Epinephrine
Amphastar Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
EPINEPHRINE INJECTION, USP
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- EPINEPHRINE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- EPINEPHRINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- EPINEPHRINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- EPINEPHRINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- EPINEPHRINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mL Syringe Carton
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mL Syringe Carton
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mL Syringe Carton
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
AVAILABLE AS:
EPINEPHRINE INJECTION, USP, 1:10,000
(0.1 mg/mL)
FOR INTRACARDIAC OR
INTRAVENOUS USE
EPINEPHRINE INJECTION, USP, 1:1000
(1 mg/mL)
FOR SUBCUTANEOUS USE
OR INTRAMUSCULAR USE
EPINEPHRINE DESCRIPTION
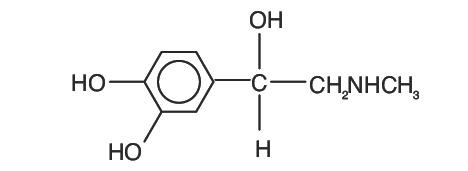
Epinephrine is the active principle of the adrenal medulla. Chemically described as (-)-3,4-Dihydroxy-α-[(methyl-amino) methyl] benzyl alcohol, it has the following structural formula:
Epinephrine 1:10,000 and 1:1000 are sterile aqueous solutions of epinephrine prepared with the aid of hydrochloric acid. Each mL of the 1:10,000 solution contains 0.1 mg epinephrine and 1 mg sodium bisulfite; the 1:1000 solution contains 1 mg epinephrine and 2.5 mg sodium bisulfite per mL. Sodium bisulfite is an antioxidant. These solutions also contain sodium chloride for adjustment of tonicity, and 10% w/v hydrochloric acid to dissolve epinephrine and to adjust pH to meet USP limits of 2.2 to 5.0. Additionally, the solutions also contain sodium citrate and citric acid as buffers for stabilization. The air above the liquid in the individual containers have been displaced by flushing with nitrogen during the filling operation. No antimicrobial preservatives have been added and each vial is intended as a single dose; once the unit is assembled and used, any remaining portion of the solution must be discarded with the entire unit.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The actions of epinephrine resemble the effects of stimulation of adrenergic nerves. To a variable degree, it acts on both alpha and beta receptor sites of sympathetic effector cells. Its most prominent actions are on the beta receptors of the heart, vascular and other smooth muscle. When given by rapid I.V. injection it produces a rapid rise in blood pressure, mainly systolic, direct stimulation of cardiac muscle which increases the strength of ventricular contraction, increases the heart rate, and constricts the arterioles in the skin, mucosa and splanchnic areas of circulation.
Epinephrine relaxes the smooth muscle of the bronchi and iris and is a physiologic antagonist of histamine.
The drug also produces an increase in blood sugar and glycogenolysis in the liver.
Blood pressure
When given by slow I.V. injection, epinephrine usually produces a moderate rise in systolic and a fall in diastolic pressure. Although some increase in pulse pressure occurs, there is usually no great elevation in mean blood pressure. Accordingly, the compensatory reflex mechanisms that cause a pronounced increase in blood pressure do not antagonize the direct cardiac actions of epinephrine as much as with catecholamines that have a predominant action on alpha receptors.
Total peripheral resistance
By action of epinephrine on beta receptors of the skeletal muscle vasculature, total peripheral resistance decreases, and blood flow is thereby enhanced. Usually, this vasodilator effect predominates so that the modest rise in systolic pressure which follows slow injection or absorption is the result of direct cardiac stimulation and increase in cardiac output. In some instances, peripheral resistance is not altered or may even rise, owing to a greater ratio of alpha to beta activity in different vascular areas.
Pharmacokinetics
Intravenous injection produces an immediate and intensified response. Following I.V. injection, epinephrine disappears rapidly from the blood stream. Subcutaneously or I.M. administered epinephrine has a rapid onset and short duration of action. Subcutaneous administration during asthmatic attacks may produce bronchodilation within 5 to 10 minutes, and maximal effects may occur within 20 minutes.
