Didanosine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use didanosine safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for didanosine for oral solution.Didanosine for Oral Solution, USPInitial U.S. Approval: 1991RECENT MAJOR CHANGES(5.7)BOXED WARNINGWARNING: PANCREATITIS, LACTIC ACIDOSIS and HEPATOMEGALY with STEATOSIS See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. Fatal and nonfatal pancreatitis. Didanosine should be suspended in patients with suspected pancreatitis and discontinued in patients with confirmed pancreatitis. (5.1) Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases. Fatal lactic acidosis has been reported in pregnant women who received the combination of didanosine and stavudine. (5.2) INDICATIONS AND USAGEDidanosine is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor for use in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 infection. (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Adult patients: Administered on an empty stomach at least 30 minutes before or 2 hours after eating. Dosing is based on body weight. (2.1) at least 60 kg less than 60 kg Preferred dosing 200 mg twice daily 125 mg twice daily Dosing for patients whose management requires once-daily frequency 400 mg once daily 250 mg once daily Pediatric patients (2 weeks old to 18 years old): Administered on an empty stomach at least 30 minutes before or 2 hours after eating. - Between 2 weeks and 8 months old, dosing is 100 mg/m2 twice daily. - For those greater than 8 months old, dosing is 120 mg/m2 twice daily but not to exceed the adult dosing recommendation. (2.1) Renal impairment: Dose reduction is recommended. (2.2) Coadministration with tenofovir: Dose reduction is recommended. Patients should be monitored closely for didanosine-associated adverse reactions. (2.3, 7.1) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 4 ounce bottle of 2 grams of Didanosine (3) 8 ounce bottle of 4 grams of Didanosine (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS(4.14.2)WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Pancreatitis: Suspension or discontinuation of didanosine may be necessary. (5.1) Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis: Suspend didanosine in patients who develop clinical symptoms or signs with or without laboratory findings. (5.2) Hepatic toxicity: Interruption or discontinuation of didanosine must be considered upon worsening of liver disease. (5.3) Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension: Discontinue didanosine in patients with evidence of non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. (5.4) Patients may develop peripheral neuropathy (5.5), retinal changes and optic neuritis (5.6), immune reconstitution syndrome (5.7), and redistribution/accumulation of body fat. (5.8) Side Effects In adults, the most common adverse reactions (greater than 10%, all grades) are diarrhea, peripheral neurologic symptoms/neuropathy, abdominal pain, nausea, headache, rash, and vomiting. (6.1) Adverse reactions in pediatric patients were consistent with those in adults. (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-850-2876 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch DRUG INTERACTIONS(4,712.3)USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSPregnancy: Fatal lactic acidosis has been reported in pregnant women who received both didanosine and stavudine with other agents. This combination should be used with caution during pregnancy and only if the potential benefit clearly outweighs the potential risk. (5.2, 8.1) Physicians are encouraged to register patients in the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry by calling 1-800-258-4263.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING: PANCREATITIS, LACTIC ACIDOSIS and HEPATOMEGALY with STEATOSIS
- 1 DIDANOSINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 DIDANOSINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 DIDANOSINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 DIDANOSINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 DIDANOSINE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Medication Guide
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/mL (2 g Bottle)
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/mL Carton (2 g Bottle)
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/mL (4 g Bottle)
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/mL Carton (4 g Bottle)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: PANCREATITIS, LACTIC ACIDOSIS and HEPATOMEGALY with STEATOSIS
Fatal and nonfatal pancreatitis has occurred during therapy with didanosine used alone or in combination regimens in both treatment-naive and treatment-experienced patients, regardless of degree of immunosuppression. Didanosine should be suspended in patients with suspected pancreatitis and discontinued in patients with confirmed pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogues alone or in combination, including didanosine and other antiretrovirals. Fatal lactic acidosis has been reported in pregnant women who received the combination of didanosine and stavudine with other antiretroviral agents. The combination of didanosine and stavudine should be used with caution during pregnancy and is recommended only if the potential benefit clearly outweighs the potential risk [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
[see Clinical Studies (14)]
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage (Adult and Pediatric Patients)
[see Clinical Studies (14)]
| at least 60 kg | less than 60 kg | |
|---|---|---|
| Preferred dosing |
200 mg twice daily |
125 mg twice daily |
| Dosing for patients whose management requires once-daily frequency |
400 mg once daily |
250 mg once daily |
Pediatric Patients (2 weeks old to 18 years old): 22
2.2 Renal Impairment
Adult Patients
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) |
Recommended Didanosine for Oral Solution Dose by Patient Weight |
|
|---|---|---|
| at least 60 kg | less than 60 kg | |
|
a 400 mg once daily (at least 60 kg) or 250 mg once daily (less than 60 kg) for patients whose management requires once-daily frequency of administration. |
||
| at least 60 |
200 mg twice dailya
|
125 mg twice dailya
|
| 30-59 |
200 mg once daily or 100 mg twice daily |
150 mg once daily or 75 mg twice daily |
| 10-29 |
150 mg once daily |
100 mg once daily |
| less than 10 |
100 mg once daily |
75 mg once daily |
Pediatric Patients
Patients Requiring Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) or Hemodialysis
2.3 Dosage Adjustment
Concomitant Therapy with Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
[See Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
Hepatic Impairment
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Allopurinol
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
4.2 Ribavirin
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Pancreatitis
Fatal and nonfatal pancreatitis has occurred during therapy with didanosine used alone or in combination regimens in both treatment-naive and treatment-experienced patients, regardless of degree of immunosuppression. Didanosine should be suspended in patients with signs or symptoms of pancreatitis and discontinued in patients with confirmed pancreatitis. Patients treated with didanosine in combination with stavudine may be at increased risk for pancreatitis.
