ENTACAPONE
Entacapone Tablets, USP
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- ENTACAPONE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS
- ENTACAPONE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- Hypotension/Syncope
- Diarrhea and Colitis
- Hallucinations
- Dyskinesia
- Other Events Reported With Dopaminergic Therapy
- Renal Toxicity
- Hepatic Impairment
- Information for Patients
- Laboratory Tests
- Special Populations
- Drug Interactions
- Protein Binding
- Drugs Metabolized by Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)
- Hormone levels
- Effect of Entacapone on the Metabolism of Other Drugs
- Carcinogenesis
- Mutagenesis
- Impairment of Fertility
- Pregnancy
- Nursing Women
- ENTACAPONE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- ENTACAPONE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
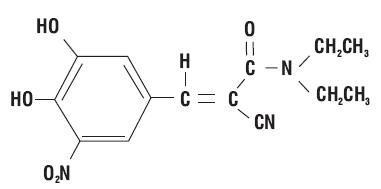
ENTACAPONE DESCRIPTION
O141535
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
O
Pharmacodynamics
COMT Activity in Erythrocytes: Studies in healthy volunteers have shown that entacapone reversibly inhibits human erythrocyte catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) activity after oral administration. There was a linear correlation between entacapone dose and erythrocyte COMT inhibition, the maximum inhibition being 82% following an 800 mg single dose. With a 200 mg single dose of entacapone, maximum inhibition of erythrocyte COMT activity is on average 65% with a return to baseline level within 8 hours.
Effect on the Pharmacokinetics of Levodopa and its Metabolites
max
Pharmacokinetics of Entacapone
max
Absorption:max
Distribution:in vitro
Metabolism and Elimination:ciscis14
Special Populations:
Hepatic Impairment:max
Renal Impairment:222
Drug InteractionsDrug Interactions
Clinical Studies
| Primary Measure from Home Diary (from an 18-hour Diary Day) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Change from Baseline at Month 6  |
p-value vs. placebo |
|||
|
Hours of Awake Time “On”
|
|||||
| Placebo |
9.2 |
+0.1 |
- |
||
| Entacapone |
9.3 |
+1.5 |
<0.001 |
||
|
Duration of “On” time after first AM dose
(hrs)
|
|||||
| Placebo |
2.2 |
0 |
- |
||
| Entacapone |
2.1 |
+0.2 |
<0.05 |
||
|
Secondary Measures from Home Diary (from an 18-hour Diary Day)
|
|||||
|
Hours of Awake Time “Off”
|
|||||
| Placebo |
5.3 |
0 |
- |
||
| Entacapone |
5.5 |
- 1.3 |
<0.001 |
||
Proportion of Awake Time “On”  |
|||||
| Placebo |
63.8 |
+0.6 |
- |
||
| Entacapone |
62.7 |
+9.3 |
<0.001 |
||
|
Levodopa Total Daily Dose (mg)
|
|||||
| Placebo |
705 |
+14 |
- |
||
| Entacapone |
701 |
- 87 |
<0.001 |
||
|
Frequency of Levodopa Daily Intakes
|
|||||
| Placebo |
6.1 |
+0.1 |
- |
||
| Entacapone |
6.2 |
- 0.4 |
<0.001 |
||
|
Other Secondary Measures
|
|||||
| |
Baseline |
Change from Baseline at Month 6 |
p-value vs. placebo |
||
Investigator’s Global (overall) % Improved |
|||||
| Placebo |
- |
28 |
- |
||
| Entacapone |
- |
56 |
<0.01 |
||
Patient’s Global (overall) % Improved |
|||||
| Placebo |
- |
22 |
- |
||
| Entacapone |
- |
39 |
N.S. |
||
|
UPDRS Total
|
|||||
| Placebo |
37.4 |
-1.1 |
- |
||
| Entacapone |
38.5 |
-4.8 |
<0.01 |
||
|
UPDRS Motor
|
|||||
| Placebo |
24.6 |
-0.7 |
- |
||
| Entacapone |
25.5 |
-3.3 |
<0.05 |
||
|
UPDRS ADL
|
|||||
| Placebo |
11 |
-0.4 |
- |
