ERBITUX
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use ERBITUX safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ERBITUX. ERBITUX (cetuximab)injection, for intravenous infusionInitial U.S. Approval: 2004BOXED WARNING WARNING: SERIOUS INFUSION REACTIONS and CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. Serious infusion reactions, some fatal, occurred in approximately 3% of patients. (5.1) Cardiopulmonary arrest and/or sudden death occurred in 2% of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck treated with Erbitux and radiation therapy and in 3% of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck treated with cetuximab in combination with platinum-based therapy with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). Closely monitor serum electrolytes, including serum magnesium, potassium, and calcium, during and after Erbitux administration. (5.2, 5.6) RECENT MAJOR CHANGESWarnings and Precautions Use of Erbitux in Combination With Radiation and Cisplatin (5.5) 03/2013 INDICATIONS AND USAGEErbitux® is an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antagonist indicated for treatment of: Head and Neck Cancer Locally or regionally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck in combination with radiation therapy. (1.1, 14.1) Recurrent locoregional disease or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck in combination with platinum-based therapy with 5-FU. (1.1, 14.1) Recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck progressing after platinum-based therapy. (1.1, 14.1) Colorectal Cancer K-Ras mutation-negative (wild-type), EGFR-expressing, metastatic colorectal cancer as determined by FDA-approved tests in combination with FOLFIRI for first-line treatment, in combination with irinotecan in patients who are refractory to irinotecan-based chemotherapy, as a single agent in patients who have failed oxaliplatin- and irinotecan-based chemotherapy or who are intolerant to irinotecan. (1.2, 5.7, 12.1, 14.2) Limitation of Use: Erbitux is not indicated for treatment of K-Ras mutation-positive colorectal cancer. (5.7, 14.2) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Premedicate with an H1 antagonist. (2.3) Administer 400 mg/m2 initial dose as a 120-minute intravenous infusion followed by 250 mg/m2 weekly infused over 60 minutes. (2.1, 2.2) Initiate Erbitux one week prior to initiation of radiation therapy. Complete Erbitux administration 1 hour prior to platinum-based therapy with 5-FU (2.1) and FOLFIRI (2.2). Reduce the infusion rate by 50% for NCI CTC Grade 1 or 2 infusion reactions and non-serious NCI CTC Grade 3 infusion reaction. (2.4) Permanently discontinue for serious infusion reactions. (2.4) Withhold infusion for severe, persistent acneiform rash. Reduce dose for recurrent, severe rash. (2.4) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 100 mg/50 mL, single-use vial (3) 200 mg/100 mL, single-use vial (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS None. (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Infusion Reactions: Immediately stop and permanently discontinue Erbitux for serious infusion reactions. Monitor patients following infusion. (5.1) Cardiopulmonary Arrest: Closely monitor serum electrolytes during and after Erbitux. (5.2, 5.6) Pulmonary Toxicity: Interrupt therapy for acute onset or worsening of pulmonary symptoms. (5.3) Dermatologic Toxicity: Limit sun exposure. Monitor for inflammatory or infectious sequelae. (2.4, 5.4) Hypomagnesemia: Periodically monitor during and for at least 8 weeks following the completion of Erbitux. Replete electrolytes as necessary. (5.6) Side EffectsThe most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥25%) are: cutaneous adverse reactions (including rash, pruritus, and nail changes), headache, diarrhea, and infection. (6) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bristol-Myers Squibb at 1-800-721-5072 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: Administer Erbitux to a pregnant woman only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. (8.1) Nursing Mothers: Discontinue nursing during and for 60 days following treatment with Erbitux. (8.3)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING: SERIOUS INFUSION REACTIONS and CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST
- 1 ERBITUX INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 ERBITUX DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 ERBITUX CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 5.1 Infusion Reactions
- 5.2 Cardiopulmonary Arrest
- 5.3 Pulmonary Toxicity
- 5.4 Dermatologic Toxicity
- 5.5 Use of Erbitux in Combination With Radiation and Cisplatin
- 5.6 Hypomagnesemia and Electrolyte Abnormalities
- 5.7 Testing in Metastatic or Advanced Colorectal Cancer Patients
- 5.8 Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Expression and Response
- 6 ERBITUX ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 ERBITUX DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: SERIOUS INFUSION REACTIONS and CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST
Infusion Reactions: Serious infusion reactions occurred with the administration of Erbitux in approximately 3% of patients in clinical trials, with fatal outcome reported in less than 1 in 1000. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , Adverse Reactions (6) .] Immediately interrupt and permanently discontinue Erbitux infusion for serious infusion reactions. [See Dosage and Administration (2.4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) .]
Cardiopulmonary Arrest: Cardiopulmonary arrest and/or sudden death occurred in 2% of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck treated with Erbitux and radiation therapy in Study 1 and in 3% of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck treated with European Union (EU)-approved cetuximab in combination with platinum-based therapy with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in Study 2. Closely monitor serum electrolytes, including serum magnesium, potassium, and calcium, during and after Erbitux administration. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.6) , Clinical Studies (14.1) .]
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN)
Erbitux® is indicated in combination with radiation therapy for the initial treatment of locally or regionally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. [See Clinical Studies (14.1) .]
Erbitux is indicated in combination with platinum-based therapy with 5-FU for the first-line treatment of patients with recurrent locoregional disease or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. [See Clinical Studies (14.1) .]
Erbitux, as a single agent, is indicated for the treatment of patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck for whom prior platinum-based therapy has failed. [See Clinical Studies (14.1) .]
1.2 Mutation-negative, EGFR-expressing Colorectal Cancer
Erbitux is indicated for the treatment of K-Ras mutation-negative (wild-type), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-expressing, metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) as determined by FDA-approved tests for this use [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) , Warnings and Precautions (5.7) , Clinical Studies (14.2) ]
- in combination with FOLFIRI (irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin) for the first-line treatment,
- in combination with irinotecan in patients who are refractory to irinotecan-based chemotherapy,
- as a single agent in patients who have failed oxaliplatin- and irinotecan-based chemotherapy or who are intolerant to irinotecan. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) , Clinical Studies (14.2) .]
Limitation of Use: Erbitux is not indicated for treatment of K-Ras mutation-positive colorectal cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) , Clinical Studies (14.2) ].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
Erbitux in combination with radiation therapy or in combination with platinum-based therapy with 5-FU:
- The recommended initial dose is 400 mg/m2 administered one week prior to initiation of a course of radiation therapy or on the day of initiation of platinum-based therapy with 5-FU as a 120-minute intravenous infusion (maximum infusion rate 10 mg/min). Complete Erbitux administration 1 hour prior to platinum-based therapy with 5-FU.
- The recommended subsequent weekly dose (all other infusions) is 250 mg/m2 infused over 60 minutes (maximum infusion rate 10 mg/min) for the duration of radiation therapy (6–7 weeks) or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity when administered in combination with platinum-based therapy with 5-FU. Complete Erbitux administration 1 hour prior to radiation therapy or platinum-based therapy with 5-FU.
Erbitux monotherapy:
- The recommended initial dose is 400 mg/m2 administered as a 120-minute intravenous infusion (maximum infusion rate 10 mg/min).