[See Adverse Reactions (6).]
5.2 Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogues alone or in combination, including didanosine and other antiretrovirals.[see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
5.3 Hepatic Toxicity
[See Adverse Reactions (6).]
5.4 Non-cirrhotic Portal Hypertension
5.5 Peripheral Neuropathy
[See Adverse Reactions (6).]
5.6 Retinal Changes and Optic Neuritis
[see Adverse Reactions (6)]
5.7 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Mycobacterium aviumPneumocystis jiroveci
5.8 Fat Redistribution
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Pancreatitis [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Lactic acidosis/severe hepatomegaly with steatosis [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatic toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Peripheral neuropathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Retinal changes and optic neuritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Adults
| Adverse Reactions | Percent of Patients* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTG 116A | ACTG 116B/117 | |||
| didanosine n=197 |
zidovudine n=212 |
didanosine n=298 |
zidovudine n=304 |
|
| * The incidences reported included all severity grades and all reactions regardless of causality. |
||||
| Diarrhea Peripheral Neurologic Symptoms/Neuropathy Abdominal Pain Rash/Pruritus Pancreatitis |
19 17 13 7 7 |
15 14 8 8 3 |
28 20 7 9 6 |
21 12 8 5 2 |
| Adverse Reactions | Percent of Patientsa,c | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI454-148b | START 2b | |||
| didanosine + stavudine + nelfinavir n=482 |
zidovudine + lamivudine + nelfinavir n=248 |
didanosine + stavudine + indinavir n=102 |
zidovudine + lamivudine + indinavir n=103 |
|
|
a Percentages based on treated subjects. b Median duration of treatment 48 weeks. c The incidences reported included all severity grades and all reactions regardless of causality. * This event was not observed in this study arm. |
||||
| Diarrhea Nausea Peripheral Neurologic Symptoms/Neuropathy Headache Rash Vomiting Pancreatitis (see below) |
70 28 26 21 13 12 1 |
60 40 6 30 16 14 * |
45 53 21 46 30 30 less than 1 |
39 67 10 37 18 35 * |
[see Warnings and Precautions (5)]
| Parameter | Percent of Patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTG 116A | ACTG 116B/117 | |||
| didanosine n=197 |
zidovudine n=212 |
didanosine n=298 |
zidovudine n=304 |
|
| ULN = upper limit of normal. |
||||
| SGOT (AST) (greater than 5 x ULN) SGPT (ALT) (greater than 5 x ULN) Alkaline phosphatase (greater than 5 x ULN) Amylase (at least 1.4 x ULN) Uric acid (greater than 12 mg/dL) |
9 9 4 17 3 |
4 6 1 12 1 |
7 6 1 15 2 |
6 6 1 5 1 |
| Parameter | Percent of Patientsa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI454-148b | START 2b | |||
| didanosine + stavudine + nelfinavir n=482 |
zidovudine + lamivudine + nelfinavir n=248 |
didanosine + stavudine + indinavir n=102 |
zidovudine + lamivudine + indinavir n=103 |
|
| ULN = upper limit of normal. NC = Not Collected. a Percentages based on treated subjects. b Median duration of treatment 48 weeks. |
||||
| Bilirubin (greater than 2.6 x ULN) SGOT (AST) (greater than 5 x ULN) SGPT (ALT) (greater than 5 x ULN) GGT (greater than 5 x ULN) Lipase (greater than 2 x ULN) Amylase (greater than 2 x ULN) |
less than 1 3 3 NC 7 NC |
less than 1 2 3 NC 2 NC |
16 7 8 5 5 8 |
8 7 5 2 5 2 |
| Parameter | Percent of Patientsa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI454-148b | START 2b | |||
| didanosine + stavudine + nelfinavir n=482 |
zidovudine + lamivudine + nelfinavir n=248 |
didanosine + stavudine + indinavir n=102 |
zidovudine + lamivudine + indinavir n=103 |
|
| NC = Not Collected. a Percentages based on treated subjects. b Median duration of treatment 48 weeks. |
||||
| Bilirubin SGOT (AST) SGPT (ALT) GGT Lipase Amylase |
7 42 37 NC 17 NC |
3 23 24 NC 11 NC |
68 53 50 28 26 31 |
55 20 18 12 19 17 |
22 2[see Clinical Studies (14)]
