Clopidogrel Bisulfate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use clopidogrel safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for clopidogrel tablets. Clopidogrel Tablets, USP Initial U.S. Approval: 1997 RECENT MAJOR CHANGES2.45.1BOXED WARNING WARNING: DIMINISHED EFFECTIVENESS IN POOR METABOLIZERSSee full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. Effectiveness of clopidogrel depends on activation to an active metabolite by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system, principally CYP2C19. (5.1) Poor metabolizers treated with clopidogrel at recommended doses exhibit higher cardiovascular event rates following acute coronary syndrome (ACS) or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) than patients with normal CYP2C19 function. (12.5) Tests are available to identify a patient's CYP2C19 genotype and can be used as an aid in determining therapeutic strategy. (12.5). Consider alternative treatment or treatment strategies in patients identified as CYP2C19 poor metabolizers. (2.3, 5.1) INDICATIONS AND USAGE12 Acute coronary syndrome For patients with non-ST-segment elevation ACS [unstable angina (UA)/non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)] including patients who are to be managed medically and those who are to be managed with coronary revascularization, clopidogrel tablets have been shown to decrease the rate of a combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction (MI), or stroke as well as the rate of a combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, MI, stroke, or refractory ischemia. (1.1) For patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), clopidogrel tablets have been shown to reduce the rate of death from any cause and the rate of a combined endpoint of death, re-infarction, or stroke. The benefit for patients who undergo primary PCI is unknown. (1.1) Recent myocardial infarction (MI), recent stroke, or established peripheral arterial disease. Clopidogrel tablets have been shown to reduce the combined endpoint of new ischemic stroke (fatal or not), new MI (fatal or not), and other vascular death. (1.2) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Acute coronary syndrome (2.1) Non-ST-segment elevation ACS (UA/NSTEMI): 300 mg loading dose followed by 75 mg once daily, in combination with aspirin (75 mg to 325 mg once daily) STEMI: 75 mg once daily, in combination with aspirin (75 mg to 325 mg once daily), with or without a loading dose and with or without thrombolytics Recent MI, recent stroke, or established peripheral arterial disease: 75 mg once daily (2.2) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS3CONTRAINDICATIONS Active pathological bleeding, such as peptic ulcer or intracranial hemorrhage (4.1) Hypersensitivity to clopidogrel or any component of the product (4.2) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Reduced effectiveness in impaired CYP2C19 function: Avoid concomitant use with omeprazole or esomeprazole. (5.1) Bleeding: clopidogrel increases risk of bleeding. Discontinue 5 days prior to elective surgery. (5.2) Discontinuation of clopidogrel: Premature discontinuation increases risk of cardiovascular events. (5.3) Recent transient ischemic attack or stroke: Combination use of clopidogrel and aspirin in these patients was not shown to be more effective than clopidogrel alone, but was shown to increase major bleeding. (5.4) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP): TTP has been reported with clopidogrel, including fatal cases. (5.5) Side Effects6.1To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact CARACO Pharmaceutical Laboratories Ltd. at 1-800-818-4555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Combination use increases risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. (7.2) Warfarin: Combination use increases risk of bleeding. (7.3) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS8.3
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING: DIMINISHED EFFECTIVENESS IN POOR METABOLIZERS
- 1 CLOPIDOGREL BISULFATE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 CLOPIDOGREL BISULFATE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CLOPIDOGREL BISULFATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 CLOPIDOGREL BISULFATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 CLOPIDOGREL BISULFATE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: DIMINISHED EFFECTIVENESS IN POOR METABOLIZERS
The effectiveness of clopidogrel is dependent on its activation to an active metabolite by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system, principally CYP2C19 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Clopidogrel at recommended doses forms less of that metabolite and has a smaller effect on platelet function in patients who are CYP2C19 poor metabolizers. Poor metabolizers with acute coronary syndrome or undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention treated with clopidogrel at recommended doses exhibit higher cardiovascular event rates than do patients with normal CYP2C19 function. Tests are available to identify a patient's CYP2C19 genotype; these tests can be used as an aid in determining therapeutic strategy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.5)]. Consider alternative treatment or treatment strategies in patients identified as CYP2C19 poor metabolizers [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
- For patients with non-ST-segment elevation ACS [unstable angina (UA)/non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)], including patients who are to be managed medically and those who are to be managed with coronary revascularization, clopidogrel tablets have been shown to decrease the rate of a combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction (MI), or stroke as well as the rate of a combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, MI, stroke, or refractory ischemia.
