DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE
Desmopressin Nasal SpraySolution USP, 0.01%
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- INFORMATION FOR THE PHARMACIST
- HOW SUPPLIED
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mL Carton Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mL Bottle Label
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE DESCRIPTION
Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP, 0.01% is a synthetic analogue of the natural pituitary hormone 8-arginine vasopressin (ADH), an antidiuretic hormone affecting renal water conservation. The structural formula for the active ingredient is:
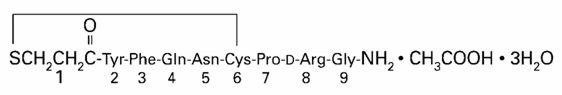
Mol. wt. 1183.34
Empirical formula: C46H64N14O12S2 • C2H4O2 • 3H2O
Chemical name: 1-(3-mercaptopropionic acid)-8-D-arginine vasopressin monoacetate (salt).
Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP, 0.01% is provided as an aqueous solution for intranasal use.
| Each mL contains: | |
| Desmopressin acetate | 0.1 mg |
| Inactives: | |
| Benzalkonium chloride solution (50% w/v) | 0.2 mg |
| Citric acid monohydrate | 1.7 mg |
| Sodium chloride | 7.5 mg |
| Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate | 4.52 mg |
| Purified water to 1 mL |
The Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP, 0.01% compression pump delivers 0.1 mL (10 mcg) of desmopressin acetate per spray.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Desmopressin nasal spray solution contains as active substance desmopressin acetate, a synthetic analogue of the natural hormone arginine vasopressin. One mL (0.1 mg) of intranasal desmopressin acetate has an antidiuretic activity of about 400 IU; 10 mcg of desmopressin acetate is equivalent to 40 IU.
- The biphasic half-lives for intranasal desmopressin acetate were 7.8 and 75.5 minutes for the fast and slow phases, compared with 2.5 and 14.5 minutes for lysine vasopressin, another form of the hormone used in this condition. As a result, intranasal desmopressin acetate provides a prompt onset of antidiuretic action with a long duration after each administration.
- The change in structure of arginine vasopressin to desmopressin acetate has resulted in a decreased vasopressor action and decreased actions on visceral smooth muscle relative to the enhanced antidiuretic activity, so that clinically effective antidiuretic doses are usually below threshold levels for effects on vascular or visceral smooth muscle.
- Desmopressin acetate administered intranasally has an antidiuretic effect about one-tenth that of an equivalent dose administered by injection.
Human Pharmacokinetics
Desmopressin acetate is mainly excreted in the urine. A pharmacokinetic study conducted in healthy volunteers and patients with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment (n=24, 6 subjects in each group) receiving single dose desmopressin acetate (2 mcg) injection demonstrated a difference in desmopressin acetate terminal half-life. Terminal half-life significantly increased from 3 hours in normal healthy patients to 9 hours in patients with severe renal impairment. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS .)
DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Central Cranial Diabetes Insipidus
Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP, 0.01% is indicated as antidiuretic replacement therapy in the management of central cranial diabetes insipidus and for management of the temporary polyuria and polydipsia following head trauma or surgery in the pituitary region. It is ineffective for the treatment of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
The use of Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP, 0.01% in patients with an established diagnosis will result in a reduction in urinary output with increase in urine osmolality and a decrease in plasma osmolality. This will allow the resumption of a more normal life-style with a decrease in urinary frequency and nocturia.
There are reports of an occasional change in response with time, usually greater than 6 months. Some patients may show a decreased responsiveness, others a shortened duration of effect. There is no evidence this effect is due to the development of binding antibodies but may be due to a local inactivation of the peptide.
Patients are selected for therapy by establishing the diagnosis by means of the water deprivation test, the hypertonic saline infusion test, and/or the response to antidiuretic hormone. Continued response to intranasal desmopressin acetate can be monitored by urine volume and osmolality.
Desmopressin acetate is also available as a solution for injection when the intranasal route may be compromised. These situations include nasal congestion and blockage, nasal discharge, atrophy of nasal mucosa, and severe atrophic rhinitis. Intranasal delivery may also be inappropriate where there is an impaired level of consciousness. In addition, cranial surgical procedures, such as transsphenoidal hypophysectomy create situations where an alternative route of administration is needed as in cases of nasal packing or recovery from surgery.
DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Desmopressin nasal spray solution is contraindicated in individuals with known hypersensitivity to desmopressin acetate or to any of the components of desmopressin nasal spray solution.
Desmopressin acetate is contraindicated in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (defined as a creatinine clearance below 50 mL/min).
