DIFLUNISAL
Rising Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
Rx only
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- DIFLUNISAL DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- DIFLUNISAL CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- General
- Hepatic Effects
- Hematological Effects
- Preexisting Asthma
- Ocular Effects
- Reye's Syndrome
- Information for Patients
- Laboratory Tests
- Drug Interactions
- Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
- Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis & Impairment Of Fertility
- Pregnancy
- Labor and Delivery
- Nursing Mothers
- Pediatric Use
- Geriatric Use
- DIFLUNISAL ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- DIFLUNISAL DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- MEDICATION GUIDE FOR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDS)
- Package label principal display panel(60 Tablets)
- Package label principal display panel(100 Tablets)
- Package label principal display panel(500 Tablets)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Cardiovascular Risk
- NSAIDs

Throughout this package insert, the term NSAID refers to a non-aspirin non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk (see WARNINGS ). - Diflunisal tablets are contraindicated for the treatment of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS ).
Gastrointestinal Risk
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events (see WARNINGS ).
DIFLUNISAL DESCRIPTION
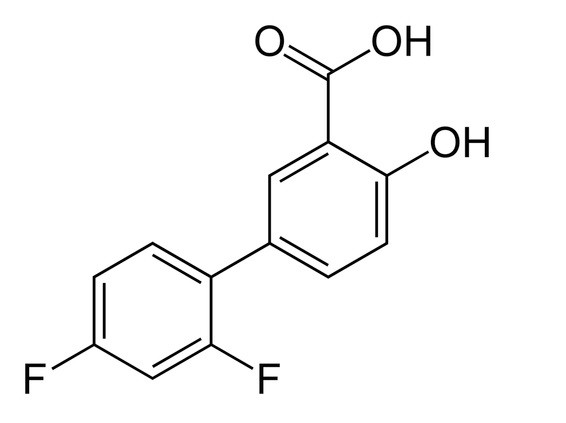
Molecular Formula: 13823
Each tablet, for oral administration, contains 500 mg diflunisal. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: Microcrystalline Cellulose (Vivapur 102), Opadry Blue (03H505000), Purified Water, USP, Sodium Stearyl Fumarate, Starch 1500 Pregelatinized, NF and Vivasol (Croscarmellose Sodium), NF.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Action
O
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Mild to Moderate Pain
Chronic Anti-Inflammatory Therapy in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Effect on Fecal Blood Loss
Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Antipyretic Activity
Uricosuric Effect
Effect on Platelet Function
O
Effect on Fecal Blood Loss
Effect on Blood Glucose
INDICATIONS & USAGE
WARNINGS
DIFLUNISAL CONTRAINDICATIONS
DESCRIPTION
WARNINGS, Anaphylactic/Anaphylactoid Reactions and PRECAUTIONS , Preexisting Asthma
WARNINGS
WARNINGS
Cardiovascular Effects
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
GI WARNINGS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypertension
Congestive Heart Failure and Edema
Gastrointestinal Effects – Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding and Perforation
prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding
Renal Effects
Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury. Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors, patients who are volume depleted, and the elderly. Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment state.
Advanced Renal Disease
No information is available from controlled clinical studies regarding the use of diflunisal tablets in patients with advanced renal disease. Therefore, treatment with diflunisal tablets is not recommended in these patients with advanced renal disease. If diflunisal tablet therapy must be initiated, close monitoring of the patient's renal function is advisable.
Anaphylactic/Anaphylactoid Reactions
As with other NSAIDs, anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions may occur in patients without known prior exposure to diflunisal tablets. Diflunisal tablets should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad. This symptom complex typically occurs in asthmatic patients who experience rhinitis with or without nasal polyps, or who exhibit severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS , Preexisting Asthma ). Emergency help should be sought in cases where an anaphylactic/ anaphylactoid reaction occurs.
Skin Reactions
NSAIDs, including diflunisal tablets, can cause serious skin adverse events such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Patients should be informed about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations and use of the drug should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Hypersensitivity Syndrome
A potentially life-threatening, apparent hypersensitivity syndrome has been reported. This multisystem syndrome includes constitutional symptoms (fever, chills), and cutaneous findings (see ADVERSE REACTIONS , Dermatologic ). It may also include involvement of major organs (changes in liver function, jaundice, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, disseminated intravascular coagulation, renal impairment, including renal failure), and less specific findings (adenitis, arthralgia, myalgia, arthritis, malaise, anorexia, disorientation). If evidence of hypersensitivity occurs, therapy with diflunisal tablets should be discontinued.
Pregnancy
In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, diflunisal tablets should be avoided because they may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Hepatic Effects
Borderline elevations of one or more liver tests may occur in up to 15% of patients taking NSAIDs including diflunisal tablets. These laboratory abnormalities may progress, may remain unchanged, or may be transient with continuing therapy. Notable elevations of ALT or AST (approximately three or more times the upper limit of normal) have been reported in approximately 1% of patients in clinical trials with NSAIDs. In addition, rare cases of severe hepatic reactions, including jaundice and fatal fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis and hepatic failure, some of them with fatal outcomes have been reported.
