Carbidopa and Levodopa
Carbidopa and Levodopa Tablets USP
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA DESCRIPTION
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets USP are a combination of carbidopa and levodopa for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and syndrome.
Carbidopa, an inhibitor of aromatic amino acid decarboxylation, is a white to yellowish white, crystalline compound or creamy white powder, slightly soluble in water, with a molecular weight of 244.24. It is designated chemically as (-)-L-α-hydrazino-α-methyl-β-(3,4-dihydroxybenzene) propanoic acid monohydrate. Its molecular formula is C10H14N2O4•H20, and its structural formula is:
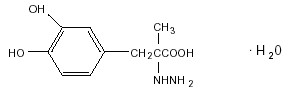
Tablet content is expressed in terms of anhydrous carbidopa, which has a molecular weight of 226.23.
Levodopa, an aromatic amino acid, is a white to slightly off-white, crystalline powder, slightly soluble in water, with a molecular weight of 197.19. It is designated chemically as (-)-L-α-amino-β-(3,4-dihydroxybenzene) propanoic acid. Its molecular formula is C9H11NO4, and its structural formula is:

Carbidopa and Levodopa Tablets USP are supplied in three strengths:
Carbidopa and Levodopa Tablets USP 25 mg/100 mg, containing 25 mg of carbidopa and 100 mg of levodopa.
Carbidopa and Levodopa Tablets USP 25 mg/250 mg, containing 25 mg of carbidopa and 250 mg of levodopa.
In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients:
25 mg/100 mg - Corn starch, D&C yellow #10 aluminum lake, FD&C yellow #6 aluminum lake (sunset yellow lake), magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and pregelatinized starch
25 mg/250 mg - Corn starch, FD&C blue #2 aluminum lake, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and pregelatinized starch.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Parkinson's disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disorder of the extrapyramidal nervous system affecting the mobility and control of the skeletal muscular system. Its characteristic features include resting tremor, rigidity, and bradykinetic movements. Symptomatic treatments, such as levodopa therapies, may permit the patient better mobility.
Current evidence indicates that symptoms of Parkinson's disease are related to depletion of dopamine in the corpus striatum. Administration of dopamine is ineffective in the treatment of Parkinson's disease apparently because it does not cross the blood-brain barrier. However, levodopa, the metabolic precursor of dopamine, does cross the blood-brain barrier, and presumably is converted to dopamine in the brain. This is thought to be the mechanism whereby levodopa relieves symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
When levodopa is administered orally it is rapidly decarboxylated to dopamine in extracerebral tissues so that only a small portion of a given dose is transported unchanged to the central nervous system. For this reason, large doses of levodopa are required for adequate therapeutic effect and these may often be accompanied by nausea and other adverse reactions, some of which are attributable to dopamine formed in extracerebral tissues.
Since levodopa competes with certain amino acids for transport across the gut wall, the absorption of levodopa may be impaired in some patients on a high protein diet.
Carbidopa inhibits decarboxylation of peripheral levodopa. It does not cross the blood-brain barrier and does not affect the metabolism of levodopa within the central nervous system.
The incidence of levodopa-induced nausea and vomiting is less with carbidopa and levodopa tablets than with levodopa. In many patients, this reduction in nausea and vomiting will permit more rapid dosage titration.
Since its decarboxylase inhibiting activity is limited to extracerebral tissues, administration of carbidopa with levodopa makes more levodopa available for transport to the brain.
Carbidopa reduces the amount of levodopa required to produce a given response by about 75 percent and, when administered with levodopa, increases both plasma levels and the plasma half-life of levodopa, and decreases plasma and urinary dopamine and homovanillic acid.
The plasma half-life of levodopa is about 50 minutes, without carbidopa. When carbidopa and levodopa are administered together, the half-life of levodopa is increased to about 1.5 hours. At steady-state, the bioavailability of carbidopa from carbidopa and levodopa tablets is approximately 99% relative to the concomitant administration of carbidopa and levodopa.
In clinical pharmacologic studies, simultaneous administration of carbidopa and levodopa produced greater urinary excretion of levodopa in proportion to the excretion of dopamine than administration of the two drugs at separate times.
Pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B6), in oral doses of 10 mg to 25 mg, may reverse the effects of levodopa by increasing the rate of aromatic amino acid decarboxylation. Carbidopa inhibits this action of pyridoxine; therefore, carbidopa and levodopa tablets can be given to patients receiving supplemental pyridoxine (vitamin B6).
CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets are indicated in the treatment of the symptoms of idiopathic Parkinson's disease (paralysis agitans), post-encephalitic parkinsonism, and symptomatic parkinsonism which may follow injury to the nervous system by carbon monoxide intoxication and/or manganese intoxication.
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets are indicated in these conditions to permit the administration of lower doses of levodopa with reduced nausea and vomiting, with more rapid dosage titration, with a somewhat smoother response, and with supplemental pyridoxine (vitamin B6).
In some patients a somewhat smoother antiparkinsonian effect results from therapy with carbidopa and levodopa tablets than with levodopa. However, patients with markedly irregular ("on-off") responses to levodopa have not been shown to benefit from carbidopa and levodopa tablets.
Although the administration of carbidopa permits control of parkinsonism and Parkinson's disease with much lower doses of levodopa, there is no conclusive evidence at present that this is beneficial other than in reducing nausea and vomiting, permitting more rapid titration, and providing a somewhat smoother response to levodopa.
Certain patients who responded poorly to levodopa have improved when carbidopa and levodopa tablets were substituted. This is most likely due to decreased peripheral decarboxylation of levodopa which results from administration of carbidopa rather than to a primary effect of carbidopa on the nervous system. Carbidopa has not been shown to enhance the intrinsic efficacy of levodopa in parkinsonian syndromes.
In considering whether to give carbidopa and levodopa tablets to patients already on levodopa who have nausea and/or vomiting, the practitioner should be aware that, while many patients may be expected to improve, some do not. Since one cannot predict which patients are likely to improve, this can only be determined by a trial of therapy.
It should be further noted that in controlled trials comparing carbidopa and levodopa tablets with levodopa, about half of the patients with nausea and/or vomiting on levodopa improved spontaneously despite being retained on the same dose of levodopa during the controlled portion of the trial.
CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA CONTRAINDICATIONS
Nonselective monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors are contraindicated for use with carbidopa and levodopa tablets. These inhibitors must be discontinued at least two weeks prior to initiating therapy with carbidopa and levodopa tablets. Carbidopa and levodopa tablets may be administered concomitantly with the manufacturer's recommended dose of an MAO inhibitor with selectivity for MAO type B (e.g., selegiline HCl) (see PRECAUTIONS , Drug Interactions ).
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any component of this drug, and in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma.
Because levodopa may activate a malignant melanoma, carbidopa and levodopa tablets should not be used in patients with suspicious, undiagnosed skin lesions or a history of melanoma.
WARNINGS
When carbidopa and levodopa tablets are to be given to patients who are being treated with levodopa, levodopa must be discontinued at least twelve hours before therapy with carbidopa and levodopa tablets is started. In order to reduce adverse reactions, it is necessary to individualize therapy. See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section before initiating therapy.
The addition of carbidopa with levodopa in the form of carbidopa and levodopa tablets reduces the peripheral effects (nausea, vomiting) due to decarboxylation of levodopa; however, carbidopa does not decrease the adverse reactions due to the central effects of levodopa. Because carbidopa permits more levodopa to reach the brain and more dopamine to be formed, certain adverse CNS effects, e.g., dyskinesias (involuntary movements), may occur at lower dosages and sooner with carbidopa and levodopa tablets than with levodopa alone.
Levodopa alone, as well as carbidopa and levodopa tablets, is associated with dyskinesias. The occurrence of dyskinesias may require dosage reduction.
As with levodopa, carbidopa and levodopa tablets may cause mental disturbances. These reactions are thought to be due to increased brain dopamine following administration of levodopa. All patients should be observed carefully for the development of depression with concomitant suicidal tendencies. Patients with past or current psychoses should be treated with caution.
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets should be administered cautiously to patients with severe cardiovascular or pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma, renal, hepatic or endocrine disease.