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders
Body as a Whole [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
Digestive Disorders
Exocrine Gland Disorders [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Hepatobiliary Disorders [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2)][see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Metabolic Disorders
Musculoskeletal Disorders
Ophthalmologic Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Use with Stavudine- and Hydroxyurea-Based Regimens
[see Warnings and Precautions (5)]
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Established Drug Interactions
[see Contraindications (4.1 and 4.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
| Drug | Effect | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
| ↑ Indicates increase. ↓ Indicates decrease. a The dosing recommendation for coadministration of didanosine delayed-release capsules and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate with respect to meal consumption differs from that of didanosine. See the complete prescribing information for didanosine delayed-release capsules. |
||
| ciprofloxacin |
↓ ciprofloxacin concentration |
Administer didanosine at least 2 hours after or 6 hours before ciprofloxacin. |
| delavirdine |
↓ delavirdine concentration |
Administer didanosine 1 hour after delavirdine. |
| ganciclovir |
↓ didanosine concentration |
If there is no suitable alternative to ganciclovir, then use in combination with didanosine with caution. Monitor for didanosine-associated toxicity. |
| indinavir |
↓ indinavir concentration |
Administer didanosine 1 hour after indinavir. |
| methadone |
↓ didanosine concentration |
Do not coadminister methadone with didanosine pediatric powder due to significant decreases in didanosine concentrations. If coadministration of methadone and didanosine is necessary, the recommended formulation of didanosine is didanosine delayed-release capsules. Patients should be closely monitored for adequate clinical response when didanosine delayed-release capsules are coadministered with methadone, including monitoring for changes in HIV RNA viral load. |
| nelfinavir |
↓ No interacion 1 hour after didanosine |
Administer nelfinavir 1 hour after didanosine. |
| tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
↓ didanosine concentration |
A dose reduction of didanosine to the following dosage once daily is recommended.a
|
[Table 8 and see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3, Table 12)][see Dosage and Administration (2.3) , Warnings and Precautions (5) ]
7.2 Predicted Drug Interactions
| Drug or Drug Class | Effect | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
| ↑ Indicates increase. ↓ Indicates decrease. a Only if other drugs are not available and if clearly indicated. If treatment with life-sustaining drugs that cause pancreatic toxicity is required, suspension of didanosine is recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. b [See Warnings and Precautions (5.6).] |
||
| Drugs that may cause pancreatic toxicity |
↑ risk of pancreatitis |
Use only with extreme cautiona
|
| Neurotoxic drugs |
↑ risk of neuropathy |
Use with cautionb
|
| Antacids containing magnesium or aluminum |
↑ side effects associated with antacid components |
Use caution with Didanosine Pediatric Powder for Oral Solution |
| Azole antifungals |
↓ ketoconazole or Itraconazole concentration |
Administer drugs such as ketoconazole or itraconazole at least 2 hours before didanosine. |
| Quinolone antibiotics (see also ciprofloxacin in Table 8) |
↓ quinolone concentration |
Consult package insert of the quinolone. |
| Tetracycline antibiotics |
↓ antibiotic concentration |
Consult package insert of the tetracycline. |
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]The combination of didanosine and stavudine should be used with caution during pregnancy and is recommended only if the potential benefit clearly outweighs the potential risk.
Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry
8.3 Nursing Mothers
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that HIV-infected mothers not breastfeed their infants to avoid risking postnatal transmission of HIV.mothers should be instructed not to breastfeed if they are receiving didanosine.
8.4 Pediatric Use
[see Dosage and Administration (2), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14)]
8.5 Geriatric Use
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)][see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]
8.6 Renal Impairment
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)][see Dosage and Administration (2)]
10 OVERDOSAGE
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
11 DESCRIPTION
[see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]
 101243
10124312 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)]
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
in vitroin vitro
| Parameter | Adult Patientsa |
n | Pediatric Patientsb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 months to 19 years |
n | 2 weeks to 4 months |
n | |||
| CSF = cerebrospinal fluid, ND = not determined. a Parameter units for adults were converted to the same units in pediatric patients to facilitate comparisons among populations: mean adult body weight = 70 kg and mean adult body surface area = 1.73 m2. b In 1-day old infants (n=10), the mean ± SD apparent oral clearance was 1523 ± 1176 mL/min/m2 and half-life was 2 ± 0.7 h. c Following IV administration. d Following IV administration in adults and IV or oral administration in pediatric patients. e Mean ± SE. f Following oral administration. g Apparent oral clearance estimate was determined as the ratio of the mean systemic clearance and the mean oral bioavailability estimate. |
||||||
| Oral bioavailability (%) |
42 ± 12 |
6 |
25 ± 20 |
46 |
ND |
|
| Apparent volume of distributionc (L/m2) |
43.7 ± 8.9 |
6 |
28 ± 15 |
49 |
ND |
|
| CSF-plasma ratiod
|
21 ± 0.03%e
|
5 |
46% (range 12 to 85%) |
7 |
ND |
|
| Systemic clearancec (mL/min/m2) |
526 ± 64.7 |
6 |
516 ± 184 |
49 |
ND |
|
| Renal clearancef (mL/min/m2) |
223 ± 85 |
6 |
240 ± 90 |
15 |
ND |
|
| Apparent oral clearanceg (mL/min/m2) |
1252 ± 154 |
6 |
2064 ± 736 |
48 |
1353 ± 759 |
41 |
| Elimination half-lifef (h) |
1.5 ± 0.4 |
6 |
0.8 ± 0.3 |
60 |
1.2 ± 0.3 |
21 |
| Urinary recovery of didanosinef (%) |
18 ± 8 |
6 |
18 ± 10 |
15 |
ND |
|
Effect of Food
max[see Dosage and Administration (2)]
Special Populations
Renal Insufficiency: [See Dosage and Administration (2.2).]
| ND = not determined due to anuria. CLcr = creatinine clearance. CL/F = apparent oral clearance. CLR = renal clearance. |
|||||
|
Parameter
|
Creatinine Clearance (mL/min)
|
||||
|
at least 90
n=12 |
60-90
n=6 |
30-59
n=6 |
10-29
n=3 |
Dialysis Patients
n=11 |
|
| CLcr (mL/min) |
112 ± 22 |
68 ± 8 |
46 ± 8 |
13 ± 5 |
ND |
| CL/F (mL/min) |
2164 ± 638 |
1566 ± 833 |
1023 ± 378 |
628 ± 104 |
543 ± 174 |
| CLR (mL/min) |
458 ± 164 |
247 ± 153 |
100 ± 44 |
20 ± 8 |
less than 10 |
| T½ (h) |
1.42 ± 0.33 |
1.59 ± 0.13 |
1.75 ± 0.43 |
2 ± 0.3 |
4.1 ± 1.2 |
Pediatric Patients:22[see Clinical Studies (14.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]
Drug Interactions
max[see Dosage and Administration (2.3 for Concomitant Therapy with Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate), Contraindications (4.1), and Drug Interactions (7.1 and 7.2)]
| % Change of Didanosine Pharmacokinetic Parametersa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug | Didanosine Dosage |
n | AUC of Didanosine (95% CI) | Cmax of Didanosine (95% CI) |
