DELFLEX
Fresenius Medical Care North America
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
The DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions, standard, low magnesium and low magnesium/low calcium, are sterile, non-pyrogenic formulations of Dextrose and Electrolytes in Water for Injection, USP, for use in peritoneal dialysis. The stay•safe exchange set utilizes an easy to use dial designed to eliminate the use of clamps and to prevent touch contamination of internal connection components. Composition, calculated osmolarity, pH and ionic concentrations are shown in the following table.

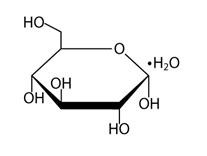
Hydrochloric Acid or Sodium Hydroxide may be added for pH adjustment; pH is 5.5 (5.0 - 6.0) Dextrose USP, is chemically designated D-glucose monohydrate (C6H12O6 • H2O) a hexose sugar freely soluble in water. It has the following structural formula:
These solutions do not contain antimicrobial agents or additional buffers. Exposure to temperatures above 25°C/77°F during transport and storage will lead to minor losses in moisture content. Higher temperatures lead to greater losses. It is unlikely that these minor losses will lead to clinically significant changes within the expiration period. Since the flexible inner bag is compounded from a specific polyvinyl chloride, water may permeate from the inner bag into the outerwrap in quantities insufficient to affect the solution significantly. Solutions in contact with the plastic inner bag can leach out certain of its chemical components in very small amounts; however, the safety of the plastic formulation is supported by biological tests for plastic containers.
Peritoneal dialysis is the process of filtering excess water and toxins from the bloodstream through a semi-permeable membrane. This process does not cure the disease, but prevents progression of symptoms. Dialysis for chronic kidney failure is essential to maintain life, unless the patient receives a kidney transplant. A peritoneal dialysis procedure utilizes the peritoneum (lining of the abdomen) as the semi-permeable membrane. The procedure is conducted by instilling peritoneal dialysis solution through a catheter in the abdomen into the peritoneal cavity. Since the peritoneum is heavily supplied with blood vessels, the contact of the solution with the peritoneum causes excess water and toxins in the bloodstream to be drawn across the membrane into the solution. This osmosis and diffusion occurs between the plasma of the patient and the peritoneal dialysis solution. After a period of time called "dwell time," the solution is then drained from the patient.
This solution does not contain potassium. In situations in which there is a normal serum potassium level or hypokalemia, the addition of potassium chloride (up to a concentration of 4 mEq/L) may be indicated to prevent severe hypokalemia. ADDITION OF POTASSIUM CHLORIDE SHOULD BE MADE AFTER CAREFUL EVALUATION OF SERUM AND TOTAL BODY POTASSIUM AND ONLY UNDER THE DIRECTION OF A PHYSICIAN.
Clinical studies have demonstrated that the use of low magnesium solutions resulted in significant increases in serum CO2 and decreases in serum magnesium levels. The decrease in magnesium levels did not cause clinically significant hypomagnesemia.
DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions are indicated in the treatment of chronic renal failure patients being maintained on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis when nondialytic medical therapy is judged to be inadequate.
None known.
Not for Intravenous Injection.
Use Aseptic Technique.
Peritoneal dialysis should be done with great care, in patients with a number of conditions, including disruption of the peritoneal membrane or diaphragm by surgery or trauma, extensive adhesions, bowel distention, undiagnosed abdominal disease, abdominal wall infection, hernias or burns, fecal fistula or colostomy, tense ascites, obesity, large polycystic kidneys, recent aortic graft replacement, lactic acidosis and severe pulmonary disease. When assessing peritoneal dialysis as the mode of therapy in such extreme situations, the benefits to the patient must be weighed against the possible complications.
Solutions containing lactate ion should be used with great care in patients with metabolic or respiratory alkalosis. Lactate should be administered with great care in those conditions in which there is an increased level or an impaired utilization of this ion, such as severe hepatic insufficiency.
An accurate fluid balance record must be kept and the weight of the patient carefully monitored to avoid over or under hydration with severe consequences, including congestive heart failure, volume depletion and shock.
Excessive use of DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solution with 4.25% dextrose during a peritoneal dialysis treatment can result in significant removal of water from the patient.
Stable patients undergoing maintenance peritoneal dialysis should have routine periodic evaluation of electrolyte blood chemistries and hematologic factors, as well as other indicators that determine the patient's ongoing status.
After removing the outer wrap, check for minute leaks by squeezing the container firmly. If leaks are found, discard the solution because the sterility may be impaired.
Serum calcium levels in patients using low calcium concentrations should be monitored and if found to be low, the peritoneal solution in use should be altered to one with a higher calcium concentration.
General:
Do not administer unless the solution is clear, all seals are intact, and there is no evidence of leaking.
Care should be taken to see that the catheter is inserted completely, since leakage around the catheter, if not controlled, can create edema from subcutaneous infiltration of the dialysis solution. This will also create an inaccurate fluid balance measurement.
