervals (e.g., at least weekly during the first month of treatment) based upon the individual circumstances of the patient. Medication should be prescribed in consideration of the frequency of visits. Provision of multiple refills is not advised early in treatment or without appropriate patient follow-up visits. Periodic assessment is necessary to determine compliance with the dosing regimen, effectiveness of the treatment plan, and overall patient progress.
Once a stable dosage has been achieved and patient assessment (e.g., urine drug screening) does not indicate illicit drug use, less frequent follow-up visits may be appropriate. A once-monthly visit schedule may be reasonable for patients on a stable dosage of medication who are making progress toward their treatment objectives. Continuation or modification of pharmacotherapy should be based on the physician’s evaluation of treatment outcomes and objectives such as:
- Absence of medication toxicity
- Absence of medical or behavioral adverse effects
- Responsible handling of medications by the patient
- Patient’s compliance with all elements of the treatment plan (including recovery-oriented activities, psychotherapy, and/or other psychosocial modalities)
- Abstinence from illicit drug use (including problematic alcohol and/or benzodiazepine use)
If treatment goals are not being achieved, the physician should reevaluate the appropriateness of continuing the current treatment.
Physicians will need to decide when they cannot appropriately provide further management for particular patients. For example, some patients may be abusing or dependent on various drugs, or unresponsive to psychosocial intervention such that the physician does not feel that he/she has the expertise to manage the patient. In such cases, the physician may want to assess whether to refer the patient to a specialist or more intensive behavioral treatment environment. Decisions should be based on a treatment plan established and agreed upon with the patient at the beginning of treatment.
Patients who continue to misuse, abuse, or divert buprenorphine products or other opioids should be provided with, or referred to, more intensive and structured treatment.
The decision to discontinue therapy with buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets after a period of maintenance should be made as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Both gradual and abrupt discontinuation of buprenorphine has been used, but the data are insufficient to determine the best method of dose taper at the end of treatment.
Patients being switched between buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets and buprenorphine and naloxone sublingual film should be started on the same dosage as the previously administered product. However, dosage adjustments may be necessary when switching between products. Because of the potentially greater relative bioavailability of buprenorphine and naloxone sublingual film compared to buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, patients switching from buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets to buprenorphine and naloxone sublingual film should be monitored for over-medication. Those switching from buprenorphine and naloxone sublingual film to buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets should be monitored for withdrawal or other indications of underdosing. In clinical studies, pharmacokinetics of buprenorphine and naloxone sublingual film was similar to the respective dosage strengths of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, although not all doses and dose combinations met bioequivalence criteria.
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are supplied as uncoated white to off-white, round tablets in two dosage strengths:
- buprenorphine/naloxone 2 mg/0.5 mg, and
- buprenorphine/naloxone 8 mg/2 mg
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets should not be administered to patients who have been shown to be hypersensitive to buprenorphine or naloxone as serious adverse reactions, including anaphylactic shock, have been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Buprenorphine can be abused in a manner similar to other opioids, legal or illicit. Prescribe and dispense buprenorphine with appropriate precautions to minimize risk of misuse, abuse, or diversion, and ensure appropriate protection from theft, including in the home. Clinical monitoring appropriate to the patient’s level of stability is essential. Multiple refills should not be prescribed early in treatment or without appropriate patient follow-up visits. [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2)].
Buprenorphine, particularly when taken by the IV route, in combination with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants (including alcohol), has been associated with significant respiratory depression and death. Many, but not all, post-marketing reports regarding coma and death associated with the concomitant use of buprenorphine and benzodiazepines involved misuse by self-injection. Deaths have also been reported in association with concomitant administration of buprenorphine with other depressants such as alcohol or other CNS depressant drugs. Patients should be warned of the potential danger of self-administration of benzodiazepines or other depressants while under treatment with buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets. [see Drug Interactions (7.3)]
In the case of overdose, the primary management should be the reestablishment of adequate ventilation with mechanical assistance of respiration, if required. Naloxone may be of value for the management of buprenorphine overdose. Higher than normal doses and repeated administration may be necessary.
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets should be used with caution in patients with compromised respiratory function (e.g., chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cor pulmonale, decreased respiratory reserve, hypoxia, hypercapnia, or pre-existing respiratory depression).
Patients receiving buprenorphine in the presence of opioid analgesics, general anesthetics, benzodiazepines, phenothiazines, other tranquilizers, sedative/hypnotics, or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) may exhibit increased CNS depression. Consider dose reduction of CNS depressants, buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, or both in situations of concomitant prescription. [see Drug Interactions (7.3)]
Buprenorphine can cause severe, possibly fatal, respiratory depression in children who are accidentally exposed to it. Store buprenorphine-containing medications safely out of the sight and reach of children and destroy any unused medication appropriately. [see Disposal of Unused Buprenorphine HCl and Naloxone HCl Sublingual Tablets (17.2)].
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu-opioid receptor and chronic administration produces physical dependence of the opioid type, characterized by withdrawal signs and symptoms upon abrupt discontinuation or rapid taper. The withdrawal syndrome is typically milder than seen with full agonists and may be delayed in onset. Buprenorphine can be abused in a manner similar to other opioids. This should be considered when prescribing or dispensing buprenorphine in situations when the clinician is concerned about an increased risk of misuse, abuse, or diversion. [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)].
Cases of cytolytic hepatitis and hepatitis with jaundice have been observed in individuals receiving buprenorphine in clinical trials and through post-marketing adverse event reports. The spectrum of abnormalities ranges from transient asymptomatic elevations in hepatic transaminases to case reports of death, hepatic failure, hepatic necrosis, hepatorenal syndrome, and hepatic encephalopathy. In many cases, the presence of pre-existing liver enzyme abnormalities, infection with hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus, concomitant usage of other potentially hepatotoxic drugs, and ongoing injecting drug use may have played a causative or contributory role. In other cases, insufficient data were available to determine the etiology of the abnormality. Withdrawal of buprenorphine has resulted in amelioration of acute hepatitis in some cases; however, in other cases no dose reduction was necessary. The possibility exists that buprenorphine had a causative or contributory role in the development of the hepatic abnormality in some cases. Liver function tests, prior to initiation of treatment is recommended to establish a baseline. Periodic monitoring of liver function during treatment is also recommended. A biological and etiological evaluation is recommended when a hepatic event is suspected. Depending on the case, buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets may need to be carefully discontinued to prevent withdrawal signs and symptoms and a return by the patient to illicit drug use, and strict monitoring of the patient should be initiated.
Cases of hypersensitivity to buprenorphine and naloxone containing products have been reported both in clinical trials and in the post-marketing experience. Cases of bronchospasm, angioneurotic edema, and anaphylactic shock have been reported. The most common signs and symptoms include rashes, hives, and pruritus. A history of hypersensitivity to buprenorphine or naloxone is a contraindication to the use of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets.