The drug becomes fixed in the tissues and is rapidly inactivated chiefly by enzymic transformation to metanephrine or normetanephrine, either of which is subsequently conjugated and excreted in the urine in the form of sulfates and glucuronides. Either sequence results in the formation of 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy-mandelic acid (vanillylmandelic acid, VMA) which is also detectable in the urine.
EPINEPHRINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
EPINEPHRINE 1:10,000
Epinephrine's cardiac effects may be of use in the treatment and prophylaxis of cardiac arrest due to various causes in the absence of ventricular fibrillation and attacks of transitory atrioventricular (AV) heart block with syncopal seizures (Stokes-Adams syndrome), but it is not used in cardiac failure or in hemorrhagic, traumatic or in cardiogenic shock. Epinephrine may be used to stimulate the heart in syncope due to complete heart block or carotid sinus hypersensitivity. Epinephrine is also used for resuscitation in cardiac arrest following anesthetic accidents. In cardiopulmonary resuscitation, intracardiac puncture and intramyocardial injection of epinephrine may be effective when external cardiac compression and attempts to restore the circulation by electrical defibillation or use of a pacemaker fail. Epinephrine is seldom used as a vasopressor except in the treatment of anaphylactic shock and under certain conditions in insulin shock.
EPINEPHRINE 1:1000
Epinephrine is the adrenergic drug of choice for the emergency treatment of acute hypersensitivity (anaphylactoid reactions to drugs, animal serums, insect stings, and other allergens): for symptomatic relief of serum sickness, urticaria, angioneurotic edema and respiratory distress due to bronchospasm.
EPINEPHRINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Epinephrine should not be used in the presence of cardiac dilatation or coronary insufficiency.
Epinephrine is contraindicated in shock during general anesthesia with halogenated hydrocarbons or cyclopropane, and in individuals with organic brain damage. Epinephrine is also contraindicated with local anesthesia of certain areas; e.g., fingers, toes, because of the danger of vasoconstriction producing sloughing of tissue; also contraindicated in labor because it may delay the second stage.
Epinephrine should not be used in those cases where vasopressor drugs may be contraindicated, e.g., in thyrotoxicosis, diabetes, in obstetrics when maternal blood pressure is in excess of 130/80, and in hypertension and other cardiovascular disorders.
WARNINGS
EPINEPHRINE 1:10,000
Contains sodium bisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown and probably low. Sulfite sensitivity is seen more frequently in asthmatic rather than in non-asthmatic people.
EPINEPHRINE 1:1000
Epinephrine is the preferred treatment for serious allergic or other emergency situations even though this product contains sodium bisulfite, a sulfite that may in other products cause allergic-type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms or life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible persons. The alternatives to using epinephrine in a life threatening situation may not be satisfactory. The presence of a sulfite in this product should not deter administration of the drug for treatment of serious allergic or other emergency situations.
Initially, epinephrine administered parenterally may produce constriction of renal blood vessels and decrease urine formation.
Use with caution in the following
Elderly; those with cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes, or hyperthyroidism; in psychoneurotic individuals; bronchial asthma and emphysema with degenerative heart disease.
Cardiovascular effects
Inadvertently induced high arterial blood pressure may result in angina pectoris (especially when coronary insufficiency is present), or aortic rupture.
Epinephrine may induce potentially serious cardiac arrhythmias in patients not suffering from heart disease and patients with organic heart disease or who are receiving drugs that sensitize the myocardium. With Epinephrine 1:10,000, a paradoxical but transient lowering of blood pressure, bradycardia and apnea may occur immediately after injection.
Cerebrovascular hemorrhage
Overdosage or inadvertent I.V. injection of epinephrine may cause cerebrovascular hemorrhage resulting from the sharp rise in the blood pressure.