- The recommended subsequent weekly dose (all other infusions) is 250 mg/m2 infused over 60 minutes (maximum infusion rate 10 mg/min) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
2.2 Colorectal Cancer
- Determine K-Ras mutation and EGFR-expression status using FDA-approved tests prior to initiating treatment. Only patients whose tumors are K-Ras mutation-negative (wild-type) should receive Erbitux.
- The recommended initial dose, either as monotherapy or in combination with irinotecan or FOLFIRI (irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin), is 400 mg/m2 administered as a 120-minute intravenous infusion (maximum infusion rate 10 mg/min). Complete Erbitux administration 1 hour prior to FOLFIRI.
- The recommended subsequent weekly dose, either as monotherapy or in combination with irinotecan or FOLFIRI, is 250 mg/m2 infused over 60 minutes (maximum infusion rate 10 mg/min) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Complete Erbitux administration 1 hour prior to FOLFIRI.
2.3 Recommended Premedication
Premedicate with an H1 antagonist (eg, 50 mg of diphenhydramine) intravenously 30–60 minutes prior to the first dose; premedication should be administered for subsequent Erbitux doses based upon clinical judgment and presence/severity of prior infusion reactions.
2.4 Dose Modifications
Infusion Reactions
Reduce the infusion rate by 50% for NCI CTC Grade 1 or 2 and non-serious NCI CTC Grade 3 infusion reaction.
Immediately and permanently discontinue Erbitux for serious infusion reactions, requiring medical intervention and/or hospitalization. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1) .]
Dermatologic Toxicity
Recommended dose modifications for severe (NCI CTC Grade 3 or 4) acneiform rash are specified in Table 1. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.4) .]
|
Severe Acneiform Rash |
Erbitux | Outcome |
Erbitux Dose Modification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st occurrence | Delay infusion 1 to 2 weeks | Improvement | Continue at 250 mg/m2 |
| No Improvement | Discontinue Erbitux | ||
| 2nd occurrence | Delay infusion 1 to 2 weeks | Improvement | Reduce dose to 200 mg/m2 |
| No Improvement | Discontinue Erbitux | ||
| 3rd occurrence | Delay infusion 1 to 2 weeks | Improvement | Reduce dose to 150 mg/m2 |
| No Improvement | Discontinue Erbitux | ||
| 4th occurrence | Discontinue Erbitux |
2.5 Preparation for Administration
Do not administer Erbitux as an intravenous push or bolus.
Administer via infusion pump or syringe pump. Do not exceed an infusion rate of 10 mg/min.
Administer through a low protein binding 0.22-micrometer in-line filter.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
The solution should be clear and colorless and may contain a small amount of easily visible, white, amorphous, cetuximab particulates. Do not shake or dilute.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
100 mg/50 mL, single-use vial
200 mg/100 mL, single-use vial
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infusion Reactions
Serious infusion reactions, requiring medical intervention and immediate, permanent discontinuation of Erbitux included rapid onset of airway obstruction (bronchospasm, stridor, hoarseness), hypotension, shock, loss of consciousness, myocardial infarction, and/or cardiac arrest. Severe (NCI CTC Grades 3 and 4) infusion reactions occurred in 2–5% of 1373 patients in Studies 1, 3, 5, and 6 receiving Erbitux, with fatal outcome in 1 patient. [See Clinical Studies (14.1, 14.2) .]
Approximately 90% of severe infusion reactions occurred with the first infusion despite premedication with antihistamines.
Monitor patients for 1 hour following Erbitux infusions in a setting with resuscitation equipment and other agents necessary to treat anaphylaxis (eg, epinephrine, corticosteroids, intravenous antihistamines, bronchodilators, and oxygen). Monitor longer to confirm resolution of the event in patients requiring treatment for infusion reactions.
Immediately and permanently discontinue Erbitux in patients with serious infusion reactions. [See Boxed Warning , Dosage and Administration (2.4) .]
5.2 Cardiopulmonary Arrest
Cardiopulmonary arrest and/or sudden death occurred in 4 (2%) of 208 patients treated with radiation therapy and Erbitux as compared to none of 212 patients treated with radiation therapy alone in Study 1. Three patients with prior history of coronary artery disease died at home, with myocardial infarction as the presumed cause of death. One of these patients had arrhythmia and one had congestive heart failure. Death occurred 27, 32, and 43 days after the last dose of Erbitux. One patient with no prior history of coronary artery disease died one day after the last dose of Erbitux. In Study 2, fatal cardiac disorders and/or sudden death occurred in 7 (3%) of 219 patients treated with EU-approved cetuximab and platinum-based therapy with 5-FU as compared to 4 (2%) of 215 patients treated with chemotherapy alone. Five of these 7 patients in the chemotherapy plus cetuximab arm received concomitant cisplatin and 2 patients received concomitant carboplatin. All 4 patients in the chemotherapy-alone arm received cisplatin. Carefully consider use of Erbitux in combination with radiation therapy or platinum-based therapy with 5-FU in head and neck cancer patients with a history of coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, or arrhythmias in light of these risks. Closely monitor serum electrolytes, including serum magnesium, potassium, and calcium, during and after Erbitux. [See Boxed Warning , Warnings and Precautions (5.6) .]
5.3 Pulmonary Toxicity
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), including 1 fatality, occurred in 4 of 1570 (<0.5%) patients receiving Erbitux in Studies 1, 3, and 6, as well as other studies, in colorectal cancer and head and neck cancer. Interrupt Erbitux for acute onset or worsening of pulmonary symptoms. Permanently discontinue Erbitux for confirmed ILD.
5.4 Dermatologic Toxicity
Dermatologic toxicities, including acneiform rash, skin drying and fissuring, paronychial inflammation, infectious sequelae (for example, S. aureus sepsis, abscess formation, cellulitis, blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis/ulcerative keratitis with decreased visual acuity, cheilitis), and hypertrichosis occurred in patients receiving Erbitux therapy. Acneiform rash occurred in 76–88% of 1373 patients receiving Erbitux in Studies 1, 3, 5, and 6. Severe acneiform rash occurred in 1–17% of patients.
Acneiform rash usually developed within the first two weeks of therapy and resolved in a majority of the patients after cessation of treatment, although in nearly half, the event continued beyond 28 days. Monitor patients receiving Erbitux for dermatologic toxicities and infectious sequelae. Instruct patients to limit sun exposure during Erbitux therapy. [See Dosage and Administration (2.4) .]
5.5 Use of Erbitux in Combination With Radiation and Cisplatin
In a controlled study, 940 patients with locally advanced SCCHN were randomized 1:1 to receive either Erbitux in combination with radiation therapy and cisplatin or radiation therapy and cisplatin alone. The addition of Erbitux resulted in an increase in the incidence of Grade 3–4 mucositis, radiation recall syndrome, acneiform rash, cardiac events, and electrolyte disturbances compared to radiation and cisplatin alone. Adverse reactions with fatal outcome were reported in 20 patients (4.4%) in the Erbitux combination arm and 14 patients (3.0%) in the control arm. Nine patients in the Erbitux arm (2.0%) experienced myocardial ischemia compared to 4 patients (0.9%) in the control arm. The main efficacy outcome of the study was progression-free survival (PFS). The addition of Erbitux to radiation and cisplatin did not improve PFS.