Because it contains naloxone, buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are highly likely to produce marked and intense withdrawal signs and symptoms if misused parenterally by individuals dependent on full opioid agonists such as heroin, morphine, or methadone. Because of the partial agonist properties of buprenorphine, buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets may precipitate opioid withdrawal signs and symptoms in such persons if administered sublingually before the agonist effects of the opioid have subsided.
Neonatal withdrawal has been reported in the infants of women treated with buprenorphine during pregnancy. From post-marketing reports, the time to onset of neonatal withdrawal signs ranged from Day 1 to Day 8 of life with most cases occurring on Day 1. Adverse events associated with the neonatal withdrawal syndrome included hypertonia, neonatal tremor, neonatal agitation, and myoclonus, and there have been reports of convulsions, apnea, respiratory depression, and bradycardia.
There have been reported deaths of opioid naive individuals who received a 2 mg dose of buprenorphine as a sublingual tablet for analgesia. Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are not appropriate as an analgesic.
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets may impair the mental or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially dangerous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery, especially during treatment induction and dose adjustment. Patients should be cautioned about driving or operating hazardous machinery until they are reasonably certain that buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablet therapy does not adversely affect his or her ability to engage in such activities.
Like other opioids, buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets may produce orthostatic hypotension in ambulatory patients.
Buprenorphine, like other opioids, may elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure and should be used with caution in patients with head injury, intracranial lesions, and other circumstances when cerebrospinal pressure may be increased. Buprenorphine can produce miosis and changes in the level of consciousness that may interfere with patient evaluation.
Buprenorphine has been shown to increase intracholedochal pressure, as do other opioids, and thus should be administered with caution to patients with dysfunction of the biliary tract.
As with other opioids, buprenorphine may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course of patients with acute abdominal conditions.
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets should be administered with caution in debilitated patients and those with myxedema or hypothyroidism, adrenal cortical insufficiency (e.g., Addison's disease); CNS depression or coma; toxic psychoses; prostatic hypertrophy or urethral stricture; acute alcoholism; delirium tremens; or kyphoscoliosis.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets was evaluated in 497 opioid-dependent subjects. The prospective evaluation of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets was supported by clinical trials using buprenorphine HCl sublingual tablets and other trials using buprenorphine sublingual solutions. In total, safety data were available from 3214 opioid-dependent subjects exposed to buprenorphine at doses in the range used in treatment of opioid addiction.
Few differences in adverse event profile were noted between buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets and buprenorphine HCl sublingual tablets or buprenorphine administered as a sublingual solution.
The following adverse events were reported to occur by at least 5% of patients in a 4-week study (Table 1).
| N (%) | N (%) | |
| Body System /Adverse Event | Buprenorphine HCl and Naloxone | |
| (COSTART Terminology) | HCl Sublingual Tablets | |
| 16 mg/day | Placebo | |
| N = 107 | N = 107 | |
| Body as a Whole | ||
| Asthenia | 7 (6.5%) | 7 (6.5%) |
| Chills | 8 (7.5%) | 8 (7.5%) |
| Headache | 39 (36.4%) | 24 (22.4%) |
| Infection | 6 (5.6%) | 7 (6.5%) |
| Pain | 24 (22.4%) | 20 (18.7%) |
| Pain Abdomen | 12 (11.2%) | 7 (6.5%) |
| Pain Back | 4 (3.7%) | 12 (11.2%) |
| Withdrawal Syndrome | 27 (25.2%) | 40 (37.4%) |
| Cardiovascular System | ||
| Vasodilation | 10 (9.3%) | 7 (6.5%) |
| Digestive System | ||
| Constipation | 13 (12.1%) | 3 (2.8%) |
| Diarrhea | 4 (3.7%) | 16 (15.0%) |
| Nausea | 16 (15.0%) | 12 (11.2%) |
| Vomiting | 8 (7.5%) | 5 (4.7%) |
| Nervous System | ||
| Insomnia | 15 (14.0%) | 17 (15.9%) |
| Respiratory System | ||
| Rhinitis | 5 (4.7%) | 14 (13.1%) |
| Skin And Appendages | ||
| Sweating | 15 (14.0%) | 11 (10.3%) |
The adverse event profile of buprenorphine was also characterized in the dose-controlled study of buprenorphine solution, over a range of doses in four months of treatment. Table 2 shows adverse events reported by at least 5% of subjects in any dose group in the dose-controlled study.
| Buprenorphine Dose* | |||||
| Body System /Adverse Event | Very Low* | Low* | Moderate* | High* | Total* |
| (COSTART Terminology) | (N=184) | (N=180) | (N=186) | (N=181) | (N=731) |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |
| *Sublingual solution. Doses in this table cannot necessarily be delivered in tablet form, but for comparison purposes: | |||||
| “Very low” dose (1 mg solution) would be less than a tablet dose of 2 mg | |||||
| “Low” dose (4 mg solution) approximates a 6 mg tablet dose | |||||
| “Moderate” dose (8 mg solution) approximates a 12 mg tablet dose | |||||
| “High” dose (16 mg solution) approximates a 24 mg tablet dose | |||||
| Body as a Whole | |||||
| Abscess | 9 (5%) | 2 (1%) | 3 (2%) | 2 (1%) | 16 (2%) |
| Asthenia | 26 (14%) | 28 (16%) | 26 (14%) | 24 (13%) | 104 (14%) |
| Chills | 11 (6%) | 12 (7%) | 9 (5%) | 10 (6%) | 42 (6%) |
| Fever | 7 (4%) | 2 (1%) | 2 (1%) | 10 (6%) | 21 (3%) |
| Flu Syndrome | 4 (2%) | 13 (7%) | 19 (10%) | 8 (4%) | 44 (6%) |
| Headache | 51 (28%) | 62 (34%) | 54 (29%) | 53 (29%) | 220 (30%) |
| Infection | 32 (17%) | 39 (22%) | 38 (20%) | 40 (22%) | 149 (20%) |
| Injury Accidental | 5 (3%) | 10 (6%) | 5 (3%) | 5 (3%) | 25 (3%) |
| Pain | 47 (26%) | 37 (21%) | 49 (26%) | 44 (24%) | 177 (24%) |
| Pain Back | 18 (10%) | 29 (16%) | 28 (15%) | 27 (15%) | 102 (14%) |
| Withdrawal Syndrome | 45 (24%) | 40 (22%) | 41 (22%) | 36 (20%) | 162 (22%) |
| Digestive System | |||||
| Constipation | 10 (5%) | 23 (13%) | 23 (12%) | 26 (14%) | 82 (11%) |
| Diarrhea | 19 (10%) | 8 (4%) | 9 (5%) | 4 (2%) | 40 (5%) |
| Dyspepsia | 6 (3%) | 10 (6%) | 4 (2%) | 4 (2%) | 24 (3%) |
| Nausea | 12 (7%) | 22 (12%) | 23 (12%) | 18 (10%) | 75 (10%) |
| Vomiting | 8 (4%) | 6 (3%) | 10 (5%) | 14 (8%) | 38 (5%) |
| Nervous System | |||||
| Anxiety | 22 (12%) | 24 (13%) | 20 (11%) | 25 (14%) | 91 (12%) |
| Depression | 24 (13%) | 16 (9%) | 25 (13%) | 18 (10%) | 83 (11%) |
| Dizziness | 4 (2%) | 9 (5%) | 7 (4%) | 11 (6%) | 31 (4%) |
| Insomnia | 42 (23%) | 50 (28%) | 43 (23%) | 51 (28%) | 186 (25%) |
| Nervousness | 12 (7%) | 11 (6%) | 10 (5%) | 13 (7%) | 46 (6%) |
| Somnolence | 5 (3%) | 13 (7%) | 9 (5%) | 11 (6%) | 38 (5%) |
| Respiratory System | |||||
| Cough Increase | 5 (3%) | 11 (6%) | 6 (3%) | 4 (2%) | 26 (4%) |
| Pharyngitis | 6 (3%) | 7 (4%) | 6 (3%) | 9 (5%) | 28 (4%) |
