Cefuroxime Axetil
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- CEFUROXIME AXETIL DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- CEFUROXIME AXETIL INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CEFUROXIME AXETIL CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- CEFUROXIME AXETIL ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- CEFUROXIME AXETIL DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- CLINICAL STUDIES
- REFERENCES
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
CEFUROXIME AXETIL DESCRIPTION
Cefuroxime axetil tablets contain cefuroxime as cefuroxime axetil. Cefuroxime
axetil is a semisynthetic, broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic for oral
administration.
Chemically, cefuroxime axetil, the 1-(acetyloxy) ethyl
ester of cefuroxime, is (RS )-1-hydroxyethyl (6R,7R)-7-[2-(2-furyl)glyoxyl-amido]-3-(hydroxymethyl)-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]-oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate,
72-(Z)-(O-methyl-oxime), 1-acetate 3-carbamate. Its molecular
formula is C20H22N4O10S, and it has a molecular weight of
510.48.
Cefuroxime axetil is in the amorphous form and has the following
structural formula:
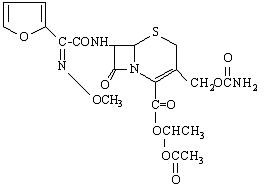
Cefuroxime axetil tablets are uncoated and contain the equivalent of 125, 250 or 500 mg of cefuroxime as cefuroxime axetil. Cefuroxime axetil tablets contain the inactive ingredients colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hydrogenated vegetable oil, microcrystalline cellulose and sodium lauryl sulfate.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Absorption and Metabolism: After oral administration,
cefuroxime axetil is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and rapidly
hydrolyzed by nonspecific esterases in the intestinal mucosa and blood to
cefuroxime. Cefuroxime is subsequently distributed throughout the extracellular
fluids. The axetil moiety is metabolized to acetaldehyde and acetic
acid.
Pharmacokinetics: Approximately 50%of serum
cefuroxime is bound to protein. Serum pharmacokinetic parameters for cefuroxime
axetil tablets are shown in Table 1.
|
Dose† (Cefuroxime Equivalent) |
Peak Plasma Concentration (mcg/mL) |
Time of Peak Plasma Concentration (hr) |
Mean Elimination Half-Life (hr) |
AUC (mcg-hr mL) |
|
125 mg |
2.1 |
2.2 |
1.2 |
6.7 |
|
250 mg |
4.1 |
2.5 |
1.2 |
12.9 |
|
500 mg |
7 |
3 |
1.2 |
27.4 |
|
1,000 mg |
13.6 |
2.5 |
1.3 |
50 |
†
Comparative Pharmacokinetic Properties: Cefuroxime axetil for oral suspension was not bioequivalent to cefuroxime axetil tablets when tested in healthy adults. The tablet and powder for oral suspension formulations are NOT substitutable on a milligram-per-milligram basis.
Food Effect on Pharmacokinetics:
Renal Excretion:
PRECAUTIONS: Geriatric Use
Microbiology: in vivo
in vitro INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Aerobic Gram-Positive Microorganisms:
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pyogenes
Aerobic Gram-Negative Microorganisms:
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae
Haemophilus parainfluenzae
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Moraxella catarrhalis
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Spirochetes:
Borrelia burgdorferi
in vitro
in vitro
Aerobic Gram-Positive Microorganisms:
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Streptococcus agalactiae
Listeria monocytogenes Enterococcus faecalis Streptococcus faecalis
Aerobic Gram-Negative Microorganisms:
Morganella morganii
Proteus inconstans
Proteus mirabilis
Providencia rettgeri
Pseudomonas Campylobacter Acinetobacter calcoaceticusLegionella Serratia Proteus vulgaris Morganella morganiiEnterobacter cloacaeCitrobacter in vitro
Anaerobic Microorganisms:
Peptococcus niger
Clostridium difficile Bacteroides fragilis
Susceptibility Tests: Dilution Techniques: 1
|
MIC (mcg/mL) |
Interpretation |
|
≤4 |
(S) Susceptible |
|
8-16 |
(I) Intermediate |
|
≥32 |
(R) Resistant |
|
Microorganism |
MIC (mcg/mL) |
|
Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 |
2-8 |
|
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 |
0.5-2 |
Diffusion Techniques: 2
|
Zone Diameter (mm) |
Interpretation |
|
≥23 |
(S) Susceptible |
|
15-22 |
(I) Intermediate |
|
≤14 |
(R) Resistant |
|
Microorganism |
Zone Diameter (mm) |
|
Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 |
20-26 |
|
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 |
27-35 |
CEFUROXIME AXETIL INDICATIONS AND USAGE
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the
effectiveness of cefuroxime axetil and other antibacterial drugs, cefuroxime
axetil should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or
strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and
susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting
or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local
epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection
of therapy.