5.6 Hypomagnesemia and Electrolyte Abnormalities
In patients evaluated during clinical trials, hypomagnesemia occurred in 55% of 365 patients receiving Erbitux in Study 5 and two other clinical trials in colorectal cancer and head and neck cancer, respectively, and was severe (NCI CTC Grades 3 and 4) in 6–17%.
In Study 2, where EU-approved cetuximab was administered in combination with platinum-based therapy, the addition of cetuximab to cisplatin and 5-FU resulted in an increased incidence of hypomagnesemia (14% vs. 6%) and of Grade 3–4 hypomagnesemia (7% vs. 2%) compared to cisplatin and 5-FU alone. In contrast, the incidences of hypomagnesemia were similar for those who received cetuximab, carboplatin, and 5-FU compared to carboplatin and 5-FU (4% vs. 4%). No patient experienced Grade 3–4 hypomagnesemia in either arm in the carboplatin subgroup.
The onset of hypomagnesemia and accompanying electrolyte abnormalities occurred days to months after initiation of Erbitux. Periodically monitor patients for hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, and hypokalemia, during and for at least 8 weeks following the completion of Erbitux. Replete electrolytes as necessary.
5.7 Testing in Metastatic or Advanced Colorectal Cancer Patients
Determination of K-Ras mutational status in colorectal tumors using an FDA-approved test indicated for this use is necessary for selection of patients for treatment with Erbitux. Erbitux is indicated only for patients with EGFR-expressing K-Ras mutation-negative (wild-type) mCRC. Erbitux is not an effective treatment for patients with colorectal cancer that harbor somatic mutations in codons 12 and 13 (exon 2). Studies 4 and 5, conducted in patients with colorectal cancer, demonstrated a benefit with Erbitux treatment only in the subset of patients whose tumors were K-Ras mutation-negative (wild-type). Erbitux is not effective for the treatment of K-Ras mutation-positive colorectal cancer as determined by an FDA-approved test for this use. [See Indications and Usage (1.2) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) , Clinical Studies (14.2) .]
Perform the assesment for K-Ras mutation status in colorectal cancer in laboratories with demonstrated proficiency in the specific technology being utilized. Improper assay performance can lead to unreliable test results.
Refer to an FDA-approved test’s package insert for instructions on the identification of patients eligible for the treatment of Erbitux.
5.8 Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Expression and Response
Because expression of EGFR has been detected in nearly all SCCHN tumor specimens, patients enrolled in the head and neck cancer clinical studies were not required to have immunohistochemical evidence of EGFR tumor expression prior to study entry.
Patients enrolled in the colorectal cancer clinical studies were required to have immunohistochemical evidence of EGFR tumor expression. Primary tumor or tumor from a metastatic site was tested with the DakoCytomation EGFR pharmDxTM test kit. Specimens were scored based on the percentage of cells expressing EGFR and intensity (barely/faint, weak-to-moderate, and strong). Response rate did not correlate with either the percentage of positive cells or the intensity of EGFR expression.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Infusion reactions [See Boxed Warning , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) .]
- Cardiopulmonary arrest [See Boxed Warning , Warnings and Precautions (5.2) .]
- Pulmonary toxicity [See Warnings and Precautions (5.3) .]
- Dermatologic toxicity [See Warnings and Precautions (5.4) .]
- Hypomagnesemia and Electrolyte Abnormalities [See Warnings and Precautions (5.6) .]
The most common adverse reactions in Erbitux clinical trials (incidence ≥25%) include cutaneous adverse reactions (including rash, pruritus, and nail changes), headache, diarrhea, and infection.
The most serious adverse reactions with Erbitux are infusion reactions, cardiopulmonary arrest, dermatologic toxicity and radiation dermatitis, sepsis, renal failure, interstitial lung disease, and pulmonary embolus.
Across Studies 1, 3, 5, and 6, Erbitux was discontinued in 3–10% of patients because of adverse reactions.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data below reflect exposure to Erbitux in 1373 patients with SCCHN or colorectal cancer in randomized Phase 3 (Studies 1 and 5) or Phase 2 (Studies 3 and 6) trials treated at the recommended dose and schedule for medians of 7 to 14 weeks. [See Clinical Studies (14) .]
Infusion reactions: Infusion reactions, which included pyrexia, chills, rigors, dyspnea, bronchospasm, angioedema, urticaria, hypertension, and hypotension occurred in 15–21% of patients across studies. Grades 3 and 4 infusion reactions occurred in 2–5% of patients; infusion reactions were fatal in 1 patient.
Infections: The incidence of infection was variable across studies, ranging from 13–35%. Sepsis occurred in 1–4% of patients.
Renal: Renal failure occurred in 1% of patients with colorectal cancer.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
Erbitux in Combination with Radiation Therapy
Table 2 contains selected adverse reactions in 420 patients receiving radiation therapy either alone or with Erbitux for locally or regionally advanced SCCHN in Study 1. Erbitux was administered at the recommended dose and schedule (400 mg/m2 initial dose, followed by 250 mg/m2 weekly). Patients received a median of 8 infusions (range 1–11).
|
Body System
Preferred Term |
Erbitux plus Radiation (n=208) |
Radiation Therapy Alone (n=212) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grades 1–4 |
Grades 3 and 4 |
Grades 1–4 |
Grades 3 and 4 |
|
| % of Patients | ||||
| a Includes cases also reported as infusion reaction. | ||||
| b Infusion reaction is defined as any event described at any time during the clinical study as “allergic reaction” or “anaphylactoid reaction”, or any event occurring on the first day of dosing described as “allergic reaction”, “anaphylactoid reaction”, “fever”, “chills”, “chills and fever”, or “dyspnea”. | ||||
| c Based on laboratory measurements, not on reported adverse reactions, the number of subjects with tested samples varied from 205–206 for Erbitux plus Radiation arm; 209–210 for Radiation alone. | ||||
| d Acneiform rash is defined as any event described as “acne”, “rash”, “maculopapular rash”, “pustular rash”, “dry skin”, or “exfoliative dermatitis”. | ||||
| Body as a Whole | ||||
| Asthenia | 56 | 4 | 49 | 5 |
| Fevera | 29 | 1 | 13 | 1 |
| Headache | 19 | <1 | 8 | <1 |
| Infusion Reactionb | 15 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| Infection | 13 | 1 | 9 | 1 |
| Chillsa | 16 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Digestive | ||||
| Nausea | 49 | 2 | 37 | 2 |
| Emesis | 29 | 2 | 23 | 4 |
| Diarrhea | 19 | 2 | 13 | 1 |
| Dyspepsia | 14 | 0 | 9 | 1 |
| Metabolic/Nutritional | ||||
| Weight Loss | 84 | 11 | 72 | 7 |
| Dehydration | 25 | 6 | 19 | 8 |
| Alanine Transaminase, highc | 43 | 2 | 21 | 1 |
| Aspartate Transaminase, highc | 38 | 1 | 24 | 1 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase, highc | 33 | <1 | 24 | 0 |
| Respiratory | ||||
| Pharyngitis | 26 | 3 | 19 | 4 |
| Skin/Appendages | ||||
| Acneiform Rashd | 87 | 17 | 10 | 1 |
| Radiation Dermatitis | 86 | 23 | 90 | 18 |
| Application Site Reaction | 18 | 0 | 12 | 1 |
| Pruritus | 16 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
The incidence and severity of mucositis, stomatitis, and xerostomia were similar in both arms of the study.