DELFLEX® Peritoneal Dialysis solutions do not include potassium. Potassium chloride should only be added under the direction of a physician after careful evaluation of both serum and total body potassium.
The overwrap must be removed immediately before use and is provided with a “Tear Open” feature to make removal easy. See instructions in Exchange Procedure section.
Disconnect from disk only when knob is in position 4 (••••).
Aseptic technique must be used throughout the procedure and at its termination in order to reduce the possibility of infection.
Significant loss of protein, amino acids and water soluble vitamins may occur during peritoneal dialysis. Replacement therapy should be provided as necessary.
Laboratory Tests:
Serum electrolytes, magnesium, bicarbonate levels and fluid balance should be periodically monitored.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
Long term animal studies with DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential or effect on fertility.
Pregnancy: Teratology Effects
Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions. It is also not known whether DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers:
Caution should be exercised when DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions are administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use:
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Adverse reactions to peritoneal dialysis include mechanical and solution related problems as well as the results of contamination of equipment or improper technique in catheter placement. Abdominal pain, bleeding, peritonitis, subcutaneous infection around a peritoneal catheter, catheter blockage, difficulty in fluid removal, and ileus are among the complications of the procedure. Solution related adverse reactions may include peritonitis, catheter site infection, electrolyte and fluid imbalances, hypovolemia, hypervolemia, hypertension, hypotension, disequilibrium syndrome and muscle cramping.
If an adverse reaction does occur, institute appropriate therapeutic procedures according to the patient's needs and conditions, and save the remainder of the fluid in the bag for evaluation if deemed necessary.
DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions are provided for intraperitoneal administration only. The mode of therapy, frequency of treatment, formulation, exchange volume, duration of dwell, and length of dialysis should be selected by the physician responsible for the treatment of the individual patient.
To avoid the risk of severe dehydration or hypovolemia and to minimize the loss of protein, it is advisable to select the peritoneal dialysis solution with lowest level of osmolarity consistent with the fluid removal requirements for that exchange.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
Additives may be incompatible. Do not store solutions containing additives.
For administration see Exchange Procedure section.
DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions are delivered in single-dose flexible bags. All DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions have overfills declared on the container label. The flexible containers have the capacity for drainage in excess of their stated fill volume for ultrafiltration from the patient.
DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions with an attached stay•safe® exchange set are available in containers as shown in the table in the Description section.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature. Brief exposure to temperatures up to 40°C/104°F may be tolerated provided the mean kinetic temperature does not exceed 25°C (77°F). However, such exposure should be minimized.
EXCHANGE PROCEDURE (Aseptic technique is required)
- Clean work surface.
- Gather supplies:
-
- Warmed stay•safe® Container -
- povidone iodine prefilled stay•safe cap -
- stay•safe Organizer (Optional) -
- Supplies if adding medication.
-
- Close stay•safe extension set clamp.
- Mask, then wash hands.
- Open the stay•safe container by tearing from a notched edge of the package overwrap. Wipe any moisture from the container. Some opacity may be observed in the plastic of the bag and/or tubing and is due to moisture absorption during the sterilization process. This is normal and does not affect the solution quality or safety. The opacity will diminish gradually.
- Place the stay•safe set on the work surface. Separate the fill and drain bag.
- Verify the integrity of the solution bag by squeezing the bag to check that there are no leaks and the solution looks clear. Color variation from clear to slightly yellow will not affect the product efficacy and may still be used. Check the expiration date. Check for correct dextrose concentration. Do not use if there is any doubt about the integrity of the solution or packaging.
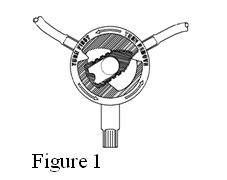
- Turn the position indicator on the stay•safe disc counter-clockwise until it fits into the cut-out portion of the colored plastic cover on the disc as illustrated in Figure 1. Remove the plastic cover while the indicator is in this position (position 1; •). Once the cover is removed, do not turn counter-clockwise.
- If adding medication, prep the medication port as instructed and add the prescribed medication. Invert the bag several times to mix the medication.
- Hang the solution bag on an I.V. pole and place the drain bag at floor level. Break the frangible in the solution bag outlet port. (If using the organizer, place the stay•safe disc in the organizer as illustrated in Figure 2.)
- Remove the stay•safe cap from it's packaging. (If using the organizer, place in the right or left notch of the organizer as illustrated in Figure 2. Place the stay•safe Extension Set in the other notch of the organizer.)

