Ciprofloxacin
Ciproflaxin Tablets
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING
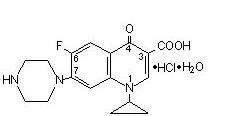
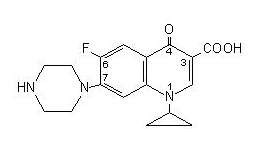
- CIPROFLOXACIN DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- MICROBIOLOGY
- CIPROFLOXACIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CIPROFLOXACIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- CIPROFLOXACIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- CIPROFLOXACIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY
- CLINICAL STUDIES
- REFERENCES
- MEDICATION GUIDE
- What is the most important information I should know about ciprofloxacin tablets?
- What are ciprofloxacin tablets?
- Who should not take ciprofloxacin tablets?
- What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking ciprofloxacin tablets?
- How should I take ciprofloxacin tablets?
- What should I avoid while taking ciprofloxacin tablets?
- What are the possible side effects of ciprofloxacin tablets?
- How should I store ciprofloxacin tablets?
- General information about ciprofloxacin tablets
- What are the ingredients in ciprofloxacin tablets?
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING
Fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin, are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This risk is further increased in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants (See WARNINGS).
Fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin, may exacerbate muscle weakness in persons with myasthenia gravis. Avoid ciprofloxacin in patients with known history of myasthenia gravis (see WARNINGS).
CIPROFLOXACIN DESCRIPTION
1718332
171833
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Absorption
| Dose (mg) |
Maximum Serum Concentration (mcg/mL) |
Area Under Curve (AUC) (mcg•hr/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| 250 500 750 1000 |
1.2 2.4 4.3 5.4 |
4.8 11.6 20.2 30.8 |
max
| Steady-state Pharmacokinetic Parameters Following Multiple Oral and I.V. Doses |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
aAUC 0-12h
bAUC 24h=AUC0-12h x 2 cAUC 24h=AUC0-8h x 3 |
||||
| Parameters |
500 mg q12h, P.O. |
400 mg q12h, I.V. |
750 mg q12h, P.O. |
400 mg q8h, I.V. |
|
AUC (mcg•hr/mL) Cmax (mcg/mL) |
13.7a 2.97 |
12.7a 4.56 |
31.6b 3.59 |
32.9c 4.07 |
Distribution
Metabolism
CONTRAINDICATIONS ; WARNINGS; PRECAUTIONS : Drug Interactions
Excretion
Drug-drug Interactions
PRECAUTIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS: PRECAUTIONS
Special Populations
max PRECAUTIONS: Geriatric Use
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
maxmaxmax
MICROBIOLOGY
in vitro In vitro
in vitro.
in vitro INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Aerobic gram-positive microorganisms
Enterococcus faecalis
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pyogenes
Aerobic gram-negative microorganisms
Campylobacter jejuni Proteus mirabilis
Citrobacter diversus Proteus vulgaris
Citrobacter freundii Providencia rettgeri
Enterobacter cloacae Providencia stuartii
Escherichia coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Haemophilus influenzae Salmonella typhi
Haemophilus parainfluenzae Serratia marcescens
Klebsiella pneumoniae Shigella boydii
Moraxella catarrhalis Shigella dysenteriae
Morganella morganii Shigella flexneri
Neisseria gonorrhoeae Shigella sonnei
Bacillus anthracis in vitro INDICATIONS AND USAGE INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
in vitro but their clinical significance is unknown.
in vitro
Aerobic gram-positive microorganisms
Staphylococcus haemolyticus
Staphylococcus hominis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Aerobic gram-negative microorganisms
Acinetobacter Iwoffi Pasteurella multocida
Aeromonas hydrophila Salmonella enteritidis
Edwardsiella tarda Vibrio cholerae
Enterobacter aerogenes Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Klebsiella oxytoca Vibrio vulnificus
Legionella pneumophila Yersinia enterocolitica
Burkholderia cepacia Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Bacteroides fragilis Clostridium difficile.