- For patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), clopidogrel tablets have been shown to reduce the rate of death from any cause and the rate of a combined endpoint of death, re-infarction, or stroke. The benefit for patients who undergo primary percutaneous coronary intervention is unknown.
The optimal duration of clopidogrel tablets therapy in ACS is unknown.
1.2 Recent MI, Recent Stroke, or Established Peripheral Arterial Disease
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Acute Coronary Syndrome
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].- For patients with non-ST-elevation ACS (UA/NSTEMI), initiate clopidogrel tablets with a single 300 mg oral loading dose and then continue at 75 mg once daily. Initiate aspirin (75 mg to 325 mg once daily) and continue in combination with clopidogrel tablets [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
- For patients with STEMI, the recommended dose of clopidogrel tablets is 75 mg once daily orally, administered in combination with aspirin (75 mg to 325 mg once daily), with or without thrombolytics. Clopidogrel tablets may be initiated with or without a loading dose [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
2.2 Recent MI, Recent Stroke, or Established Peripheral Arterial Disease
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]2.3 CYP2C19 Poor Metabolizers
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.5)]2.4 Use with Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI)
Avoid using omeprazole or esomeprazole with clopidogrel tablets. Omeprazole and esomeprazole significantly reduce the antiplatelet activity of clopidogrel. When concomitant administration of a PPI is required, consider using another acid-reducing agent with minimal or no CYP2C19 inhibitory effect on the formation of clopidogrel active metabolite [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 75 mg tablets: Pink, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets imprinted with “894” on one side and plain on the other side
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Active Bleeding
4.2 Hypersensitivity
[see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Diminished Antiplatelet Activity Due to Impaired CYP2C19 Function
Clopidogrel is a prodrug. Inhibition of platelet aggregation by clopidogrel is achieved through an active metabolite. The metabolism of clopidogrel to its active metabolite can be impaired by genetic variations in CYP2C19 [see Boxed Warning] and by concomitant medications that interfere with CYP2C19.Proton Pump Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of clopidogrel tablets with omeprazole or esomeprazole because both significantly reduce the antiplatelet activity of clopidogrel [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.2 General Risk of Bleeding
5.3 Discontinuation of Clopidogrel
5.4 Patients with Recent Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) or Stroke
5.5 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
[see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Bleeding
CURE
| Event | Clopidogrel (+ aspirin)  (n=6259) |
Placebo (+ aspirin)  (n=6303) |
|---|---|---|
Major bleeding |
3.7 Major bleeding event rates for clopidogrel + aspirin by age were: <65 years = 2.5%, ≥65 to <75 years = 4.1%, ≥75 years = 5.9% |
2.7 Major bleeding event rates for placebo + aspirin by age were: <65 years = 2.1%, ≥65 to <75 years = 3.1%, ≥75 years = 3.6% |
| Life-threatening bleeding |
2.2 |
1.8 |
| Fatal |
0.2 |
0.2 |
| 5 g/dL hemoglobin drop |
0.9 |
0.9 |
| Requiring surgical intervention |
