Carisoprodol and Aspirin
CARISOPRODOL AND ASPIRIN 200MG/325MG USP Rx Only
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- CARISOPRODOL AND ASPIRIN DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- CARISOPRODOL AND ASPIRIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CARISOPRODOL AND ASPIRIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- CARISOPRODOL AND ASPIRIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- CARISOPRODOL AND ASPIRIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- PACKAGE LABEL, PRINCIPLE DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
CARISOPRODOL AND ASPIRIN DESCRIPTION
Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets, USP is a combination product containing carisoprodol, a centrally-acting muscle relaxant, plus aspirin, an analgesic with antipyretic and antiinflammatory properties.
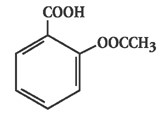
Chemically, carisoprodol is (+)-2-Methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol carbamate isopropylcarbamate. Carisoprodol is a white, crystalline powder, having a mild, characteristic odor and a bitter taste. It is very slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol, in chloroform, and in acetone. Its molecular formula is C12H24N204, with a molecular weight of 260.34. The structural formula is:

CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Carisoprodol: Carisoprodol is a centrally-acting muscle relaxant that does not directly relax tense skeletal muscles in man. The mode of action of carisoprodol in relieving acute muscle spasm of local origin has not been clearly identified, but may be related to its sedative properties. In animals, carisoprodol has been shown to produce muscle relaxation by blocking interneuronal activity and depressing transmission of polysynaptic neurons in the spinal cord and in the descending reticular formation of the brain. The onset of action is rapid and lasts four to six hours.
Carisoprodol is metabolized in the liver and is excreted by the kidneys. It is dialyzable by peritoneal and hemodialysis.
Aspirin: Aspirin is a nonnarcotic analgesic with antiinflammatory and antipyretic activity. Inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis appears to account for most of its antiinflammatory and for at least part of its analgesic and antipyretic properties.
Aspirin is rapidly absorbed and almost totally hydrolyzed to salicylic acid following oral administration. Although aspirin has a half-life of only about 15 minutes, the apparent biologic half-life of salicylic acid in the therapeutic plasma concentration range is between 6 and 12 hours. Salicylic acid is eliminated by renal excretion and by biotransformation to inactive metabolites. Clearance of salicylic acid in the high-dose range is sensitive to urinary pH (see Drug Interactions) and is reduced by renal dysfunction.
CARISOPRODOL AND ASPIRIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CARISOPRODOL AND ASPIRIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
Acute intermittent porphyria; bleeding disorders; allergic or idiosyncratic reactions to carisoprodol, aspirin, or related compounds.
WARNINGS
On very rare occasions, the first dose of carisoprodol has been followed by an idiosyncratic reaction with symptoms appearing within minutes or hours. These may include extreme weakness, transient quadriplegia, dizziness, ataxia, temporary loss of vision, diplopia, mydriasis, dysarthria, agitation, euphoria, confusion, and disorientation. Although symptoms usually subside over the course of the next several hours, discontinue Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets and initiate appropriate supportive and symptomatic therapy, which may include epinephrine and/or antihistamines. In severe cases, corticosteroids may be necessary. Severe reactions have been manifested by asthmatic episodes, fever, weakness, dizziness, angioneurotic edema, smarting eyes, hypotension, and anaphylactoid shock.
The effects of carisoprodol with agents such as alcohol, other CNS depressants, or psychotropic drugs may be additive. Appropriate caution should be exercised with patients who may take one or more of these agents simultaneously with Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets.
PRECAUTIONS
To avoid excessive accumulation of carisoprodol, aspirin, or their metabolites, use Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets with caution in patients with compromised liver or kidney function, or in elderly or debilitated patients (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Use with caution in patients with history of gastritis or peptic ulcer, in patients on anticoagulant therapy, and in addiction-prone individuals.
Information for Patients
Caution patients that this drug may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a motor vehicle or operating machinery.
Caution patients with a predisposition for gastrointestinal bleeding that concomitant use of aspirin and alcohol may have an additive effect in this regard.