| Rhinitis | 27 (15%) | 16 (9%) | 15 (8%) | 21 (12%) | 79 (11%) |
| Skin and Appendages | |||||
| Sweat | 23 (13%) | 21 (12%) | 20 (11%) | 23 (13%) | 87 (12%) |
| Special Senses | |||||
| Runny Eyes | 13 (7%) | 9 (5%) | 6 (3%) | 6 (3%) | 34 (5%) |
The most frequently reported post-marketing adverse event not observed in clinical trials was peripheral edema.
Buprenorphine is metabolized to norbuprenorphine primarily by cytochrome CYP3A4; therefore, potential interactions may occur when buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are given concurrently with agents that affect CYP3A4 activity. The concomitant use of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets with CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., azole antifungals such as ketoconazole, macrolide antibiotics such as erythromycin, and HIV protease inhibitors) should be monitored and may require dose-reduction of one or both agents.
The interaction of buprenorphine with CYP3A4 inducers has not been studied; therefore, it is recommended that patients receiving buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets be monitored for signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal if inducers of CYP3A4 (e.g., efavirenz, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin) are co-administered [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
Three classes of antiretroviral agents have been evaluated for CYP3A4 interactions with buprenorphine. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) do not appear to induce or inhibit the P450 enzyme pathway, thus no interactions with buprenorphine are expected. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) are metabolized principally by CYP3A4. Efavirenz, nevirapine and etravirine are known CYP3A inducers whereas delaviridine is a CYP3A inhibitor. Significant pharmacokinetic interactions between NNRTIs (e.g., efavirenz and delavirdine) and buprenorphine have been shown in clinical studies, but these pharmacokinetic interactions did not result in any significant pharmacodynamic effects. It is recommended that patients who are on chronic buprenorphine treatment have their dose monitored if NNRTIs are added to their treatment regimen. Studies have shown some antiretroviral protease inhibitors (PIs) with CYP3A4 inhibitory activity (nelfinavir, lopinavir/ritonavir, ritonavir) have little effect on buprenorphine pharmacokinetic and no significant pharmacodynamic effects. Other PIs with CYP3A4 inhibitory activity (atazanavir and atazanavir/ritonavir) resulted in elevated levels of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine and patients in one study reported increased sedation. Symptoms of opioid excess have been found in post-marketing reports of patients receiving buprenorphine and atazanavir with and without ritonavir concomitantly. Monitoring of patients taking buprenorphine and atazanavir with and without ritonavir is recommended, and dose reduction of buprenorphine may be warranted.
There have been a number of post-marketing reports regarding coma and death associated with the concomitant use of buprenorphine and benzodiazepines. In many, but not all of these cases, buprenorphine was misused by self-injection. Preclinical studies have shown that the combination of benzodiazepines and buprenorphine altered the usual ceiling effect on buprenorphine-induced respiratory depression, making the respiratory effects of buprenorphine appear similar to those of full opioid agonists. Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets should be prescribed with caution to patients taking benzodiazepines or other drugs that act on the CNS, regardless of whether these drugs are taken on the advice of a physician or are being abused/misused. Patients should be warned that it is extremely dangerous to self-administer non-prescribed benzodiazepines while taking buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, and should also be cautioned to use benzodiazepines concurrently with buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets only as directed by their physician.
Pregnancy Category C.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets or buprenorphine/naloxone in pregnant women. Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Effects on embryo-fetal development were studied in Sprague-Dawley rats and Russian white rabbits following oral (1:1) and intramuscular (IM) (3:2) administration of mixtures of buprenorphine and naloxone. Following oral administration to rats and rabbits, no teratogenic effects were observed at buprenorphine doses up to 250 mg/kg/day and 40 mg/kg/day, respectively (estimated exposure approximately 150 times and 50 times, respectively, the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m² basis). No definitive drug-related teratogenic effects were observed in rats and rabbits at IM doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure approximately 20 times and 35 times, respectively, the recommended human daily dose of 16 mg on a mg/m² basis). Acephalus was observed in one rabbit fetus from the low-dose group and omphalocele was observed in two rabbit fetuses from the same litter in the mid-dose group; no findings were observed in fetuses from the high-dose group. Following oral administration of buprenorphine to rats, dose-related post-implantation losses, evidenced by increases in the numbers of early resorptions with consequent reductions in the numbers of fetuses, were observed at doses of 10 mg/kg/day or greater (estimated exposure approximately 6 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m² basis). In the rabbit, increased post-implantation losses occurred at an oral dose of 40 mg/kg/day. Following IM administration in the rat and the rabbit, post-implantation losses, as evidenced by decreases in live fetuses and increases in resorptions, occurred at 30 mg/kg/day.
Buprenorphine was not teratogenic in rats or rabbits after IM or subcutaneous (SC) doses up to 5 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure was approximately 3 and 6 times, respectively, the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m2 basis), after IV doses up to 0.8 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure was approximately 0.5 times and equal to, respectively, the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m2 basis), or after oral doses up to 160 mg/kg/day in rats (estimated exposure was approximately 95 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m2 basis) and 25 mg/kg/day in rabbits (estimated exposure was approximately 30 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m2 basis). Significant increases in skeletal abnormalities (e.g., extra thoracic vertebra or thoraco-lumbar ribs) were noted in rats after SC administration of 1 mg/kg/day and up (estimated exposure was approximately 0.6 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m2 basis), but were not observed at oral doses up to 160 mg/kg/day. Increases in skeletal abnormalities in rabbits after IM administration of 5 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure was approximately 6 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m2 basis) or oral administration of 1 mg/kg/day or greater (estimated exposure was approximately equal to the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m2 basis) were not statistically significant.