Late Radiation Toxicity
The overall incidence of late radiation toxicities (any grade) was higher in Erbitux in combination with radiation therapy compared with radiation therapy alone. The following sites were affected: salivary glands (65% versus 56%), larynx (52% versus 36%), subcutaneous tissue (49% versus 45%), mucous membrane (48% versus 39%), esophagus (44% versus 35%), skin (42% versus 33%). The incidence of Grade 3 or 4 late radiation toxicities was similar between the radiation therapy alone and the Erbitux plus radiation treatment groups.
Study 2: EU-Approved Cetuximab in Combination with Platinum-based Therapy with 5-Fluorouracil
Study 2 used EU-approved cetuximab. Since U.S.-licensed Erbitux provides approximately 22% higher exposure relative to the EU-approved cetuximab, the data provided below may underestimate the incidence and severity of adverse reactions anticipated with Erbitux for this indication. However, the tolerability of the recommended dose is supported by safety data from additional studies of Erbitux [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Table 3 contains selected adverse reactions in 434 patients with recurrent locoregional disease or metastatic SCCHN receiving EU-approved cetuximab in combination with platinum-based therapy with 5-FU or platinum-based therapy with 5-FU alone in Study 2. Cetuximab was administered at 400 mg/m2 for the initial dose, followed by 250 mg/m2 weekly. Patients received a median of 17 infusions (range 1–89).
|
System Organ Class
Preferred Term |
EU-Approved Cetuximab plus Platinum-based Therapy with 5-FU (n=219) |
Platinum-based Therapy with 5-FU Alone (n=215) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grades 1–4 |
Grades 3 and 4 |
Grades 1–4 |
Grades 3 and 4 |
|
| % of Patients | ||||
| a Infusion reaction defined as any event of “anaphylactic reaction”, “hypersensitivity”, “fever and/or chills”, “dyspnea”, or “pyrexia” on the first day of dosing. | ||||
| b Infection – this term excludes sepsis-related events which are presented separately. | ||||
| c Acneiform rash defined as any event described as “acne”, “dermatitis acneiform”, “dry skin”, “exfoliative rash”, “rash”, “rash erythematous”, “rash macular”, “rash papular”, or “rash pustular”. | ||||
| Chemotherapy = cisplatin + 5-fluorouracil or carboplatin + 5-fluorouracil | ||||
| Eye Disorders | ||||
| Conjunctivitis | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 54 | 4 | 47 | 4 |
| Diarrhea | 26 | 5 | 16 | 1 |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
| Pyrexia | 22 | 0 | 13 | 1 |
| Infusion Reactiona | 10 | 2 | <1 | 0 |
| Infections and Infestations | ||||
| Infectionb | 44 | 11 | 27 | 8 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
| Anorexia | 25 | 5 | 14 | 1 |
| Hypocalcemia | 12 | 4 | 5 | 1 |
| Hypokalemia | 12 | 7 | 7 | 5 |
| Hypomagnesemia | 11 | 5 | 5 | 1 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Acneiform Rashc | 70 | 9 | 2 | 0 |
| Rash | 28 | 5 | 2 | 0 |
| Acne | 22 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Dermatitis Acneiform | 15 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Dry Skin | 14 | 0 | <1 | 0 |
| Alopecia | 12 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
For cardiac disorders, approximately 9% of subjects in both the EU-approved cetuximab plus chemotherapy and chemotherapy-only treatment arms in Study 2 experienced a cardiac event. The majority of these events occurred in patients who received cisplatin/5-FU, with or without cetuximab as follows: 11% and 12% in patients who received cisplatin/5-FU with or without cetuximab, respectively, and 6% or 4% in patients who received carboplatin/5-FU with or without cetuximab, respectively. In both arms, the incidence of cardiovascular events was higher in the cisplatin with 5-FU containing subgroup. Death attributed to cardiovascular event or sudden death was reported in 3% of the patients in the cetuximab plus platinum-based therapy with 5-FU arm and 2% in the platinum-based chemotherapy with 5-FU alone arm.
Colorectal Cancer
Study 4: EU-Approved Cetuximab in Combination with FOLFIRI
Study 4 used EU-approved cetuximab. U.S.-licensed Erbitux provides approximately 22% higher exposure to cetuximab relative to the EU-approved cetuximab. The data provided below for Study 4 is consistent in incidence and severity of adverse reactions with those seen for Erbitux in this indication. The tolerability of the recommended dose is supported by safety data from additional studies of Erbitux [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Table 4 contains selected adverse reactions in 667 patients with K-Ras mutation-negative (wild-type), EGFR-expressing, metastatic colorectal cancer receiving EU-approved cetuximab plus FOLFIRI or FOLFIRI alone in Study 4 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]. Cetuximab was administered at the recommended dose and schedule (400 mg/m2 initial dose, followed by 250 mg/m2 weekly). Patients received a median of 26 infusions (range 1–224).
|
Body System
Preferred Term |
EU-Approved Cetuximab plus FOLFIRI (n=317) |
FOLFIRI Alone (n=350) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grades 1–4b |
Grades 3 and 4 |
Grades 1–4 |
Grades 3 and 4 |
|
| % of Patients | ||||
| a Adverse reactions occurring in at least 10% of Erbitux combination arm with a frequency at least 5% greater than that seen in the FOLFIRI arm. | ||||
| b Adverse reactions were graded using the NCI CTC, V 2.0. | ||||
| c Infusion related reaction is defined as any event meeting the medical concepts of allergy/anaphylaxis at any time during the clinical study or any event occurring on the first day of dosing and meeting the medical concepts of dyspnea and fever or by the following events using MedDRA preferred terms: “acute myocardial infarction”, “angina pectoris”, “angioedema”, “autonomic seizure”, “blood pressure abnormal”, “blood pressure decreased”, “blood pressure increased”, “cardiac failure”, “cardiopulmonary failure”, “cardiovascular insufficiency”, “clonus”, “convulsion”, “coronary no-reflow phenomenon”, “epilepsy”, “hypertension”, “hypertensive crisis”, “hypertensive emergency”, “hypotension”, “infusion related reaction”, “loss of consciousness”, “myocardial infarction”, “myocardial ischaemia”, “prinzmetal angina”, “shock”, “sudden death”, “syncope”, or “systolic hypertension”. | ||||
| d Acne-like rash is defined by the events using MedDRA preferred terms and included “acne”, “acne pustular”, “butterfly rash”, “dermatitis acneiform”, “drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms”, “dry skin”, “erythema”, “exfoliative rash”, “folliculitis”, “genital rash”, “mucocutaneous rash”, “pruritus”, “rash”, “rash erythematous”, “rash follicular”, “rash generalized”, “rash macular”, “rash maculopapular”, “rash maculovesicular”, “rash morbilliform”, “rash papular”, “rash papulosquamous”, “rash pruritic”, “rash pustular”, “rash rubelliform”, “rash scarlatiniform”, “rash vesicular”, “skin exfoliation”, “skin hyperpigmentation”, “skin plaque”, “telangiectasia”, or “xerosis”. | ||||
| Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | ||||
| Neutropenia | 49 | 31 | 42 | 24 |
| Eye Disorders | ||||
| Conjunctivitis | 18 | <1 | 3 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Diarrhea | 66 | 16 | 60 | 10 |
| Stomatitis | 31 | 3 | 19 | 1 |
| Dyspepsia | 16 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
| Infusion-related Reactionc | 14 | 2 | <1 | 0 |
| Pyrexia | 26 | 1 | 14 | 1 |
| Infections and Infestations | ||||
| Paronychia | 20 | 4 | <1 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Weight Decreased | 15 | 1 | 9 | 1 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
| Anorexia | 30 | 3 | 23 | 2 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Acne-like Rashd | 86 | 18 | 13 | <1 |
| Rash | 44 | 9 | 4 | 0 |
| Dermatitis Acneiform | 26 | 5 | <1 | 0 |
| Dry Skin | 22 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Acne | 14 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 14 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Palmar-plantar Erythrodysesthesia Syndrome | 19 | 4 | 4 | <1 |
| Skin Fissures | 19 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
Erbitux Monotherapy
Table 5 contains selected adverse reactions in 242 patients with K-Ras mutation-negative (wild-type), EGFR-expressing, metastatic colorectal cancer who received best supportive care (BSC) alone or with Erbitux in Study 5 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]. Erbitux was administered at the recommended dose and schedule (400 mg/m2 initial dose, followed by 250 mg/m2 weekly). Patients received a median of 17 infusions (range 1–51).