Susceptibility Tests
Dilution Techniques
1
Enterobacteriaceae,Enterococcus faecalis,Staphylococcus Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes,Pseudomonas aeruginosaa
| MIC (mcg/mL) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| ≤ 1 2 ≥ 4 |
Susceptible (S) Intermediate (I) Resistant (R) |
Haemophilus influenzae Haemophilus parainfluenzaeb
| MIC (mcg/mL) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| ≤ 1 |
Susceptible (S) |
b Haemophilus influenzae Haemophilus parainfluenzae Haemophilus 1
Neisseria gonorrhoeaec
| MIC (mcg/mL) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| ≤ 0.06 0.12 – 0.5 ≥ 1 |
Susceptible (S) Intermediate (I) Resistant (R) |
| Organism | MIC (mcg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
|
a This quality control range is applicable to only H. influenzae ATCC 49247 tested by a broth microdilution procedure using Haemophilus Test Medium (HTM)1. b C. jejuni ATCC 33560 tested by broth microdilution procedure using cation adjusted Mueller Hinton broth with 2.5 to 5% lysed horse blood in a microaerophilic environment at 36 to 37oC for 48 hours and for 42oC at 24 hours2, respectively. c N. gonorrhoeae ATCC 49226 tested by agar dilution procedure using GC agar and 1% defined growth supplement in a 5% CO2 environment at 35 to 37oC for 20 to 24 hours3. |
||
|
E. faecalis
E. coli H. influenzae a P. aeruginosa S. aureus C. jejuni b N. gonorrhoeae c |
ATCC 29212 ATCC 25922 ATCC 49247 ATCC 27853 ATCC 29213 ATCC 33560 ATCC 49226 |
0.25 – 2 0.004 – 0.015 0.004 – 0.03 0.25 – 1 0.12 – 0.5 0.06 – 0.25 and 0.03 – 0.12 0.001 – 0.008 |
Diffusion Techniques
3
EnterobacteriaceaeEnterococcus faecalisStaphylococcusStreptococcus pneumoniaeStreptococcus pyogenesPseudomonas aeruginosaa
| Zone Diameter (mm) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| ≥ 21 16 – 20 ≤ 15 |
Susceptible (S) Intermediate (I) Resistant (R) |
Haemophilus influenzae Haemophilus parainfluenzaeb:
| Zone Diameter (mm) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| ≥ 21 |
Susceptible (S) |
Neisseria gonorrhoeaec
| Zone Diameter (mm) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| ≥ 41 28 – 40 ≤ 27 |
Susceptible (S) Intermediate (I) Resistant (R) |
| Organism | Zone Diameter (mm) | |
|---|---|---|
|
a These quality control limits are applicable to only H. influenzae ATCC 49247 testing using Haemophilus Test Medium (HTM)3. b These quality control limits are applicable only to tests conducted with N. gonorrhoeae ATCC 49226 performed by disk diffusion using GC agar base and 1% defined growth supplement. |
||
|
E. coli
H. influenzae a N. gonorrhoeae b P. aeruginosa S. aureus |
ATCC 25922 ATCC 49247 ATCC 49226 ATCC 27853 ATCC 25923 |
30 – 40 34 – 42 48 – 58 25 – 33 22 – 30 |
CIPROFLOXACIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adult Patients
Urinary Tract Infections Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Serratia marcescens, Proteus mirabilis, Providencia rettgeri, Morganella morganii, Citrobacter diversus, Citrobacter freundii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecalis.
Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis in females Escherichia coli Staphylococcus saprophyticus.
Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis Escherichia coli Proteus mirabilis.
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae. Moraxella catarrhalis
Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Acute Sinusitis Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis.
Skin and Skin Structure Infections Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia stuartii, Morganella morganii, Citrobacter freundii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pyogenes.
Bone and Joint Infections Enterobacter cloacae, Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Complicated Intra-Abdominal Infections Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Bacteroides fragilis.
Infectious Diarrhea Escherichia coli Campylobacter jejuni, Shigella boydii†, Shigella dysenteriae, Shigella flexneri Shigella sonnei†
Typhoid Fever (Enteric Fever) Salmonella typhi.
Uncomplicated cervical and urethral gonorrhea Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Pediatric patients (1 to 17 years of age)
Complicated Urinary Tract Infections and Pyelonephritis Escherichia coli.
WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use, ADVERSE REACTIONS CLINICAL STUDIES ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY
Adult and Pediatric Patients
Inhalational anthrax Bacillus anthracis.
5 INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION).
†
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
CIPROFLOXACIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions .
WARNINGS
Tendinopathy and Tendon Rupture
Exacerbation of Myasthenia Gravis
PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patients ADVERSE REACTIONS: Post-Marketing Adverse Event Reports.