||
| Entacapone |
11.2 |
-1.8 |
<0.05 |
||
| Primary Measure from Home Diary (for a 24-hour Diary Day) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Change from Baseline at Month 6  |
p-value vs. placebo |
|
|
Percent of Awake Time “On”
|
|||
| Placebo |
60.8 |
+2 |
- |
| Entacapone |
60 |
+6.7 |
<0.05 |
|
Secondary Measures from Home Diary (for a 24-hour Diary Day)
|
|||
|
Hours of Awake Time “Off”
|
|||
| Placebo |
6.6 |
- 0.3 |
- |
| Entacapone |
6.8 |
- 1.2 |
<0.01 |
|
Hours of Awake Time “On”
|
|||
| Placebo |
10.3 |
+ 0.4 |
- |
| Entacapone |
10.2 |
+ 1 |
N.S. |
|
Levodopa Total Daily Dose (mg)
|
|||
| Placebo |
758 |
+ 19 |
- |
| Entacapone |
804 |
- 93 |
<0.001 |
|
Frequency of Levodopa Daily Intakes
|
|||
| Placebo |
6 |
+ 0.2 |
- |
| Entacapone |
6.2 |
0 |
N.S. |
|
Other Secondary Measures
|
|||
| |
Baseline |
Change from Baseline at Month 6 |
p-value vs. placebo |
Investigator’s Global (overall) % Improved |
|||
| Placebo |
- |
21 |
- |
| Entacapone |
- |
34 |
<0.05 |
Patient’s Global (overall) % Improved |
|||
| Placebo |
- |
20 |
- |
| Entacapone |
- |
31 |
<0.05 |
UPDRS Total |
|||
| Placebo |
35.6 |
+2.8 |
- |
| Entacapone |
35.1 |
-0.6 |
<0.05 |
UPDRS Motor |
|||
| Placebo |
22.6 |
+1.2 |
- |
| Entacapone |
22 |
-0.9 |
<0.05 |
UPDRS ADL |
|||
| Placebo |
11.7 |
+1.1 |
- |
| Entacapone |
11.9 |
0 |
<0.05 |
Withdrawal of entacapone
| Primary Measures | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Change from Baseline at Month 6 |
p-value vs. placebo (LOCF) |
||||
UPDRS ADL |
||||||
| Placebo |
12 |
+0.5 |
- |
|||
| Entacapone |
12.4 |
-0.4 |
<0.05 |
|||
UPDRS Motor |
||||||
| Placebo |
24.1 |
+0.1 |
- |
|||
| Entacapone |
24.9 |
-2.5 |
<0.05 |
|||
Hours of Awake Time “On” (Home diary) |
||||||
| Placebo |
10.1 |
+0.5 |
- |
|||
| Entacapone |
10.2 |
+1.1 |
N.S. |
|||
|
Secondary Measures
|
||||||
| |
Baseline |
Change from Baseline at Month 6 |
p-value vs. placebo |
|||
UPDRS Total |
||||||
| Placebo |
37.7 |
+0.6 |
- |
|||
| Entacapone |
39 |
-3.4 |
<0.05 |
|||
Percent of Awake Time “On” (Home diary) |
||||||
| Placebo |
59.8 |
+3.5 |
- |
|||
| Entacapone |
62 |
+6.5 |
N.S. |
|||
Hours of Awake Time “Off” (Home diary) |
||||||
| Placebo |
6.8 |
-0.6 |
- |
|||
| Entacapone |
6.3 |
-1.2 |
0.07 |
|||
Levodopa Total Daily Dose (mg) |
||||||
| Placebo |
572 |
+4 |
– |
|||
| Entacapone |
566 |
-35 |
N.S. |
|||
Frequency of Levodopa Daily Intake |
||||||
| Placebo
|
5.6 |
+0.2 |
– |
|||
| Entacapone |
5.4 |
0 |
<0.01 |
|||
Global (overall) % Improved |
||||||
| Placebo
|
– |
34 |
– |
|||
| Entacapone |
– |
38 |
N.S. |
|||
INDICATIONS
ENTACAPONE CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
Drugs Metabolized By Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT)
PRECAUTIONS
Hypotension/Syncope
Diarrhea and Colitis
Hallucinations
Dopaminergic therapy in Parkinson’s Disease patients has been associated with hallucinations. In clinical trials, hallucinations developed in approximately 4% of patients treated with 200 mg entacapone or placebo. Hallucinations led to drug discontinuation and premature withdrawal from clinical trials in 0.8% and 0% of patients treated with 200 mg entacapone and placebo, respectively. Hallucinations led to hospitalization in 1% and 0.3% of patients in the 200 mg entacapone and placebo groups, respectively.
