DIVALPROEX SODIUM
Bryant Ranch Prepack
Bryant Ranch Prepack
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Divalproex sodium extended release tablets safely and effectively.See full prescribing information for divalproex sodium extended release tablets. Divalproex Sodium Extended Release Tablets for Oral use. Initial U.S. approval:2000BOXED WARNINGWARNING: LIFE THREATENING ADVERSE REACTIONS See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. Hepatotoxicity, including fatalities, usually during first 6 months of treatment. Children under the age of two years are at considerably higher risk of fatal hepatotoxicity. Monitor patients closely, and perform liver function tests prior to therapy and at frequent intervals thereafter (5.1) Teratogenicity, including neural tube defects (5.2) Pancreatitis, including fatal hemorrhagic cases (5.3) RECENT MAJOR CHANGESWarnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.9, 5.11, 5.13, 5.14, 5.15) 3/2008Pediatric Use (8.4) 3/2008INDICATIONS AND USAGEDivalproex sodium extended-release tablets are indicated for: Acute treatment of manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar disorder, with or without psychotic features (1.1) Monotherapy and adjunctive therapy of complex partial seizures and simple and complex absence seizures; adjunctive therapy in patients with multiple seizure types that include absence seizures (1.2) Prophylaxis of migraine headaches (1.3) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets are intended for once-a-day oral administration. Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets should be swallowed whole and should not be crushed or chewed. Mania:- Initial dose is 25 mg/kg/day, increasing as rapidly as possible to achieve therapeutic response or desired plasma level (2.1). The maximum recommended dosage is 60 mg/kg/day. (2.1, 2.2) Complex Partial Seizures: Start at 10 to 15 mg/kg/day, increasing at 1 week intervals by 5 to 10 mg/kg/day to achieve optimal clinical response; if response is not satisfactory, check valproate plasma level; see full prescribing information for conversion to monotherapy (2.2). The maximum recommended dosage is 60 mg/kg/day. (2.1, 2.2). Absence Seizures: Start at 15 mg/kg/day, increasing at 1 week intervals by 5 to 10 mg/kg/day until seizure control or limiting side effects (2.2). The maximum recommended dosage is 60 mg/kg/day. (2.1, 2.2). Migraine: The recommended starting dose is 500 mg/day for 1 week, thereafter increasing to 1000 mg/day (2.3). DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSTablets: 250 mg and 500 mg (3)CONTRAINDICATIONS Hepatic disease or significant hepatic dysfunction (4, 5.1) Known hypersensitivity to the drug (4, 5.10) Urea cycle disorders (4, 5.4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Hepatotoxicity; monitor liver function tests (5.1) Teratogenic effects; weigh divalproex sodium extended-release tablets benefits of use during pregnancy against risk to the fetus (5.2) Pancreatitis; Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets should ordinarily be discontinued (5.3) Suicidal behavior or ideation; Antiepileptic drugs, including divalproex sodium extended-release tablets, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior (5.5) Thrombocytopenia; monitor platelet counts and coagulation tests (5.6) Hyperammonemia and hyperammonemic encephalopathy; measure ammonia level if unexplained lethargy and vomiting or changes in mental status, and also with concomitant topiramate use; consider discontinuation of valproate therapy (5.4, 5.7, 5.8) Hypothermia; Hypothermia has been reported during valproate therapy with or without associated hyperammonemia. This adverse reaction can also occur in patients using concomitant topiramate (5.9) Multi-organ hypersensitivity reaction; discontinue divalproex sodium extended-release tablets (5.10) Somnolence in the elderly can occur. Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets dosage should be increased slowly and with regular monitoring for fluid and nutritional intake (5.12) Side Effects Most common adverse reactions (reported >5%) reported in adult studies are nausea, somnolence, dizziness, vomiting, asthenia, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, rash, diarrhea, increased appetite, tremor, weight gain, back pain, alopecia, headache, fever, anorexia, constipation, diplopia, ambylopia/blurred, ataxia, nystagmus, emotional lability, thinking abnormal, amnesia, flu syndrome, infection, bronchitis, rhinitis, ecchymosis, peripheral edema, insomnia, nervousness, depression, pharyngitis, dyspnea, tinnitus (6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4). Most common, drug-related adverse reactions (reported >5% and twice the rate of placebo) reported in the controlled pediatric mania study are nausea, upper abdominal pain, somnolence, increased ammonia, gastritis and rash. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Wockhardt USA LLC., at 1-800-346-6854 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS Hepatic enzyme-inducing drugs (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine, primidone, phenobarbital, rifampin) can increase valproate clearance, while enzyme inhibitors (e.g., felbamate) can decrease valproate clearance. Therefore increased monitoring of valproate and concomitant drug concentrations and dose adjustment is indicated whenever enzyme inducing or inhibiting drugs are introduced or withdrawn (7.1) Aspirin, carbapenem antibiotics: Monitoring of valproate concentrations are recommended (7.1) Co-administration of valproate can affect the pharmacokinetics of other drugs (e.g. diazepam, ethosuximide, lamotrigine, phenytoin) by inhibiting their metabolism or protein binding displacement (7.2) Dosage adjustment of amitryptyline/nortryptyline, warfarin, and zidovudine may be necessary if used concomitantly with divalproex sodium extended-release tablets (7.2) Topiramate: Hyperammonemia and encephalopathy (5.8, 7.3) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets can cause congenital malformations including neural tube defects (5.2, 8.1) Pediatric: Children under the age of two years are at considerably higher risk of fatal hepatotoxicity (5.1, 8.4) Geriatric: reduce starting dose; increase dosage more slowly; monitor fluid and nutritional intake, and somnolence (5.12, 8.5)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- BOXED WARNING
- RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
- 1DIVALPROEX SODIUM INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2DIVALPROEX SODIUM DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4DIVALPROEX SODIUM CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 5.1Hepatotoxicity
- 5.2Teratogenicity/Usage in Pregnancy
- 5.3Pancreatitis
- 5.4Urea Cycle Disorders
- 5.5Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
- 5.6Thrombocytopenia
- 5.7Hyperammonemia
- 5.8Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy associated with Concomitant Topiramate Use
- 5.9Hypothermia
- 5.10Multi-Organ Hypersensitivity Reactions
- 5.11Interaction with Carbapenem Antibiotics
- 5.12Somnolence in the Elderly
- 5.13Monitoring: Drug Plasma Concentration
- 5.14Effect on Ketone and Thyroid function Tests
- 5.15Effect on HIV and CMV Viruses Replication
- 6DIVALPROEX SODIUM ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10OVERDOSAGE
- 11DIVALPROEX SODIUM DESCRIPTION
- 12CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
BOXED WARNING
WARNING: LIFE THREATENING ADVERSE REACTIONSHepatotoxicity
Hepatic failure resulting in fatalities has occurred in patients receiving valproic acid and its derivatives. Children under the age of two years are at a considerably increased risk of developing fatal hepatotoxicity, especially those on multiple anticonvulsants, those with congenital metabolic disorders, those with severe seizure disorders accompanied by mental retardation, and those with organic brain disease. When divalproex sodium extended-release tablets are used in this patient group, it should be used with extreme caution and as a sole agent. The benefits of therapy should be weighed against the risks. The incidence of fatal hepatotoxicity decreases considerably in progressively older patient groups.
These incidents usually have occurred during the first six months of treatment. Serious or fatal hepatotoxicity may be preceded by non-specific symptoms such as malaise, weakness, lethargy, facial edema, anorexia, and vomiting. In patients with epilepsy, a loss of seizure control may also occur. Patients should be monitored closely for appearance of these symptoms. Liver function tests should be performed prior to therapy and at frequent intervals thereafter, especially during the first six months [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Teratogenicity
Valproate can produce teratogenic effects such as neural tube defects (e.g., spina bifida). Accordingly, the use of divalproex sodium extended-release tablets in women of childbearing potential requires that the benefits of its use be weighed against the risk of injury to the fetus. This is especially important when the treatment of a spontaneously reversible condition not ordinarily associated with permanent injury or risk of death (e.g., migraine) is contemplated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
An information sheet describing the teratogenic potential of valproate is available for patients [see Patient Counseling Information (17.8)].
Pancreatitis
Cases of life-threatening pancreatitis have been reported in both children and adults receiving valproate. Some of the cases have been described as hemorrhagic with a rapid progression from initial symptoms to death. Cases have been reported shortly after initial use as well as after several years of use. Patients and guardians should be warned that abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and/or anorexia can be symptoms of pancreatitis that require prompt medical evaluation. If pancreatitis is diagnosed, valproate should ordinarily be discontinued. Alternative treatment for the underlying medical condition should be initiated as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
1INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1Mania
1.2Epilepsy
Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets are indicated as monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in the treatment of adult patients and pediatric patients down to the age of 10 years with complex partial seizures that occur either in isolation or in association with other types of seizures. Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets are also indicated for use as sole and adjunctive therapy in the treatment of simple and complex absence seizures in adults and children 10 years of age or older, and adjunctively in adults and children 10 years of age or older with multiple seizure types that include absence seizures.