As with levodopa, care should be exercised in administering carbidopa and levodopa tablets to patients with a history of myocardial infarction who have residual atrial, nodal, or ventricular arrhythmias.
In such patients, cardiac function should be monitored with particular care during the period of initial dosage adjustment, in a facility with provisions for intensive cardiac care.As with levodopa, treatment with carbidopa and levodopa tablets may increase the possibility of upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage in patients with a history of peptic ulcer.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS): Sporadic cases of a symptom complex resembling NMS have been reported in association with dose reductions or withdrawal of therapy with carbidopa and levodopa tablets. Therefore, patients should be observed carefully when the dosage of carbidopa and levodopa tablets is reduced abruptly or discontinued, especially if the patient is receiving neuroleptics.
NMS is an uncommon but life-threatening syndrome characterized by fever or hyperthermia. Neurological findings, including muscle rigidity, involuntary movements, altered consciousness, mental status changes; other disturbances, such as autonomic dysfunction, tachycardia, tachypnea, sweating, hyper- or hypotension; laboratory findings, such as creatine phosphokinase elevation, leukocytosis, myoglobinuria, and increased serum myoglobin have been reported.
The early diagnosis of this condition is important for the appropriate management of these patients. Considering NMS as a possible diagnosis and ruling out other acute illnesses (e.g., pneumonia, systemic infection, etc.) is essential. This may be especially complex if the clinical presentation includes both serious medical illness and untreated or inadequately treated extrapyramidal signs and symptoms (EPS). Other important considerations in the differential diagnosis include central anticholinergic toxicity, heat stroke, drug fever, and primary central nervous system (CNS) pathology.
The management of NMS should include: 1) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring and 2) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available.
Dopamine agonists, such as bromocriptine, and muscle relaxants, such as dantrolene, are often used in the treatment of NMS, however, their effectiveness has not been demonstrated in controlled studies.
PRECAUTIONS
General
As with levodopa, periodic evaluations of hepatic, hematopoietic, cardiovascular, and renal function are recommended during extended therapy.
Patients with chronic wide-angle glaucoma may be treated cautiously with carbidopa and levodopa tablets provided the intraocular pressure is well controlled and the patient is monitored carefully for changes in intraocular pressure during therapy.
The patient should be informed that carbidopa and levodopa tablets are an immediate-release formulation of carbidopa-levodopa that is designed to begin release of ingredients within 30 minutes. It is important that carbidopa and levodopa tablets be taken at regular intervals according to the schedule outlined by the physician. The patient should be cautioned not to change the prescribed dosage regimen and not to add any additional antiparkinson medications, including other carbidopa-levodopa preparations, without first consulting the physician.
Patients should be advised that sometimes a 'wearing-off' effect may occur at the end of the dosing interval. The physician should be notified if such response poses a problem to life-style.
Patients should be advised that occasionally, dark color (red, brown, or black) may appear in saliva, urine, or sweat after ingestion of carbidopa and levodopa tablets. Although the color appears to be clinically insignificant, garments may become discolored.
The patient should be advised that a change in diet to foods that are high in protein may delay the absorption of levodopa and may reduce the amount taken up in the circulation.
Excessive acidity also delays stomach emptying, thus delaying the absorption of levodopa. Iron salts (such as in multi-vitamin tablets) may also reduce the amount of levodopa available to the body. The above factors may reduce the clinical effectiveness of the levodopa or carbidopa-levodopa therapy.
NOTE: The suggested advice to patients being treated with carbidopa and levodopa tablets is intended to aid in the safe and effective use of this medication. It is not a disclosure of all possible adverse or intended effects.
Laboratory Tests
Abnormalities in laboratory tests may include elevations of liver function tests such as alkaline phosphatase, SGOT (AST), SGPT (ALT), lactic dehydrogenase, and bilirubin. Abnormalities in blood urea nitrogen and positive Coombs test have also been reported. Commonly, levels of blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, and uric acid are lower during administration of carbidopa and levodopa tablets than with levodopa.
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets may cause a false-positive reaction for urinary ketone bodies when a test tape is used for determination of ketonuria. This reaction will not be altered by boiling the urine specimen. False-negative tests may result with the use of glucose-oxidase methods of testing for glucosuria.