Pulmonary edema
Fatalities may also result from pulmonary edema because of the peripheral constriction and cardiac stimulation produced.
PRECAUTIONS
Although epinephrine can produce ventricular fibrillation, its actions in restoring electrical activity in asystole and in enhancing defibrillation are well documented. However, it should be used with caution in patients with ventricular fibrillation.
In patients with prefibrillatory rhythm, I.V. epinephrine must be used with extreme caution because of its excitatory action on the heart. Since the myocardium is sensitized to the drug by many anesthetic agents, epinephrine may convert asystole to ventricular fibrillation if used in the treatment of anesthetic cardiac accidents.
Hypovolemia
Use is not a substitute for the replacement of blood, plasma, fluids, and electrolytes, which should be restored promptly when loss has occurred.
Drug interactions
Epinephrine must not be administered concomitantly with other sympathomimetic drugs (such as isoproterenol) because of possible additive effects and increased toxicity. Combined effects may induce serious cardiac arrhythmias. They may be administered alternately when the preceding effect of other such drugs has subsided.
Epinephrine is readily destroyed by alkalies and oxidizing agents (e.g., oxygen, chlorine, bromine, iodine, permanganates, chromates, nitrites, and salts of easily reducible metals, especially iron).
The effects of epinephrine may be potentiated by tricyclic antidepressants, certain antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine, tripelennamine, chlorpheniramine) and sodium I-thyroxine.
In obstetrics, if vasopressor drugs are used either to correct hypotension or added to the local anesthetic solution, some oxytocic drugs may cause severe persistent hypertension; even rupture of a cerebral blood vessel may occur during the postpartum period.
All vasopressors should be used cautiously in patients taking monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors.
Cyclopropane or halogenated hydrocarbon anesthetics such as halothane which sensitize the myocardium may induce cardiac arrhythmia. (See Contraindications.) When encountered, such arrhythmias may respond to administration of a beta-adrenergic blocking drug.
Diruretic agents may decrease vascular response to pressor drugs such as epinephrine.
Epinephrine may antagonize the neuron blockade produced by guanethidine resulting in decreased antihypertensive effect and requiring increased dosage of the latter.
Use of epinephrine with excessive doses of digitalis, mercurial diuretics or other drugs that sensitize the heart to arrhythmias is not recommended.
Rapidly acting vasodilators such as nitrites or alpha-blocking agents may counteract the marked pressor effects of epinephrine.
Propranolol administered concomitantly with epinephrine may block the beta-adrenergic effects of epinephrine, causing hypertension.
Usage in Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects - Pregnancy Category C
Epinephrine is teratogenic in small animals when given in doses about 25 times the human dose. There are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. Use during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Usage in Labor and Delivery
Parenteral administration of epinephrine, if used to support blood pressure during low or other spinal anesthesia for delivery, can cause acceleration of fetal heart rate and should not be used in obstetrics when maternal blood pressure exceeds 130/80.
Usage in Children
Epinephrine should be administered with caution to infants and children. Syncope has occurred following the administration of epinephrine to asthmatic children.
EPINEPHRINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Transient and minor
Anxiety, headache, fear, and palpitations often occur with therapeutic doses, especially in hyperthyroid and hypertensive individuals.
Cardiac arrhythmias and excessive rise in blood pressure may occur with therapeutic doses or inadvertent overdosage.
Local
Repeated local injections can result in necrosis at sites of injection from vascular constriction.
Systemic
Cerebral hemorrhage; hemiplegia; subarachnoid hemorrhage; anginal pain in patients with angina pectoris; anxiety; restlessness; throbbing headache; tremor; weakness; dizziness; pallor; respiratory difficulty; palpitation; apprehensiveness; sweating; nausea; vomiting. "Epinephrine-fastness" can occur with prolonged use.
OVERDOSAGE
Symptoms
Erroneous administration of large doses of epinephrine may lead to precordial distress, vomiting, headache, dyspnea, as well as unusually elevated blood pressure.