| ↑ Indicates increase. ↓ Indicates decrease. ↔ Indicates no change, or mean increase or decrease of less than 10%. a The 95% confidence intervals for the percent change in the pharmacokinetic parameter are displayed. b HIV-infected patients. c 90% CI. d Comparisons are made to a parallel control group not receiving methadone (n=10) eComparisons are made to historical controls (n=68, pooled from 3 studies) conducted in healthy subjects. The number of subjects evaluated for AUC and Cmax is 15 and 16, respectively. f For results of drug interaction studies between the enteric-coated formulation of didanosine (didanosine delayed-release capsules) and methadone, see the complete prescribing information for didanosine delayed-release capsules. g Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. h For results of drug interaction studies between the enteric-coated formulation of didanosine (didanosine delayed-release capsules) and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, see the complete prescribing information for didanosine delayed-release capsules. i Patients less than 60 kg with creatinine clearance of at least 60 mL/min. NA = Not available. |
||||
|
allopurinol,
|
|
|||
| renally impaired, 300 mg/day
|
200 mg single dose |
2 |
↑ 312% |
↑ 232% |
| healthy volunteer, 300 mg/day for 7 days
|
400 mg single dose |
14 |
↑ 113% |
↑ 69% |
| ciprofloxacin, 750 mg every 12 hours for 3 days, 2 hours before didanosine
|
200 mg every 12 hours for 3 days |
8b
|
↓ 16% |
↓ 28% |
|
ganciclovir, 1000 mg every 8 hours, 2 hours after didanosine indinavir, 800 mg single dose, |
200 mg every 12 hours |
12 |
↑ 111% |
NA |
| simultaneous |
200 mg single dose |
16 |
↔ |
↔ |
| 1 hour before didanosine
|
200 mg single dose |
16 |
↓ 17% (-27, -7%)c |
↓ 13% (-28, 5%)c |
| ketoconazole, 200 mg/day for 4 days, 2 hours before didanosine
|
375 mg every 12 hours for 4 days |
12b
|
↔ |
↓ 12% |
|
methadone, chronic maintenance dosef
|
200 mg single dose |
16d
|
↓ 57% |
↓ 66% |
| 400 mg single dose |
15, 16e
|
↓ 29% (-40, -16%)c |
↓ 41% (-54, -26%)c |
|
|
tenofovir,g,h 300 mg once daily, 1 hour after didanosine
|
250i mg or 400 mg once daily for 7 days |
14 |
↑ 44% (31, 59%)c |
↑ 28% (11, 48%)c |
| loperamide, 4 mg every 6 hours for 1 day
|
300 mg single dose |
12b
|
↔ |
↓ 23% |
| metoclopramide, 10 mg single dose
|
300 mg single dose |
12b
|
↔ |
↑ 13% |
| ranitidine, 150 mg single dose, 2 hours before didanosine |
375 mg single dose |
12b
|
↑ 14% |
↑ 13% |
| rifabutin, 300 or 600 mg/day for 12 days |
167 mg or 250 mg every 12 hours for 12 days |
11 |
↑ 13% (-1, 27%) |
↑ 17% (-4, 38%) |
| ritonavir, 600 mg every 12 hours for 4 days |
200 mg every 12 hours for 4 days |
12 |
↓ 13% (0, 23%) |
↓ 16% (5, 26%) |
| stavudine, 40 mg every 12 hours for 4 days |
100 mg every 12 hours for 4 days |
10 |
↔ |
↔ |
| sulfamethoxazole, 1000 mg single dose |
200 mg single dose |
8b
|
↔ |
↔ |
| trimethoprim, 200 mg single dose |
200 mg single dose |
8b
|
↔ |
↑ 17% (-23, 77%) |
| zidovudine, 200 mg every 8 hours for 3 days |
200 mg every 12 hours for 3 days |
6b
|
↔ |
↔ |
| % Change of Coadministered Drug Pharmacokinetic Parametersa |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug | Didanosine Dosage |
n | AUC of Coadministered Drug (95% CI) |
Cmax of Coadministered Drug (95% CI) |
| ↑ Indicates increase. ↓ Indicates decrease. ↔ Indicates no change, or mean increase or decrease of less than 10%. a The 95% confidence intervals for the percent change in the pharmacokinetic parameter are displayed. b HIV-infected patients. c Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. d Patients less than 60 kg with creatinine clearance of at least 60 mL/min. NA = Not available. |
||||
|
ciprofloxacin
|
|
|||
| 750 mg every 12 hours for 3 days, 2 hours before didanosine |
200 mg every 12 hours for 3 days |
8b
|
↓ 26% |
↓ 16% |
| 750 mg single dose |
buffered placebo tablet |
12 |
↓ 98% |
↓ 93% |
|
delavirdine, 400 mg single dose simultaneous |
125 mg or 200 mg every 12 hours |
12b
|
↓ 32% |
↓ 53% |
| 1 hour before didanosine |
125 mg or 200 mg every 12 hours |