Caution patients that dosage of medications used for gout, arthritis, or diabetes may have to be adjusted when aspirin is administered or discontinued (see Drug Interactions).
Drug Interactions
Clinically important interactions may occur when certain drugs are administered concomitantly with aspirin or aspirin-containing drugs.
1. Oral Anticoagulants-By interfering with platelet function or decreasing plasma prothrombin concentration, aspirin enhances the potential for bleeding in patients on anticoagulants.
2. Methotrexate-aspirin enhances the toxic effects of this drug.
3. Probenecid and Sulfinpyrazone-large doses of aspirin reduce the uricosuric effect of both drugs. Renal excretion of salicylate may also be reduced.
4. Oral Antidiabetic Drugs-enhancement of hypoglycemia may occur.
5. Antacids-to the extent that they raise urinary pH, antacids may substantially decrease plasma salicylate concentrations; conversely, their withdrawal can result in a substantial increase.
6. Ammonium Chloride-this and other drugs that acidify a relatively alkaline urine can elevate plasma salicylate concentrations.
7. Ethyl Alcohol-enhanced aspirin-induced fecal blood loss has been reported.
8. Corticosteroids-salicylate plasma levels may be decreased when adrenal corticosteroids are given, and may be increased substantially when they are discontinued.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term studies have been done with Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C .Adequate animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets. It is also not known whether Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed. Studies in rodents have shown salicylates to be teratogenic when given in early gestation, and embryocidal when given in later gestation in doses considerably greater than usual therapeutic doses in humans. Studies in women who took aspirin during pregnancy have not demonstrated an increased incidence of congenital abnormalities in the offspring.
Labor and Delivery
Nursing Mothers
Pediatric Use
CARISOPRODOL AND ASPIRIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
If severe reactions occur, discontinue Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets and initiate appropriate symptomatic and supportive therapy.
The following side effects which have occurred with the administration of the individual ingredients alone may also occur with the combination.
Carisoprodol:
Central Nervous System: Drowsiness is the most frequent complaint and along with other CNS effects may require dosage reduction. Observed less frequently are dizziness, vertigo and ataxia. Tremor, agitation, irritability, headache, depressive reactions, syncope and insomnia have been infrequent or rare.
Idiosyncratic: Idiosyncratic reactions are very rare. They are usually seen within the period of the first to fourth dose in patients having had no previous contact with the drug (see WARNINGS).
Allergic: Skin rash erythema multiforme, pruritus, eosinophilia and fixed drug eruptions with cross-reaction to meprobamate have been reported. If allergic reactions occur, discontinue Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets and treat symptomatically. In evaluating possible allergic reactions, also consider allergy to excipients.
Cardiovascular: Tachycardia, postural hypotension and facial flushing.
Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress and hiccup.
Hematologic: No serious blood dyscrasias have been attributed to carisoprodol alone.
Leukopenia and pancytopenia have been reported, very rarely, in situations in which other drugs or viral infections may have been responsible.
Aspirin:
The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of aspirin have been gastrointestinal, including nausea, vomiting, gastritis, occult bleeding, constipation and diarrhea. Gastric erosion, angioedema, asthma rash, pruritus and urticaria have been reported less commonly. Tinnitus is a sign of high serum salicylate levels (see OVERDOSAGE).
Aspirin Intolerance: Allergic type reactions in aspirin-sensitive individuals may involve the respiratory tract or the skin. Symptoms of the former range from rhinorrhea and shortness of breath to severe asthma, and the latter may consist of urticaria, edema, rash or angioedema (giant hives). These may occur independently or in combination.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Abuse: In clinical use, abuse has been rare.
Dependence: In clinical use, dependence with Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets have been rare and there have been no reports of significant abstinence signs, nevertheless, the following information on the individual ingredients should be kept in mind.
