Diclofenac Sodium
Bryant Ranch Prepack
Bryant Ranch Prepack
Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, USP 40-8780 Revised – March 2011
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Rx only
Prescribing Information
- NSAIDs may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk. (See WARNINGS).
- Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS).
Gastrointestinal Risk
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events (See WARNINGS).
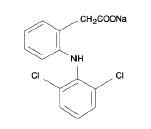
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are a benzeneacetic acid derivative. The chemical name is 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino] benzeneacetic acid, monosodium salt. The molecular weight is 318.13. Its molecular formula is C14H10Cl2NNaO2, and it has the following structural formula
Each enteric-coated tablet for oral administration contains 50 mg or 75 mg of diclofenac sodium. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: aluminum hydrate, colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polysorbate 80, polyvinyl acetate phthalate, propylene glycol, silica, sodium alginate, sodium starch glycolate (Type A), stearic acid, synthetic black iron oxide, talc, and titanium dioxide.
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities in animal models. The mechanism of action of diclofenac sodium delayed-release, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but may be related to prostaglandin synthetase inhibition.
Absorption
Diclofenac is 100% absorbed after oral administration compared to IV administration as measured by urine recovery. However, due to first-pass metabolism, only about 50% of the absorbed dose is systemically available (see Table 1). Food has no significant effect on the extent of diclofenac absorption. However, there is usually a delay in the onset of absorption of 1 to 4.5 hours and a reduction in peak plasma levels of <20%.
| PK Parameter | Normal Healthy Adults (18-48 yrs.) | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean |
Coefficient of
Variation (%) |
|
| Absolute Bioavailability (%) [N = 7] |
55 |
40 |
| Tmax (hr) [N = 12] |
5.3 |
28 |
| Oral Clearance (CL/F; mL/min) [N = 12] |
895 |
56 |
| Renal Clearance (% unchanged drug in urine) [N = 7] |
<1 |
-- |
| Apparent Volume of Distribution (V/F; L/kg) [N = 56] |
1.4 |
58 |
| Terminal Half-life (hr) [N = 56] |
2.3 |
48 |
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of diclofenac sodium is 1.4 L/kg.
Diclofenac is more than 99% bound to human serum proteins, primarily to albumin. Serum protein binding is constant over the concentration range (0.15 to 105 mcg/mL) achieved with recommended doses.
Diclofenac diffuses into and out of the synovial fluid. Diffusion into the joint occurs when plasma levels are higher than those in the synovial fluid, after which the process reverses and synovial fluid levels are higher than plasma levels. It is not known whether diffusion into the joint plays a role in the effectiveness of diclofenac.
Metabolism
Five diclofenac metabolites have been identified in human plasma and urine. The metabolites include 4'-hydroxy-, 5-hydroxy-, 3'-hydroxy-, 4',5-dihydroxy- and 3'-hydroxy-4'-methoxy diclofenac. The major diclofenac metabolite, 4'-hydroxy-diclofenac, has very weak pharmacologic activity. The formation of 4’-hydroxy- diclofenac is primarily mediated by CPY2C9. Both diclofenac and its oxidative metabolites undergo glucuronidation or sulfation followed by biliary excretion. Acylglucuronidation mediated by UGT2B7 and oxidation mediated by CPY2C8 may also play a role in diclofenac metabolism. CYP3A4 is responsible for the formation of minor metabolites, 5-hydroxy- and 3’-hydroxy-diclofenac. In patients with renal dysfunction, peak concentrations of metabolites 4'-hydroxy- and 5-hydroxy-diclofenac were approximately 50% and 4% of the parent compound after single oral dosing compared to 27% and 1% in normal healthy subjects.
Excretion
Diclofenac is eliminated through metabolism and subsequent urinary and biliary excretion of the glucuronide and the sulfate conjugates of the metabolites. Little or no free unchanged diclofenac is excreted in the urine. Approximately 65% of the dose is excreted in the urine and approximately 35% in the bile as conjugates of unchanged diclofenac plus metabolites. Because renal elimination is not a significant pathway of elimination for unchanged diclofenac, dosing adjustment in patients with mild to moderate renal dysfunction is not necessary. The terminal half-life of unchanged diclofenac is approximately 2 hours.
