CEFOTAXIME
Prescribing information Cefotaxime for Injection, USP Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefotaxime for injection and other antibacterial drugs, cefotaxime for injection should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- CEFOTAXIME DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- CEFOTAXIME INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CEFOTAXIME CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- CEFOTAXIME ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- CEFOTAXIME DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
CEFOTAXIME DESCRIPTION
2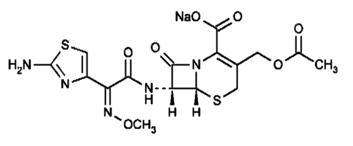
1616572
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
1423
Microbiology
Aerobes, Gram-positive:
Enterococcus
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus
Aerobes, Gram-negative:
Acinetobacter
Citrobacter
Enterobacter
Escherichia
Haemophilus influenzae
Haemophilus parainfluenzae
Klebsiella
Morganella morganii
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Neisseria meningitidis
Proteus mirabilis
Proteus vulgaris
Providencia rettgeri
Providencia stuartii
Serratia marcescens
NOTE: Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Anaerobes:
BacteroidesBacteroidesfragilis
Note: Clostridium difficile
FusobacteriumFusobacterium nucleatum
Peptococcus
Peptostreptococcus
in vitro but the clinical significance is unknown. in vitro
Aerobes, Gram-negative:
Providencia
Salmonella Salmonella typhi
Shigella
in vitro1
in vitroPseudomonas aeruginosa
Susceptibility Tests
Dilution techniques:1
organismsaHaemophilus Neisseria gonorrhoeaeStreptococcus
| MIC (mcg/mL) |
Interpretation |
|---|---|
| ≤8 16-32 ≥64 |
Susceptible (S) Intermediate (I) Resistant (R) |
| MIC (mcg/mL) | Interpretationc |
|---|---|
| ≤2 | Susceptible (S) |
| MIC (mcg/mL) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| ≤0.5 1 ≥2 |
Susceptible (S) Intermediate (I) Resistant (R) |
| MIC (mcg/mL) | Interpretationc |
|---|---|
| ≤0.5 | Susceptible (S) |
2
2
| Microorganism |
MIC (mcg/mL) |
|---|---|
|
Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 Haemophilus influenzae a ATCC 49247 Streptococcus pneumoniae b ATCC 49619 Neisseria gonorrhoeae c ATCC 49226 |
0.06-0.25 1-4 4-16 0.12-0.5 0.06-0.25 0.015-0.06 |
2
2
Diffusion Techniques:
3
aHaemophilusNeisseria gonorrhoeae Streptococcus
| MIC (mcg/mL) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| ≥23 15-22 ≤14 |
Susceptible (S) Intermediate (I) Resistant (R) |
| Zone Diameter (mm) |
Interpretationc |
|---|---|
| ≥26 | Susceptible (S) |
| Zone Diameter (mm) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| ≥28 26-27 ≤25 |
Susceptible (S) Intermediate (I) Resistant (R) |
| Zone Diameter (mm) | Interpretationc |
|---|---|
| ≥31 | Susceptible (S) |
3
3
| Microorganism | Zone Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|
|
Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 Haemophilus influenzae a ATCC 49247 Neisseria gonorrhoeae b ATCC 49226 |
29-35 25-31 18-22 31-29 38-48 |
3
Anaerobic Techniques:
4
| MIC (mcg/mL) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
|
≤16 32 ≥64 |
Susceptible (S) Intermediate (I) Resistant (R) |
| Microorganism | MIC (mcg/mL) |
|---|---|
|
Bacteroides fragilis
a
ATCC 25285 Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron ATCC 29741 Eubacterium lantem ATCC 43055 |
8-32 16-64 64-256 |
CEFOTAXIME INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Treatment
- Lower respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia, caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae (formerly Diplococcus pneumoniae), Streptococcus pyogenes* (Group A streptococci) and other streptococci (excluding enterococci, e.g., Enterococcus faecalis), Staphylococcus aureus (penicillinase and non-penicillinase producing), Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, Haemophilus influenzae (including ampicillin resistant strains), Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Proteus mirabilis, Serratia marcescens*, Enterobacter species, indole positive Proteus and Pseudomonas species (including P. aeruginosa).
- Genitourinary infections. Urinary tract infections caused by Enterococcus species, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus*, (penicillinase and non-penicillinase producing), Citrobacter species, Enterobacter species, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris*, Providencia stuartii, Morganella morganii*, Providencia rettgeri*, Serratia marcescens and Pseudomonas species (including P. aeruginosa). Also, uncomplicated gonorrhea (cervical/urethral and rectal) caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae , including penicillinase producing sjtrains.
-
Gynecologic infections, including pelvic inflammatory disease, endometritis and pelvic cellulitis caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus species, Enterococcus species, Enterobacter species*, Klebsiella species*, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Bacteroides species (including Bacteroides fragilis*), Clostridium species, and anaerobic cocci (including Peptostreptococcus species and Peptococcus species) and Fusobacterium species (including F. Nucleatum*). Cefotaxime, like other cephalosporins, has no activity against Chlamydia trachomatis.