Cases of falsely diagnosed pheochromocytoma in patients on carbidopa-levodopa therapy have been reported very rarely. Caution should be exercised when interpreting the plasma and urine levels of catecholamines and their metabolites in patients on levodopa or carbidopa-levodopa therapy.
Drug Interactions
Caution should be exercised when the following drugs are administered concomitantly with carbidopa and levodopa tablets.
Symptomatic postural hypotension has occurred when carbidopa and levodopa tablets were added to the treatment of a patient receiving antihypertensive drugs. Therefore, when therapy with carbidopa and levodopa tablets is started, dosage adjustment of the antihypertensive drug may be required.
For patients receiving MAO inhibitors (Type A or B), see CONTRAINDICATIONS . Concomitant therapy with selegiline and carbidopa-levodopa may be associated with severe orthostatic hypotension not attributable to carbidopa-levodopa alone (see CONTRAINDICATIONS ).
There have been rare reports of adverse reactions, including hypertension and dyskinesia, resulting from the concomitant use of tricyclic antidepressants and carbidopa and levodopa tablets.
Dopamine D2 receptor antagonists (e.g., phenothiazines, butyrophenones, risperidone) and isoniazid may reduce the therapeutic effects of levodopa. In addition, the beneficial effects of levodopa in Parkinson's disease have been reported to be reversed by phenytoin and papaverine. Patients taking these drugs with carbidopa and levodopa Tablets should be carefully observed for loss of therapeutic response. Iron salts may reduce the bioavailability of levodopa and carbidopa. The clinical relevance is unclear. Although metoclopramide may increase the bioavailability of levodopa by increasing gastric emptying, metoclopramide may also adversely affect disease control by its dopamine receptor antagonistic properties.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a two-year bioassay of carbidopa and levodopa tablets, no evidence of carcinogenicity was found in rats receiving doses of approximately two times the maximum daily human dose of carbidopa and four times the maximum daily human dose of levodopa.
In reproduction studies with carbidopa and levodopa tablets, no effects on fertility were found in rats receiving doses of approximately two times the maximum daily human dose of carbidopa and four times the maximum daily human dose of levodopa.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. No teratogenic effects were observed in a study in mice receiving up to 20 times the maximum recommended human dose of carbidopa and levodopa tablets. There was a decrease in the number of live pups delivered by rats receiving approximately two times the maximum recommended human dose of carbidopa and approximately five times the maximum recommended human dose of levodopa during organogenesis. Carbidopa and levodopa tablets caused both visceral and skeletal malformations in rabbits at all doses and ratios of carbidopa/levodopa tested, which ranged from 10 times/5 times the maximum recommended human dose of carbidopa/levodopa to 20 times/10 times the maximum recommended human dose of carbidopa/levodopa.
There are no adequate or well-controlled studies in pregnant women. It has been reported from individual cases that levodopa crosses the human placental barrier, enters the fetus, and is metabolized. Carbidopa concentrations in fetal tissue appeared to be minimal. Use of carbidopa and levodopa tablets in women of child-bearing potential requires that the anticipated benefits of the drug be weighed against possible hazards to mother and child.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when carbidopa and levodopa tablets are administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. Use of the drug in patients below the age of 18 is not recommended.
CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions reported with carbidopa and levodopa tablets have included dyskinesias, such as choreiform, dystonic, and other involuntary movements and nausea.
The following other adverse reactions have been reported with carbidopa and levodopa tablets:
Body as a Whole: chest pain, asthenia.
Cardiovascular: cardiac irregularities, hypotension, orthostatic effects including orthostatic hypotension, hypertension, syncope, phlebitis, palpitation.
Gastrointestinal: dark saliva, gastrointestinal bleeding, development of duodenal ulcer, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, dyspepsia, dry mouth, taste alterations.
Hematologic: agranulocytosis, hemolytic and non-hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia.
Hypersensitivity: angioedema, urticaria, pruritus, Henoch-Schonlein purpura, bullous lesions (including pemphigus-like reactions).
Musculoskeletal: back pain, shoulder pain, muscle cramps.