NOTE: CEFUROXIME AXETIL TABLETS AND
CEFUROXIME AXETIL FOR ORAL SUSPENSION ARE NOT BIOEQUIVALENT AND ARE NOT
SUBSTITUTABLE ON A MILLIGRAM-PER-MILLIGRAM BASIS (SEE CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Cefuroxime Axetil Tablets: Cefuroxime axetil tablets are
indicated for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate infections caused
by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed
below:
1.
Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes.
NOTE:
The usual drug of choice in the treatment and prevention of streptococcal
infections, including the prophylaxis of rheumatic fever, is penicillin given by
the intramuscular route. Cefuroxime axetil tablets are generally effective in
the eradication of streptococci from the nasopharynx; however, substantial data
establishing the efficacy of cefuroxime in the subsequent prevention of
rheumatic fever are not available. Please also note that in all clinical trials,
all isolates had to be sensitive to both penicillin and cefuroxime. There are no
data from adequate and well-controlled trials to demonstrate the effectiveness
of cefuroxime in the treatment of penicillin-resistant strains of Streptococcus pyogenes.
2.
Acute Bacterial Otitis Media
caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae (including beta-lactamase–producing
strains), Moraxella catarrhalis (including
beta-lactamase–producing strains), or Streptococcus
pyogenes.
3.
Acute
Bacterial Maxillary Sinusitis caused by Streptococcus
pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae
(non-beta-lactamase–producing strains only). (See
CLINICAL STUDIES
section.)
NOTE: In view of the insufficient numbers of isolates of
beta-lactamase–producing strains of Haemophilus influenzae
and Moraxella catarrhalis that were obtained
from clinical trials with cefuroxime axetil tablets for patients with acute
bacterial maxillary sinusitis, it was not possible to adequately evaluate the
effectiveness of cefuroxime axetil tablets for sinus infections known,
suspected, or considered potentially to be caused by beta-lactamase–producing
Haemophilus influenzae or Moraxella catarrhalis.
4.
Acute Bacterial Exacerbations of
Chronic Bronchitis and Secondary Bacterial Infections of Acute Bronchitis
caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae (beta-lactamase negative strains),
or Haemophilus parainfluenzae (beta-lactamase
negative strains). (See
DOSAGE AND
ADMINISTRATION
section and
CLINICAL STUDIES
section.)
5.
Uncomplicated Skin and Skin-Structure
Infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus
(including beta-lactamase–producing strains) or Streptococcus pyogenes.
6.
Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections
caused by Escherichia coli or Klebsiella pneumoniae.
7.
Uncomplicated Gonorrhea,
urethral and endocervical, caused by penicillinase-producing and
non-penicillinase–producing strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
and uncomplicated gonorrhea, rectal, in females, caused by
non-penicillinase–producing strains of Neisseria
gonorrhoeae.
8. Early Lyme Disease (erythema
migrans) caused by Borrelia burgdorferi.
CEFUROXIME AXETIL CONTRAINDICATIONS
Cefuroxime axetil products are contraindicated in patients with known allergy to the cephalosporin group of antibiotics.
WARNINGS
CEFUROXIME AXETIL TABLETS AND CEFUROXIME AXETIL FOR ORAL
SUSPENSION ARE NOT BIOEQUIVALENT AND ARE THEREFORE NOT SUBSTITUTABLE ON A
MILLIGRAM-PER-MILLIGRAM BASIS (SEE CLINICAL
PHARMACOLOGY).
BEFORE THERAPY WITH
CEFUROXIME AXETIL PRODUCTS IS INSTITUTED, CAREFUL INQUIRY SHOULD BE MADE TO
DETERMINE WHETHER THE PATIENT HAS HAD PREVIOUS HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS TO
CEFUROXIME AXETIL PRODUCTS, OTHER CEPHALOSPORINS, PENICILLINS, OR OTHER DRUGS.
IF THIS PRODUCT IS TO BE GIVEN TO PENICILLIN-SENSITIVE PATIENTS, CAUTION SHOULD
BE EXERCISED BECAUSE CROSS-HYPERSENSITIVITY AMONG BETA-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS HAS
BEEN CLEARLY DOCUMENTED AND MAY OCCUR IN UP TO 10%OF PATIENTS WITH A HISTORY OF
PENICILLIN ALLERGY. IF A CLINICALLY SIGNIFICANT ALLERGIC REACTION TO CEFUROXIME
AXETIL PRODUCTS OCCURS, DISCONTINUE THE DRUG AND INSTITUTE APPROPRIATE THERAPY.
SERIOUS ACUTE HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS MAY REQUIRE TREATMENT WITH EPINEPHRINE
AND OTHER EMERGENCY MEASURES, INCLUDING OXYGEN, INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS, INTRAVENOUS
ANTIHISTAMINES, CORTICOSTEROIDS, PRESSOR AMINES, AND AIRWAY MANAGEMENT, AS
CLINICALLY INDICATED.