12b
|
↑ 20% |
↑ 18% |
| ganciclovir, 1000 mg every 8 hours, 2 hours after didanosine |
200 mg every 12 hours |
12b
|
↓ 21% |
NA |
|
indinavir, 800 mg single dose simultaneous |
200 mg single dose |
16 |
↓ 84% |
↓ 82% |
| 1 hour before didanosine |
200 mg single dose |
16 |
↓ 11% |
↓ 4% |
|
ketoconazole, 200 mg/day for 4 days, 2 hours before didanosine |
375 mg every 12 hours for 4 days |
12b
|
↓ 14% |
↓ 20% |
|
nelfinavir, 750 mg single dose, 1 hour after didanosine |
200 mg single dose |
10b
|
↑ 12% |
↔ |
| dapsone, 100 mg single dose |
200 mg every 12 hours for 14 days |
6b
|
↔ |
↔ |
| ranitidine, 150 mg single dose, 2 hours before didanosine |
375 mg single dose |
12b
|
↓ 16% |
↔ |
| ritonavir, 600 mg every 12 hours for 4 days |
200 mg every 12 hours for 4 days |
12 |
↔ |
↔ |
| stavudine, 40 mg every 12 hours for 4 days |
100 mg every 12 hours for 4 days |
10b
|
↔ |
↑ 17% |
| sulfamethoxazole, 1000 mg single dose |
200 mg single dose |
8b
|
↓ 11% (-17, -4%) |
↓ 12% (-28, 8%) |
| tenofovir,c 300 mg once daily 1 hour after didanosine |
250d mg or 400 mg once daily for 7 days |
14 |
↔ |
↔ |
| trimethoprim, 200 mg single dose |
200 mg single dose |
8b
|
↑ 10% (-9, 34%) |
↓ 22% (-59, 49%) |
| zidovudine, 200 mg every 8 hours for 3 days |
200 mg every 12 hours for 3 days |
6b
|
↓ 10% (-27, 11%) |
↓ 16.5% (-53, 47%) |
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Antiviral Activity in Cell Culture
50
Resistance
Cross-resistance
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Escherichia coliin vitroin vitroin vitroSalmonellain vivo
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adult Patients
Combination Therapy
3310103

| Week 48 Status | Percent of Patients with HIV-1 RNA less than 400 copies/mL (less than 50 copies/mL) |
|
|---|---|---|
| didanosine/stavudine/nelfinavir n=503 |
lamivudine/zidovudine/ nelfinavir n=253 |
|
| * p less than 0.05 for the differences between treatment groups, by Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test. a Patients achieved virologic response [two consecutive viral loads less than 400 (less than 50) copies/mL] and maintained it to Week 48. b Includes viral rebound and failing to achieve confirmed less than 400 (less than 50) copies/mL by Week 48. c Includes lost to follow-up, noncompliance, withdrawal, and pregnancy. |
||
| Respondera
|
50* (34*) |
59 (47) |
| Virologic failureb
|
36 (57) |
32 (48) |
| Death or disease progression |
less than 1 (less than 1) |
1 (less than 1) |
| Discontinued due to adverse events |
4 (2) |
2 (less than 1) |
| Discontinued due to other reasonsc
|
6 (3) |
4 (2) |
| Never initiated treatment |
4 (4) |
2 (2) |
Monotherapy
14.2 Pediatric Patients
2222
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Didanosine for Oral Solution, USP
20 mg/mL Initial Solution
10 mg/mL Final Admixture
- Immediately mix one part of the 20 mg/mL initial solution with one part of Maximum Strength Mylanta® Liquid for a final dispensing concentration of 10 mg didanosine per mL. For patient home use, the admixture should be dispensed in appropriately sized, flint-glass or plastic (HDPE, PET, or PETG) bottles with child-resistant closures.
- Instruct the patient to shake the admixture thoroughly prior to use and to store the tightly closed container in the refrigerator.
Storage
Store
®
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See Medication Guide.
17.1 Pancreatitis
17.2 Peripheral Neuropathy
17.3 Lactic Acidosis and Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis
17.4 Hepatic Toxicity
17.5 Non-cirrhotic Portal Hypertension
17.6 Retinal Changes and Optic Neuritis
17.7 Fat Redistribution
17.8 Concomitant Therapy
17.9 General Information
- Do not share needles or other injection equipment.
- Do not share personal items that can have blood or body fluids on them, like toothbrushes and razor blades.