Desmopressin acetate is contraindicated in patients with hyponatremia or a history of hyponatremia.
WARNINGS
- For intranasal use only.
- Desmopressin nasal spray solution should only be used in patients where orally administered formulations are not feasible.
- Very rare cases of hyponatremia have been reported from world-wide postmarketing experience in patients treated with desmopressin acetate. Desmopressin acetate is a potent antidiuretic which, when administered, may lead to water intoxication and/or hyponatremia. Unless properly diagnosed and treated hyponatremia can be fatal. Therefore, fluid restriction is recommended and should be discussed with the patient and/or guardian. Careful medical supervision is required.
- When desmopressin nasal spray solution is administered, in particular in pediatric and geriatric patients, fluid intake should be adjusted downward in order to decrease the potential occurrence of water intoxication and hyponatremia. (See PRECAUTIONS , Pediatric Use and Geriatric Use .) All patients receiving desmopressin acetate therapy should be observed for the following signs or symptoms associated with hyponatremia: headache, nausea/vomiting, decreased serum sodium weight gain, restlessness, fatigue, lethargy, disorientation, depressed reflexes, loss of appetite, irritability, muscle weakness, muscle spasms or cramps and abnormal mental status such as hallucinations, decreased consciousness and confusion. Severe symptoms may include one or a combination of the following: seizure, coma and/or respiratory arrest. Particular attention should be paid to the possibility of the rare occurrence of an extreme decrease in plasma osmolality that may result in seizures which could lead to coma.
- Desmopressin acetate should be used with caution in patients with habitual or psychogenic polydipsia who may be more likely to drink excessive amounts of water, putting them at greater risk of hyponatremia.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Intranasal desmopressin acetate at high dosage has infrequently produced a slight elevation of blood pressure, which disappeared with a reduction in dosage. The drug should be used with caution in patients with coronary artery insufficiency and/or hypertensive cardiovascular disease because of possible rise in blood pressure.
Desmopressin acetate should be used with caution in patients with conditions associated with fluid and electrolyte imbalance, such as cystic fibrosis, heart failure and renal disorders because these patients are prone to hyponatremia.
Rare severe allergic reactions have been reported with desmopressin acetate. Anaphylaxis has been reported rarely with intravenous and intranasal administration of desmopressin acetate.
Central Cranial Diabetes Insipidus
Since desmopressin acetate is used intranasally, changes in the nasal mucosa such as scarring, edema, or other disease may cause erratic, unreliable absorption in which case intranasal desmopressin acetate should not be used. For such situations, desmopressin acetate injection should be considered.
Information for Patients
Ensure that in children administration is under adult supervision in order to control the dose intake. Patients should be informed that the desmopressin nasal spray solution bottle accurately delivers 50 doses of 10 mcg each. Any solution remaining after 50 doses should be discarded since the amount delivered thereafter may be substantially less than 10 mcg of drug. No attempt should be made to transfer remaining solution to another bottle. Patients should be instructed to read accompanying directions on use of the spray pump carefully before use.
Fluid intake should be adjusted downward based upon discussion with the physician.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests for following the patient with central cranial diabetes insipidus or post-surgical or head trauma-related polyuria and polydipsia include urine volume and osmolality. In some cases plasma osmolality measurements may be required.
Drug Interactions
Although the pressor activity of desmopressin acetate is very low compared to the antidiuretic activity, use of large doses of intranasal desmopressin acetate with other pressor agents should only be done with careful patient monitoring. The concomitant administration of drugs that may increase the risk of water intoxication with hyponatremia, (e.g., tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors, chlorpromazine, opiate analgesics, NSAIDs, lamotrigine and carbamazepine) should be performed with caution.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies with desmopressin acetate have not been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential or effects on fertility.
Pregnancy
Fertility studies have not been done. Teratology studies in rats and rabbits at doses from 0.05 to 10 mcg/kg/day (approximately 0.1 times the maximum systemic human exposure in rats and up to 38 times the maximum systemic human exposure in rabbits based on surface area, mg/m2) revealed no harm to the fetus due to desmopressin acetate. There are, however, no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Several publications of desmopressin acetate’s use in the management of diabetes insipidus during pregnancy are available; these include a few anecdotal reports of congenital anomalies and low birth weight babies. However, no causal connection between these events and desmopressin acetate has been established. A fifteen year Swedish epidemiologic study of the use of desmopressin acetate in pregnant women with diabetes insipidus found the rate of birth defects to be no greater than that in the general population; however, the statistical power of this study is low. As opposed to preparations containing natural hormones, desmopressin acetate in antidiuretic doses has no uterotonic action and the physician will have to weigh the therapeutic advantages against the possible risks in each case.