Nervous System/Psychiatric: psychotic episodes including delusions, hallucinations, and paranoid ideation, neuroleptic malignant syndrome (see WARNINGS ), bradykinetic episodes ("on-off" phenomenon), confusion, agitation, dizziness, somnolence, dream abnormalities including nightmares, insomnia, paresthesia, headache, depression with or without development of suicidal tendencies, dementia, increased libido. Convulsions also have occurred; however, a causal relationship with carbidopa and levodopa tablets has not been established.
Respiratory: dyspnea, upper respiratory infection.
Skin: rash, increased sweating, alopecia, dark sweat.
Urogenital: urinary tract infection, urinary frequency, dark urine.
Laboratory Tests: decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit; abnormalities in alkaline phosphatase, SGOT (AST), SGPT (ALT), lactic dehydrogenase, bilirubin, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), Coombs test; elevated serum glucose; white blood cells, bacteria, and blood in the urine.
Other adverse reactions that have been reported with levodopa alone and with various carbidopa-levodopa formulations, and may occur with carbidopa and levodopa tablets are:
Body as a Whole: abdominal pain and distress, fatigue.
Cardiovascular: myocardial infarction.
Gastrointestinal: gastrointestinal pain, dysphagia, sialorrhea, flatulence, bruxism, burning sensation of the tongue, heartburn, hiccups.
Metabolic: edema, weight gain, weight loss.
Musculoskeletal: leg pain.
Nervous System/Psychiatric: ataxia, extrapyramidal disorder, falling, anxiety, gait abnormalities, nervousness, decreased mental acuity, memory impairment, disorientation, euphoria, blepharospasm (which may be taken as an early sign of excess dosage; consideration of dosage reduction may be made at this time), trismus, increased tremor, numbness, muscle twitching, activation of latent Horner's syndrome, peripheral neuropathy.
Respiratory: pharyngeal pain, cough.
Skin: malignant melanoma (see also CONTRAINDICATIONS ), flushing.
Special Senses: oculogyric crises, diplopia, blurred vision, dilated pupils.
Urogenital: urinary retention, urinary incontinence, priapism.
Miscellaneous: bizarre breathing patterns, faintness, hoarseness, malaise, hot flashes, sense of stimulation.
Laboratory Tests: decreased white blood cell count and serum potassium; increased serum creatinine and uric acid; protein and glucose in urine.
OVERDOSAGE
Management of acute overdosage with carbidopa and levodopa tablets is the same as management of acute overdosage with levodopa. Pyridoxine is not effective in reversing the actions of carbidopa and levodopa tablets.
General supportive measures should be employed, along with immediate gastric lavage. Intravenous fluids should be administered judiciously and an adequate airway maintained. Electrocardiographic monitoring should be instituted and the patient carefully observed for the development of arrhythmias; if required, appropriate anti-arrhythmic therapy should be given. The possibility that the patient may have taken other drugs as well as carbidopa and levodopa tablets should be taken into consideration. To date, no experience has been reported with dialysis; hence, its value in overdosage is not known.
Based on studies in which high doses of levodopa and/or carbidopa were administered, a significant proportion of rats and mice given single oral doses of levodopa of approximately 1500 to 2000 mg/kg are expected to die.
A significant proportion of infant rats of both sexes are expected to die at a dose of 800 mg/kg. A significant proportion of rats are expected to die after treatment with similar doses of carbidopa. The addition of carbidopa in a 1:10 ratio with levodopa increases the dose at which a significant proportion of mice are expected to die to 3360 mg/kg.
CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The optimum daily dosage of carbidopa and levodopa tablets must be determined by careful titration in each patient.
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets are available in a 1:4 ratio of carbidopa to levodopa (carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP 25 mg/100 mg) as well as 1:10 ratio (carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP 25 mg/250 mg and carbidopa and levodopa lablets, USP 10 mg/100 mg). Tablets of the two ratios may be given separately or combined as needed to provide the optimum dosage.
Studies show that peripheral dopa decarboxylase is saturated by carbidopa at approximately 70 to 100 mg a day. Patients receiving less than this amount of carbidopa are more likely to experience nausea and vomiting.