|
Body System
Preferred Term |
Erbitux plus BSC (n=118) |
BSC alone (n=124) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grades 1–4b |
Grades 3 and 4 |
Grades 1–4 |
Grades 3 and 4 |
|
| % of Patients | ||||
| a Adverse reactions occurring in at least 10% of Erbitux plus BSC arm with a frequency at least 5% greater than that seen in the BSC alone arm. | ||||
| b Adverse reactions were graded using the NCI CTC, V 2.0. | ||||
| c Infusion reaction is defined as any event (chills, rigors, dyspnea, tachycardia, bronchospasm, chest tightness, swelling, urticaria, hypotension, flushing, rash, hypertension, nausea, angioedema, pain, sweating, tremors, shaking, drug fever, or other hypersensitivity reaction) recorded by the investigator as infusion-related. | ||||
| Dermatology/Skin | ||||
| Rash/Desquamation | 95 | 16 | 21 | 1 |
| Dry Skin | 57 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 47 | 2 | 11 | 0 |
| Other-Dermatology | 35 | 0 | 7 | 2 |
| Nail Changes | 31 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Constitutional Symptoms | ||||
| Fatigue | 91 | 31 | 79 | 29 |
| Fever | 25 | 3 | 16 | 0 |
| Infusion Reactionsc | 18 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Rigors, Chills | 16 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Pain | ||||
| Pain-Other | 59 | 18 | 37 | 10 |
| Headache | 38 | 2 | 11 | 0 |
| Bone Pain | 15 | 4 | 8 | 2 |
| Pulmonary | ||||
| Dyspnea | 49 | 16 | 44 | 13 |
| Cough | 30 | 2 | 19 | 2 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Nausea | 64 | 6 | 50 | 6 |
| Constipation | 53 | 3 | 38 | 3 |
| Diarrhea | 42 | 2 | 23 | 2 |
| Vomiting | 40 | 5 | 26 | 5 |
| Stomatitis | 32 | 1 | 10 | 0 |
| Other-Gastrointestinal | 22 | 12 | 16 | 5 |
| Dehydration | 13 | 5 | 3 | 0 |
| Mouth Dryness | 12 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Taste Disturbance | 10 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Infection | ||||
| Infection without neutropenia | 38 | 11 | 19 | 5 |
| Musculoskeletal | ||||
| Arthralgia | 14 | 3 | 6 | 0 |
| Neurology | ||||
| Neuropathy-sensory | 45 | 1 | 38 | 2 |
| Insomnia | 27 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| Confusion | 18 | 6 | 10 | 2 |
| Anxiety | 14 | 1 | 5 | 1 |
| Depression | 14 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
Erbitux in Combination with Irinotecan
The most frequently reported adverse reactions in 354 patients treated with Erbitux plus irinotecan in clinical trials were acneiform rash (88%), asthenia/malaise (73%), diarrhea (72%), and nausea (55%). The most common Grades 3–4 adverse reactions included diarrhea (22%), leukopenia (17%), asthenia/malaise (16%), and acneiform rash (14%).
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. Immunogenic responses to cetuximab were assessed using either a double antigen radiometric assay or an ELISA assay. Due to limitations in assay performance and sampling timing, the incidence of antibody development in patients receiving Erbitux has not been adequately determined. Non-neutralizing anti-cetuximab antibodies were detected in 5% (49 of 1001) of evaluable patients without apparent effect on the safety or antitumor activity of Erbitux.
The incidence of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to Erbitux with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Erbitux. Because these reactions are reported from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Aseptic meningitis
- Mucosal inflammation
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
A drug interaction study was performed in which Erbitux was administered in combination with irinotecan. There was no evidence of any pharmacokinetic interactions between Erbitux and irinotecan.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of Erbitux in pregnant women. Based on animal models, EGFR has been implicated in the control of prenatal development and may be essential for normal organogenesis, proliferation, and differentiation in the developing embryo. Human IgG is known to cross the placental barrier; therefore, Erbitux may be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus, and has the potential to cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Erbitux should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Pregnant cynomolgus monkeys were treated weekly with 0.4 to 4 times the recommended human dose of cetuximab (based on body surface area) during the period of organogenesis (gestation day [GD] 20–48). Cetuximab was detected in the amniotic fluid and in the serum of embryos from treated dams at GD 49. No fetal malformations or other teratogenic effects occurred in offspring. However, significant increases in embryolethality and abortions occurred at doses of approximately 1.6 to 4 times the recommended human dose of cetuximab (based on total body surface area).
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether Erbitux is secreted in human milk. IgG antibodies, such as Erbitux, can be excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Erbitux, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. If nursing is interrupted, based on the mean half-life of cetuximab [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ], nursing should not be resumed earlier than 60 days following the last dose of Erbitux.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Erbitux in pediatric patients have not been established. The pharmacokinetics of cetuximab, in combination with irinotecan, were evaluated in pediatric patients with refractory solid tumors in an open-label, single-arm, dose-finding study. Erbitux was administered once-weekly, at doses up to 250 mg/m2, to 27 patients ranging from 1 to 12 years old; and in 19 patients ranging from 13 to 18 years old. No new safety signals were identified in pediatric patients. The pharmacokinetic profiles of cetuximab between the two age groups were similar at the 75 and 150 mg/m2 single dose levels. The volume of the distribution appeared to be independent of dose and approximated the vascular space of 2–3 L/m2. Following a single dose of 250 mg/m2, the geometric mean AUC0-inf (CV%) value was 17.7 mg•h/mL (34%) in the younger age group (1–12 years, n=9) and 13.4 mg•h/mL (38%) in the adolescent group (13–18 years, n=6). The mean half-life of cetuximab was 110 hours (range 69 to 188 hours) for the younger age group, and 82 hours (range 55 to 117 hours) for the adolescent age group.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 1662 patients who received Erbitux with irinotecan, FOLFIRI or Erbitux monotherapy in six studies of advanced colorectal cancer, 588 patients were 65 years of age or older. No overall differences in safety or efficacy were observed between these patients and younger patients.