Treatment
Most toxic effects can be counteracted by injection of an alpha-adrenergic blocker and a beta-adrenergic blocker. In the event of a sharp rise in blood pressure, rapid acting vasodilators such as the nitrites, or alpha-adrenergic blocking agents can counteract the marked pressor effects. If prolonged hypotension follows, it may be necessary to administer another pressor drug, such as norepinephrine.
If an epinephrine overdose induces pulmonary edema that interferes with respiration, treatment consists of a rapidly acting alpha-adrenergic blocking drug such as phentolamine and/or intermittent positive pressure respiration.
Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias consists of a beta-adrenergic blocking drug such as propranolol.
Epinephrine overdosage can also cause transient bradycardia followed by tachycardia; these may be accompanied by potentially fatal cardiac arrhythmias. Ventricular premature contractions may appear within one minute after injection and may be followed by multifocal ventricular tachycardia (prefibrillation rhythm). Subsidence of the ventricular effects may be followed by atrial tachycardia, and occasionally, by atrioventricular block.
Overdosage sometimes results in extreme pallor and coldness of the skin, metabolic acidosis and kidney failure. Take suitable corrective measures.
EPINEPHRINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Please note that the optional STICK-GARD® Safety Needle, featured with stock number 2016 is interchangeable with a standard needle.
EPINEPHRINE 1:10,000
As Cardiac Stimulant
Intravenous or Intracardiac Injection
Administer by I.V. injection and/or in cardiac arrest, by intracardiac injection into the left ventricular chamber. Intracardiac injection should only be administered by personnel well trained in the technique, if there has not been sufficient time to establish an intravenous route.
Adult Dosage
1–10 mL (0.1 – 1 mg of epinephrine), repeated every five minutes, if necessary.
Pediatric Dosage
0.05 – 0.1 mL/ kg of body weight (0.005 – 0.01 mg/ kg) e.g., 2 kg infant would receive 0.1 – 0.2 mL of epinephrine 1:10,000.
NOTE: Do not inject if fibrillation is occurring.
As Vasopressor (Anaphylaxis)
Intravenous Injection
Adult Dosage
1–2.5 mL (0.1 – 0.25 mg of epinephrine), administered slowly. May be repeated every 5 to 15 minutes as needed.
Pediatric Dosage
3 mL (0.3 mg of epinephrine), repeated every 15 minutes for 3 or 4 doses, if necessary.
EPINEPHRINE 1:1000
Anaphylactic shock - due to insect stings, etc.
Intramuscular or Subcutaneous Injection
Adult Dosage
0.2 mL – 0.5 mL (0.2 mg – 0.5 mg), repeated every 10 to 15 minutes as needed. As much as 1 mL (1 mg) per dose may be administered if necessary.
Subcutaneous Injection
Pediatric Dosage
0.01 mL/ kg of body weight (0.01 mg/ kg of body weight) or 0.3 mg per square meter of body surface, up to a maximum of 0.5 mg per dose, repeated every 15 minutes for 2 doses, then every 4 hours as needed.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Adult Dosage
The effect of the I.V. administration of epinephrine 1:10,000 may last only a few minutes, so the I.V. epinephrine may be followed with 0.3 mL of 1:1000 (0.3 mg) subcutaneously.
NOTE: Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
HOW SUPPLIED
In unit-use packages containing a MIN-I-JET® disposable syringe.
EPINEPHRINE INJECTION, USP, 1:10,000 (0.1 mg/ mL)
| Stock No. | NDC No. | Size | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1016 | 0548-1016-00 | FOR I.V. USE | 10 mL |
EPINEPHRINE INJECTION, USP, 1:10,000 (0.1 mg/ mL)
| Stock No. | NDC No. | Size | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 0548-2016-00 | FOR I.V. USE | 10 mL |
Twenty-five unit-use packages per carton.
Manufactured under U.S. Pat. No. 4,834,716, Reissue No. 33,617 STICK-GARD® Safety Needle.