Nursing Mothers
There have been no controlled studies in nursing mothers. A single study in a post-partum woman demonstrated a marked change in plasma, but little if any change in assayable desmopressin acetate in breast milk following an intranasal dose of 10 mcg. It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when desmopressin acetate is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Central Cranial Diabetes Insipidus
Desmopressin nasal spray solution has been used in children with diabetes insipidus. Use in infants and children will require careful fluid intake restriction to prevent possible hyponatremia and water intoxication. (See WARNINGS .) The dose must be individually adjusted to the patient with attention in the very young to the danger of an extreme decrease in plasma osmolality with resulting convulsions. Dose should start at 0.05 mL or less.
Since the spray cannot deliver less than 0.1 mL (10 mcg), smaller doses should be administered using the rhinal tube delivery system. Do not use the nasal spray in pediatric patients requiring less than 0.1 mL (10 mcg) per dose.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of desmopressin nasal spray solution did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. Desmopressin acetate is contraindicated in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (defined as a creatinine clearance below 50 mL/min). (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY , Human Pharmacokinetics and CONTRAINDICATIONS .)
Use of desmopressin nasal spray solution in geriatric patients will require careful fluid intake restriction to prevent possible hyponatremia and water intoxication. (See WARNINGS .)
There are reports of an occasional change in response with time, usually greater than 6 months. Some patients may show a decreased responsiveness, others a shortened duration of effect. There is no evidence this effect is due to the development of binding antibodies but may be due to a local inactivation of the peptide.
DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Infrequently, high dosages of intranasal desmopressin acetate have produced transient headache and nausea. Nasal congestion, rhinitis and flushing have also been reported occasionally along with mild abdominal cramps. These symptoms disappeared with reduction in dosage. Nosebleed, sore throat, cough and upper respiratory infections have also been reported.
The following table lists the percentage of patients having adverse experiences without regard to relationship to study drug from the pooled pivotal study data for nocturnal enuresis.
| ADVERSE REACTION | PLACEBO (N=59) % |
DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE 20 mcg (N=60) % |
DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE 40 mcg (N=61) % |
|---|---|---|---|
| BODY AS A WHOLE | |||
| Abdominal Pain | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Asthenia | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Chills | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Headache | 0 | 2 | 5 |
| NERVOUS SYSTEM | |||
| Dizziness | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| RESPIRATORY SYSTEM | |||
| Epistaxis | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| Nostril Pain | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Rhinitis | 2 | 8 | 3 |
| DIGESTIVE SYSTEM | |||
| Gastrointestinal Disorder | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Nausea | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| SPECIAL SENSES | |||
| Conjunctivitis | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Edema Eyes | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Lachrymation Disorder | 0 | 0 | 2 |
Post Marketing
There have been rare reports of hyponatremic convulsions associated with concomitant use with the following medications: oxybutinin and imipramine.
See WARNINGS for the possibility of water intoxication and hyponatremia.
OVERDOSAGE
Signs of overdose may include confusion, drowsiness, continuing headache, problems with passing urine and rapid weight gain due to fluid retention. (See WARNINGS .) In case of overdosage, the dose should be reduced, frequency of administration decreased, or the drug withdrawn according to the severity of the condition. There is no known specific antidote for desmopressin acetate or desmopressin nasal spray solution.
An oral LD50 has not been established. An intravenous dose of 2 mg/kg in mice demonstrated no effect.
DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Central Cranial Diabetes Insipidus
Desmopressin nasal spray solution dosage must be determined for each individual patient and adjusted according to the diurnal pattern of response. Response should be estimated by two parameters: adequate duration of sleep and adequate, not excessive, water turnover. Patients with nasal congestion and blockage have often responded well to intranasal desmopressin acetate. The usual dosage range in adults is 0.1 to 0.4 mL daily, either as a single dose or divided into two or three doses. Most adults require 0.2 mL daily in two divided doses. The morning and evening doses should be separately adjusted for an adequate diurnal rhythm of water turnover. For children aged 3 months to 12 years, the usual dosage range is 0.05 to 0.3 mL daily, either as a single dose or divided into two doses. About 1/4 to 1/3 of patients can be controlled by a single daily dose of desmopressin acetate administered intranasally. Fluid restriction should be observed. (See WARNINGS , PRECAUTIONS , Pediatric Use and Geriatric Use .)