In rabbits, buprenorphine produced statistically significant pre-implantation losses at oral doses of 1 mg/kg/day or greater and post-implantation losses that were statistically significant at IV doses of 0.2 mg/kg/day or greater (estimated exposure approximately 0.3 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m2 basis).
Dystocia was noted in pregnant rats treated intramuscularly with buprenorphine 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 3 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m² basis). Fertility, peri-, and postnatal development studies with buprenorphine in rats indicated increases in neonatal mortality after oral doses of 0.8 mg/kg/day and up (approximately 0.5 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m² basis), after IM doses of 0.5 mg/kg/day and up (approximately 0.3 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m² basis), and after SC doses of 0.1 mg/kg/day and up (approximately 0.06 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m² basis). Delays in the occurrence of righting reflex and startle response were noted in rat pups at an oral dose of 80 mg/kg/day (approximately 50 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m² basis).
Buprenorphine passes into breast milk. Breast-feeding is not advised in mothers treated with buprenorphine products.
An apparent lack of milk production during general reproduction studies with buprenorphine in rats caused decreased viability and lactation indices.
The safety and effectiveness of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets have not been established in pediatric patients.
Clinical studies of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, or buprenorphine HCl sublingual tablets did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they responded differently than younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of buprenorphine and naloxone is unknown. Since both drugs are extensively metabolized, the plasma levels will be expected to be higher in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment. However, it is not known whether both drugs are affected to the same degree. Therefore, dosage should be adjusted and patients should be watched for signs and symptoms of precipitated opioid withdrawal.
No differences in buprenorphine pharmacokinetics were observed between 9 dialysis-dependent and 6 normal patients following IV administration of 0.3 mg buprenorphine. The effects of renal failure on naloxone pharmacokinetics are unknown.
Buprenorphine is a Schedule III narcotic under the Controlled Substances Act.
Under the Drug Addiction Treatment Act (DATA) codified at 21 U.S.C. 823(g), prescription use of this product in the treatment of opioid dependence is limited to physicians who meet certain qualifying requirements, and who have notified the Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS) of their intent to prescribe this product for the treatment of opioid dependence and have been assigned a unique identification number that must be included on every prescription.
Buprenorphine, like morphine and other opioids, has the potential for being abused and is subject to criminal diversion. This should be considered when prescribing or dispensing buprenorphine in situations when the clinician is concerned about an increased risk of misuse, abuse, or diversion. Healthcare professionals should contact their state professional licensing board or state controlled substances authority for information on how to prevent and detect abuse or diversion of this product.
Patients who continue to misuse, abuse, or divert buprenorphine products or other opioids should be provided with, or referred to, more intensive and structured treatment.
Abuse of buprenorphine poses a risk of overdose and death. This risk is increased with the abuse of buprenorphine and alcohol and other substances, especially benzodiazepines.
The physician may be able to more easily detect misuse or diversion by maintaining records of medication prescribed including date, dose, quantity, frequency of refills, and renewal requests of medication prescribed.
Proper assessment of the patient, proper prescribing practices, periodic reevaluation of therapy, and proper handling and storage of the medication are appropriate measures that help to limit abuse of opioid drugs.
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu-opioid receptor and chronic administration produces physical dependence of the opioid type, characterized by moderate withdrawal signs and symptoms upon abrupt discontinuation or rapid taper. The withdrawal syndrome is typically milder than seen with full agonists and may be delayed in onset [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
A neonatal withdrawal syndrome has been reported in the infants of women treated with buprenorphine during pregnancy. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
The manifestations of acute overdose include pinpoint pupils, sedation, hypotension, respiratory depression, and death.
In the event of overdose, the respiratory and cardiac status of the patient should be monitored carefully. When respiratory or cardiac functions are depressed, primary attention should be given to the re-establishment of adequate respiratory exchange through provision of a patent airway and institution of assisted or controlled ventilation. Oxygen, IV fluids, vasopressors, and other supportive measures should be employed as indicated.
In the case of overdose, the primary management should be the re-establishment of adequate ventilation with mechanical assistance of respiration, if required. Naloxone may be of value for the management of buprenorphine overdose. Higher than normal doses and repeated administration may be necessary. The long duration of action of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets should be taken into consideration when determining the length of treatment and medical surveillance needed to reverse the effects of an overdose. Insufficient duration of monitoring may put patients at risk.
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are uncoated white to off-white, round tablets, debossed with on one side and a numeric imprint identifying the product and strength on the other side. It contains buprenorphine HCl, a mu-opioid receptor partial agonist and a kappa-opioid receptor antagonist, and naloxone HCl dihydrate, an opioid receptor antagonist, at a ratio of 4:1 (ratio of free bases). It is intended for sublingual administration and is available in two dosage strengths, 2 mg buprenorphine with 0.5 mg naloxone and 8 mg buprenorphine with 2 mg naloxone. Each sublingual tablet also contains citric acid anhydrous, crospovidone, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, mannitol, N&A lemon FL, pregelatinized starch (maize), povidone, sodium citrate, and sucralose micronized.
Chemically, buprenorphine HCl is (2S)-2-[17-Cyclopropylmethyl-4,5α-epoxy-3-hydroxy-6-methoxy-6α,14-ethano-14α-morphinan-7α-yl]-3,3dimethylbutan-2-ol hydrochloride. It has the following chemical structure:
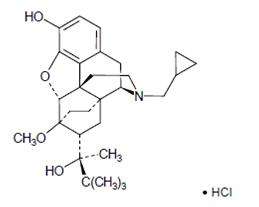
Buprenorphine HCl has the molecular formula C29 H41 NO4 • HCl and the molecular weight is 504.10. It is a white or off-white crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water, freely soluble in methanol, soluble in alcohol, and practically insoluble in cyclohexane.
Chemically, naloxone HCl dihydrate is 17-Allyl-4, 5 α -epoxy-3, 14-dihydroxymorphinan-6-one hydrochloride dihydrate. It has the following chemical structure:
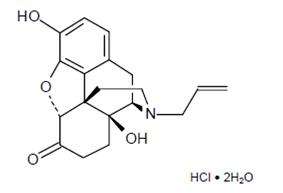
Naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate has the molecular formula C19H21NO4 • HCl • 2H2O and the molecular weight is 399.87. It is a white to slightly off-white powder and is freely soluble in water, soluble in alcohol, and practically insoluble in toluene and ether.