Simple absence is defined as very brief clouding of the sensorium or loss of consciousness accompanied by certain generalized epileptic discharges without other detectable clinical signs. Complex absence is the term used when other signs are also present.
1.3Migraine
Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets are indicated for prophylaxis of migraine headaches. There is no evidence that divalproex sodium extended-release tablets are useful in the acute treatment of migraine headaches. Because it may be a hazard to the fetus, divalproex sodium extended-release tablets should be considered for women of childbearing potential only after this risk has been thoroughly discussed with the patient and weighed against the potential benefits of treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Patient Counseling Information (17.3)].
2DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1Mania
2.2Epilepsy
2.3Migraine
2.4Conversion from Divalproex Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets to Divalproex Sodium Extended-Release Tablets
| Divalproex Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets Total Daily Dose (mg) |
Divalproex Sodium Extended-Release Tablets (mg) |
|---|---|
| 500*-625 |
750 |
| 750*-875 |
1000 |
| 1000*-1125 |
1250 |
| 1250-1375 |
1500 |
| 1500-1625 |
1750 |
| 1750 |
2000 |
| 1875-2000 |
2250 |
| 1225-2250 |
2500 |
| 2375 |
2750 |
| 2500-2750 |
3000 |
| 2875 |
3250 |
| 3000-3125 | 3500 |
min
2.5General Dosing Advice
>>
3DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets should not be administered to patients with hepatic disease or significant hepatic dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
- Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with known urea cycle disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
5WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1Hepatotoxicity
5.2Teratogenicity/Usage in Pregnancy
5.3Pancreatitis
5.4Urea Cycle Disorders
5.5Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
| Indication |
Placebo Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients |
Drug Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients |
Relative Risk: Incidence of Events in Drug Patients/Incidence in Placebo Patients |
Risk Difference: Additional Drug Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epilepsy |
1.0 |
3.4 |
3.5 |
2.4 |
| Psychiatric |
5.7 |
8.5 |
1.5 |
2.9 |
| Other |
1.0 |
1.8 |
1.9 |
0.9 |
| Total |
2.4 |
4.3 |
1.8 |
1.9 |
5.6Thrombocytopenia
95.7Hyperammonemia
5.8Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy associated with Concomitant Topiramate Use
5.9Hypothermia
005.10Multi-Organ Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.11Interaction with Carbapenem Antibiotics
5.12Somnolence in the Elderly
5.13Monitoring: Drug Plasma Concentration
5.14Effect on Ketone and Thyroid function Tests
5.15Effect on HIV and CMV Viruses Replication
6ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1Mania
| Adverse Event |
Divalproex Sodium Extended-Release Tablets (n=338) |
Placebo (n=263) |
|---|---|---|
| Somnolence |
26% |
14% |
| Dyspepsia |
23% | 11% |
| Nausea |
19% | 13% |
| Vomiting |
13% | 5% |
| Diarrhea |
12% | 8% |
| Dizziness |
12% | 7% |
| Pain |
11% | 10% |
| Abdominal Pain |
10% | 5% |
| Accidental injury |
6% | 5% |
| Asthenia |
6% | 5% |
| Pharyngitis |
6% | 5% |
6.2 Epilepsy
| Body System/Event |
Divalproex Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets (%) (n=77) |
Placebo (%) (n=70) |
|---|---|---|
| Body as a Whole |
|
|
| Headache |
31 |
21 |
| Asthenia |
27 |
7 |
| Fever |
6 |
4 |
| Gastrointestinal System |
|
|
| Nausea |
48 |
14 |
| Vomiting |
27 |
7 |
| Abdominal pain |
23 |
6 |
| Diarrhea |
13 |
6 |
| Anorexia |
12 |
0 |
| Dyspepsia |
8 |
4 |
