Cefazolin
General Injectables & Vaccines, Inc.
Cefazolin 500mg Injection, USP Single Dose Vial
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Cefazolin Indications and Usage
- Contraindications
- Warnings
- Precautions
- Side Effects
- Dosage and Administration
- How Supplied
- Sample Outer Label
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefazolin Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Cefazolin Injection, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
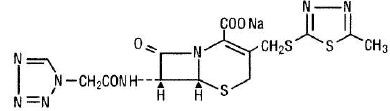
Cefazolin Injection, USP is a sterile semi-synthetic cephalosporin for parenteral administration (Intramuscular or Intravenous). It is the sodium salt of 3-{[(5-methyl-1,-3,-4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio]-methyl}-8-oxo-7-[2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)acetamido]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid.
Structural Formula:
Clinical Pharmacology
Human PharmacologyMicrobiology
In vitroin vitro
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Escherichia coli
Proteus mirabilis
Klebsiella
Enterobacter aerogenes
Haemophilus influenzae
Proteus vulgarisEnterobacter Morganella morganiiProvidencia rettgeriSerratiaPseudomonas, Mima, Herellea
Disk Susceptibility Tests
Disk Diffusion Techniques -
- Susceptible organisms produce zones of 18 mm or greater, indicating that the tested organism is likely to respond to therapy.
- Organisms of intermediate susceptibility produce zones 15 to 17 mm, indicating that the tested organism would be susceptible if high dosage is used or if the infection is confined to tissues and fluids (e.g., urine), in which high antibiotic levels are attained.
- Resistant organisms produce zones of 14 mm or less, indicating that other therapy should be selected.
in vitro
S. aureus
Dilution Techniques
S. aureus
E. coli
Cefazolin Indications and Usage
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefazolin for Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Cefazolin for Injection, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such date, local epidemiology and susceptibility patters may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Cefazolin for Injection, USP is indicated in the treatment of the following serious infections due to susceptible organisms:
Respiratory Tract Infections:
Due to S. pneumoniae, Klebsiella species, Haemophilus influenzae, S. aureus (pennicillin-sensitive and penicillin resistant) , and group A beta-hemolytic streptococci.
Injectable benzathine penicillin is considered to be the drug of choice in
treatment and prevention of streptococcal infections, including the prophylaxis
of rheumatic fever. Cefazolin is effective in the eradication of streptococci
from the nasopharynx; however, data establishing the efficacy of cefazolin in
the subsequent prevention of rheumatic fever are not available at present.
Due to E. coli, P. mirabilis, Klebsiella species and some strains of enterobacter and enterococci.
Skin and Skin Structure Infections:Due to S. aureus (pennicillin-sensitive and penicillin resistant), S. pyogenes, and other strains of streptococci.
Biliary Tract Infections:Due to E. coli, various strains of streptococci, P. mirabilis, Klebsiella species and Staphylococcus aureus.
Bone and Joint Infections:Due to S. aureus.
Genital Infections:(i.e., prostatitis, epididymitis) due to E. coli, P. mirabilis, Klebsiella species and some strains of enterococci.
Septicemia:Due to S. pneumoniae, S. aureus (pennicillin-sensitive and penicillin resistant) P. mirabilis, E. coli, and Klebsiella species
Endocarditis:Due to S. aureus (pennicillin-sensitive and penicillin resistant), and group A beta hemolytic streptococci.
Appropriate culture and susceptibility studies should be performed to determine susceptibility of the causative organism to cefazolin.
Perioperative Prophylaxis:The prophylactic administration of cefazolin preoperatively, intraoperatively, and postoperatively may reduce the incidence of certain postoperative infections in patients undergoing surgical procedures which are classified as contaminated or potentially contaminated (e.g., vaginal hysterectomy, and cholecystectomy in high-risk patients such as those older than 70 years, with acute cholecystitis, obstructive jaundice, or common duct bile stones).
The perioperative use of cefazolin may also be effective in surgical patients in whom infection at the operative site would present a serious risk (e.g., during open-heart surgery and prosthetic arthroplasty).
The prophylactic administration of cefazolin should usually be discontinued within a 24-hour period after the surgical procedure. In surgery where the occurrence of infection may be particularly devastating (e.g., open-heart surgery and prosthetic arthroplasty), the prophylactic administration of cefazolin may be continued for 3 to 5 days following the completion of surgery.
If there are signs of infection, specimens for cultures should be obtained for the identification of the causative organism so that appropriate therapy may be instituted. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION)
Contraindications
Cefazolin for Injection, USP is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to the cephalosporin group of antibiotics.
Warnings
Before therapy with Cefazolin Injection, USP is instituted, careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has had previous hypersensitivity reactions to cefazolin, cephalosporins, penicillins, or other drugs. If this product is given to penicillin-sensitive patients, caution should be exercised because cross-hypersensitivity among beta-lactam antibiotics has been clearly documented and may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy. If an allergic reaction to Cefazolin Injection, USP occurs, discontinue treatment with the drug. Serious acute hypersensitivity reactions may require treatment with epinephrine and other emergency measures, including oxygen, IV fluids, IV antihistamines, corticosteroids, pressor amines, and airway management, as clinically indicated.
Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents, including cefazolin, and may range in severity from mild to life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present diarrhea subsequent to the administration of antibacterial agents.Clostridium difficile
C. difficile
Precautions
Prolonged use of cefazolin may result in the overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms. Careful clinical observation of the patient is essential.
Prescribing Cefazolin for Injection, USP is the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection of a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
When cefazolin is administered to patients with low urinary output because of impaired renal function, lower daily dosage is required (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
As with other beta-lactam antibiotics, seizures may occur if inappropriately high doses are administered to patients with impaired renal function (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Cefazolin Injection, USP, as with all cephalosporins, should be prescribed with caution in individuals with a history of gastrointestinal disease, particularly colitis.