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets contain buprenorphine and naloxone. Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu-opioid receptor and an antagonist at the kappa-opioid receptor. Naloxone is a potent antagonist at mu-opioid receptors and produces opioid withdrawal signs and symptoms in individuals physically dependent on full opioid agonists when administered parenterally.
Subjective Effects:
Comparisons of buprenorphine to full opioid agonists such as methadone and hydromorphone suggest that sublingual buprenorphine produces typical opioid agonist effects which are limited by a ceiling effect.
In opioid-experienced subjects who were not physically dependent, acute sublingual doses of buprenorphine/naloxone tablets produced opioid agonist effects which reached a maximum between doses of 8 mg/2 mg and 16 mg/4 mg buprenorphine/naloxone.
Opioid agonist ceiling-effects were also observed in a double-blind, parallel group, dose-ranging comparison of single doses of buprenorphine sublingual solution (1, 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 mg), placebo and a full agonist control at various doses. The treatments were given in ascending dose order at intervals of at least one week to 16 opioid-experienced subjects who were not physically dependent. Both active drugs produced typical opioid agonist effects. For all measures for which the drugs produced an effect, buprenorphine produced a dose-related response. However, in each case, there was a dose that produced no further effect. In contrast, the highest dose of the full agonist control always produced the greatest effects. Agonist objective rating scores remained elevated for the higher doses of buprenorphine (8 to 32 mg) longer than for the lower doses and did not return to baseline until 48 hours after drug administration. The onset of effects appeared more rapidly with buprenorphine than with the full agonist control, with most doses nearing peak effect after 100 minutes for buprenorphine compared to 150 minutes for the full agonist control.
Physiologic Effects:
Buprenorphine in IV (2, 4, 8, 12 and 16 mg) and sublingual (12 mg) doses has been administered to opioid-experienced subjects who were not physically dependent to examine cardiovascular, respiratory, and subjective effects at doses comparable to those used for treatment of opioid dependence. Compared to placebo, there were no statistically significant differences among any of the treatment conditions for blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, O2 saturation, or skin temperature across time. Systolic BP was higher in the 8 mg group than placebo (3-hour AUC values). Minimum and maximum effects were similar across all treatments. Subjects remained responsive to low voice and responded to computer prompts. Some subjects showed irritability, but no other changes were observed.
The respiratory effects of sublingual buprenorphine were compared with the effects of methadone in a double-blind, parallel group, dose ranging comparison of single doses of buprenorphine sublingual solution (1, 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 mg) and oral methadone (15, 30, 45, or 60 mg) in non-dependent, opioid-experienced volunteers. In this study, hypoventilation not requiring medical intervention was reported more frequently after buprenorphine doses of 4 mg and higher than after methadone. Both drugs decreased O2 saturation to the same degree.
Effect of Naloxone:
Physiologic and subjective effects following acute sublingual administration of buprenorphine tablets and buprenorphine/naloxone tablets were similar at equivalent dose levels of buprenorphine. Naloxone had no clinically significant effect when administered by the sublingual route, although blood levels of the drug were measurable. Buprenorphine/naloxone, when administered sublingually to an opioid-dependent cohort, was recognized as an opioid agonist, whereas when administered intramuscularly, combinations of buprenorphine with naloxone produced opioid antagonist actions similar to naloxone. This finding suggests that the naloxone in buprenorphine/naloxone tablets may deter injection of buprenorphine/naloxone tablets by persons with active substantial heroin or other full mu-opioid dependence. However, clinicians should be aware that some opioid-dependent persons, particularly those with a low level of full mu-opioid physical dependence or those whose opioid physical dependence is predominantly to buprenorphine, abuse buprenorphine/naloxone combinations by the intravenous or intranasal route. In methadone-maintained patients and heroin-dependent subjects, IV administration of buprenorphine/naloxone combinations precipitated opioid withdrawal signs and symptoms and was perceived as unpleasant and dysphoric. In morphine-stabilized subjects, intravenously administered combinations of buprenorphine with naloxone produced opioid antagonist and withdrawal signs and symptoms that were ratio-dependent; the most intense withdrawal signs and symptoms were produced by 2:1 and 4:1 ratios, less intense by an 8:1 ratio.
Absorption:
Plasma levels of buprenorphine and naloxone increased with the sublingual dose of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets (Table 3). There was wide inter-patient variability in the sublingual absorption of buprenorphine and naloxone, but within subjects the variability was low. Both Cmax and AUC of buprenorphine increased in a linear fashion with the increase in dose (in the range of 4 mg to 16 mg), although the increase was not directly dose-proportional.
Naloxone did not affect the pharmacokinetics of buprenorphine and both buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl. At the three naloxone doses of 1, 2, and 4 mg, levels above the limit of quantitation (0.05 ng/mL) were not detected beyond 2 hours in seven of eight subjects. In one individual, at the 4 mg dose, the last measurable concentration was at 8 hours. Within each subject (for most of the subjects), across the doses there was a trend toward an increase in naloxone concentrations with increase in dose. Mean peak naloxone levels ranged from 0.11 ng/mL to 0.28 ng/mL in the dose range of 1 to 4 mg.
| Dose | Analyte | Mean | C max | T max | AUC inf | t 1/2 |
| SD | (ng/mL) | (h) | (h•ng/mL) | (h) | ||
| *Naloxone Cmax expressed as pg/mL. Naloxone AUCinf expressed as h•pg/mL | ||||||
| 2 mg/0.5 mg | Buprenorphine | Mean | 0.947 | 1.72 | 8.654 | 33.41 |
| SD | 0.374 | 0.60 | 2.854 | 13.01 | ||
| Norbuprenorphine | Mean | 0.312 | 2.26 | 14.52 | 56.09 | |
| SD | 0.140 | 2.03 | 5.776 | 31.14 | ||
| Naloxone* | Mean | 54.1 | 0.77 | 137.3 | 5.00 | |
| SD | 23.0 | 0.26 | 43.10 | 5.52 | ||
| 8 mg/2 mg | Buprenorphine | Mean | 3.37 | 1.53 | 30.45 | 32.82 |
| SD | 1.80 | 0.66 | 13.03 | 9.81 | ||
| Norbuprenorphine | Mean | 1.40 | 2.17 | 54.91 | 41.96 | |
| SD | 1.08 | 2.63 | 36.01 | 17.92 | ||
| Naloxone* | Mean | 193 | 0.81 | 480.8 | 6.25 | |
| SD | 91.2 | 0.19 | 201.0 | 3.14 | ||
Distribution:
Buprenorphine is approximately 96% protein bound, primarily to alpha and beta globulin.