Pregnant Women
THE SAFETY AND EFFECTIVENESS OF CIPROFLOXACIN IN PREGNANT AND LACTATING WOMEN HAVE NOT BEEN ESTABLISHED. PRECAUTIONS: Pregnancy, Nursing Mothers
Pediatrics
INDICATIONS AND USAGE ADVERSE REACTIONS
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY
Cytochrome P450 (CYP450)
Central Nervous System Disorders
PRECAUTIONS: General, Information for Patients, Drug Interactions ADVERSE REACTIONS
Theophylline
SERIOUS AND FATAL REACTIONS HAVE BEEN REPORTED IN PATIENTS RECEIVING CONCURRENT ADMINISTRATION OF CIPROFLOXACIN AND THEOPHYLLINE.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- fever, rash, or severe dermatologic reactions (e.g., toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome);
- vasculitis; arthralgia; myalgia; serum sickness;
- allergic pneumonitis;
- interstitial nephritis; acute renal insufficiency or failure;
- hepatitis; jaundice; acute hepatic necrosis or failure;
- anemia, including hemolytic and aplastic; thrombocytopenia, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; leukopenia; agranulocytosis; pancytopenia; and/or other hematologic abnormalities.
Pseudomembranous Colitis
Clostridium difficile C. difficile.
C. difficile C. difficile
C. difficile C. difficile
Peripheral neuropathy
Syphilis
PRECAUTIONS
General
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY
Central Nervous System
WARNINGS, Information for Patients, Drug Interactions
Renal Impairment
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Photosensitivity/Phototoxicity
ADVERSE REACTIONS/Post-Marketing Adverse Events
Information for Patients
- to contact their healthcare provider if they experience pain, swelling, or inflammation of a tendon, or weakness or inability to use one of their joints; rest and refrain from exercise; and discontinue ciprofloxacin treatment. The risk of severe tendon disorder with fluoroquinolones is higher in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants.
- that fluoroquinolones like ciprofloxacin may cause worsening of myasthenia gravis symptoms, including muscle weakness and breathing problems. Patients should call their healthcare provider right away if they have any worsening muscle weakness or breathing problems.
- that antibacterial drugs including ciprofloxacin tablets should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When ciprofloxacin tablets are prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by ciprofloxacin tablets or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
- that ciprofloxacin may be taken with or without meals and to drink fluids liberally. As with other quinolones, concurrent administration of ciprofloxacin with magnesium/aluminum antacids, or sucralfate, didanosine chewable/buffered tablets or pediatric powder, other highly buffered drugs, or with other products containing calcium, iron or zinc should be avoided. Ciprofloxacin may be taken two hours before or six hours after taking these products. Ciprofloxacin should not be taken with dairy products (like milk or yogurt) or calcium-fortified juices alone since absorption of ciprofloxacin may be significantly reduced; however, ciprofloxacin may be taken with a meal that contains these products.
- that ciprofloxacin may be associated with hypersensitivity reactions, even following a single dose, and to discontinue the drug at the first sign of a skin rash or other allergic reaction.
- that photosensitivity/phototoxicity has been reported in patients receiving quinolones. Patients should minimize or avoid exposure to natural or artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while taking quinolones. If patients need to be outdoors while using quinolones, they should wear loose-fitting clothes that protect skin from sun exposure and discuss other sun protection measures with their physician. If a sunburn-like reaction or skin eruption occurs, patients should contact their physician.
- that peripheral neuropathies have been associated with ciprofloxacin use. If symptoms of peripheral neuropathy including pain, burning, tingling, numbness and/or weakness develop, they should discontinue treatment and contact their physicians.
- that ciprofloxacin may cause dizziness and lightheadedness; therefore, patients should know how they react to this drug before they operate an automobile or machinery or engage in activities requiring mental alertness or coordination.
- that ciprofloxacin increases the effects of tizanidine. Patients should not use ciprofloxacin if they are already taking tizanidine.
- that ciprofloxacin may increase the effects of theophylline and caffeine. There is a possibility of caffeine accumulation when products containing caffeine are consumed while taking quinolones.
- that convulsions have been reported in patients receiving quinolones, including ciprofloxacin, and to notify their physician before taking this drug if there is a history of this condition.
- that ciprofloxacin has been associated with an increased rate of adverse events involving joints and surrounding tissue structures (like tendons) in pediatric patients (less than 18 years of age). Parents should inform their child’s physician if the child has a history of joint-related problems before taking this drug. Parents of pediatric patients should also notify their child’s physician of any joint-related problems that occur during or following ciprofloxacin therapy. (See WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use and ADVERSE REACTIONS .)