0.7 |
0.7 |
| Hemorrhagic strokes |
0.1 |
0.1 |
| Requiring inotropes |
0.5 |
0.5 |
| Requiring transfusion (≥4 units) |
1.2 |
1 |
| Other major bleeding |
1.6 |
1 |
| Significantly disabling |
0.4 |
0.3 |
| Intraocular bleeding with significant loss of vision |
0.05 |
0.03 |
| Requiring 2 to 3 units of blood |
1.3 |
0.9 |
Minor bleeding |
5.1 |
2.4 |
COMMIT
| Type of bleeding | Clopidogrel(+ aspirin) (n=22961) | Placebo (+ aspirin) (n=22891) |
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
Major  Major noncerebral Fatal Hemorrhagic stroke Fatal |
0.6 0.4 0.2 0.2 0.2 |
0.5 0.3 0.2 0.2 0.2 |
0.59 0.48 0.9 0.91 0.81 |
| Other noncerebral bleeding (non-major) |
3.6 |
3.1 |
0.005 |
| Any noncerebral bleeding |
3.9 |
3.4 |
0.004 |
Other Adverse Events
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
- Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia/pancytopenia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
- Eye disorders: Eye (conjunctival, ocular, retinal) bleeding
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Gastrointestinal and retroperitoneal hemorrhage with fatal outcome, colitis (including ulcerative or lymphocytic colitis), pancreatitis, stomatitis, gastric/duodenal ulcer, diarrhea
- General disorders and administration site condition: Fever, hemorrhage of operative wound
- Hepato-biliary disorders: Acute liver failure, hepatitis (non-infectious), abnormal liver function test
- Immune system disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions, anaphylactoid reactions, serum sickness
- Musculoskeletal, connective tissue and bone disorders: Musculoskeletal bleeding, myalgia, arthralgia, arthritis
- Nervous system disorders: Taste disorders, fatal intracranial bleeding, headache
- Psychiatric disorders: Confusion, hallucinations
- Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Bronchospasm, interstitial pneumonitis, respiratory tract bleeding
- Renal and urinary disorders: Increased creatinine levels
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Maculopapular or erythematous rash, urticaria, bullous dermatitis, eczema, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, angioedema, erythema multiforme, skin bleeding, lichen planus, generalized pruritus
- Vascular disorders: Vasculitis, hypotension
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP2C19 Inhibitors
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Dosage and Administration (2.4)]Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI)
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
7.2 Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
7.3 Warfarin (CYP2C9 Substrates)
in vitr8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B2
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
8.6 Renal Impairment
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].8.7 Hepatic Impairment
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12SH1616224
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
1212.2 Pharmacodynamics
12Geriatric Patients
Renally-Impaired Patients
Hepatically-Impaired Patients
Gender
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Effect of Food
0-24max
Metabolism
maxmaxmax
Elimination
14
Drug Interactions
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI)
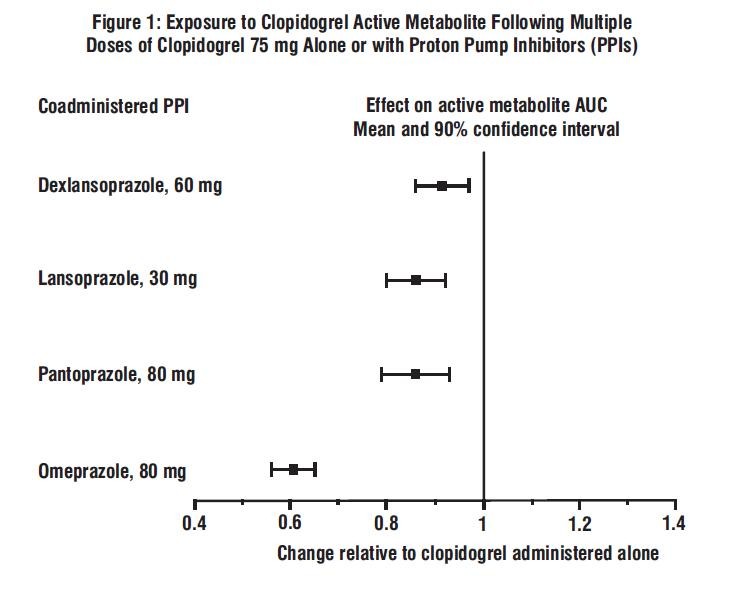
12.5 Pharmacogenomics
ex vivo| Dose | Ultrarapid (n=10) | Extensive (n=10) | Intermediate (n=10) | Poor (n=10) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values are mean (SD) |
|||||
| Cmax (ng/mL) |
300 mg (24 h) |
24 (10) |
32 (21) |