Naloxone is approximately 45% protein bound, primarily to albumin.
Metabolism:
Buprenorphine undergoes both N-dealkylation to norbuprenorphine and glucuronidation. The N-dealkylation pathway is mediated primarily by the CYP3A4. Norbuprenorphine, the major metabolite, can further undergo glucuronidation. Norbuprenorphine has been found to bind opioid receptors in-vitro; however, it has not been studied clinically for opioid-like activity. Naloxone undergoes direct glucuronidation to naloxone-3-glucuronide as well as N-dealkylation, and reduction of the 6-oxo group.
Elimination:
A mass balance study of buprenorphine showed complete recovery of radiolabel in urine (30%) and feces (69%) collected up to 11 days after dosing. Almost all of the dose was accounted for in terms of buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, and two unidentified buprenorphine metabolites. In urine, most of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine was conjugated (buprenorphine, 1% free and 9.4% conjugated; norbuprenorphine, 2.7% free and 11% conjugated). In feces, almost all of the buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine were free (buprenorphine, 33% free and 5% conjugated; norbuprenorphine, 21% free and 2% conjugated). Based on all studies performed with buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, buprenorphine has a mean elimination half-life from plasma ranging from 24 to 42 hours and naloxone has a mean elimination half-life from plasma ranging from 2 to 12 hours.
Drug-drug Interactions:
CYP3A4 Inhibitors and Inducers: Subjects receiving buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets should be monitored if inhibitors of CYP3A4 such as azole antifungal agents (e.g., ketoconazole), macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin) or HIV protease inhibitors and may require dose-reduction of one or both agents. The interaction of buprenorphine with all CYP3A4 inducers has not been studied, therefore it is recommended that patients receiving buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets be monitored for signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal if inducers of CYP3A4 (e.g., phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin) are co-administered [See Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Buprenorphine has been found to be a CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 inhibitor and its major metabolite, norbuprenorphine, has been found to be a moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor in in-vitro studies employing human liver microsomes. However, the relatively low plasma concentrations of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine resulting from therapeutic doses are not expected to raise significant drug-drug interaction concerns.
Carcinogenicity:
A carcinogenicity study of buprenorphine/naloxone (4:1 ratio of the free bases) was performed in Alderley Park rats. Buprenorphine/naloxone was administered in the diet at doses of approximately 7, 31, and 123 mg/kg/day for 104 weeks (estimated exposure was approximately 4, 18, and 44 times the recommended human sublingual dose of 16 mg/4 mg buprenorphine/naloxone based on buprenorphine AUC comparisons). A statistically significant increase in Leydig cell adenomas was observed in all dose groups. No other drug-related tumors were noted.
Carcinogenicity studies of buprenorphine were conducted in Sprague-Dawley rats and CD-1 mice. Buprenorphine was administered in the diet to rats at doses of 0.6, 5.5, and 56 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure was approximately 0.4, 3, and 35 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m2 basis) for 27 months. As in the buprenorphine/naloxone carcinogenicity study in rat, statistically significant dose-related increases in Leydig cell tumors occurred. In an 86-week study in CD-1 mice, buprenorphine was not carcinogenic at dietary doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure was approximately 30 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m2 basis).
Mutagenicity:
The 4:1 combination of buprenorphine and naloxone was not mutagenic in a bacterial mutation assay (Ames test) using four strains of S. typhimurium and two strains of E. coli. The combination was not clastogenic in an in vitro cytogenetic assay in human lymphocytes or in an IV micronucleus test in the rat.
Buprenorphine was studied in a series of tests utilizing gene, chromosome, and DNA interactions in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Results were negative in yeast (S. cerevisiae) for recombinant, gene convertant, or forward mutations; negative in Bacillus subtilis “rec” assay, negative for clastogenicity in CHO cells, Chinese hamster bone marrow and spermatogonia cells, and negative in the mouse lymphoma L5178Y assay.
Results were equivocal in the Ames test: negative in studies in two laboratories, but positive for frame shift mutation at a high dose (5mg/plate) in a third study. Results were positive in the Green-Tweets (E. coli) survival test, positive in a DNA synthesis inhibition (DSI) test with testicular tissue from mice, for both in vivo and in vitro incorporation of [3H]thymidine, and positive in unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) test using testicular cells from mice.
Impairment of Fertility:
Dietary administration of buprenorphine in the rat at dose levels of 500 ppm or greater (equivalent to approximately 47 mg/kg/day or greater; estimated exposure approximately 28 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m2 basis) produced a reduction in fertility demonstrated by reduced female conception rates. A dietary dose of 100 ppm (equivalent to approximately 10 mg/kg/day; estimated exposure approximately 6 times the recommended human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg on a mg/m2 basis) had no adverse effect on fertility.
Clinical data on the safety and efficacy of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl were derived from studies of buprenorphine sublingual tablet formulations, with and without naloxone, and from studies of sublingual administration of a more bioavailable ethanolic solution of buprenorphine.
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets were studied in 575 patients, buprenorphine HCl sublingual tablets in 1834 patients and buprenorphine sublingual solutions in 2470 patients. A total of 1270 women received buprenorphine in those clinical trials. Dosing recommendations are based on data from one trial of both tablet formulations and two trials of the ethanolic solution. All trials used buprenorphine in conjunction with psychosocial counseling as part of a comprehensive addiction treatment program. There were no clinical studies conducted to assess the efficacy of buprenorphine as the only component of treatment
In a double-blind placebo- and active-controlled study, 326 heroin-addicted subjects were randomly assigned to either buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, 16 mg/4 mg per day; buprenorphine HCl sublingual tablets, 16 mg per day; or placebo sublingual tablets. For subjects randomized to either active treatment, dosing began with one 8 mg buprenorphine HCl on Day 1, followed by 16 mg (two 8 mg tablets) of buprenorphine HCl on Day 2. On Day 3, those randomized to receive buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets were switched to the combination tablet. Subjects randomized to placebo received one placebo tablet on Day 1 and two placebo tablets per day thereafter for four weeks. Subjects were seen daily in the clinic (Monday through Friday) for dosing and efficacy assessments. Take-home doses were provided for weekends. Subjects were instructed to hold the medication under the tongue for approximately 5 to 10 minutes until completely dissolved. Subjects received counseling regarding HIV infection and up to one hour of individualized counseling per week. The primary study comparison was to assess the efficacy of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets and buprenorphine HCl sublingual tablets individually against placebo sublingual tablets. The percentage of thrice-weekly urine samples that were negative for non-study opioids was statistically higher for both buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets and buprenorphine HCl sublingual tablets than for placebo sublingual tablets.