- that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
Drug Interactions
max
WARNINGS
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
in vitro
E. coli
79
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
in vivo
2
24
2
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects. Pregnancy Category C
8
9 In utero
10in utero
8,9 WARNINGS
22 WARNINGS
Nursing Mothers
Pediatric Use
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY
Inhalational Anthrax (Post-Exposure)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Complicated Urinary Tract Infection and Pyelonephritis
Escherichia coli. ADVERSE REACTIONS CLINICAL STUDIES
Cystic Fibrosis
Geriatric Use
Boxed Warning, WARNINGS, ADVERSE REACTIONS/Post-Marketing Adverse Event Reports).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
CIPROFLOXACIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
Side Effects in Adult Patients
BODY AS A WHOLE:
CARDIOVASCULAR:
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM:
GASTROINTESTINAL:
HEMIC/LYMPHATIC:
METABOLIC/NUTRITIONAL:
MUSCULOSKELETAL:
RENAL/UROGENITAL:
RESPIRATORY:
SKIN/HYPERSENSITIVITY:
SPECIAL SENSES:
Side Effects in Pediatric Patients
| Findings Involving Joint or Peri-articular Tissues as Assessed by the IPSC | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ciprofloxacin | Comparator | |
| * The study was designed to demonstrate that the arthropathy rate for the ciprofloxacin group did not exceed that of the control group by more than + 6%. At both the 6 week and 1 year evaluations, the 95% confidence interval indicated that it could not be concluded that ciprofloxacin group had findings comparable to the control group. |
||
| All Patients (within 6 weeks) |
31/335 (9.3%) |
21/349 (6%) |
| 95% Confidence Interval* |
(-0.8%, +7.2%) |
|
| Age Group |
||
| ≥ 12 months < 24 months ≥ 2 years < 6 years ≥ 6 years < 12 years ≥ 12 years to 17 years |
1/36 (2.8%) 5/124 (4%) 18/143 (12.6%) 7/32 (21.9%) |
0/41 3/118 (2.5%) 12/153 (7.8%) 6/37 (16.2 %) |
| All Patients (within 1 year) |
46/335 (13.7%) |
33/349 (9.5%) |
| 95% Confidence Interval* |
(-0.6%, + 9.1%) |
|
In this trial, the overall incidence rates of adverse events regardless of relationship to study drug and within 6 weeks of treatment initiation were 41% (138/335) in the ciprofloxacin group versus 31% (109/349) in the comparator group. The most frequent events were gastrointestinal: 15% (50/335) of ciprofloxacin patients compared to 9% (31/349) of comparator patients. Serious adverse events were seen in 7.5% (25/335) of ciprofloxacin-treated patients compared to 5.7% (20/349) of control patients. Discontinuation of drug due to an adverse event was observed in 3% (10/335) of ciprofloxacin-treated patients versus 1.4% (5/349) of comparator patients. Other adverse events that occurred in at least 1% of ciprofloxacin patients were diarrhea 4.8%, vomiting 4.8%, abdominal pain 3.3%, accidental injury 3%, rhinitis 3%, dyspepsia 2.7%, nausea 2.7%, fever 2.1%, asthma 1.8% and rash 1.8%.
In addition to the events reported in pediatric patients in clinical trials, it should be expected that events reported in adults during clinical trials or post-marketing experience may also occur in pediatric patients.
Post-Marketing Adverse Event Reports
PRECAUTIONS
INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION .
Adverse Laboratory Changes
OVERDOSAGE
CIPROFLOXACIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
ADULTS
| ADULT DOSAGE GUIDELINES | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infection | Severity | Dose | Frequency | Usual Durations† |
|
* used in conjunction with metronidazole † Generally ciprofloxacin should be continued for at least 2 days after the signs and symptoms of infection have disappeared, except for inhalational anthrax (post-exposure). ** Drug administration should begin as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed exposure. This indication is based on a surrogate endpoint, ciprofloxacin serum concentrations achieved in humans, reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit.4 For a discussion of ciprofloxacin serum concentrations in various human populations, see INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION . |
||||
| Urinary Tract |
Acute Uncomplicated Mild/Moderate Severe/Complicated |
250 mg 250 mg 500 mg |
q 12 h q 12 h q 12 h |
3 Days 7 to 14 Days 7 to 14 Days |
| Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis |
Mild/Moderate |
500 mg |
q 12 h |
28 Days |
| Lower Respiratory Tract |
Mild/Moderate Severe/Complicated |
500 mg 750 mg |
q 12 h q 12 h |
7 to 14 days 7 to 14 days |
| Acute Sinusitis |
Mild/Moderate |
500 mg |
q 12 h |
10 days |
| Skin and Skin Structure |
Mild/Moderate Severe/Complicated |
500 mg 750 mg |
q 12 h q 12 h |
7 to 14 Days 7 to 14 Days |
| Bone and Joint |
Mild/Moderate Severe/Complicated |
500 mg 750 mg |
q 12 h q 12 h |
≥ 4 to 6 weeks ≥ 4 to 6 weeks |
| Intra-Abdominal* |
Complicated |
500 mg |
q 12 h |
7 to 14 Days |
| Infectious Diarrhea |
Mild/Moderate/Severe |
500 mg |
q 12 h |
5 to 7 Days |
| Typhoid Fever |
Mild/Moderate |
500 mg |
q 12 h |
10 Days |
| Urethral and Cervical Gonococcal Infections |
Uncomplicated |
250 mg |
single dose |
single dose |
| Inhalational anthrax (post-exposure)** |
|
500 mg |
q 12 h |
60 Days |
Conversion of I.V. to Oral Dosing in Adults
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
| Equivalent AUC Dosing Regimens | |
|---|---|
| Ciprofloxacin Oral Dosage | Equivalent Ciprofloxacin I.V. Dosage |
| 250 mg Tablet q 12 h 500 mg Tablet q 12 h 750 mg Tablet q 12 h |
200 mg I.V. q 12 h 400 mg I.V. q 12 h 400 mg I.V. q 8 h |
Adults with Impaired Renal Function
| RECOMMENDED STARTING AND MAINTENANCE DOSES FOR PATIENTS WITH IMPAIRED RENAL FUNCTION | |
|---|---|
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | Dose |
| > 50 30 – 50 5 – 29 Patients on hemodialysis or Peritoneal dialysis |
See Usual Dosage. 250 – 500 mg q 12 h 250 – 500 mg q 18 h 250 – 500 mg q 24 h (after dialysis) |
Weight (kg) x (140 - age)
PEDIATRICS
Ciprofloxacin tablets should be administered orally as described in the Dosage Guidelines table. An increased incidence of adverse events compared to controls, including events related to joints and/or surrounding tissues, has been observed. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS and CLINICAL STUDIES .)
|
* The total duration of therapy for complicated urinary tract infection and pyelonephritis in the clinical trial was determined by the physician. The mean duration of treatment was 11 days (range 10 to 21 days). ** Drug administration should begin as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed exposure to Bacillus anthracis spores. This indication is based on a surrogate endpoint, ciprofloxacin serum concentrations achieved in humans, reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit.5For a discussion of ciprofloxacin serum concentrations in various human populations, see INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION . |
|||||
|
PEDIATRIC DOSAGE GUIDELINES
|
|||||
| Infection |
Route of Administration |
Dose (mg/kg) |
Frequency |
Total Duration |
|
| Complicated Urinary Tract or Pyelonephritis |
Intravenous |
6 to 10 mg/kg (maximum 400 mg per dose; not to be exceeded even in patients weighing > 51 kg) |
Every 8 hours |
10-21 days* |
|
| (patients from 1 to 17 years of age) |
Oral |
10 mg/kg to 20 mg/kg (maximum 750 mg per dose; not to be exceeded even in patients weighing > 51 kg) |
Every 12 hours |
||
| Inhalational Anthrax (Post- Exposure)** |
Intravenous |
10 mg/kg (maximum 400 mg per dose) |
Every 12 hours |
60 days |
|
| Oral |
15 mg/kg (maximum 500 mg per dose) |
Every 12 hours |
|||
Pediatric patients with moderate to severe renal insufficiency were excluded from the clinical trial of complicated urinary tract infection and pyelonephritis. No information is available on dosing adjustments necessary for pediatric patients with moderate to severe renal insufficiency (i.e., creatinine clearance of < 50 mL/min/1.73m2).