Clostridium
difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of
nearly all antibacterial agents, including cefuroxime, and may range in severity
from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters
the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C.
difficile.
C. difficile produces
toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing
strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and
mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and
may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with
diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since
CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of
antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing
antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may
need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein
supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C.
difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically
indicated.
PRECAUTIONS
®®
in vitroin vivo2
22
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY INDICATIONS AND USAGE ADVERSE REACTIONS DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION CLINICAL STUDIES
CEFUROXIME AXETIL ADVERSE REACTIONS
CEFUROXIME AXETIL TABLETS IN CLINICAL TRIALS: Multiple-Dose
Dosing Regimens: 7 to 10 Days Dosing:
Using
multiple doses of cefuroxime axetil tablets, 912 patients were treated with
cefuroxime axetil (125 to 500 mg twice daily). There were no deaths or permanent
disabilities thought related to drug toxicity. Twenty (2.2%) patients
discontinued medication due to adverse events thought by the investigators to be
possibly, probably, or almost certainly related to drug toxicity. Seventeen
(85%) of the 20 patients who discontinued therapy did so because of
gastrointestinal disturbances, including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and
abdominal pain. The percentage of cefuroxime axetil tablet-treated patients who
discontinued study drug because of adverse events was very similar at daily
doses of 1,000, 500, and 250 mg (2.3%, 2.1%, and 2.2%, respectively). However,
the incidence of gastrointestinal adverse events increased with the higher
recommended doses.
The following adverse events were thought by the
investigators to be possibly, probably, or almost certainly related to
cefuroxime axetil tablets in multiple-dose clinical trials (n = 912 cefuroxime
axetil-treated patients).
|
Incidence ≥1% |
Diarrhea/loose stools 3.7% Nausea/vomiting 3% Transient elevation in AST 2% Transient elevation in ALT 1.6% Eosinophilia 1.1% Transient elevation in LDH 1% |
|
Incidence <1%but >0.1% |
Abdominal pain Abdominal cramps Flatulence Indigestion Headache Vaginitis Vulvar itch Rash Hives Itch Dysuria Chills Chest pain Shortness of breath Mouth ulcers Swollen tongue Sleepiness Thirst Anorexia Positive Coombs test |
5-Day Experience (see CLINICAL STUDIES section):
In Clinical Trials for Early Lyme Disease With 20 Days Dosing:
Single-Dose Regimen for Uncomplicated Gonorrhea:
|
Incidence ≥1% |
Nausea/vomiting 6.8% Diarrhea 4.2% |
|
Incidence <1%but >0.1% |
Abdominal pain Dyspepsia Erythema Rash Pruritus Vaginal candidiasis Vaginal itch Vaginal discharge Headache Dizziness Somnolence Muscle cramps Muscle stiffness Muscle spasm of neck Tightness/pain in chest Bleeding/pain in urethra Kidney pain Tachycardia Lockjaw-type reaction |
POSTMARKETING EXPERIENCE WITH CEFUROXIME AXETIL PRODUCTS
General:
Gastrointestinal: WARNINGS
Hematologic:
Hepatic:
Neurologic:
Skin:
Urologic:
CEPHALOSPORIN-CLASS ADVERSE REACTIONS
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION OVERDOSAGE
OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of cephalosporins can cause cerebral irritation leading to convulsions. Serum levels of cefuroxime can be reduced by hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
CEFUROXIME AXETIL DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
NOTE: CEFUROXIME AXETIL TABLETS AND CEFUROXIME AXETIL FOR ORAL
SUSPENSION ARE NOT BIOEQUIVALENT AND ARE NOT SUBSTITUTABLE ON A
MILLIGRAM-PER-MILLIGRAM BASIS (SEE CLINICAL
PHARMACOLOGY).
|
Population/Infection |
Dosage |
Duration (days) |
|
Adolescents and Adults (13 years and older) |
||
|
Pharyngitis/tonsillitis |
250 mg b.i.d. |
10 |
|
Acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis |
250 mg b.i.d. |
10 |
|
Acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis |
250 or 500 mg b.i.d. |
10* |
|
Secondary bacterial infections of acute bronchitis |
250 or 500 mg b.i.d. |
5-10 |
|
Uncomplicated skin and skin-structure infections |
250 or 500 mg b.i.d. |
10 |
|
Uncomplicated urinary tract infections |
250 mg b.i.d. |
7-10 |
|
Uncomplicated gonorrhea |
1,000 mg once |
single dose |
|
Early Lyme disease |
500 mg b.i.d. |
20 |
|
Pediatric Patients (who can swallow tablets whole) |
||
|
Acute otitis media |
250 mg b.i.d. |
10 |
|
Acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis |
250 mg b.i.d. |
10 |
Patients With Renal Failure:
HOW SUPPLIED
Cefuroxime Axetil Tablets, USP 250 mg
of cefuroxime (as cefuroxime axetil), are white to off-white, uncoated,
capsule-shaped tablets with “A33” debossed on one side and plain on the other
side.