23 (11) |
11 (4) |
| 600 mg (24 h) |
36 (13) |
44 (27) |
39 (23) |
17 (6) |
|
| 75 mg (Day 5) |
12 (6) |
13 (7) |
12 (5) |
4 (1) |
|
| 150 mg (Day 5) |
16 (9) |
19 (5) |
18 (7) |
7 (2) |
|
IPA (%) |
300 mg (24 h) |
40 (21) |
39 (28) |
37 (21) |
24 (26) |
| 600 mg (24 h) |
51 (28) |
49 (23) |
56 (22) |
32 (25) |
|
| 75 mg (Day 5) |
56 (13) |
58 (19) |
60 (18) |
37 (23) |
|
| 150 mg (Day 5) |
68 (18) |
73 (9) |
74 (14) |
61 (14) |
|
VASP-PRI (%) |
300 mg (24 h) |
73 (12) |
68 (16) |
78 (12) |
91 (12) |
| 600 mg (24 h) |
51 (20) |
48 (20) |
56 (26) |
85 (14) |
|
| 75 mg (Day 5) |
40 (9) |
39 (14) |
50 (16) |
83 (13) |
|
| 150 mg (Day 5) |
20 (10) |
24 (10) |
29 (11) |
61 (18) |
|
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
in vitro in vivo
2
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Acute Coronary Syndrome
CURE| Outcome | Clopidogrel (+ aspirin)  (n=6259) |
Placebo (+ aspirin)  (n=6303) |
Relative Risk Reduction (%) (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary outcome (Cardiovascular death, MI, Stroke) |
582 (9.3%) |
719 (11.4%) |
20% (10.3, 27.9) p < 0.001 |
All Individual Outcome Events: |
|||
| CV death |
318 (5.1%) |
345 (5.5%) |
7% (-7.7, 20.6) |
| MI |
324 (5.2%) |
419 (6.6%) |
23% (11, 33.4) |
| Stroke |
75 (1.2%) |
87 (1.4%) |
14% (-17.7, 36.6) |


COMMIT
i.e.
| Event | Clopidogrel (+ aspirin) (N=22961) | Placebo (+ aspirin) (N=22891) | Odds ratio (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Composite endpoint: Death, MI, or Stroke |
2121 (9.2%) |
2310 (10.1%) |
0.91 (0.86, 0.97) |
0.002 |
|
Death
Non-fatal MI  Non-fatal Stroke  |
1726 (7.5%) 270 (1.2%) 127 (0.6%) |
1845 (8.1%) 330 (1.4%) 142 (0.6%) |
0.93 (0.87, 0.99) 0.81 (0.69, 0.95) 0.89 (0.7, 1.13) |
0.029 0.011 0.33 |




14.2 Recent Myocardial Infarction, Recent Stroke, or Established Peripheral Arterial Disease
CAPRIE| Patients |
Clopidogrel n=9599 |
Aspirin
n=9586 |
| Ischemic stroke (fatal or not) |
438 (4.6%) |
461 (4.8%) |
| MI (fatal or not) |
275 (2.9%) |
333 (3.5%) |
| Other vascular death |
226 (2.4%) |
226 (2.4%) |
| Total |
939 (9.8%) |
1020 (10.6%) |

14.3 Lack of Established Benefit of Clopidogrel plus Aspirin in Patients with Multiple Risk Factors or Established Vascular Disease
CHARISMA16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
[See Medication Guide (17.6)]
17.1 Benefits and Risks
- Summarize the effectiveness features and potential side effects of clopidogrel tablets.
- Tell patients to take clopidogrel tablets exactly as prescribed.
- Remind patients not to discontinue clopidogrel tablets without first discussing it with the physician who prescribed clopidogrel tablets.
17.2 Bleeding
- will bruise and bleed more easily.
- will take longer than usual to stop bleeding.
- should report any unanticipated, prolonged, or excessive bleeding, or blood in their stool or urine.
17.3 Other Signs and Symptoms Requiring Medical Attention
- Inform patients that TTP is a rare but serious condition that has been reported with clopidogrel and other drugs in this class of drugs.
- Instruct patients to get prompt medical attention if they experience any of the following symptoms that cannot otherwise be explained: fever, weakness, extreme skin paleness, purple skin patches, yellowing of the skin or eyes, or neurological changes.
17.4 Invasive Procedures
- inform physicians and dentists that they are taking clopidogrel tablets before any invasive procedure is scheduled.
- tell the doctor performing the invasive procedure to talk to the prescribing health care professional before stopping clopidogrel tablets.