When co-administered with voriconazole (inhibitor of CYP2C9, 2C19 and 3A4 enzyme), the Cmax and AUC of diclofenac increased by 114% and 78%, respectively (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Pediatric: The pharmacokinetic of diclofenac sodium delayed-release has not been investigated in pediatric patients.
Race: Pharmacokinetics differences due to race have not been identified.
Hepatic Insufficiency: Hepatic metabolism accounts for almost 100% of diclofenac sodium delayed-release elimination, so patients with hepatic disease may require reduced doses of diclofenac sodium delayed-release compared to patients with normal hepatic function.
Renal Insufficiency: Diclofenac pharmacokinetics has been investigated in subjects with renal insufficiency. No differences in the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac have been detected in studies of patients with renal impairment. In patients with renal impairment (inulin clearance 60 to 90, 30 to 60, and <30 mL/min; N=6 in each group), AUC values and elimination rate were comparable to those in healthy subjects.
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use diclofenac sodium delayed-release. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS).
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are indicated:
• For relief of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis
• For relief of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
• For acute or long-term use in the relief of signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to diclofenac.
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release should not be given to patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients (see WARNINGS, Anaphylactoid Reactions, and PRECAUTIONS, Preexisting Asthma).
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release is contraindicated for the treatment of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS).
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. All NSAIDs, both COX-2 selective and nonselective, may have a similar risk. Patients with known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease may be at greater risk. To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the signs and/or symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID does increase the risk of serious GI events (see WARNINGS, GI Effects).
Two large, controlled, clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10-14 days following CABG surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
NSAIDs can lead to onset of new hypertension or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking thiazides or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets, should be used with caution in patients with hypertension. Blood pressure (BP) should be monitored closely during the initiation of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
Fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients taking NSAIDs. Diclofenac sodium delayed-release should be used with caution in patients with fluid retention or heart failure.
NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium delayed-release, can cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients, who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy, is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occur in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3-6 months, and in about 2%-4% of patients treated for one year. These trends continue with longer duration of use, increasing the likelihood of developing a serious GI event at some time during the course of therapy. However, even short-term therapy is not without risk.
NSAIDs should be prescribed with extreme caution in those with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding who use NSAIDs have a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing a GI bleed compared to patients with neither of these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk for GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, older age, and poor general health status. Most spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in elderly or debilitated patients and therefore, special care should be taken in treating this population.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse GI event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible duration. Patients and physicians should remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during NSAID therapy and promptly initiate additional evaluation and treatment if a serious GI adverse event is suspected. This should include discontinuation of the NSAID until a serious GI adverse event is ruled out. For high risk patients, alternate therapies that do not involve NSAIDs should be considered.
Caution should be used when initiating treatment with diclofenac sodium delayed-release in patients with considerable dehydration.
Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury. Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors, and the elderly. Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment state.
Advanced Renal Disease
No information is available from controlled clinical studies regarding the use of diclofenac sodium delayed-release in patients with advanced renal disease. Therefore, treatment with diclofenac sodium delayed-release is not recommended in these patients with advanced renal disease. If diclofenac sodium delayed-release therapy must be initiated, close monitoring of the patient's renal function is advisable.
Elevations of one or more liver tests may occur during therapy with diclofenac sodium delayed-release. These laboratory abnormalities may progress, may remain unchanged, or may be transient with continued therapy. Borderline elevations (i.e., less than 3 times the ULN [ULN = the upper limit of the normal range]) or greater elevations of transaminases occurred in about 15% of diclofenac-treated patients. Of the markers of hepatic function, ALT (SGPT) is recommended for the monitoring of liver injury.
In clinical trials, meaningful elevations (i.e., more than 3 times the ULN) of AST (GOT) (ALT was not measured in all studies) occurred in about 2% of approximately 5,700 patients at some time during diclofenac treatment. In a large, open-label, controlled trial of 3,700 patients treated for 2-6 months, patients were monitored first at 8 weeks and 1,200 patients were monitored again at 24 weeks. Meaningful elevations of ALT and/or AST occurred in about 4% of patients and included marked elevations (i.e., more than 8 times the ULN) in about 1% of the 3,700 patients. In that open-label study, a higher incidence of borderline (less than 3 times the ULN), moderate (3-8 times the ULN), and marked (>8 times the ULN) elevations of ALT or AST was observed in patients receiving diclofenac when compared to other NSAIDs. Elevations in transaminases were seen more frequently in patients with osteoarthritis than in those with rheumatoid arthritis.