In a double-blind, double-dummy, parallel-group study comparing buprenorphine ethanolic solution to a full agonist active control, 162 subjects were randomized to receive the ethanolic sublingual solution of buprenorphine at 8 mg/day (a dose which is roughly comparable to a dose of 12 mg/3 mg per day of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets or 12 mg per day of buprenorphine HCl sublingual tablets ), or two relatively low doses of active control, one of which was low enough to serve as an alternative to placebo, during a 3 to 10 day induction phase, a 16-week maintenance phase and a 7-week detoxification phase. Buprenorphine was titrated to maintenance dose by Day 3; active control doses were titrated more gradually.
Maintenance dosing continued through Week 17, and then medications were tapered by approximately 20% to 30% per week over Weeks 18 - 24, with placebo dosing for the last two weeks. Subjects received individual and/or group counseling weekly.
Based on retention in treatment and the percentage of thrice-weekly urine samples negative for non-study opioids, buprenorphine was more effective than the low dose of the control, in keeping heroin addicts in treatment and in reducing their use of opioids while in treatment. The effectiveness of buprenorphine, 8 mg per day was similar to that of the moderate active control dose, but equivalence was not demonstrated.
In a dose-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group, 16-week study, 731 subjects were randomized to receive one of four doses of buprenorphine ethanolic solution: 1 mg, 4 mg, 8 mg, and 16 mg. Buprenorphine was titrated to maintenance doses over 1 to 4 days and continued for 16 weeks. Subjects received at least one session of AIDS education and additional counseling ranging from one hour per month to one hour per week, depending on site.
Based on retention in treatment and the percentage of thrice-weekly urine samples negative for non-study opioids, the three highest tested doses were superior to the 1 mg dose. Therefore, this study showed that a range of buprenorphine doses may be effective. The 1 mg dose of buprenorphine sublingual solution can be considered to be somewhat lower than a 2 mg tablet dose. The other doses used in the study encompass a range of tablet doses from approximately 6 mg to approximately 24 mg.
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are available as follows:
2 mg/0.5 mg – Each white to off-white, round tablet debossed with  on one side and 154 on the other side. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 30 (NDC 0228-3154-03) and 90 (NDC 0228-3154-09) with a child-resistant closure.
on one side and 154 on the other side. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 30 (NDC 0228-3154-03) and 90 (NDC 0228-3154-09) with a child-resistant closure.
8 mg/2 mg – Each white to off-white, round tablet debossed with  on one side and 155 on the other side. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 30 (NDC 0228-3155-03) and 90 (NDC 0228-3155-09) with a child-resistant closure.
on one side and 155 on the other side. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 30 (NDC 0228-3155-03) and 90 (NDC 0228-3155-09) with a child-resistant closure.
Store at 20( to 25(C (68( to 77(F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in USP.
CAUTION: DEA Order Form Required.
Patients should be advised to store buprenorphine-containing medications safely and out of sight and reach of children. Destroy any unused medication appropriately [see Disposal of Unused Buprenorphine HCl and Naloxone HCl Sublingual Tablets (17.2)]
Rx only
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide)
Before initiating treatment with buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, explain the points listed below to caregivers and patients. Instruct patients to read the Medication Guide each time buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are dispensed because new information may be available.
- Patients should be warned that it is extremely dangerous to self-administer non-prescribed benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) while taking buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets. Patients prescribed benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants should be cautioned to use them only as directed by their physician. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Interactions (7.3)]
- Patients should be advised that buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tabletscontain an opioid that can be a target for people who abuse prescription medications or street drugs. Patients should be cautioned to keep their tablets in a safe place, and to protect them from theft.
- Patients should be instructed to keep buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tabletsin a secure place, out of the sight and reach of children. Accidental or deliberate ingestion by a child may cause respiratory depression that can result in death. Patients should be advised that if a child is exposed to buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, medical attention should be sought immediately.
- Patients should be advised never to give buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tabletsto anyone else, even if he or she has the same signs and symptoms. It may cause harm or death.
- Patients should be advised that selling or giving away this medication is against the law.
- Patients should be cautioned that buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tabletsmay impair the mental or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially dangerous tasks such as driving or operating machinery. Caution should be taken especially during drug induction and dose adjustment and until individuals are reasonably certain that buprenorphine therapy does not adversely affect their ability to engage in such activities. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Patients should be advised not to change the dosage of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tabletswithout consulting their physician.
- Patients should be advised to take buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tabletsonce a day.
- Patients should be informed that buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tabletscan cause drug dependence and that withdrawal signs and symptoms may occur when the medication is discontinued.
- Patients seeking to discontinue treatment with buprenorphine for opioid dependence should be advised to work closely with their physician on a tapering schedule and should be apprised of the potential to relapse to illicit drug use associated with discontinuation of opioid agonist/partial agonist medication-assisted treatment.
- Patients should be cautioned that, like other opioids, buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tabletsmay produce orthostatic hypotension in ambulatory individuals. [see Warnings and Precautions. (5.12)]
- Patients should inform their physician if any other prescription medications, over-the-counter medications, or herbal preparations are prescribed or currently being used. [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2 and 7.3)]
- Women of childbearing potential, who become pregnant or are planning to become pregnant, should be advised to consult their physician regarding the possible effects of using buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tabletsduring pregnancy. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
- Patients should be warned that buprenorphine passes into breast milk. Breast-feeding is not advised in mothers treated with buprenorphine products. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]
- Patients should inform their family members that, in the event of emergency, the treating physician or emergency room staff should be informed that the patient is physically dependent on an opioid and that the patient is being treated with buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets.
- Refer to the Medication Guide for additional information regarding the counseling information.
Unused buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets should be disposed of as soon as they are no longer needed. Unused tablets should be flushed down the toilet.
Manufactured by:
Actavis Elizabeth LLC
200 Elmora Avenue
Elizabeth, NJ 07207 USA
40-9206
Revised – April 2013
Buprenorphine HCl and Naloxone HCl Dihydrate Sublingual Tablets (CIII)
| IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical emergency and can result in death. If a child accidentally uses buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, get emergency help right away. |
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking to your doctor. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you have questions about buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets.
Share the important information in this Medication Guide with members of your household.
What is the most important information I should know about buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets?
- Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets can cause serious and life-threatening breathing problems. Call your doctor right away or get emergency help if:
- You feel faint, dizzy, or confused
- Your breathing gets much slower than is normal for you
These can be signs of an overdose or other serious problems.
- Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets contain an opioid that can cause physical dependence.
- Do not stop taking buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets without talking to your doctor. You could become sick with uncomfortable withdrawal signs and symptoms because your body has become used to this medicine
- Physical dependence is not the same as drug addiction
- Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are not for occasional or “as needed” use
- An overdose, and even death, can happen if you take benzodiazepines, sedatives, tranquilizers, or alcohol while using buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets. Ask your doctor what you should do if you are taking one of these.