The nasal spray pump can only deliver doses of 0.1 mL (10 mcg) or multiples of 0.1 mL. If doses other than these are required, the rhinal tube delivery system may be used.
The spray pump must be primed prior to the first use. To prime pump, press down four (4) times. The bottle will now deliver 10 mcg of drug per spray. Discard desmopressin nasal spray solution after 50 sprays since the amount delivered thereafter per spray may be substantially less than 10 mcg of drug.
Geriatric Use
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Human Pharmacokinetics , CONTRAINDICATIONS , and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use .)
INFORMATION FOR THE PHARMACIST
Instruction For Assembly of Spray Pump
Assemble Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP, 0.01% prior to dispensing to the patient, according to the following instructions:
1. Open the carton and remove the spray pump and solution bottle.
2. Assemble the desmopressin nasal spray solution by unscrewing the white cap from the solution bottle and screwing the spray pump tightly onto the bottle. Make sure the protective cap is on the spray pump.
3. Return desmopressin nasal spray solution bottle to the carton for dispensing to the patient.
HOW SUPPLIED
Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP, 0.01% is available in a 5 mL bottle with a nasal spray pump dispenser with dust cover and patient instruction sheet delivering 50 sprays of 10 mcg (NDC 60505-0815-0).
Store at 25°C (77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]; excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F). STORE BOTTLE IN UPRIGHT POSITION.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Manufactured by: Manufactured for:
Apotex Inc. Apotex Corp.
Toronto, Ontario Weston, Florida
Canada M9L 1T9 33326
317218 September 2011
PATIENT INSTRUCTION GUIDE
Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP, 0.01%
Rx Only
A better way to deliver Desmopressin Nasal Spray Soluti on USP
Delivering Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP Mor e Efficiently
Your doctor has prescribed Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP as antidiuretic hormone replacement therapy. Follow the dosage schedule that is specified. The convenient nasal spray pump provides an efficient, reliable way to administer your medication. It is important, however, to adhere completely to the following instructions so that you will always receive a consistent dose of your medication.
NOTE: In the event that the pharmacist has not assembled the spray pump, unscrew the white cap from the solution bottle and screw the spray pump tightly onto the bottle. Make sure the protective cap is on the spray pump.
CAUSION
The nasal spray pump accurately delivers 50 doses of 10 micrograms each. Any solution remaining after 50 doses should be discarded since the amount delivered thereafter per actuation may be substantially less than 10 micrograms of drug. Do not transfer any remaining solution to another bottle. Please read the following instructions carefully before using the spray pump.
Ensure that in children administration is under adult supervision in order to control the dose intake.
If you accidentally deliver/administer too much of a dose, immediately telephone your doctor or a certified Regional Poison Center for advice. Possible signs of overdose may include confusion, drowsiness, continuing headache, problems with passing urine and rapid weight gain due to fluid retention.
Using Your Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP Pump
1. Remove protective cap.
2. The spray pump must be primed prior to the first use. To prime pump, press down 4 times.
3. Once primed, the spray pump delivers 10 micrograms of medication each time it is pressed. To administer a 10-microgram dose, place the spray nozzle in nostril and press the spray pump once. If a higher dose has been prescribed, spray half the dose in each nostril. The spray pump cannot be used for doses less than 10 micrograms or doses other than multiples of 10 micrograms.
4. Replace the protective cap on bottle after use. The pump will stay primed for up to one week. If the product has not been used for a period of one week, re-prime the pump by pressing once.
5. We have included a convenient check-off chart to assist you in keeping track of medication doses used. This will help assure that you receive 50 "full doses" of medication. Please note that the bottle has been filled with extra solution to accommodate the initial priming activity.
1. Retain with medication or affix in convenient location.
2. Starting with dose #1, check off after each administration.
3. Discard medication after 50 doses.
Store at 25°C (77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]; excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F). STORE BOTTLE IN UPRIGHT POSITION.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Manufactured by: Manufactured for:
Apotex Inc. Apotex Corp.
Toronto, Ontario Weston, Florida
Canada M9L 1T9 33326
317218 September 2011
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mL Carton Label
APOTEX CORP. NDC 60505-0815-0
Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP, 0.01%
Rx Only
5 mL

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mL Bottle Label
APOTEX CORP. NDC 60505-0815-0
Desmopressin Nasal Spray Solution USP, 0.01%
Rx Only
5 mL

DESMOPRESSIN ACETATEDESMOPRESSIN ACETATE SPRAY
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||