Dosage is best initiated with one tablet of carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/100 mg three times a day. This dosage schedule provides 75 mg of carbidopa per day. Dosage may be increased by one tablet every day or every other day, as necessary, until a dosage of eight tablets of carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/100 mg a day is reached.
If carbidopa and levodopa tablets10 mg/100 mg is used, dosage may be initiated with one tablet three or four times a day.
However, this will not provide an adequate amount of carbidopa for many patients. Dosage may be increased by one tablet every day or every other day until a total of eight tablets (2 tablets q.i.d.) is reached.
Levodopa must be discontinued at least twelve hours before starting carbidopa and levodopa tablets. A daily dosage of carbidopa and levodopa tablets should be chosen that will provide approximately 25 percent of the previous levodopa dosage. Patients who are taking less than 1500 mg of levodopa a day should be started on one tablet of carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/100 mg three or four times a day. The suggested starting dosage for most patients taking more than 1500 mg of levodopa is one tablet of carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/250 mg three or four times a day
Therapy should be individualized and adjusted according to the desired therapeutic response. At least 70 to 100 mg of carbidopa per day should be provided. When a greater proportion of carbidopa is required, one tablet of carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/100 mg may be substituted for each tablet of carbidopa and levodopa 10 mg/100 mg. When more levodopa is required, carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/250 mg should be substituted for carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/100 mg or carbidopa and levodopa 10 mg/100 mg. If necessary, the dosage of carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/250 mg may be increased by one-half or one tablet every day or every other day to a maximum of eight tablets a day. Experience with total daily dosages of carbidopa greater than 200 mg is limited.
Because both therapeutic and adverse responses occur more rapidly with carbidopa and levodopa tablets than with levodopa alone, patients should be monitored closely during the dose adjustment period. Specifically, involuntary movements will occur more rapidly with carbidopa and levodopa tablets than with levodopa. The occurrence of involuntary movements may require dosage reduction. Blepharospasm may be a useful early sign of excess dosage in some patients.
Standard drugs for Parkinson's disease, other than levodopa without a decarboxylase inhibitor, may be used concomitantly while carbidopa and levodopa tablets are being administered, although dosage adjustments may be required.
Sporadic cases of a symptom complex resembling Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) have been associated with dose reductions and withdrawal of carbidopa and levodopa tablets. Patients should be observed carefully if abrupt reduction or discontinuation of carbidopa and levodopa tablets is required, especially if the patient is receiving neuroleptics. (See WARNINGS .)
If general anesthesia is required, carbidopa and levodopa tablets may be continued as long as the patient is permitted to take fluids and medication by mouth.
If therapy is interrupted temporarily, the patient should be observed for symptoms resembling NMS, and the usual daily dosage may be administered as soon as the patient is able to take oral medication.
HOW SUPPLIED
Carbidopa and Levodopa Tablets, USP 25 mg/100 mg are available for oral administration as yellow, mottled, round, tablets, imprinted “R” on one side and “539” and bisect on the other side. They are supplied as follows:
Unit Dose Blisters of 10 x 10 (NDC 0904-6237-61).
Carbidopa and Levodopa Tablets, USP 25 mg/250 mg are available for oral administration as light blue, mottled, round, scored tablets, imprinted “R” on one side and “540” and bisect on the other side. They are supplied as follows:
Unit Dose Blisters of 10 x 10 (NDC 0904-6238-61).
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container [see USP].
CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA TABLETS USP
25 mg/100 mg and 25 mg/250 mg
Manufactured by:
Actavis Elizabeth LLC
Elizabeth, NJ 07207
Distributed by:
MAJOR PHARMACEUTICALS
Livonia, MI 48150
Revised: January 2010
Representative sample of labeling (see the HOW SUPPLIED section for complete listing):
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 25 mg/250 mg BOTTLE LABEL
NDC 0904-6238-61
CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA TABLETS USP
Rx only
10 x 10 Unit Dose Tablets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 25 mg/100 mg LABEL
CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA TABLETS USP
NDC 0904-6237-61
Rx only
10 x 10 Unit Dose Tablets

Carbidopa and LevodopaCarbidopa and Levodopa TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Carbidopa and LevodopaCarbidopa and Levodopa TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||