Clinical studies of Erbitux conducted in patients with head and neck cancer did not include sufficient number of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
10 OVERDOSAGE
The maximum single dose of Erbitux administered is 1000 mg/m2 in one patient. No adverse events were reported for this patient.
11 DESCRIPTION
Erbitux® (cetuximab) is a recombinant, human/mouse chimeric monoclonal antibody that binds specifically to the extracellular domain of the human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Cetuximab is composed of the Fv regions of a murine anti-EGFR antibody with human IgG1 heavy and kappa light chain constant regions and has an approximate molecular weight of 152 kDa. Cetuximab is produced in mammalian (murine myeloma) cell culture.
Erbitux is a sterile, clear, colorless liquid of pH 7.0 to 7.4, which may contain a small amount of easily visible, white, amorphous cetuximab particulates. Erbitux is supplied at a concentration of 2 mg/mL in either 100 mg (50 mL) or 200 mg (100 mL), single-use vials. Cetuximab is formulated in a solution with no preservatives, which contains 8.48 mg/mL sodium chloride, 1.88 mg/mL sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate, 0.41 mg/mL sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate, and Water for Injection, USP.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR, HER1, c-ErbB-1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that is a member of a subfamily of type I receptor tyrosine kinases including EGFR, HER2, HER3, and HER4. The EGFR is constitutively expressed in many normal epithelial tissues, including the skin and hair follicle. Expression of EGFR is also detected in many human cancers including those of the head and neck, colon, and rectum.
Cetuximab binds specifically to the EGFR on both normal and tumor cells, and competitively inhibits the binding of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and other ligands, such as transforming growth factor-alpha. In vitro assays and in vivo animal studies have shown that binding of cetuximab to the EGFR blocks phosphorylation and activation of receptor-associated kinases, resulting in inhibition of cell growth, induction of apoptosis, and decreased matrix metalloproteinase and vascular endothelial growth factor production. Signal transduction through the EGFR results in activation of wild-type K-Ras protein. However, in cells with activating K-Ras somatic mutations, the mutant K-Ras protein is continuously active and appears independent of EGFR regulation.
In vitro, cetuximab can mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) against certain human tumor types. In vitro assays and in vivo animal studies have shown that cetuximab inhibits the growth and survival of tumor cells that express the EGFR. No anti-tumor effects of cetuximab were observed in human tumor xenografts lacking EGFR expression. The addition of cetuximab to radiation therapy or irinotecan in human tumor xenograft models in mice resulted in an increase in anti-tumor effects compared to radiation therapy or chemotherapy alone.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Effects on Electrocardiogram (ECG)
The effect of cetuximab on QT interval was evaluated in an open-label, single-arm, monotherapy trial in 37 subjects with advanced malignancies who received an initial dose of 400 mg/m2, followed by weekly infusions of 250 mg/m2 for a total of 5 weeks. No large changes in the mean QT interval of >20 ms from baseline were detected in the trial based on the Fridericia correction method. A small increase in the mean QTc interval of <10 ms cannot be excluded because of the limitations in the trial design.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Erbitux administered as monotherapy or in combination with concomitant chemotherapy or radiation therapy exhibits nonlinear pharmacokinetics. The area under the concentration time curve (AUC) increased in a greater than dose proportional manner while clearance of cetuximab decreased from 0.08 to 0.02 L/h/m2 as the dose increased from 20 to 200 mg/m2, and at doses >200 mg/m2, it appeared to plateau. The volume of the distribution for cetuximab appeared to be independent of dose and approximated the vascular space of 2–3 L/m2.
Following the recommended dose regimen (400 mg/m2 initial dose; 250 mg/m2 weekly dose), concentrations of cetuximab reached steady-state levels by the third weekly infusion with mean peak and trough concentrations across studies ranging from 168 to 235 and 41 to 85 µg/mL, respectively. The mean half-life of cetuximab was approximately 112 hours (range 63–230 hours). The pharmacokinetics of cetuximab were similar in patients with SCCHN and those with colorectal cancer.
Erbitux had an approximately 22% (90% confidence interval; 6%, 38%) higher systemic exposure relative to the EU-approved cetuximab used in Studies 2 and 4 based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis. [See Clinical Studies (14.1) .]
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to test cetuximab for carcinogenic potential, and no mutagenic or clastogenic potential of cetuximab was observed in the Salmonella-Escherichia coli (Ames) assay or in the in vivo rat micronucleus test. Menstrual cyclicity was impaired in female cynomolgus monkeys receiving weekly doses of 0.4 to 4 times the human dose of cetuximab (based on total body surface area). Cetuximab-treated animals exhibited increased incidences of irregular or absent cycles, as compared to control animals. These effects were initially noted beginning week 25 of cetuximab treatment and continued through the 6-week recovery period. In this same study, there were no effects of cetuximab treatment on measured male fertility parameters (ie, serum testosterone levels and analysis of sperm counts, viability, and motility) as compared to control male monkeys. It is not known if cetuximab can impair fertility in humans.
13.2 Animal Pharmacology and/or Toxicology
In cynomolgus monkeys, cetuximab, when administered at doses of approximately 0.4 to 4 times the weekly human exposure (based on total body surface area), resulted in dermatologic findings, including inflammation at the injection site and desquamation of the external integument. At the highest dose level, the epithelial mucosa of the nasal passage, esophagus, and tongue were similarly affected, and degenerative changes in the renal tubular epithelium occurred. Deaths due to sepsis were observed in 50% (5/10) of the animals at the highest dose level beginning after approximately 13 weeks of treatment.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Studies 2 and 4 were conducted outside the U.S. using an EU-approved cetuximab as the clinical trial material. Erbitux provides approximately 22% higher exposure relative to the EU-approved cetuximab used in Studies 2 and 4; these pharmacokinetic data, together with the results of Studies 2, 4, and other clinical trial data establish the efficacy of Erbitux at the recommended dose in SCCHN and mCRC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
14.1 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN)
Study 1 was a randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of 424 patients with locally or regionally advanced SCCHN. Patients with Stage III/IV SCCHN of the oropharynx, hypopharynx, or larynx with no prior therapy were randomized (1:1) to receive either Erbitux plus radiation therapy or radiation therapy alone. Stratification factors were Karnofsky performance status (60–80 versus 90–100), nodal stage (N0 versus N+), tumor stage (T1–3 versus T4 using American Joint Committee on Cancer 1998 staging criteria), and radiation therapy fractionation (concomitant boost versus once-daily versus twice-daily). Radiation therapy was administered for 6–7 weeks as once-daily, twice-daily, or concomitant boost. Erbitux was administered as a 400 mg/m2 initial dose beginning one week prior to initiation of radiation therapy, followed by 250 mg/m2 weekly administered 1 hour prior to radiation therapy for the duration of radiation therapy (6–7 weeks).