| Bottles of 20 |
NDC 54868-4987-0 |
| Bottles of 30 |
NDC 54868-4987-1 |
Cefuroxime Axetil Tablets, USP 500 mg
of cefuroxime (as cefuroxime axetil), are white to off-white, uncoated,
capsule-shaped tablets with “A34” debossed on one side and plain on the other
side.
| Bottles of 15 |
NDC 54868-5022-2 |
| Bottles of 20 |
NDC 54868-5022-1 |
| Bottles of 30 |
NDC 54868-5022-0 |
| Bottles of 60 |
NDC 54868-5022-3 |
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F);
excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room
Temperature]. Replace cap securely after each opening.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Cefuroxime Axetil Tablets: Acute Bacterial
Maxillary Sinusitis:
One adequate and well-controlled study was
performed in patients with acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis. In this study
each patient had a maxillary sinus aspirate collected by sinus puncture before
treatment was initiated for presumptive acute bacterial sinusitis. All patients
had to have radiographic and clinical evidence of acute maxillary sinusitis. As
shown in the following summary of the study, the general clinical effectiveness
of cefuroxime axetil tablets was comparable to an oral antimicrobial agent that
contained a specific betalactamase inhibitor in treating acute maxillary
sinusitis. However, sufficient microbiology data were obtained to demonstrate
the effectiveness of cefuroxime axetil tablets in treating acute bacterial
maxillary sinusitis due only to Streptococcus pneumoniae
or non-beta-lactamase–producing Haemophilus
influenzae. An insufficient number of beta-lactamase–producing Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella
catarrhalis isolates were obtained in this trial to adequately evaluate
the effectiveness of cefuroxime axetil tablets in the treatment of acute
bacterial maxillary sinusitis due to these 2 organisms.
This study
enrolled 317 adult patients, 132 patients in the United States and 185 patients
in South America. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to cefuroxime axetil
250 mg twice daily or an oral antimicrobial agent that contained a specific
beta-lactamase inhibitor. An intent-to-treat analysis of the submitted clinical
data yielded the following results:
|
|
U.S. Patients* |
South American Patients† |
||
|
Cefuroxime Axetil (n = 49) |
Control (n = 43) |
Cefuroxime Axetil (n = 87) |
Control (n = 89) |
|
|
Clinical success (cure + improvement) |
65% |
53% |
77% |
74% |
|
Clinical cure |
53% |
44% |
72% |
64% |
|
Clinical improvement |
12% |
9% |
5% |
10% |
†
Haemophilus influenzae Haemophilus influenzaeStreptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus pneumoniae
Safety: PP
Early Lyme Disease:
Borrelia burgdorferi
|
|
Part I (1 Month Posttreatment)* |
Part II (1 Year Posttreatment)† |
||
|
Cefuroxime Axetil (n = 125) |
Doxycycline (n = 108) |
Cefuroxime Axetil (n = 105‡) |
Doxycycline (n = 83‡) |
|
|
Satisfactory clinical outcome§ |
91% |
93% |
84% |
87% |
|
Clinical cure/success |
72% |
73% |
73% |
73% |
|
Clinical improvement |
19% |
19% |
10% |
13% |
†
‡
§
Safety: P PP
Secondary Bacterial Infections of Acute Bronchitis: ®®
|
|
CAE-516 and CAE-517* |
CAEA4001 and CAEA4002† |
||
|
5 day (n = 127) |
10 day (n = 139) |
5 day (n = 173) |
10 day (n = 192) |
|
|
Clinical success (cure + improvement) |
80% |
87% |
84% |
82% |
|
Clinical cure |
61% |
70% |
73% |
72% |
|
Clinical improvement |
19% |
17% |
11% |
10% |
†
Safety:
REFERENCES
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically. 3rd ed. Approved Standard NCCLS Document M7-A3, Vol. 13, No. 25. Villanova, Pa: NCCLS; 1993.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests. 4th ed. Approved Standard NCCLS Document M2-A4, Vol. 10, No. 7. Villanova, Pa: NCCLS; 1990.
®®
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
Relabeling and Repackaging by:
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Cefuroxime Axetil Tablets, USP 250 mg

Cefuroxime Axetil Tablets, USP 500 mg

Cefuroxime AxetilCefuroxime Axetil TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cefuroxime AxetilCefuroxime Axetil TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||