Carisoprodol: In dogs, no withdrawal symptoms occurred after abrupt cessation of carisoprodol from dosages as high as 1 gm/kg/day. In a study in man, abrupt cessation of 100 mg/kg/day (about five times the recommended daily adult dosage) was followed in some subjects by mild withdrawal symptoms such as abdominal cramps, insomnia, chills, headache and nausea. Delirium and convulsions did not occur (see PRECAUTIONS).
OVERDOSAGE
Signs and Symptoms: Any of the following which have been reported with the individual ingredients may occur and may be modified to a varying degree by the effects of the other ingredients present in Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets.
Carisoprodol: Stupor, coma, shock, respiratory depression and very rarely, death. Overdosage with carisoprodol in combination with alcohol, other CNS depressants, or psychotropic agents can have additive effects, even when one of the agents has been taken in the usually recommended dosage.
Aspirin: Headache, tinnitus, hearing difficulty, dim vision, dizziness, lassitude, hyperpnea, rapid breathing, thirst, nausea, vomiting, sweating and occasionally diarrhea are characteristic of mild to moderate salicylate poisoning. Salicylate poisoning should be considered in children with symptoms of vomiting, hyperpnea, and hyperthermia.
Hyperpnea is an early sign of salicylate poisoning, but dyspnea supervenes at plasma levels above 50 mg/dl. These respiratory changes eventually lead to serious acid-base disturbances, Metabolic acidosis is a constant finding in infants but occurs in older children only with severe poisoning; adults usually exhibit respiratory alkalosis initially and acidosis terminally.
Other symptoms of severe salicylate poisoning include hyperthermia, dehydration, delirium and mental disturbances. Skin eruptions, GI hemorrhage, or pulmonary edema are less common.
Early CNS stimulation is replaced by increasing depression, stupor, and coma. Death is usually due to respiratory failure or cardiovascular collapse.
Treatment:
General: Provide symptomatic and supportive treatment, as indicated. Any drug remaining in the stomach should be removed using appropriate procedures and caution to protect the airway and prevent aspiration, especially in the stuporous or comatose patient. Incomplete gastric emptying with delayed absorption of carisoprodol has been reported as a cause for relapse. Should respiration or blood pressure become compromised, respiratory assistance, central nervous system stimulants and pressor agents should be administered cautiously as indicated.
Carisoprodol: The following have been used successfully in overdosage with the related drug meprobamate: diuretics, osmotic (mannitol) diuresis, peritoneal dialysis, and hemodialysis (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY). Careful monitoring of urinary output is necessary and caution should be taken to avoid overhydration. Carisoprodol can be be measured in biological fluid by gas chromatography (Douglas, J.F., et al: J Pharm Sci 58:145, 1969).
Aspirin: Since there are no specific antidotes for salicylate poisoning, the aim of treatment is to enhance elimination of salicylate and prevent or reduce further absorption; to correct any fluid electrolyte or metabolic imbalance; and to provide general and cardiorespiratory support. If acidosis is present, intravenous sodium bicarbonate must be given, along with adequate hydration, until salicylate levels decrease to within the therapeutic range. To enhance elimination, forced diuresis and alkalinization of the urine may be beneficial. The need for hemoperfusion or hemodialysis is rare and should be used only when other measures have failed.
CARISOPRODOL AND ASPIRIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Usual Adult Dosage: 1 or 2 tablets, four times daily.
Not recommended for use in children under age twelve (see PRECAUTIONS).
HOW SUPPLIED
- 12634-438-91 UD Blister Pack
- 12634-438-58 Blister Pack Card of 28
- 12634-438-97 Bottle of 7
- 12634-438-84 Bottle of 14
- 12634-438-78 Bottle of 28
Repackaged and Distributed by:
Apotheca, Inc.
Phoenix, AZ 85006
PACKAGE LABEL, PRINCIPLE DISPLAY PANEL
28 Tablets NDC 12634-438-78
Carisoprodol and Aspirin Tablets, USP
Rx Only 200mg/325mg
Each Tablet Contains:
Carisoprodol 200mg
Aspirin 325mg

Carisoprodol and AspirinCarisoprodol and Aspirin TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||