- Remove the protective cap from the stay•safe disc and discard. Remove the cap from the extension set by twisting the connection counter-clockwise. (If using the organizer, leave the capped end of the extension set in the organizer and twist the extension set connector counter-clockwise to remove the set from its cap.) Aseptically connect the extension set to the connector on the stay•safe disc. Twist clockwise to secure the connection.
- Remove your mask. The system will not be opened again during the exchange.
- Open the extension set clamp. Patient outflow (drain) will start immediately.
- When patient drain is complete, turn the disc position indicator to Position 2 (••). This will start the flush from the solution bag to the drain bag.
- After approximately 5 seconds, turn the disc position indicator to Position 3 (•••). This will start the patient fill.
- When fill is complete, turn the disc position indicator to Position 4 (••••). This will insert the closure pin of the disc into the extension set connector and seal the system.
- Remove the white protective cover from the new stay•safe cap and reserve for later use. Do not discard.
- Remove the extension set from stay•safe disc and attach the new stay•safe cap. Twist clockwise to secure the connection.
- Seal the disc by attaching the white protective cover from the stay•safe cap to the disc connector. Twist clockwise to secure the connection and prevent leakage from the used system.
- Observe the drained dialysate for cloudiness and measure the amount drained. Discard fluid and used set as instructed by the training facility. In case of cloudiness, save the fluid and the exchange set and immediately call the dialysis center.
Fresenius Medical Care North America
920 Winter Street
Waltham, MA 02451
1-800-323-5188
89-908-85 REV 07/11
Principal Display Panel - NDC 49230-197-95

Principal Display Panel - NDC 49230-200-95

Principal Display Panel - NDC 49230-203-95

DELFLEXDextrose Monohydrate, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Lactate, Calcium Chloride, Magnesium Chloride Solution
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DELFLEXDextrose Monohydrate, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Lactate, Calcium Chloride, Magnesium Chloride Solution
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DELFLEXDextrose Monohydrate, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Lactate, Calcium Chloride, Magnesium Chloride Solution
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DELFLEXDextrose Monohydrate, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Lactate, Calcium Chloride, Magnesium Chloride Solution
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DELFLEXDextrose Monohydrate, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Lactate, Calcium Chloride, Magnesium Chloride Solution
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DELFLEXDextrose Monohydrate, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Lactate, Calcium Chloride, Magnesium Chloride Solution
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||