| Constipation |
5 |
1 |
| Nervous System |
|
|
| Somnolence |
27 |
11 |
| Tremor |
25 |
6 |
| Dizziness |
25 |
13 |
| Diplopia |
16 |
9 |
| Amblyopia/Blurred Vision |
12 |
9 |
| Ataxia |
8 |
1 |
| Nystagmus | 8 |
1 |
| Emotional Lability | 6 |
4 |
| Thinking Abnormal |
6 |
0 |
| Amnesia |
5 |
1 |
| Respiratory System |
|
|
| Flu Syndrome |
12 | 9 |
| Infection |
12 |
6 |
| Bronchitis |
5 |
1 |
| Rhinitis |
5 |
4 |
| Other |
|
|
| Alopecia |
6 |
1 |
| Weight Loss |
6 |
0 |
| Body System/Events |
High Dose (%)
(n=131) |
Low Dose (%)
(n=134) |
| Body as a Whole |
|
|
| Asthenia |
21 |
10 |
| Digestive System |
|
|
| Nausea |
34 |
26 |
| Diarrhea |
23 |
19 |
| Vomiting |
23 |
15 |
| Abdominal pain |
12 |
9 |
| Anorexia |
11 |
4 |
| Dyspepsia |
11 |
10 |
| Hemic/Lymphatic System |
|
|
| Thrombocytopenia |
24 |
1 |
| Ecchymosis |
5 |
4 |
| Metabolic/Nutritional |
|
|
| Weight Gain |
9 |
4 |
| Peripheral Edema |
8 |
3 |
| Nervous System |
|
|
| Tremor |
57 |
19 |
| Somnolence |
30 |
18 |
| Dizziness |
18 |
13 |
| Insomnia |
15 |
9 |
| Nervousnes |
11 |
7 |
| Amnesia |
7 |
4 |
| Nystagmus |
7 |
1 |
| Depression |
5 |
4 |
| Respiratory System |
|
|
| Infection |
20 |
13 |
| Pharynigits |
8 |
2 |
| Dyspnea |
5 |
1 |
| Skin and Appendages |
|
|
| Alopecia | 24 |
13 |
| Special Senses |
|
|
| Amblyopia/Blurred Vision |
8 |
4 |
| Tinnitus |
7 |
1 |
6.3Migraine
| Body System Event |
Divalproex Sodium Extended- Release (n=122) |
Placebo (n=115) |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal System |
|
|
| Nausea |
15% |
9% |
| Dyspepsia |
7% | 4% |
| Diarrhea |
7% | 3% |
| Vomiting |
7% | 2% |
| Abdominal pain |
7% | 5% |
| Nervous System |
|
|
| Somnolence |
7% | 2% |
| Other |
|
|
| Infection |
15% | 14% |
| Body System Reaction |
Divalproex Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets (n=202) |
Placebo (n=81) |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal System |
|
|
| Nausea |
31% |
10% |
| Dyspepsia |
13% | 9% |
| Diarrhea |
12% | 7% |
| Vomiting |
11% | 1% |
| Abdominal pain |
9% | 4% |
| Increased appetite |
6% | 4% |
| Nervous System |
|
|
| Asthenia |
20% | 9% |
| Somnolence |
17% | 5% |
| Dizziness |
12% | 6% |
| Tremor |
9% | 0% |
| Other |
|
|
| Weight gain |
8% | 2% |
| Back pain |
8% | 6% |
| Alopecia |
7% | 1% |
6.4Other Patient Populations
7DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1Effects of Co-Administered Drugs on Valproate Clearance Valproate Clearance
7.2Effects of Valproate on Other Drugs
7.3Topiramate
Concomitant administration of topiramate with valproic acid has also been associated with hypothermia in patients who have tolerated either drug alone. It may be prudent to examine blood ammonia levels in patients in whom the onset of hypothermia has been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.9)].8USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1Pregnancy
22
22
8.3Nursing Mothers
8.4Pediatric Use
Mania
Migraine Prophylaxis
Epilepsy
Pediatric Safety
Safety Studies-Mania
| Adverse reaction- prefered term |
Divalproex sodium Extended-Release Tablets (n=76) |
Placebo (n=74) |
|---|---|---|
| Nausea |
9% |
1% |
| Upper abdominal Pain |
8% |
1% |
| Somnolence |
7% |
1% |
| Increased Ammonia |
5% |
0% |
| Gastritis |
5% |
0% |
| Rash |
5% |
1% |
Safety Study-Open Label Mania Safety Data
Safety Study-Epilepsy (open label)
Safety Studies-Migraine (controlled and open label)
Prior Safety Experience
Nonclinical Developmental Toxicology
8.5Geriatric Use
8.6Effect of Disease
Liver Disease10OVERDOSAGE
11DESCRIPTION
Divalproex sodium is a stable co-ordination compound comprised of sodium valproate and valproic acid in a 1:1 molar relationship and formed during the partial neutralization of valproic acid with 0.5 equivalent of sodium hydroxide.