Dyskinesia
Other Events Reported With Dopaminergic Therapy
Rhabdomyolysis
Hyperpyrexia and Confusion
Melanoma:
any
Renal Toxicity
In a 1 year toxicity study, entacapone (plasma exposure 20 times that in humans receiving the maximum recommended daily dose of 1600 mg) caused an increased incidence in male rats of nephrotoxicity that was characterized by regenerative tubules, thickening of basement membranes, infiltration of mononuclear cells and tubular protein casts. These effects were not associated with changes in clinical chemistry parameters, and there is no established method for monitoring for the possible occurrence of these lesions in humans. Although this toxicity could represent a species-specific effect, there is not yet evidence that this is so.
Hepatic Impairment
Patients with hepatic impairment should be treated with caution. The AUC and Cmax of entacapone approximately doubled in patients with documented liver disease compared to controls. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics of Entacapone and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Information for Patients
Laboratory Tests
Special Populations
Drug Interactions
In vitro
Protein Binding
In vitro
Drugs Metabolized by Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)
Hormone levels
Effect of Entacapone on the Metabolism of Other Drugs
Carcinogenesis
2
Mutagenesis
in vitro in vivo
Impairment of Fertility
Pregnancy
Nursing Women
Pediatric Use
ENTACAPONE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse Event Incidence in Controlled Clinical Studies
|
SYSTEM ORGAN CLASS |
|||
| Preferred term |
Entacapone (n = 603) % of patients |
Placebo (n = 400) % of patients |
|
|
SKIN AND APPENDAGES DISORDERS
|
|||
| Sweating increased |
2 |
1 |
|
|
MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISORDERS
|
|||
| Back pain |
2 |
1 |
|
|
CENTRAL & PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
DISORDERS |
|||
| Dyskinesia |
25 |
15 |
|
| Hyperkinesia |
10 |
5 |
|
| Hypokinesia |
9 |
8 |
|
| Dizziness |
8 |
6 |
|
|
SPECIAL SENSES, OTHER DISORDERS
|
|||
| Taste perversion |
1 |
0 |
|
|
PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS
|
|||
| Anxiety |
2 |
1 |
|
| Somnolence |
2 |
0 |
|
| Agitation |
1 |
0 |
|
|
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM DISORDERS
|
|||
| Nausea |
14 |
8 |
|
| Diarrhea |
10 |
4 |
|
| Abdominal pain |
8 |
4 |
|
| Constipation |
6 |
4 |
|
| Vomiting |
4 |
1 |
|
| Mouth dry |
3 |
0 |
|
| Dyspepsia |
2 |
1 |
|
| Flatulence |
2 |
0 |
|
| Gastritis |
1 |
0 |
|
| Gastrointestinal disorders nos |
1 |
0 |
|
|
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS
|
|||
| Dyspnea |
3 |
1 |
|
|
PLATELET, BLEEDING & CLOTTING DISORDERS
|
|||
| Purpura |
2 |
1 |
|
|
URINARY SYSTEM DISORDERS
|
|||
| Urine discoloration |
10 |
0 |
|
|
BODY AS A WHOLE - GENERAL DISORDERS
|
|||
| Back pain Fatigue Asthenia |
4 6 2 |
2 4 1 |
|
|
RESISTANCE MECHANISM DISORDERS
|
|||
| Infection bacterial |
1 |
0 |
|
Effects of gender and age on adverse reactions
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
OVERDOSAGE
Management of Overdose
Management of entacapone overdose is symptomatic; there is no known antidote to entacapone. Hospitalization is advised, and general supportive care is indicated. There is no experience with hemodialysis or hemoperfusion, but these procedures are unlikely to be of benefit, because entacapone is highly bound to plasma proteins. An immediate gastric lavage and repeated doses of charcoal over time may hasten the elimination of entacapone by decreasing its absorption/reabsorption from the GI tract. The adequacy of the respiratory and circulatory systems should be carefully monitored and appropriate supportive measures employed. The possibility of drug interactions, especially with catechol-structured drugs, should be borne in mind.
ENTACAPONE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Patients With Impaired Hepatic Function:max
Withdrawing Patients from Entacapone Tablets:
HOW SUPPLIED
203
Storage
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 47335-203-88
Entacapone Tablets, USP
200 mg
Rx only
100 TABLETS
SUN PHARMA

ENTACAPONEENTACAPONE TABLET, FILM COATED
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||