Almost all meaningful elevations in transaminases were detected before patients became symptomatic. Abnormal tests occurred during the first 2 months of therapy with diclofenac in 42 of the 51 patients in all trials who developed marked transaminase elevations.
In postmarketing reports, cases of drug-induced hepatotoxicity have been reported in the first month, and in some cases, the first 2 months of therapy, but can occur at any time during treatment with diclofenac. Postmarketing surveillance has reported cases of severe hepatic reactions, including liver necrosis, jaundice, fulminant hepatitis with and without jaundice, and liver failure. Some of these reported cases resulted in fatalities or liver transplantation.
Physicians should measure transaminases periodically in patients receiving long-term therapy with diclofenac, because severe hepatotoxicity may develop without a prodrome of distinguishing symptoms. The optimum times for making the first and subsequent transaminase measurements are not known. Based on clinical trial data and postmarketing experiences, transaminases should be monitored within 4 to 8 weeks after initiating treatment with diclofenac. However, severe hepatic reactions can occur at any time during treatment with diclofenac.
If abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, if clinical signs and/or symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dark urine, etc.), diclofenac sodium delayed-release should be discontinued immediately.
To minimize the possibility that hepatic injury will become severe between transaminase measurements, physicians should inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, diarrhea, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flu-like" symptoms), and the appropriate action patients should take if these signs and symptoms appear.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse liver related event in patients treated with diclofenac sodium delayed-release, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest duration possible. Caution should be exercised in prescribing diclofenac sodium delayed-release with concomitant drugs that are known to be potentially hepatotoxic (e.g., antibiotics, anti-epileptics).
As with other NSAIDs, anaphylactic reactions may occur both in patients with the aspirin triad and in patients without known sensitivity to NSAIDs or known prior exposure to diclofenac sodium delayed-release. Diclofenac sodium delayed-release should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad. This symptom complex typically occurs in asthmatic patients who experience rhinitis with or without nasal polyps, or who exhibit severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS, Preexisting Asthma.) Anaphylaxis-type reactions have been reported with NSAID products, including with diclofenac products, such as diclofenac sodium delayed-release. Emergency help should be sought in cases where an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium delayed-release, can cause serious skin adverse events such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Patients should be informed about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations and use of the drug should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, diclofenac sodium delayed-release should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets cannot be expected to substitute for corticosteroids or to treat corticosteroid insufficiency. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to disease exacerbation. Patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should have their therapy tapered slowly if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids.
The pharmacological activity of diclofenac sodium delayed-release in reducing fever and inflammation may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, painful conditions.
Anemia is sometimes seen in patients receiving NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium delayed-release. This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium delayed-release, should have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs or symptoms of anemia.
NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown to prolong bleeding time in some patients. Unlike aspirin, their effect on platelet function is quantitatively less, of shorter duration, and reversible. Patients receiving diclofenac sodium delayed-release who may be adversely affected by alterations in platelet function, such as those with coagulation disorders or patients receiving anticoagulants, should be carefully monitored.
Patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma. The use of aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma has been associated with severe bronchospasm which can be fatal. Since cross-reactivity, including bronchospasm, between aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, diclofenac sodium delayed-release should not be administered to patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity and should be used with caution in patients with preexisting asthma.
Patients should be informed of the following information before initiating therapy with an NSAID and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy. Patients should also be encouraged to read the NSAID Medication Guide that accompanies each prescription dispensed.
- Diclofenac sodium delayed-release, like other NSAIDs, may cause serious CV side effects, such as MI or stroke, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious CV events can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, slurring of speech, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Effects).
- Diclofenac sodium delayed-release, like other NSAIDs, can cause GI discomfort and, rarely, more serious GI side effects, such as ulcers and bleeding, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS, Gastrointestinal (GI) Effects: Risk of GI Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation).
- Diclofenac sodium delayed-release, like other NSAIDs, can cause serious skin side effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, SJS, and TEN, which may result in hospitalizations and even death. Although serious skin reactions may occur without warning, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of skin rash and blisters, fever, or other signs of hypersensitivity such as itching, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms. Patients should be advised to stop the drug immediately if they develop any type of rash and contact their physicians as soon as possible.