Chemically it is designated as sodium hydrogen bis(2-propylpentanoate). Divalproex sodium has the following structure:
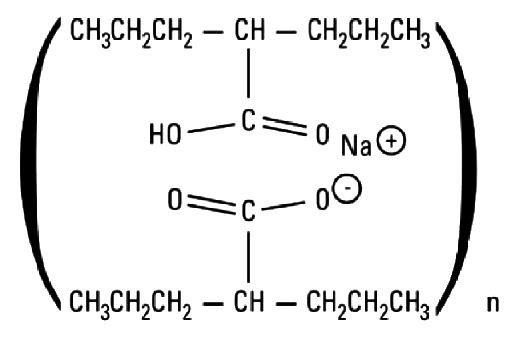
12CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1Mechanism of Action
12.2Pharmacodynamics
12.3Pharmacokinetics
Absorption/Bioavailabilitymax
maxmin
| Study Population |
Regimens |
Relative | Bioavailability |
|
|
|
Divalproex Sodium Extended-Release Tablets vs. Divalproex Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets |
AUC24
|
Cmax
|
Cmin
|
| Healthy Volunteers (N=35) |
1000 and 1500 mgDivalproex sodium extended-release tablets vs 875 and 1250 mg Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets |
1.059 |
0.882 |
1.173 |
| Patients with epilepsy on concomitant enzyme-inducing antiepilepsy drugs (N = 64) |
1000 and 5000 mgDivalproex sodium extended-release tablets vs 875 and 4250 mg Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets |
1.008 |
0.899 |
1.022 |
Distribution
Metabolism
Elimination
22
22
Special Populations
2
13NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Enter section text here
13.1Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
CarcinogenesisMutagenesis
Fertility
CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1Mania
The effectiveness of divalproex sodium extended-release tablets for the treatment of acute mania is based in part on studies establishing the effectiveness of divalproex sodium delayed release tablets for this indication. Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets effectiveness was confirmed in one randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group, 3-week, multicenter study. The study was designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of divalproex sodium extended-release tablets in the treatment of bipolar I disorder, manic or mixed type, in adults. Adult male and female patients who had a current DSM-IV TR primary diagnosis of bipolar I disorder, manic or mixed type, and who were hospitalized for acute mania, were enrolled into this study. Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets was initiated at a dose of 25 mg/kg/day given once daily, increased by 500 mg/day on Day 3, then adjusted to achieve plasma valproate concentrations in the range of 85-125 mcg/mL. Mean daily divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets doses for observed cases were 2362 mg (range: 500-4000), 2874 mg (range: 1500-4500), 2993 mg (range: 1500-4500), 3181 mg (range: 1500-5000), and 3353 mg (range: 1500-5500) at Days 1, 5, 10, 15, and 21, respectively. Mean valproate concentrations were 96.5 mcg/mL, 102.1 mcg/mL, 98.5 mcg/mL, 89.5 mcg/mL at Days 5, 10, 15 and 21, respectively. Patients were assessed on the Mania Rating Scale (MRS; score ranges from 0-52).
Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets was significantly more effective than placebo in reduction of the MRS total score.
14.2Epilepsy
The efficacy of valproate in reducing the incidence of complex partial seizures (CPS) that occur in isolation or in association with other seizure types was established in two controlled trials. In one, multiclinic, placebo controlled study employing an add-on design, (adjunctive therapy) 144 patients who continued to suffer eight or more CPS per 8 weeks during an 8 week period of monotherapy with doses of either carbamazepine or phenytoin sufficient to assure plasma concentrations within the “therapeutic range” were randomized to receive, in addition to their original antiepilepsy drug (AED), either divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets or placebo. Randomized patients were to be followed for a total of 16 weeks. The following Table presents the findings.