Therefore, when cephalosporins are used in the treatment of patients with pelvic inflammatory disease and C. trachomatis is one of the suspected pathogens, appropriate anti-chlamydial coverage should be added. - Bacteremia/Septicemia caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, and Serratia marcescens, Staphylococcus aureus andStreptococcus species (including S. pneumonia).
- Skin and skin structure infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus (penicillinase and non-penicillinase producing),Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A streptococci) and other streptococci, Enterococcus species, Acinetobacter species*, Escherichia coli, Citrobacter species (including C. freundii*), Enterobacter species, Klebsiella species, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris*, Morganella morganii, Providencia rettgeri*, Pseudomonas species, Serratia marcescens, Bacteroides species, and anaerobic cocci (including Peptostreptococcus* species and Peptococcus species).
- Intra-abdominal infections including peritonitis caused by Streptococcus species*, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, Bacteroides species, and anaerobic cocci (including Peptostreptococcus* species and Peptococcus * species) Proteus mirabilis*, and Clostridium species*.
- Bone and/or joint infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus (penicillinase and non-penicillinase producing strains), Streptococcus species (including S. pyogenes*), Pseudomonas species (including P. aeruginosa*), and Proteus mirabilis*.
-
Central nervous system infections, e.g., meningitis and ventriculitis, caused by Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae* and Escherichia coli*.
faecalisPseudomonas in vitro
Prevention
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
CEFOTAXIME CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Clostridium difficileC. difficile.
C. difficileC. difficile
C. difficile C. difficile
PRECAUTIONS
General
2
5
Weight (kg) x (140 - age)
Information for Patients
Drug Interactions
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis
22Pregnancy Teratogenic Effects Pregnancy Category B:
22Nonteratogenic Effects
Nursing Mothers
Pediatric Use
Geriatric Use
PRECAUTIONSGeneral
CEFOTAXIME ADVERSE REACTIONS
Clinical Trials Experience
The most frequent adverse reactions (greater than 1%) are
Less frequent adverse reactions (less than 1%) are:
Post-Marketing Experience
Cephalosporin Class Labeling
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION OVERDOSAGE
OVERDOSAGE
CEFOTAXIME DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adults
GUIDELINES FOR DOSAGE OF CEFOTAXIME FOR INJECTION
| Type of Infection |
Daily Dose grams) |
Frequency and Route |
|---|---|---|
| Gonococcal urethritis/cervicitis in males and females Rectal gonorrhea in females Rectal gonorrhea in males Uncomplicated infections Moderate to severe infections Infections commonly needing antibiotics in higher dosage (e.g., septicemia) Life-threatening infections |
0.5 0.5 1 2 3-6 6-8 up to 12 |
0.5 gram IM (single dose) 0.5 gram IM (single dose) 1 gram IM (single dose) 1 gram every 12 hours IM or IV 1-2 grams every 8 hours IM or IV 2 grams every 6-8 hours IV 2 grams every 4 hours IV |
Cesarean Section Patients
Neonates, Infants, and Children
Geriatric Use
RECAUTIONS, GeneralPRECAUTIONS, Geriatric UseImpaired Renal Function
PRECAUTIONS, General.NOTE:
Preparation of Cefotaxime for injection Sterile
| Strength | Diluent (mL) |
Withdrawable Volume (mL) |
Approximate Concentration (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg vial (IM) 1 g vial (IM) 2 g vial (IM) 500 mg vial (IV) 1 g vial (IV) 2 g vial (IV) |
2 3 5 10 10 10 |
2.2 3.4 6 10.2 10.4 11 |
230 300 330 50 95 180 |
For intramuscular use:
For intravenous use:
NOTE:
IM Administration:
IV Administration:
Compatibility and Stability
(Preparation of Cefotaxime for injection)| Strength |
Reconstituted Concentration mg/mL |
Stability at or below 220C |
Stability under Refrigeration (at or below 50C) Original Containers |
Plastic Syringes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg vial IM 1 g vial IM 2 g vial IM 500 mg vial IV 1 g vial IV 2 g vial IV |
230 300 330 50 95 180 |
12 hours 12 hours 12 hours 24 hours 24 hours 12 hours |
7 days 7 days 7 days 7 days 7 days 7 days |
5 days 5 days 5 days 5 days 5 days 5 days |
00®
NOTE:
HOW SUPPLIED
NOTE:
REFERENCES
- Richmond, M. H. and Sykes R. B.: The ß-Lactamases of Gram-Negative Bacteria and their Possible Physiological Role, Advances in Microbial Physiology 9:31-88, 1973.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically - Third Edition. Approved Standard NCCLS Document M7-A3, Vol. 13, No. 25, NCCLS, Villanova, PA, December, 1993.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance Standard for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests - Fifth Edition. Approved Standard NCCLS Document M2-A5, Vol. 13, No. 24, NCCLS, Villanova, PA, December, 1993.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Anaerobic Bacteria - Third Edition. Approved Standard NCCLS Document M11-A3, NCCLS, Villanova, PA, December, 1993.
- Cockcroft, D.W. and Gault, M.H.: Prediction of Creatinine Clearance from Serum Creatinine, Nephron 16:31-41, 1976.
Distributed by:



CEFOTAXIMECEFOTAXIME INJECTION, POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CEFOTAXIMECEFOTAXIME INJECTION, POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CEFOTAXIMECEFOTAXIME INJECTION, POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!