- Patients should promptly report signs or symptoms of unexplained weight gain or edema to their physicians.
- Patients should be informed of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and “flu-like” symptoms). If these occur, patients should be instructed to stop therapy and seek immediate medical therapy. (see WARNINGS, Hepatic Effects).
- Patients should be informed of the signs of an anaphylactic reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). If these occur, patients should be instructed to seek immediate emergency help (see WARNINGS, Anaphylactic Reactions).
- In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, diclofenac sodium delayed-release should be avoided because it will cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
Because serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, physicians should monitor for signs or symptoms of GI bleeding. In patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium delayed-release, the CBC and a chemistry profile (including transaminase levels) should be checked periodically. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver or renal disease develop, systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.) or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, diclofenac sodium delayed-release should be discontinued.
Aspirin: When diclofenac sodium delayed-release is administered with aspirin, its protein binding is reduced. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known; however, as with other NSAIDs, concomitant administration of diclofenac and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential of increased adverse effects.
Methotrexate: NSAIDs have been reported to competitively inhibit methotrexate accumulation in rabbit kidney slices. This may indicate that they could enhance the toxicity of methotrexate. Caution should be used when NSAIDs are administered concomitantly with methotrexate.
Cyclosporine: Diclofenac sodium delayed-release, like other NSAIDs, may affect renal prostaglandins and increase the toxicity of certain drugs. Therefore, concomitant therapy with diclofenac sodium delayed-release may increase cyclosporine’s nephrotoxicity. Caution should be used when diclofenac is administered concomitantly with cyclosporine.
ACE-Inhibitors: Reports suggest that NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. This interaction should be given consideration in patients taking NSAIDs concomitantly with ACE inhibitors.
Furosemide: Clinical studies, as well as post-marketing observations, have shown that diclofenac sodium delayed-release can reduce the natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazides in some patients. This response has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. During concomitant therapy with NSAIDs, the patient should be observed closely for signs of renal failure (see WARNINGS, Renal Effects), as well as to assure diuretic efficacy.
Lithium: NSAIDs have produced an elevation of plasma lithium levels and a reduction in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15% and the renal clearance was decreased by approximately 20%. These effects have been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis by the NSAID. Thus, when NSAIDs and lithium are administered concurrently, subjects should be observed carefully for signs of lithium toxicity.
Warfarin: The effects of warfarin and NSAIDs on GI bleeding are synergistic, such that users of both drugs together have a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone.
CYP2C9 Inhibitors or Inducers: Diclofenac is metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes, predominantly by CYP2C9. Co-administration of diclofenac with CYP2C9 inhibitors (e.g. voriconazole) may enhance the exposure and toxicity of diclofenac whereas co-administration with CYP2C9 inducers (e.g. rifampin) may lead to compromised efficacy of diclofenac. Use caution when dosing diclofenac with CYP2C9 inhibitors or inducers; a dosage adjustment may be warranted (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics, Drug Interactions).
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C
Reproductive studies conducted in rats and rabbits have not demonstrated evidence of developmental abnormalities. However, animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women.
Nonteratogenic Effects: Because of the known effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of ductus arteriosus), use during pregnancy (particularly late pregnancy) should be avoided.
In rat studies with NSAIDs, as with other drugs known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, an increased incidence of dystocia, delayed parturition, and decreased pup survival occurred. The effects of diclofenac sodium delayed-release on labor and delivery in pregnant women are unknown.
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from diclofenac sodium delayed-release, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
As with any NSAIDs, caution should be exercised in treating the elderly (65 years and older).
In patients taking diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets, or other NSAIDs, the most frequently reported adverse experiences occurring in approximately 1%-10% of patients are:
Gastrointestinal experiences including: abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, gross bleeding/perforation, heartburn, nausea, GI ulcers (gastric/duodenal) and vomiting.
Abnormal renal function, anemia, dizziness, edema, elevated liver enzymes, headaches, increased bleeding time, pruritus, rashes and tinnitus.