17.5 Concomitant Medications
[see Warnings and Precautions (5)]17.6 Medication Guide
MEDICATION GUIDE
Clopidogrel Tablets, USP
What is the most important information I should know about clopidogrel tablets?
1. Clopidogrel tablets may not work as well in people who:
- have certain genetic factors that affect how the body breaks down clopidogrel. Your doctor may do genetic tests to make sure clopidogrel tablets are right for you.
- take certain medicines, especially omeprazole (Prilosec ®*) or esomeprazole (Nexium ®*). Your doctor may change the medicine you take for stomach acid problems while you take clopidogrel tablets.
- you may bruise and bleed more easily
- you are more likely to have nose bleeds
- it will take longer for any bleeding to stop
- unexpected bleeding or bleeding that lasts a long time
- blood in your urine (pink, red or brown urine)
- red or black stools (looks like tar)
- bruises that happen without a known cause or get larger
- cough up blood or blood clots
- vomit blood or your vomit looks like coffee grounds
What are clopidogrel tablets?
- chest pain due to heart problems
- poor circulation in their legs (peripheral arterial disease)
- a heart attack
- a stroke
Who should not take clopidogrel tablets?
- currently have a condition that causes bleeding, such as a stomach ulcer
- are allergic to clopidogrel or other ingredients in clopidogrel tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in clopidogrel tablets.
- have a history of bowel (gastrointestinal) or stomach ulcers
- have a history of bleeding problems
- plan to have surgery or a dental procedure. See “How should I take clopidogrel tablets?”
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if clopidogrel tablets will harm your unborn baby
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if clopidogrel passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take clopidogrel tablets or breastfeed. You should not do both without talking to your doctor.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take
What is the most important information I should know about clopidogrel tablets?
Especially tell your doctor if you take
- aspirin, especially if you have had a stroke. Always talk to your doctor about whether you should take aspirin along with clopidogrel tablets to treat your condition.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of NSAID medicines if you are not sure.
- warfarin (Coumadin®*, Jantoven®*)
How should I take clopidogrel tablets?
- Take clopidogrel tablets exactly as your doctor tells you.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking clopidogrel tablets without talking to your doctor first. Stopping clopidogrel tablets may increase your risk of heart attack or stroke.
- Take clopidogrel tablets with aspirin as instructed by your doctor.
- You can take clopidogrel tablets with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, take clopidogrel tablets as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose. Take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take 2 doses of clopidogrel tablets at the same time unless your doctor tells you to.
- If you take too many clopidogrel tablets, call your doctor or go to the nearest emergency room right away.
- Talk with your doctor about stopping your clopidogrel tablets before you have surgery. Your doctor may tell you to stop taking clopidogrel tablets at least 5 days before you have surgery to avoid excessive bleeding during surgery.
Clopidogrel tablets can cause serious side effects including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about clopidogrel tablets?”
-
A blood clotting problem called Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP). TTP can happen with clopidogrel tablets, sometimes after a short time (less than 2 weeks). TTP is a blood clotting problem where blood clots form in blood vessels; and can happen anywhere in the body. TTP needs to be treated in a hospital right away, because it may cause death. Get medical help right away if you have any of these symptoms and they can not be explained by another medical condition:
- purplish spots (called purpura) on the skin or in the mouth (mucous membranes) due to bleeding under the skin
- your skin or the whites of your eyes are yellow (jaundice)
- you feel tired or weak
- your skin looks very pale
- fever
- fast heart rate or feeling short of breath
- headache
- speech changes
- confusion
- coma
- stroke
- seizure
- low amount of urine, or urine that is pink or has blood in it
- stomach area (abdominal) pain
- nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- vision changes
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store clopidogrel tablets?
- Store clopidogrel tablets at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F)
General information about clopidogrel tablets
What are the ingredients in clopidogrel tablets?
Active ingredient:
Inactive ingredients:
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Caraco Pharmaceutical Laboratories, Ltd.
Sun Pharmaceutical Ind. Ltd.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 47335-894-81
Clopidogrel Tablets, USP
75 mg
Rx only
90 TABLETS
SUN PHARMA
PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.

Clopidogrel BisulfateClopidogrel Bisulfate TABLET, FILM COATED
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!