- Do not have any kind of sex without protection. Always practice safe sex by using a latex or polyurethane condom or other barrier method to lower the chance of sexual contact with semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
- Do not breastfeed. It is not known if didanosine can be passed to your baby in your breast milk and whether it could harm your baby. Also, mothers with HIV-1 should not breastfeed because HIV-1 can be passed to the baby in breast milk.
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
Medication Guide
Didanosine for Oral Solution, USP
What is the most important information I should know about didanosine for oral solution?
Didanosine for oral solution may cause serious side effects, including:
Swelling of your pancreas (pancreatitis) that may cause death. Pancreatitis can happen at any time during your treatment with didanosine for oral solution.
- have had pancreatitis
- have advanced HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection
- have kidney problems
- drink alcoholic beverages
- take a medicine called ZERIT® (stavudine)
It is important to call your healthcare provider right away if you have:
- stomach pain
- swelling of your stomach
- nausea and vomiting
- fever
Build-up of acid in your blood (lactic acidosis). Lactic acidosis must be treated in the hospital as it may cause death.
- have liver problems
- are pregnant. There have been deaths reported in pregnant women who get lactic acidosis after taking didanosine for oral solution and ZERIT (stavudine).
- are overweight
- have been treated for a long time with other medicines to treat HIV
It is important to call your health care provider right away if you:
- feel weak or tired
- have unusual (not normal) muscle pain
- have trouble breathing
- have stomach pain with nausea and vomiting
- feel cold, especially in your arms and legs
- feel dizzy or light-headed
- have a fast or irregular heartbeat
Liver problems.
It is important to call your healthcare provider right away if you have:
- yellowing of your skin or the white of your eyes (jaundice)
- dark urine
- pain on the right side of your stomach
- swelling of your stomach
- easy bruising or bleeding
- loss of appetite
- nausea or vomiting
- vomiting blood or dark colored stools (bowel movements)
What is didanosine for oral solution?
Who should not take didanosine for oral solution?
Do not take didanosine for oral solution if you take:
- ZYLOPRIM®, LOPURIN®, ALOPRIM® (allopurinol)
- COPEGUS®, REBETOL®, RIBASPHERE®, RIBAVIRIN®, VIRAZOLE® (ribavirin)
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking didanosine for oral solution?
- have or had kidney problems
- have or had liver problems (such as hepatitis)
- have or had persistent numbness, tingling, or pain in the hands or feet (neuropathy)
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if didanosine for oral solution will harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant while taking didanosine for oral solution. You and your healthcare provider will decide if you should take didanosine for oral solution while you are pregnant.
Pregnancy Registry: There is a pregnancy registry for women who take antiviral medicines during pregnancy. The purpose of the registry is to collect information about the health of you and your baby. Talk to your doctor about how you can take part in this registry.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Do not breastfeed. It is not known if didanosine can be passed to your baby in your breast milk and whether it could harm your baby. Also, mothers with HIV-1 should not breastfeed because HIV-1 can be passed to the baby in the breast milk.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take,
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- VIREAD® (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate)
- DROXIA®, HYDREA® (hydroxyurea)
- RESCRIPTOR® (delavirdine mesylate)
- CYTOVENE®, VALCYTE® (ganciclovir)
- CRIXIVAN® (indinavir)
- DOLOPHINE® HYDROCHLORIDE, METHADOSE® (methadone)
- VIRACEPT® (nelfinavir)
- antacids
- antifungal medicines such as NIZORAL® (ketoconazole) or SPORANOX® (itraconazole)
- quinolone antibiotics such as CIPRO®, PROQUIN® XR (ciprofloxacin)
- tetracycline antibiotics such as BRISTACYCLINE®, SUMYCIN® (tetracycline)
- alcoholic beverages
How should I take didanosine for oral solution?
- Take didanosine for oral solution exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how much didanosine for oral solution to take and when to take it.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose. Do not change your dose of didanosine for oral solution without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Do not take didanosine for oral solution with food. Take didanosine for oral solution on an empty stomach at least 30 minutes before or 2 hours after you eat.
- Try not to miss a dose, but if you do, take it as soon as possible. If it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and continue your regular dosing schedule.
- Some medicines should not be taken at the same time of day that you take didanosine for oral solution. Check with your healthcare provider.
- If your kidneys are not working well, your healthcare provider will need to do regular blood and urine tests to check how they are working while you take didanosine for oral solution. Your healthcare provider may also lower your dosage of didanosine for oral solution if your kidneys are not working well.
- If you take too much didanosine for oral solution, contact a poison control center or emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking didanosine for oral solution?