HOW SUPPLIED
Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg
Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 500 mg
Store at
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY
WARNINGS
22
CLINICAL STUDIES
Complicated Urinary Tract Infection and Pyelonephritis – Efficacy in Pediatric Patients
|
*Patients with baseline pathogen(s) eradicated and no new infections or superinfections/total number of patients. There were 5.5% (6/211) ciprofloxacin and 9.5% (22/231) comparator patients with superinfections or new infections. |
||
| |
Ciprofloxacin
|
Comparator
|
| Randomized Patients |
337 |
352 |
| Per Protocol Patients |
211 |
231 |
| Clinical Response at 5 to 9 Days Post-Treatment |
95.7% (202/211) |
92.6% (214/231) |
| |
95% CI [-1.3%, 7.3%] |
|
| Bacteriologic Eradication by Patient at 5 to 9 Days Post-Treatment* |
84.4% (178/211) |
78.3% (181/231) |
| |
95% CI [-1.3%, 13.1%] |
|
| Bacteriologic Eradication of the Baseline Pathogen at 5 to 9 Days Post-Treatment |
|
|
|
Escherichia coli
|
156/178 (88%) |
161/179 (90%) |
INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX IN ADULTS AND PEDIATRICS – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use 5
50550B. anthracis max67
B. anthracis
REFERENCES
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically-Fifth Edition. Approved Standard NCCLS Document M7-A5, Vol. 20, No. 2, NCCLS, Wayne, PA, January, 2000.
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Methods for Antimicrobial Dilution and Disk Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria; Approved Guideline., CLSI Document M45-A, Vol. 26, No. 19, CLSI, Wayne, PA, 2006.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests-Seventh Edition. Approved Standard NCCLS Document M2-A7, Vol. 20, No. 1, NCCLS, Wayne, PA, January, 2000.
- Report presented at the FDA’s Anti-Infective Drug and Dermatological Drug Product’s Advisory Committee meeting, March 31, 1993, Silver Spring, MD. Report available from FDA, CDER, Advisors and Consultants Staff, HFD-21, 1901 Chapman Avenue, Room 200, Rockville, MD 20852, USA.
- 21 CFR 314.510 (Subpart H – Accelerated Approval of New Drugs for Life-Threatening Illnesses).
- Kelly DJ, et al. Serum concentrations of penicillin, doxycycline, and ciprofloxacin during prolonged therapy in rhesus monkeys. J Infect Dis 1992; 166:1184-7.
- Friedlander AM, et al. Postexposure prophylaxis against experimental inhalational anthrax. J Infect Dis 1993; 167:1239-42.
- Friedman J, Polifka J. Teratogenic effects of drugs: a resource for clinicians (TERIS). Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2000:149-195.
- Loebstein R, Addis A, Ho E, et al. Pregnancy outcome following gestational exposure to fluoroquinolones: a multicenter prospective controlled study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42(6):1336-1339.
- Schaefer C, Amoura-Elefant E, Vial T, et al. Pregnancy outcome after prenatal quinolone exposure. Evaluation of a case registry of the European network of teratology information services (ENTIS). Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1996;69:83-89.
Aurolife Pharma LLC
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Revised: 03/2011
MEDICATION GUIDE
Ciprofloxacin Tablets, USP
What is the most important information I should know about ciprofloxacin tablets?
-
Tendon rupture or swelling of the tendon (tendinitis)
- Tendons are tough cords of tissue that connect muscles to bones.
- Pain, swelling, tears, and inflammation of tendons including the back of the ankle (Achilles), shoulder, hand, or other tendon sites can happen in people of all ages who take fluoroquinolone antibiotics, including ciprofloxacin tablets. The risk of getting tendon problems is higher if you:
- are over 60 years of age
- are taking steroids (corticosteroids)
- have had a kidney, heart, or lung transplant.
- Swelling of the tendon (tendinitis) and tendon rupture (breakage) have also happened in patients who take fluoroquinolones who do not have the above risk factors.
- Other reasons for tendon ruptures can include:
- physical activity or exercise
- kidney failure
- tendon problems in the past, such as in people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Call your healthcare provider right away at the first sign of tendon pain, swelling or inflammation. Stop taking ciprofloxacin tablets until tendinitis or tendon rupture has been ruled out by your healthcare provider. Avoid exercise and using the affected area. The most common area of pain and swelling is the Achilles tendon at the back of your ankle. This can also happen with other tendons. Talk to your healthcare provider about the risk of tendon rupture with continued use of ciprofloxacin tablets. You may need a different antibiotic that is not a fluoroquinolone to treat your infection.
- Tendon rupture can happen while you are taking or after you have finished taking ciprofloxacin tablets. Tendon ruptures have happened up to several months after patients have finished taking their fluoroquinolone.