A patient with symptoms and/or signs suggesting liver dysfunction, or in whom an abnormal liver test has occurred, should be evaluated for evidence of the development of a more severe hepatic reaction while on therapy with diflunisal tablets. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), diflunisal tablets should be discontinued.
Hematological Effects
Anemia is sometimes seen in patients receiving NSAIDs, including diflunisal tablets. This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including diflunisal tablets, should have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs or symptoms of anemia.
NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown to prolong bleeding time in some patients. Unlike aspirin, their effect on platelet function is quantitatively less, of shorter duration, and reversible. Patients receiving diflunisal tablets who may be adversely affected by alterations in platelet function, such as those with coagulation disorders or patients receiving anticoagulants, should be carefully monitored.
Preexisting Asthma
Patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma. The use of aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma has been associated with severe bronchospasm which can be fatal. Since cross reactivity, including bronchospasm, between aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, diflunisal tablets should not be administered to patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity and should be used with caution in patients with preexisting asthma.
Ocular Effects
Because of reports of adverse eye findings with agents of this class, it is recommended that patients who develop eye complaints during treatment with diflunisal tablets have ophthalmologic studies.
Reye's Syndrome
Acetylsalicylic acid has been associated with Reye’s syndrome. Because diflunisal is a derivative of salicylic acid, the possibility of its association with Reye’s syndrome cannot be excluded.
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed of the following information before initiating therapy with an NSAID and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy. Patients should also be encouraged to read the NSAID Medication Guide that accompanies each prescription dispensed.
- Diflunisal tablets, like other NSAIDs, may cause serious CV side effects, such as MI or stroke, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious CV events can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, slurring of speech, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Effects ).
- Diflunisal tablets, like other NSAIDs, can cause GI discomfort and, rarely, serious GI side effects, such as ulcers and bleeding, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS, Gastrointestinal Effects - Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation ).
- Diflunisal tablets, like other NSAIDs, can cause serious skin side effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, SJS, and TEN, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious skin reactions may occur without warning, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of skin rash and blisters, fever, or other signs of hypersensitivity such as itching, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms. Patients should be advised to stop the drug immediately if they develop any type of rash and contact their physicians as soon as possible.
- Patients should promptly report signs or symptoms of unexplained weight gain or edema to their physicians.
- Patients should be informed of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flu-like" symptoms). If these occur, patients should be instructed to stop therapy and seek immediate medical therapy.
- Patients should be informed of the signs of an anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). If these occur, patients should be instructed to seek immediate emergency help (see WARNINGS ).
- In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, diflunisal tablets should be avoided because they may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
Laboratory Tests
Because serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, physicians should monitor for signs or symptoms of GI bleeding. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, should have their CBC and a chemistry profile checked periodically. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver or renal disease develop, systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.) or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, diflunisal tablets should be discontinued.
Drug Interactions
ACE-inhibitors and Angiotensin II Anagonists
Acetaminophen
In normal volunteers, concomitant administration of diflunisal and acetaminophen resulted in an approximate 50% increase in plasma levels of acetaminophen. Acetaminophen had no effect on plasma levels of diflunisal. Since acetaminophen in high doses has been associated with hepatotoxicity, concomitant administration of diflunisal tablets and acetaminophen should be used cautiously, with careful monitoring of patients.
Antacids
Aspirin
When diflunisal is administered with aspirin, its protein binding is reduced, although the clearance of free diflunisal is not altered. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known; however, as with other NSAIDs, concomitant administration of diflunisal tablets and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential of increased adverse effects.
Cyclosporine
Diuretics
WARNINGS , Renal Effects
Lithium
Methotrexate
NSAIDs
The administration of diflunisal to normal volunteers receiving indomethacin decreased the renal clearance and significantly increased the plasma levels of indomethacin. In some patients the combined use of indomethacin and diflunisal has been associated with fatal gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Therefore, indomethacin and diflunisal tablets should not be used concomitantly.
Sulindac
Naproxen
Oral Anticoagulants
Tolbutamide
In diabetic patients receiving diflunisal and tolbutamide, no significant effects were seen on tolbutamide plasma levels or fasting blood glucose.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis & Impairment Of Fertility
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy category C
Nonteratogenic Effects
Labor and Delivery
In rat studies with NSAIDs, as with other drugs known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, an increased incidence of dystocia, delayed parturition, and decreased pup survival occurred. The effects of diflunisal tablets on labor and delivery in pregnant women are unknown.