- Alcohol. Do not drink alcohol while you take didanosine for oral solution. Alcohol may increase your risk of getting pain and swelling of your pancreas (pancreatitis) or may damage your liver.
What are the possible side effects of didanosine for oral solution?
“What is the most important information I should know about didanosine for oral solution?”
- Vision changes. You should have regular eye exams while you take didanosine for oral solution.
- Peripheral neuropathy. Symptoms include: numbness, tingling, or pain in your hands or feet. This condition is more likely to happen in people who have had it before, in patients taking medicines that affect the nerves, and in people with advanced HIV disease. A child may not notice these symptoms. Ask your child's healthcare provider for the signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy in children.
- Changes in your immune system (immune reconstitution syndrome). Your immune system may get stronger and begin to fight infections that have been hidden in your body for a long time. Tell your healthcare provider if you start having new or worse symptoms of infection after you start taking HIV medicine.
- Changes in body fat (fat redistribution). Changes in body fat have been seen in people who take antiretroviral medicines. These changes may include:
- more fat in or around your
- less fat in your
- diarrhea
- stomach pain
- nausea
- vomiting
- headache
- rash
How should I store didanosine for oral solution?
- Safely throw away any unused didanosine for oral solution after 30 days.
Keep didanosine for oral solution and all medicines out of the reach of children and pets.
General information about the safe and effective use of didanosine for oral solution
- Do not share needles or other injection equipment.
- Do not share personal items that can have blood or body fluids on them, like toothbrushes and razor blades.
-
Do not have any kind of sex without protection. Always practice safe sex by using a latex or polyurethane condom or other barrier method to lower the chance of sexual contact with semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
What are the ingredients in didanosine for oral solution?
Active Ingredient:
Inactive Ingredients:
Pediatric Oral Solution: ®
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/mL (2 g Bottle)
NDC 65862-109-02
Didanosine for Oral Solution, USP
2 g
PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication
Guide provided separately to each patient.
Rx only
AUROBINDO

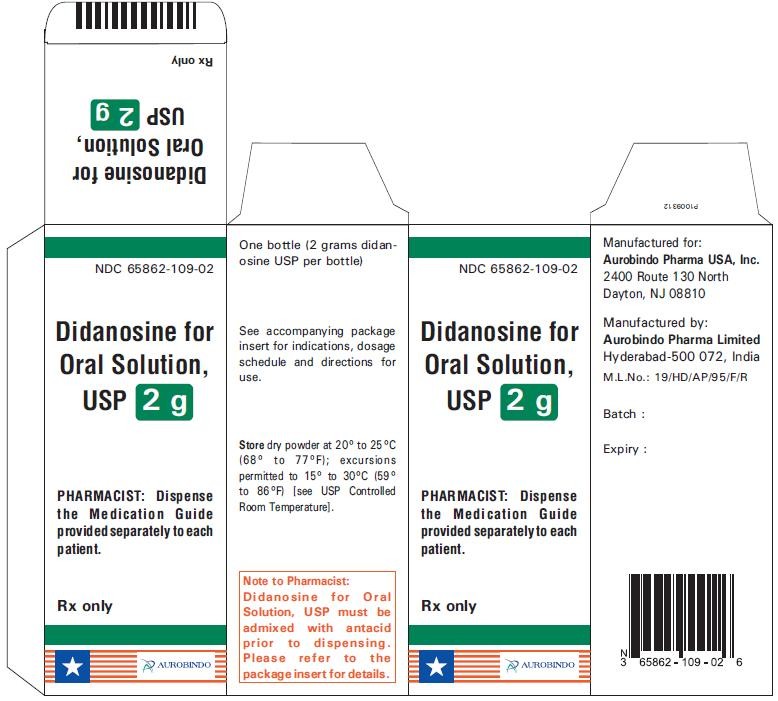
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/mL Carton (2 g Bottle)
NDC 65862-109-02
Didanosine for Oral Solution, USP
2 g
PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide
provided separately to each patient.
Rx only
AUROBINDO
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/mL (4 g Bottle)
NDC 65862-110-04
Didanosine for Oral Solution, USP
4 g
PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication
Guide provided separately to each patient.
Rx only
AUROBINDO

PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/mL Carton (4 g Bottle)
NDC 65862-110-04
Didanosine for Oral Solution, USP
4 g
PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide
provided separately to each patient.
Rx only
AUROBINDO

DidanosineDidanosine POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DidanosineDidanosine POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!