- Get medical help right away if you get any of the following signs or symptoms of a tendon rupture:
- hear or feel a snap or pop in a tendon area
- bruising right after an injury in a tendon area
- unable to move the affected area or bear weight
- Worsening of myasthenia gravis (a disease which causes muscle weakness). Fluoroquinolones like ciprofloxacin tablets may cause worsening of myasthenia gravis symptoms, including muscle weakness and breathing problems. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any worsening muscle weakness or breathing problems.
See the section “What are the possible side effects of ciprofloxacin tablets?” for more information about side effects.
What are ciprofloxacin tablets?
Who should not take ciprofloxacin tablets?
- have ever had a severe allergic reaction to an antibiotic known as a fluoroquinolone, or are allergic to any of the ingredients in ciprofloxacin tablets. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure. See the list of ingredients in ciprofloxacin tablets at the end of this Medication Guide.
- also take a medicine called tizanidine. Serious side effects from tizanidine are likely to happen.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking ciprofloxacin tablets?
“What is the most important information I should know about ciprofloxacin tablets?”
Tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have tendon problems
- have central nervous system problems (such as epilepsy)
- have nerve problems
- have or anyone in your family has an irregular heartbeat, especially a condition called “QT prolongation”
- have a history of seizures
- have kidney problems. You may need a lower dose of ciprofloxacin tablets if your kidneys do not work well.
- have rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or other history of joint problems
- have trouble swallowing pills
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if ciprofloxacin tablets will harm your unborn child.
- are breast-feeding or planning to breast-feed. Ciprofloxacin passes into breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide whether you will take ciprofloxacin tablets or breastfeed.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins and herbal and dietary supplements. Ciprofloxacin tablets and other medicines can affect each other causing side effects. The risk of getting tendon problems is higher if you:
- an NSAID (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug). Many common medicines for pain relief are NSAIDs. Taking an NSAID while you take ciprofloxacin tablets or other fluoroquinolones may increase your risk of central nervous system effects and seizures. See “ What are the possible side effects of ciprofloxacin tablets? ”.
- a blood thinner
- tizanidine. You should not take ciprofloxacin tablets if you are already taking tizanidine. See “ Who should not take ciprofloxacin tablets? ”
- theophylline
- glyburide. See “ What are the possible side effects of ciprofloxacin tablets? ”
- phenytoin
- products that contain caffeine
- a medicine to control your heart rate or rhythm (antiarrhythmics) See “ What are the possible side effects of ciprofloxacin tablets? ”
- an anti-psychotic medicine
- a tricyclic antidepressant
- a water pill (diuretic)
- a steroid medicine. Corticosteroids taken by mouth or by injection may increase the chance of tendon injury. See “ What is the most important information I should know about ciprofloxacin tablets? ”
- methotrexate
- Probenecid
- Metoclopromide
- Certain medicines may keep ciprofloxacin tablets from working correctly. Take ciprofloxacin tablets either 2 hours before or 6 hours after taking these products:
- an antacid, multivitamin, or other product that has magnesium, calcium, aluminum, iron, or zinc
- sucralfate
- didanosine.
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if any of your medicines are listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take ciprofloxacin tablets?
- Take ciprofloxacin tablets exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Take ciprofloxacin tablets in the morning and evening at about the same time each day. Swallow the tablet whole. Do not split, crush or chew the tablet. Tell your healthcare provider if you can not swallow the tablet whole.
- Ciprofloxacin tablets can be taken with or without food.
- Ciprofloxacin tablets should not be taken with dairy products (like milk or yogurt) or calcium-fortified juices alone, but may be taken with a meal that contains these products.
- Drink plenty of fluids while taking ciprofloxacin tablets.
- Do not skip any doses, or stop taking ciprofloxacin tablets even if you begin to feel better, until you finish your prescribed treatment, unless:
- you have tendon effects (see “ What is the most important information I should know about ciprofloxacin tablets? ”),
- you have a serious allergic reaction (see “ What are the possible side effects of ciprofloxacin tablets? ”), or
- your healthcare provider tells you to stop.
- If you miss a dose of ciprofloxacin tablets, take them as soon as you remember. Do not take two doses at the same time, and do not take more than two doses in one day.
- If you take too much, call your healthcare provider or get medical help immediately.
If you have been prescribed ciprofloxacin tablets after being exposed to anthrax:
- Ciprofloxacin tablets have been approved to lessen the chance of getting anthrax disease or worsening of the disease after you are exposed to the anthrax bacteria germ.