Nursing Mothers
Diflunisal is excreted in human milk in concentrations of 2 to 7% of those in plasma. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from diflunisal, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Geriatric Use
As with any NSAID, caution should be exercised in treating the elderly (65 years and older) since advancing age appears to increase the possibility of adverse reactions. Elderly patients seem to tolerate ulceration or bleeding less well than other individuals and many spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in this population (see WARNINGS , Gastrointestinal Effects – Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation ).
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection and it may be useful to monitor renal function (see WARNINGS , Renal Effects ).
DIFLUNISAL ADVERSE REACTIONS
Incidence Greater Than 1%
Gastrointestinal
Psychiatric
Central Nervous System
Special Senses
Dermatologic
Miscellaneous
Incidence Less Than 1 in 100
Dermatologic
Gastrointestinal
Hematologic
Genitourinary
Psychiatric
Central Nervous System
Special Senses
Hypersensitivity Reactions
PRECAUTIONS
Miscellaneous
Causal Relationship Unknown
Respiratory
Cardiovascular
Musculoskeletal
Genitourinary
Special Senses
Miscellaneous
PRECAUTIONS, General
Potential Adverse Effects
OVERDOSAGE
50
DIFLUNISAL DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
WARNINGS
Maintenance doses higher than 1500 mg a day are not recommended.
Tablets should be swallowed whole, not crushed or chewed.
HOW SUPPLIED
Manufactured By:
Manufactured For:
Rising Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
MEDICATION GUIDE FOR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDS)
Rx only
(See the end of this Medication Guide for a list of prescription NSAID medicines.)
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines may increase the chance of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death.
- with longer use of NSAID medicines
- in people who have heart disease
NSAID medicines should never be used right before or after a heart surgery called a “coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).”
NSAID medicines can cause ulcers and bleeding in the stomach and intestines at any time during treatment. Ulcers and bleeding:
- can happen without warning symptoms
- may cause death
- taking medicines called “corticosteroids” and “anticoagulants”
- longer use
- smoking
- drinking alcohol
- older age
- having poor health
NSAID medicines should only be used:
- exactly as prescribed
- at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
- for the shortest time needed
What are Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
- different types of arthritis
- menstrual cramps and other types of short-term pain
Who should not take a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)?
Do not take an NSAID medicine:
- if you had an asthma attack, hives, or other allergic reaction with aspirin or any other NSAID medicine
- for pain right before or after heart bypass surgery
Tell your healthcare provider:
- about all of your medical conditions.
- about all of the medicines you take. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Keep a list of your medicines to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist.
- if you are pregnant. NSAID medicines should not be used by pregnant women late in their pregnancy.
- if you are breastfeeding. Talk to your doctor.
What are the possible side effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
| Serious Side effects include: | Other side effects include: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- chest pain
- weakness in one part or side of your body
- slurred speech
- swelling of the face or throat
Stop your NSAID medicine and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- nausea
- more tired or weaker than usual
- itching
- your skin or eyes look yellow
- stomach pain
- flu-like symptoms
- vomit blood
- there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and sticky like tar
- unusual weight gain
- skin rash or blisters with fever
- swelling of the arms and legs, hands and feet
Other information about Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Aspirin is an NSAID medicine but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain, stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
- Some of these NSAID medicines are sold in lower doses without a prescription (over-the-counter). Talk to your healthcare provider before using over-the-counter NSAIDs for more than 10 days.
NSAID medicines that need a prescription
|
Generic Name
|
Tradename
|
| Celecoxib |
Celebrex |
| Diclofenac |
Cataflam, Voltaren, Arthrotec (combined with misoprostol) |
| Diflunisal |
Dolobid |
| Etodolac |
Lodine, Lodine XL |
| Fenoprofen |
Nalfon, Nalfon 200 |
| Flurbiprofen |
Ansaid |
| Ibuprofen |
Motrin, Tab-Profen, Vicoprofen |
| Indomethacin |
Indocin, Indocin SR, Indo-Lemmon, Indomethagan |
| Ketoprofen |
Oruvail |
| Ketorolac |
Toradol |
| Mefenamic Acid |
Ponstel |
| Meloxicam |
Mobic |
| Nabumetone |
Relafen |
| Naproxen |
Naprosyn, Anaprox, Anaprox DS, EC-Naproxyn, Naprelan, Naprapac (copackaged with lansoprazole) |
| Oxaprozin |
Daypro |
| Piroxicam |
Feldene |
| Sulindac |
Clinoril |
| Tolmetin |
Tolectin, Tolectin DS, Tolectin 600 |
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Manufactured By:
Manufactured For:
Rising Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Package label principal display panel(60 Tablets)
PHARMACIST:
®
Usual Dosage:
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.

Package label principal display panel(100 Tablets)
PHARMACIST:
®
Usual Dosage:
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.

Package label principal display panel(500 Tablets)
PHARMACIST:
®
Usual Dosage:
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.

DIFLUNISALDIFLUNISAL TABLET, FILM COATED
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||