- Call a doctor or get emergency help right away if you:
- Feel sleepy and uncoordinated
- Have blurred vision
- Have slurred speech
- Cannot think well or clearly
- Have slowed reflexes and breathing
- Do not inject (“shoot-up”) buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets.
- Injecting this medicine may cause life-threatening infections and other serious health problems.
- Injecting buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets may cause serious withdrawal symptoms such as pain, cramps, vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety, sleep problems, and cravings.
- In an emergency, have family members tell the emergency department staff that you are physically dependent on an opioid and are being treated with buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets.
What are buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets?
- Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are a prescription medicine used to treat adults who are addicted to (dependent on) opioid drugs (either prescription or illegal); as part of a complete treatment program that also includes counseling and behavioral therapy.
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are a controlled substance (CIII) because they contain buprenorphine, which can be a target for people who abuse prescription medicines or street drugs. Keep your buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets in a safe place to protect them from theft. Never give your buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets to anyone else; they can cause death or harm them. Selling or giving away this medicine is against the law. - It is not known if buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are safe or effective in children.
Who should not take buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets?
Do not take buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets if you are allergic to buprenorphine or naloxone.
What should I tell my doctor before taking buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets?
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets may not be right for you. Before taking buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, tell your doctor if you:
- Have trouble breathing or lung problems
- Have an enlarged prostate gland (men)
- Have a head injury or brain problem
- Have problems urinating
- Have a curve in your spine that affects your breathing
- Have liver or kidney problems
- Have gallbladder problems
- Have adrenal gland problems
- Have Addison’s disease
- Have low thyroid (hypothyroidism)
- Have a history of alcoholism
- Have mental problems such as hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that are not there)
- Have any other medical condition
- Are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets will harm your unborn baby. If you take buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets while pregnant, your baby may have symptoms of withdrawal at birth. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- Are breast feeding or plan to breast feed. Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl can pass into your milk and may harm the baby. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets. Breast feeding is not recommended while taking buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets may affect the way other medicines work and other medicines may affect how buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets work. Some medicines may cause serious or life-threatening medical problems when taken with buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets.
Sometimes the doses of certain medicines and buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets may need to be changed if used together. Do not take any medicine while using buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets until you have talked with your doctor. Your doctor will tell you if it is safe to take other medicines while you are using buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets.
Be especially careful about taking other medicines that may make you sleepy, such as pain medicines, tranquilizers, antidepressant medicines, sleeping pills, anxiety medicines or antihistamines.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor or pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How should I take buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets?
- Always take buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets exactly as your doctor tells you. Your doctor may change your dose after seeing how it affects you. Do not change your dose unless your doctor tells you to change it.
- Do not take buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets more often than prescribed by your doctor.
- If you are prescribed a dose of 2 or more buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets at the same time:
- Ask your doctor for instructions on the right way to take buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets
- Follow the same instructions every time you take a dose of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets
- Put the tablets under your tongue. Let them dissolve completely.
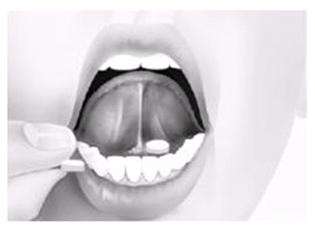
- While buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are dissolving, do not chew or swallow the tablets because the medicine will not work as well.
- Talking while the tablets are dissolving can affect how well the medicine in buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets are absorbed.
- If you miss a dose of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, take your medicine when you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take 2 doses at the same time unless your doctor tells you to. If you are not sure about your dosing, call your doctor.
- Do not stop taking buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets suddenly. You could become sick and have withdrawal symptoms because your body has become used to the medicine. Physical dependence is not the same as drug addiction. Your doctor can tell you more about the differences between physical dependence and drug addiction. To have fewer withdrawal symptoms, ask your doctor how to stop using buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets the right way.
- If you take too many buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets or overdose, call Poison Control or get emergency medical help right away.
What should I avoid while taking buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets?
- Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or perform any other dangerous activities until you know how this medication affects you. Buprenorphine can cause drowsiness and slow reaction times. This may happen more often in the first few weeks of treatment when your dose is being changed, but can also happen if you drink alcohol or take other sedative drugs when you take buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets.
- You should not drink alcohol while using buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets, as this can lead to loss of consciousness or even death.
What are the possible side effects of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets?
Buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets can cause serious side effects including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets?”
- Respiratory problems. You have a higher risk of death and coma if you take buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets with other medicines, such as benzodiazepines.
- Sleepiness, dizziness, and problems with coordination
- Dependency or abuse
- Liver problems. Call your doctor right away if you notice any of these signs of liver problems: Your skin or the white part of your eyes turning yellow (jaundice), urine turning dark, stools turning light in color, you have less of an appetite, or you have stomach (abdominal) pain or nausea. Your doctor should do tests before you start taking and while you take buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets.
- Allergic reaction. You may have a rash, hives, swelling of your face, wheezing, or loss of blood pressure and consciousness. Call a doctor or get emergency help right away.
- Opioid withdrawal. This can include: shaking, sweating more than normal, feeling hot or cold more than normal, runny nose, watery eyes, goose bumps, diarrhea, vomiting and muscle aches. Tell your doctor if you develop any of these symptoms.
- Decrease in blood pressure. You may feel dizzy if you get up too fast from sitting or lying down.
Common side effects of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets include:
- Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Increased sweating
- Constipation
- Drug withdrawal syndrome
- Decrease in sleep (insomnia)
- Pain
- Swelling of the extremities
Tell your doctor about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets?
- Store buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets at room temperature.
- Keep buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets in a safe place, out of the sight and reach of children.
How should I dispose of unused buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets?
- Dispose of unused buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets as soon as you no longer need them.
- Flush unused tablets down the toilet.
General information about the safe and effective use of buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets for a condition for which they were not prescribed. Do not give buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them and it is against the law.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about buprenorphine HCl and naloxone HCl sublingual tablets. If you would like more information, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information that is written for healthcare professionals. For more information, call Actavis at 1-800-432-8534.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Actavis Elizabeth LLC
200 Elmora Avenue
Elizabeth, NJ 07207 USA
40-9206
(MG 41-1155/0213)


Buprenorphine hydrochloride and naloxone hydrochloride dihydrateBuprenorphine hydrochloride and naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Buprenorphine hydrochloride and naloxone hydrochloride dihydrateBuprenorphine hydrochloride and naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||