Additional adverse experiences reported occasionally include:
Body as a Whole: fever, infection, sepsis
Cardiovascular System: congestive heart failure, hypertension, tachycardia, syncope
Digestive System: dry mouth, esophagitis, gastric/peptic ulcers, gastritis, gastrointestinal bleeding, glossitis, hematemesis, hepatitis, jaundice
Hemic and Lymphatic System: ecchymosis, eosinophilia, leukopenia, melena, purpura, rectal bleeding, stomatitis, thrombocytopenia
Metabolic and Nutritional: weight changes
Nervous System: anxiety, asthenia, confusion, depression, dream abnormalities, drowsiness, insomnia, malaise, nervousness, paresthesia, somnolence, tremors, vertigo
Respiratory System: asthma, dyspnea
Skin and Appendages: alopecia, photosensitivity, sweating increased
Special Senses: blurred vision
Urogenital System: cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, oliguria/polyuria, proteinuria, renal failure
Other adverse reactions, which occur rarely are:
Body as a Whole: anaphylactic reactions, appetite changes, death
Cardiovascular System: arrhythmia, hypotension, myocardial infarction, palpitations, vasculitis
Digestive System: colitis, eructation, fulminant hepatitis with and without jaundice, liver failure, liver necrosis, pancreatitis
Hemic and Lymphatic System: agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, lymphadenopathy, pancytopenia
Metabolic and Nutritional: hyperglycemia
Nervous System: convulsions, coma, hallucinations, meningitis
Respiratory System: respiratory depression, pneumonia
Skin and Appendages: angioedema, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, urticaria
Special Senses: conjunctivitis, hearing impairment
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdoses are usually limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which are generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression and coma may occur, but are rare. Anaphylactoid reactions have been reported with therapeutic ingestion of NSAIDs, and may occur following an overdose.
Patients should be managed by symptomatic and supportive care following a NSAID overdose. There are no specific antidotes. Emesis and/or activated charcoal (60 to 100 g in adults, 1 to 2 g/kg in children) and/or osmotic cathartic may be indicated in patients seen within 4 hours of ingestion with symptoms or following a large overdose (5 to 10 times the usual dose). Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use diclofenac sodium delayed-release. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS).
After observing the response to initial therapy with diclofenac sodium delayed-release, the dose and frequency should be adjusted to suit an individual patient’s needs.
For the relief of osteoarthritis, the recommended dosage is 100-150 mg/day in divided doses (50 mg b.i.d. or t.i.d., or 75 mg b.i.d.).
For the relief of rheumatoid arthritis, the recommended dosage is 150-200 mg/day in divided doses (50 mg t.i.d. or q.i.d., or 75 mg b.i.d.).
For the relief of ankylosing spondylitis, the recommended dosage is 100-125 mg/day, administered as 25 mg q.i.d., with an extra 25-mg dose at bedtime if necessary.
Different formulations of diclofenac (diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets; diclofenac sodium extended-release tablets; diclofenac potassium immediate-release tablets) are not necessarily bioequivalent even if the milligram strength is the same.
Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets, USP are available as follows:
-
50 mg — Each white, round, enteric-coated tablet printed with
 on one side and 550 on the other side with black ink contains 50 mg of Diclofenac Sodium, USP. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 60 (NDC 0228-2550-06), 100 (NDC 0228-2550-11) and 1000 (NDC 0228-2550-96).
on one side and 550 on the other side with black ink contains 50 mg of Diclofenac Sodium, USP. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 60 (NDC 0228-2550-06), 100 (NDC 0228-2550-11) and 1000 (NDC 0228-2550-96).
-
-
75 mg — Each white, round, enteric-coated tablet printed with
 on one side and 551 on the other side with black ink contains 75 mg of Diclofenac Sodium, USP. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 60 (NDC 0228-2551-06), 100 (NDC 0228-2551-11), and 1000 (NDC 0228-2551-96).
on one side and 551 on the other side with black ink contains 75 mg of Diclofenac Sodium, USP. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 60 (NDC 0228-2551-06), 100 (NDC 0228-2551-11), and 1000 (NDC 0228-2551-96).
-
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
Protect from moisture.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
Manufactured by: Actavis Elizabeth LLC
200 Elmora Avenue, Elizabeth, NJ 07207 USA
40-8780
Revised — March 2011
Medication Guide for
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
(See the end of this Medication Guide for a list of prescription NSAID medicines.)