Of the 424 randomized patients, the median age was 57 years, 80% were male, 83% were Caucasian, and 90% had baseline Karnofsky performance status ≥80. There were 258 patients enrolled in U.S. sites (61%). Sixty percent of patients had oropharyngeal, 25% laryngeal, and 15% hypopharyngeal primary tumors; 28% had AJCC T4 tumor stage. Fifty-six percent of the patients received radiation therapy with concomitant boost, 26% received once-daily regimen, and 18% twice-daily regimen.
The main outcome measure of this trial was duration of locoregional control. Overall survival was also assessed. Results are presented in Table 6.
| Erbitux + Radiation (n=211) |
Radiation Alone (n=213) |
Hazard Ratio (95% CIa) |
Stratified Log-rank p-value |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a CI = confidence interval | ||||
| Locoregional Control | ||||
| Median duration (months) | 24.4 | 14.9 | 0.68 (0.52–0.89) | 0.005 |
| Overall Survival | ||||
| Median duration (months) | 49.0 | 29.3 | 0.74 (0.57–0.97) | 0.03 |
Study 2 was an open-label, randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of 442 patients with recurrent locoregional disease or metastatic SCCHN.
Patients with no prior therapy for recurrent locoregional disease or metastatic SCCHN were randomized (1:1) to receive EU-approved cetuximab plus cisplatin or carboplatin and 5-FU, or cisplatin or carboplatin and 5-FU alone. Choice of cisplatin or carboplatin was at the discretion of the treating physician. Stratification factors were Karnofsky performance status (<80 versus ≥80) and previous chemotherapy. Cisplatin (100 mg/m2, Day 1) or carboplatin (AUC 5, Day 1) plus intravenous 5-FU (1000 mg/m2/day, Days 1–4) were administered every 3 weeks (1 cycle) for a maximum of 6 cycles in the absence of disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Cetuximab was administered at a 400 mg/m2 initial dose, followed by a 250 mg/m2 weekly dose in combination with chemotherapy. Patients demonstrating at least stable disease on cetuximab in combination with chemotherapy were to continue cetuximab monotherapy at 250 mg/m2 weekly, in the absence of disease progression or unacceptable toxicity after completion of 6 planned courses of platinum-based therapy. For patients where treatment was delayed because of the toxic effects of chemotherapy, weekly cetuximab was continued. If chemotherapy was discontinued for toxicity, cetuximab could be continued as monotherapy until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Of the 442 randomized patients, the median age was 57 years, 90% were male, 98% were Caucasian, and 88% had baseline Karnofsky performance status ≥80. Thirty-four percent of patients had oropharyngeal, 25% laryngeal, 20% oral cavity, and 14% hypopharyngeal primary tumors. Fifty-three percent of patients had recurrent locoregional disease only and 47% had metastatic disease. Fifty-eight percent had AJCC Stage IV disease and 21% had Stage III disease. Sixty-four percent of patients received cisplatin therapy and 34% received carboplatin as initial therapy. Approximately fifteen percent of the patients in the cisplatin alone arm switched to carboplatin during the treatment period.
The main outcome measure of this trial was overall survival. Results are presented in Table 7 and Figure 1.
| EU-Approved Cetuximab + Platinum-based Therapy + 5-FU (n=222) |
Platinum-based Therapy + 5-FU (n=220) |
Hazard Ratio (95% CIa) |
Stratified Log-rank p-value |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a CI = confidence interval | ||||
| b CMH = Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel | ||||
| Overall Survival | ||||
| Median duration (months) | 10.1 | 7.4 | 0.80 (0.64, 0.98) | 0.034 |
| Progression-free Survival | ||||
| Median duration (months) | 5.5 | 3.3 | 0.57 (0.46, 0.72) | <0.0001 |
| EU-Approved Cetuximab + Platinum-based Therapy + 5-FU (n=222) |
Platinum-based Therapy + 5-FU (n=220) |
Odds Ratio (95% CIa) |
CMHb test p-value |
|
| Objective Response Rate | 35.6% | 19.5% | 2.33 (1.50, 3.60) | 0.0001 |
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curve for Overall Survival in Patients with Recurrent Locoregional Disease or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
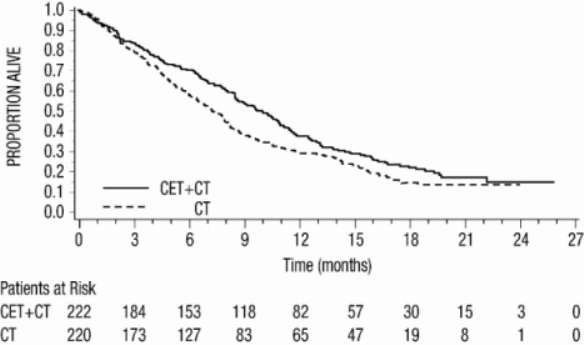
CT = Platinum-based therapy with 5-FU
CET = EU-approved cetuximab
In exploratory subgroup analyses of Study 2 by initial platinum therapy (cisplatin or carboplatin), for patients (N=284) receiving cetuximab plus cisplatin with 5-FU compared to cisplatin with 5-FU alone, the difference in median overall survival was 3.3 months (10.6 versus 7.3 months, respectively; HR 0.71; 95% CI 0.54, 0.93). The difference in median progression-free survival was 2.1 months (5.6 versus 3.5 months, respectively; HR 0.55; 95% CI 0.41, 0.73). The objective response rate was 39% and 23% respectively (OR 2.18; 95% CI 1.29, 3.69). For patients (N=149) receiving cetuximab plus carboplatin with 5-FU compared to carboplatin with 5-FU alone, the difference in median overall survival was 1.4 months (9.7 versus 8.3 months; HR 0.99; 95% CI 0.69, 1.43). The difference in median progression-free survival was 1.7 months (4.8 versus 3.1 months, respectively; HR 0.61; 95% CI 0.42, 0.89). The objective response rate was 30% and 15% respectively (OR 2.45; 95% CI 1.10, 5.46).
Study 3 was a single-arm, multicenter clinical trial in 103 patients with recurrent or metastatic SCCHN. All patients had documented disease progression within 30 days of a platinum-based chemotherapy regimen. Patients received a 20-mg test dose of Erbitux on Day 1, followed by a 400 mg/m2 initial dose, and 250 mg/m2 weekly until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The median age was 57 years, 82% were male, 100% Caucasian, and 62% had a Karnofsky performance status of ≥80.
The objective response rate was 13% (95% confidence interval 7%–21%). Median duration of response was 5.8 months (range 1.2–5.8 months).
14.2 Colorectal Cancer
Erbitux Clinical Trials in Mutation-negative (Wild-type), EGFR-expressing, Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Study 4 was a randomized, open-label, multicenter, study of 1217 patients with EGFR-expressing metastatic colorectal cancer. Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive either EU-approved cetuximab in combination with FOLFIRI or FOLFIRI alone as first-line treatment. Stratification factors were Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (0 and 1 versus 2) and region (sites in Western Europe versus Eastern Europe versus other).