| Add on Treatment |
Number of Patients |
Baseline Incidence |
Experimental Incidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets |
75 |
16.0 |
8.9* |
| Placebo |
69 |
14.5 |
11.5 |

| Treatment |
Number of Patients |
Baseline Incidence |
Randomized Phase Incidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| High dose Valproate |
131 |
13.2 |
10.7* |
| Low dose Valproate |
134 |
14.2 |
13.8 |

14.3Migraine

16HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Divalproex sodium extended-release 250 mg tablets are available as white, oval shaped film coated biconvex beveled edge tablets, debossed with W on one side and 724 on other side. Each divalproex sodium extended-release tablet contains divalproex sodium equivalent to 250 mg of valproic acid in the following packaging sizes:
Bottles of 30 (NDC 64679-724-01)
Bottles of 100 (NDC 64679-724-02)
Bottles of 500 (NDC 64679-724-03)
Unit Dose Pack
of 100 (10 x 10) (NDC 64679-724-04)
Divalproex sodium extended-release 500 mg tablets are available as dark grey colored, oval shaped film coated biconvex tablets, debossed with W725 on one side and plain on other side. Each divalproex sodium extended-release tablet contains divalproex sodium equivalent to 500 mg of valproic acid in the following packaging sizes:
Bottles of 30 (NDC 64679-725-01)
Bottles of 100 (NDC 64679-725-02)
Bottles of 500 (NDC 64679-725-03)
Unit Dose Pack
of 100 (10x10) (NDC 64679-725-04)
Recommended Storage
Store at 200-250C (680-770F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature
17PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1Hepatotoxicity
Patients and guardians should be warned that nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, anorexia, diarrhea, asthenia, and/or jaundice can be symptoms of hepatotoxicity and, therefore, require further medical evaluation promptly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
17.2Pancreatitis
Patients and guardians should be warned that abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and/or anorexia can be symptoms of pancreatitis and, therefore, require further medical evaluation promptly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
17.3Teratogenicity/Usage in Pregnancy
17.4Suicidal Thinking and Behavior
17.5Hyperammonemia
17.6CNS depression
17.7Multi-organ Hypersensitivity Reaction
Patients should be instructed that a fever associated with other organ system involvement (rash, lymphadenopathy, etc.) may be drug-related and should be reported to the physician immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
17.8 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
Important Information for Women Who Could Become Pregnant About the Use of divalproex sodium extended-release tablets.Please read this leaflet carefully before you take any of this medication. This leaflet provides a summary of important information about taking this medication to women who could become pregnant. If you have any questions or concerns, or want more information about this medication, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
Information For Women Who Could Become Pregnant
You can only obtain this medication by prescription from your doctor. The decision to use this medicine should be made by you and your doctor based on your health needs and medical condition.
Before starting this medicine, you should know that using this medicine during pregnancy causes an increased chance of birth defects in your baby. These birth defects may include spina bifida and other defects where the spinal canal does not close normally. These defects usually occur in 1 to 2 out of every 1000 babies born in the United States. Studies show that for babies born to epileptic women who took valproate in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, these defects occur in 1 to 2 out of every 100 babies.
Use of valproate during pregnancy also increases the chance of other birth defects such as of the heart, bones, and other parts of the body. Studies suggest that other medicines used to treat your condition may be less likely to cause these defects.
Information For Women Who Are Planning to Get Pregnant
Women using valproate who plan to get pregnant should discuss their treatment options with their doctor.
Information For Women Who Become Pregnant
If you become pregnant while taking valproate, you should contact your doctor immediately.
Other Important Information
- You should take your medicine exactly as prescribed by your doctor to get the most benefit from your medicine and reduce the risk of side effects.
- If you have taken more than the prescribed dose, contact your hospital emergency room or local poison center immediately.
- Your medicine was prescribed for your particular condition. Do not use it for another condition or give the drug to others.
Facts About Birth Defects
It is important to know that birth defects may occur even in children born to women who are not taking any medicines and do not have other risk factors.
This summary provides important information about the use of divalproex sodium extended-release tablets to women who could become pregnant. If you would like more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist to let you read the professional labeling and then discuss it with them. If you have any questions or concerns about taking this medication, you should discuss them with your doctor.
Manufactured by:
Wockhardt Limited,
Mumbai, India.
Distributed by:
Wockhardt USA LLC.
20 Waterview Blvd.
Parsippany, NJ 07054,
USA.
Divalproex 500mg ER Tablet
DIVALPROEX SODIUMDIVALPROEX SODIUM TABLET, FILM COATED, EXTENDED RELEASE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||