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Non- Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
-
NSAID medicines may increase the chance of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death.
-
-
This chance increases:
-
- with longer use of NSAID medicines
- in people who have heart disease
NSAID medicines should never be used right before or after a heart surgery called a
-
“coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).”
NSAID medicines can cause ulcers and bleeding in the stomach and intestines at any time during treatment. Ulcers and bleeding:
- can happen without warning symptoms
- may cause death
The chance of a person getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
- taking medicines called “corticosteroids” and “anticoagulants”
- longer use
- smoking
- drinking alcohol
- older age
- having poor health
NSAID medicines should only be used:
- exactly as prescribed
- at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
- for the shortest time needed
What are Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as:
- different types of arthritis
- menstrual cramps and other types of short-term pain
Who should not take a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)?
Do not take an NSAID medicine:
- if you had an asthma attack, hives, or other allergic reaction with aspirin or any other NSAID medicine
- for pain right before or after heart bypass surgery
Tell your healthcare provider:
- about all your medical conditions.
- about all of the medicines you take. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Keep a list of your medicines to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist.
- if you are pregnant. NSAID medicines should not be used by pregnant women late in their pregnancy.
- if you are breastfeeding. Talk to your doctor.
What are the possible side effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
| Serious side effects include: | Other side effects include: |
| • heart attack | • stomach pain |
| • stroke | • constipation |
| • high blood pressure | • diarrhea |
| • heart failure from body swelling (fluid retention) | • gas |
| • kidney problems including kidney failure | • heartburn |
| • bleeding and ulcers in the stomach and intestine | • nausea |
| • low red blood cells (anemia) | • vomiting |
| • life-threatening skin reactions |
|
| • life-threatening allergic reactions | |
| Continued on reverse side | |
| Continued | |
| Serious side effects include: | Other side effects include: |
| • liver problems including liver failure | • dizziness |
| • asthma attacks in people who have asthma |
Get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
| • shortness of breath or trouble breathing | • slurred speech |
| • chest pain | • swelling of the face |
| • weakness in one part or side of your body | • or throat |
Stop your NSAID medicine and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
| • nausea | •there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and sticky like tar |
| • more tired or weaker than usual | |
| • itching | •unusual weight gain |
| • your skin or eyes look yellow | • skin rash or blisters with fever |
| • stomach pain | • swelling of the arms and legs, hands and feet |
| • flu-like symptoms | |
| • vomit blood |
These are not all the side effects with NSAID medicines. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information about NSAID medicines. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Other information about Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Aspirin is an NSAID medicine but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain, stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
- Some of these NSAID medicines are sold in lower doses without a prescription (over-the-counter). Talk to your healthcare provider before using over-the-counter NSAIDs for more than 10 days.
| Generic Name | Tradename |
| * Vicoprofen contains the same dose of ibuprofen as over-the-counter (OTC) NSAIDs, and is usually used for less than 10 days to treat pain. The OTC NSAID label warns that long term continuous use may increase the risk of heart attack or stroke. |
|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | |
| Celecoxib | Celebrex |
| Diclofenac | Cataflam, Voltaren, Arthrotec (combined with misoprostol) |
| Diflunisal | Dolobid |
| Etodolac | Lodine, Lodine XL |
| Fenoprofen | Nalfon, Nalfon 200 |
| Flurbirofen | Ansaid |
| Ibuprofen | Motrin, Tab-Profen, Vicoprofen (combined with hydrocodone), Combunox (combined with oxycodone) |
| Indomethacin | Indocin, Indocin SR, Indo-Lemmon, Indomethagan |
| Ketoprofen | Oruvail |
| Ketorolac | Toradol |
| Mefenamic Acid | Ponstel |
| Meloxicam | Mobic |
| Nabumetone | Relafen |
| Naproxen | Naprosyn, Anaprox, Anaprox DS, EC-Naproxyn, Naprelan, Naprapac (copackaged with lansoprazole) |
| Oxaprozin | Daypro |
| Piroxicam | Feldene |
| Sulindac | Clinoril |
| Tolmetin | Tolectin, Tolectin DS, Tolectin 600 |
Diclofenac Sodium DR 75mg Tablet
Diclofenac SodiumDiclofenac Sodium TABLET, DELAYED RELEASE
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||