In unit-use packages containing a Luer-Jet™ Luer-Lock Prefilled Syringe.
| Stock No. | NDC No. | Size | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3316 | 0548-3316-00 | FOR I.V. USE | 10 mL |
Ten unit-use packages per carton.
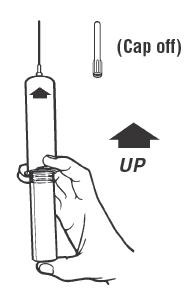
Syringe Assembly Directions
The MIN-I-JET® syringe with needle, illustrated below, is the basic unit upon which all the other syringe systems are built; slight adaptations and/ or additional auxiliary parts create the other syringe systems. Assembly directions remain essentially the same.
USE ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE
Do not assemble until ready to use.

|

|
|
| Remove protective caps. Align vial such that the injector needle is centered on the stopper. |
Thread vial into injector 3 half turns, or until needle penetrates stopper. |
Remove needle cap and expel air. |
Protect the solution from light, extreme heat and freezing.
Store at controlled room temperature 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
NOTE: Do not use the injection if its color is pinkish or darker than slightly yellow or if it contains a precipitate.
Rx Only
INTERNATIONAL MEDICATION SYSTEMS, LIMITED
SO. El Monte, CA 91733, U.S.A.
An Amphastar Pharmaceuticals Company
REV. 11-08
6910140M
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mL Syringe Carton
MIN-I-JET®
Prefilled Syringe
Rx Only
NDC 0548-1016-00
STOCK NO. 1016
EPINEPHRINE
INJ., USP
1:10,000
(0.1 mg/mL)
1 mg
per
10 mL
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE
PROTECT FROM LIGHT
MIN-I-JET® 21 G. X 11/2" NEEDLE
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mL Syringe Carton
FEATURING STICK-GARD®
18 G. SAFETY INJECTOR
Rx Only
NDC 0548-2016-00
STOCK NO. 2016
EPINEPHRINE
INJ., USP
1:10,000
(0.1 mg/mL)
1 mg
per
10 mL
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE
PROTECT FROM LIGHT
STICK-GARD® PREFILLED SYRINGE
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mL Syringe Carton
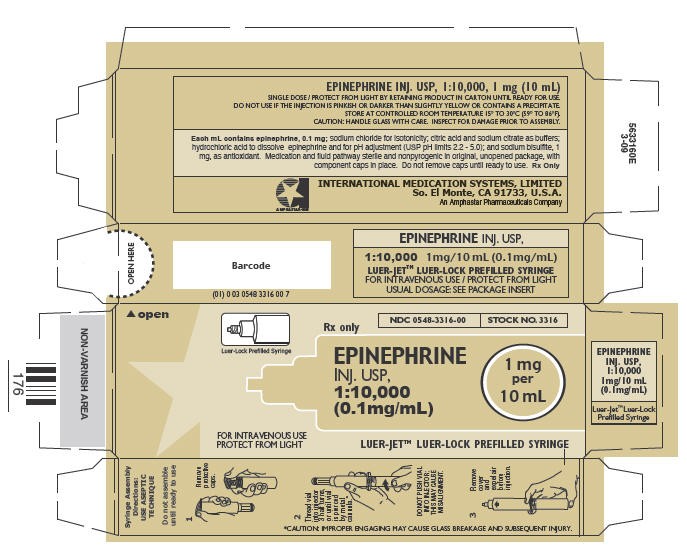
Leur-Lock Prefilled Syringe
Rx Only
NDC 0548-3316-00
STOCK NO. 3316
EPINEPHRINE
INJ. USP,
1:10,000
(0.1mg/mL)
1 mg
per
10 mL
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE
PROTECT FROM LIGHT
LUER-JET™ LUER-LOCK PREFILLED SYRINGE
EpinephrineEpinephrine INJECTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
EpinephrineEpinephrine INJECTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
EpinephrineEpinephrine INJECTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||