- Take ciprofloxacin tablets exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not stop taking ciprofloxacin tablets without talking with your healthcare provider. If you stop taking ciprofloxacin tablets too soon, it may not keep you from getting the anthrax disease.
- Side effects may happen while you are taking ciprofloxacin tablets. When taking your ciprofloxacin tablets to prevent anthrax infection, you and your healthcare provider should talk about whether the risks of stopping ciprofloxacin tablets too soon are more important than the risks of side effects with ciprofloxacin tablets.
- If you are pregnant, or plan to become pregnant while taking ciprofloxacin tablets, you and your healthcare provider should decide whether the benefits of taking ciprofloxacin tablets for anthrax are more important than the risks.
What should I avoid while taking ciprofloxacin tablets?
- Ciprofloxacin tablets can make you feel dizzy and lightheaded. Do not drive, operate machinery, or do other activities that require mental alertness or coordination until you know how ciprofloxacin tablets affects you.
- Avoid sunlamps, tanning beds, and try to limit your time in the sun. Ciprofloxacin tablets can make your skin sensitive to the sun (photosensitivity) and the light from sunlamps and tanning beds. You could get severe sunburn, blisters or swelling of your skin. If you get any of these symptoms while taking ciprofloxacin tablets, call your healthcare provider right away. You should use a sunscreen and wear a hat and clothes that cover your skin if you have to be in sunlight.
What are the possible side effects of ciprofloxacin tablets?
- Ciprofloxacin tablets can cause side effects that may be serious or even cause death. See “What is the most important information I should know about ciprofloxacin tablets?”
- Central Nervous System Effects
Seizures have been reported in people who take fluoroquinolone antibiotics including ciprofloxacin tablets. Tell your healthcare provider if you have a history of seizures. Ask your healthcare provider whether taking ciprofloxacin tablets will change your risk of having a seizure.
Central Nervous System (CNS) side effects may happen as soon as after taking the first dose of ciprofloxacin tablets. Talk to your healthcare provider right away if you get any of these side effects, or other changes in mood or behavior:
- feel dizzy
- seizures
- hear voices, see things, or sense things that are not there (hallucinations)
- feel restless
- tremors
- feel anxious or nervous
- confusion
- depression
- trouble sleeping
- nightmares
- feel more suspicious (paranoia)
- suicidal thoughts or acts
- Serious allergic reactions
Allergic reactions can happen in people taking fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin tablets, even after only one dose. Stop taking ciprofloxacin tablets and get emergency medical help right away if you get any of the following symptoms of a severe allergic reaction:
- hives
- trouble breathing or swallowing
- swelling of the lips, tongue, face
- throat tightness, hoarseness
- rapid heartbeat
- faint
- yellowing of the skin or eyes. Stop taking ciprofloxacin tablets and tell your healthcare provider right away if you get yellowing of your skin or white part of your eyes, or if you have dark urine. These can be signs of a serious reaction to ciprofloxacin tablets (a liver problem).
- Skin rash
- Serious heart rhythm changes (QT prolongation and torsade de pointes)
- who are elderly
- with a family history of prolonged QT interval
- with low blood potassium (hypokalemia)
- who take certain medicines to control heart rhythm (antiarrhythmics)
- Intestine infection (Pseudomembranous colitis)
- Changes in sensation and possible nerve damage (Peripheral Neuropathy)
Damage to the nerves in arms, hands, legs, or feet can happen in people who take fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin tablets. Talk with your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms of peripheral neuropathy in your arms, hands, legs, or feet:
- pain
- burning
- tingling
- numbness
- weakness
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- Sensitivity to sunlight (photosensitivity)
See “ What should I avoid while taking ciprofloxacin tablets? ”
- Joint Problems
Increased chance of problems with joints and tissues around joints in children under 18 years old. Tell your child’s healthcare provider if your child has any joint problems during or after treatment with ciprofloxacin tablets.
The most common side effects of ciprofloxacin tablets include:
- nausea
- headache
- diarrhea
- vomiting
- vaginal yeast infection
- changes in liver function tests
- pain or discomfort in the abdomen
These are not all the possible side effects of ciprofloxacin tablets. Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you, or that does not go away.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store ciprofloxacin tablets?
Store at
Keep ciprofloxacin tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about ciprofloxacin tablets
What are the ingredients in ciprofloxacin tablets?
Aurolife Pharma LLC
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.

CiprofloxacinCiprofloxacin TABLET, FILM COATED
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||