Drug InteractionsProbenecid may decrease renal tubular secretion of cephalosporins when used concurrently, resulting in increased and more prolonged cephalosporin blood levels.
Drug/Laboratory Test InteractionsA false positive reaction for glucose in the urine may occur with Benedict’s solution, Fehling’s solution or with CLINITEST® tablets, but not with enzyme-based tests such as CLINISTIX®.
Positive direct and indirect antiglobulin (Coombs) tests have occurred; these may also occur in neonates whose mothers received cephalosporins before delivery.
Carcinogenesis/MutagenesisMutagenicity studies and long-term studies in animals to determine the carcinogenic potential of cefazolin have not been performed.
Pregnancy Teratogenic Effects Pregnancy Category BReproduction studies have been performed in rats, mice, and rabbits at doses up to 25 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to cefazolin. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Labor and DeliveryWhen cefazolin has been administered prior to caesarean section, drug levels in cord blood have been approximately one quarter to one third of maternal drug levels. The drug appears to have no adverse effect on the fetus.
Nursing MothersCefazolin is present in very low concentrations in the milk of nursing mothers. Caution should be exercised when cefazolin is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric UseSafety and effectiveness for use in premature infants and neonates have not been established. See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION for recommended dosage in pediatric patients older than 1 month.
Information for PatientsPatients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including cefazolin should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Cefazolin Injection, USP is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may: (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment, and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by cefazolin or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Side Effects
The following reactions have been reported:
Gastrointestinal
Diarrhea, oral candidiasis (oral thrush), vomiting, nausea,
stomach cramps, anorexia, and pseudomembranous colitis. Onset of
pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibiotic treatment
(see WARNINGS).
Nausea and vomiting have been reported rarely.
Allergic
Anaphylaxis, eosinophilia, itching, drug fever, skin rash,
Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Hepatic and Renal
Local Reactions
Other Reactions
Dosage and Administration
Usual Adult Dosage:
| Type of Infection |
Dose |
Frequency |
| Moderate to severe infections |
500 mg to 1 gram |
every 6 to 8 hrs. |
| Mild infections caused by susceptible gram + cocci |
250 mg to 500 mg |
every 8 hrs. |
| Acute, uncomplicated urinary tract infections |
1 gram |
every 12 hrs. |
| Pneumococcal pneumonia |
500 mg |
every 12 hrs |
| Sever, life-threatening infections (e.g., endocarditis, septicemia)* |
1 gram to 1.5 grams |
every 6 hrs |
Perioperative Prophylactic Use
Dosage Adjustment for Patients With Reduced Renal Function
Pediatric Dosage
| Weight |
|
25 mg/kg/day divided into 3 doses |
|
25 mg/kg/day divided into 4 doses |
|
| Lbs |
Kg |
Approximate single dose mg/q8h |
Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 125 mg/mL |
Approximate single dose mg/q6h |
Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 125 mg/mL |
| 10 | 4.5 | 40 mg | 0.35 mL |
30 mg |
0.25 mL |
| 20 |
9.0 |
75 mg |
0.60 mL |
55 mg |
0.45 mL |
| 30 |
13.6 |
115 mg |
0.90 mL |
85 mg |
0.70 mL |
| 40 |
18.1 |
150 mg |
1.20 mL |
115 mg |
0.90 mL |
| 50 |
22.7 |
190 mg |
1.50 mL |
140 mg |
1.10 mL |
| Weight |
|
50 mg/kg/day divided into 3 doses |
|
50 mg/kg/day divided into 4 doses |
|
| Lbs |
Kg |
Approximate single dose mg/q8h |
Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 25 mg/mL |
Approximate single dose mg/q6h |
Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 225 mg/mL |
| 10 |
4.5 |
75 mg |
0.35 mL |
55 mg |
0.25 mL |
| 20 |
9.0 |
150 mg |
0.70 mL |
110 mg |
0.50 mL |
| 30 |
13.6 |
225 mg |
1.00 mL |
170 mg |
0.75 mL |
| 40 |
18.1 | 300 mg |
1.35 mL |
225 mg |
1.00 mL |
| 50 |
22.7 |
375 mg |
1.70 mL |
285 mg |
1.25 mL |
RECONSTITUTION
Preparation of Parenteral Solution
oo
Single dose Via
| Vial Size |
Amount of diluent |
Approximate concentration |
Appriximate Available volume |
| 500 mg |
2 mL |
225 mg/mL |
2.2 mL |
| 1 gram |
2.5 mL | 330 mg/mL |
3 mL |
ADMINISTRATION
Intramuscular Administration
Intravenous Administration
- Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- 5% or 10% Dextrose Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose in Lactated Ringer's Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose and 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose and 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose and 0.2% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- Lactate Ringer's Injection, USP
- Invert Sugar 5% or 10% in Sterile Water for Injection
- Ringer's Injection, USP
- 5% Sodium Bicarbonate Injection, USP
How Supplied
Cefazolin Injection, USP is supplied in vials containing cefazolin sodium equivalent to 500 mg or 1 gram cefazolin and in infusion bottles containing cefazolin sodium equivalent to 1 gram cefazolin:
| NDC 10019-610-01 |
500 mg/10 mL vial, Carton of 25 vials |
| NDC 10019-611-03 |
1 g/10 mL vial, Carton of 25 vials |
| NDC 10019-611-01 |
1 g/100 mL vial, Carton of 10 bottles |
Rx Only
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Sample Outer Label

CefazolinCefazolin Sodium INJECTION, POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||