FOLFIRI regimen included 14-day cycles of irinotecan (180 mg/m2 administered intravenously on Day 1), folinic acid (400 mg/m2 [racemic] or 200 mg/m2 [L-form] administered intravenously on Day 1), and 5-FU (400 mg/m2 bolus on Day 1 followed by 2400 mg/m2 as a 46-hour continuous infusion). Cetuximab was administered as a 400 mg/m2 initial dose on Day 1, Week 1, followed by 250 mg/m2 weekly administered 1 hour prior to chemotherapy. Study treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
Of the 1217 randomized patients, the median age was 61 years, 60% were male, 86% were Caucasian, and 96% had a baseline ECOG performance status 0–1, 60% had primary tumor localized in colon, 84% had 1–2 metastatic sites and 20% had received prior adjuvant and/or neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Demographics and baseline characteristics were similar between study arms.
K-Ras mutation status was available for 1079/1217 (89%) of the patients: 676 (63%) patients had K-Ras mutation-negative (wild-type) tumors and 403 (37%) patients had K-Ras mutation-positive tumors where testing assessed for the following somatic mutations in codons 12 and 13 (exon 2): G12A, G12D, G12R, G12C, G12S, G12V, G13D [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ].
Baseline characteristics and demographics in the K-Ras mutation-negative (wild-type) subset were similar to that seen in the overall population [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ].
The main outcome measure of this trial was progression-free survival assesed by an independent review committee (IRC). Overall survival and response rate were also assessed. A statistically significant improvement in PFS was observed for the cetuximab plus FOLFIRI arm compared with the FOLFIRI arm (median PFS 8.9 vs 8.1 months, HR 0.85 [95% CI 0.74, 0.99], p-value=0.036). Overall survival was not significantly different at the planned, final analysis based on 838 events [HR=0.93, 95% CI (0.8, 1.1), p-value 0.327].
Results of the planned PFS and ORR analysis in all randomized patients and post-hoc PFS and ORR analysis in subgroups of patients defined by K-Ras mutation status, and post-hoc analysis of updated OS based on additional follow-up (1000 events) in all randomized patients and in subgroups of patients defined by K-Ras mutation status are presented in Table 8 and Figure 2. The treatment effect in the all-randomized population for PFS was driven by treatment effects limited to patients who have K-Ras mutation-negative (wild-type) tumors. There is no evidence of effectiveness in the subgroup of patients with K-Ras mutation-positive tumors.
| All Randomized |
K-Ras Mutation-negative (Wild-type) |
K-Ras Mutation-positive | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU-Approved Cetuximab plus FOLFIRI (n=608) |
FOLFIRI (n=609) |
EU-Approved Cetuximab plus FOLFIRI (n=320) |
FOLFIRI (n=356) |
EU-Approved Cetuximab plus FOLFIRI (n=216) |
FOLFIRI (n=187) |
|
| a Based on the Stratified Log-rank test. | ||||||
| b Post-hoc updated OS analysis, results based on an additional 162 events. | ||||||
| Progression-Free Survival | ||||||
| Number of Events (%) | 343 (56) | 371 (61) | 165 (52) | 214 (60) | 138 (64) | 112 (60) |
| Median (months) (95% CI) |
8.9 (8.0, 9.4) |
8.1 (7.6, 8.8) |
9.5 (8.9, 11.1) |
8.1 (7.4, 9.2) |
7.5 (6.7, 8.7) |
8.2 (7.4, 9.2) |
| HR (95% CI) | 0.85 (0.74, 0.99) | 0.70 (0.57, 0.86) | 1.13 (0.88, 1.46) | |||
| p-valuea | 0.0358 | |||||
| Overall Survivalb | ||||||
| Number of Events (%) | 491 (81) | 509 (84) | 244 (76) | 292 (82) | 189 (88) | 159 (85) |
| Median (months) (95% CI) |
19.6 (18, 21) |
18.5 (17, 20) |
23.5 (21, 26) |
19.5 (17, 21) |
16.0 (15, 18) |
16.7 (15, 19) |
| HR (95% CI) | 0.88 (0.78, 1.0) | 0.80 (0.67, 0.94) | 1.04 (0.84, 1.29) | |||
| Objective Response Rate | ||||||
| ORR (95% CI) | 46% (42, 50) | 38% (34, 42) | 57% (51, 62) | 39% (34, 44) | 31% (25, 38) | 35% (28, 43) |
Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier Curve for Overall Survival in the K-Ras Mutation-negative (Wild-type) Population in Study 4

Study 5 was a multicenter, open-label, randomized, clinical trial conducted in 572 patients with EGFR-expressing, previously treated, recurrent mCRC. Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive either Erbitux plus best supportive care (BSC) or BSC alone. Erbitux was administered as a 400 mg/m2 initial dose, followed by 250 mg/m2 weekly until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Of the 572 randomized patients, the median age was 63 years, 64% were male, 89% were Caucasian, and 77% had baseline ECOG performance status of 0–1. Demographics and baseline characteristics were similar between study arms. All patients were to have received and progressed on prior therapy including an irinotecan-containing regimen and an oxaliplatin-containing regimen.
K-Ras status was available for 453/572 (79%) of the patients: 245 (54%) patients had K-Ras mutation-negative (wild-type) tumors and 208 (46%) patients had K-Ras mutation-positive tumors where testing assessed for the following somatic mutations in codons 12 and 13 (exon 2): G12A, G12D, G12R, G12C, G12S, G12V, G13D [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ].
The main outcome measure of the study was overall survival. Results are presented in Table 9 and Figure 3.
| All Randomized |
K-Ras Mutation-negative (Wild-type) |
K-Ras Mutation-positive | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erbitux plus BSC (N=287) |
BSC (N=285) |
Erbitux plus BSC (N=117) |
BSC (N=128) |
Erbitux plus BSC (N=108) |
BSC (N=100) |
|
| a Based on the Stratified Log-rank test. | ||||||
| Median (months) (95% CI) |
6.1 (5.4, 6.7) |
4.6 (4.2, 4.9) |
8.6 (7.0, 10.3) |
5.0 (4.3, 5.7) |
4.8 (3.9, 5.6) |
4.6 (3.6, 4.9) |
| HR (95% CI) |
0.77 (0.64, 0.92) |
0.63 (0.47, 0.84) |
0.91 (0.67, 1.24) |
|||
| p-valuea | 0.0046 | |||||
Figure 3: Kaplan-Meier Curve for Overall Survival in Patients with K-Ras Mutation-negative (Wild-type) Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in Study 5

Study 6 was a multicenter, clinical trial conducted in 329 patients with EGFR-expressing recurrent mCRC. Tumor specimens were not available for testing for K-Ras mutation status. Patients were randomized (2:1) to receive either Erbitux plus irinotecan (218 patients) or Erbitux monotherapy (111 patients). Erbitux was administered as a 400 mg/m2 initial dose, followed by 250 mg/m2 weekly until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. In the Erbitux plus irinotecan arm, irinotecan was added to Erbitux using the same dose and schedule for irinotecan as the patient had previously failed. Acceptable irinotecan schedules were 350 mg/m2 every 3 weeks, 180 mg/m2 every 2 weeks, or 125 mg/m2 weekly times four doses every 6 weeks. Of the 329 patients, the median age was 59 years, 63% were male, 98% were Caucasian, and 88% had baseline Karnofsky performance status ≥80. Approximately two-thirds had previously failed oxaliplatin treatment.
The efficacy of Erbitux plus irinotecan or Erbitux monotherapy, based on durable objective responses, was evaluated in all randomized patients and in two pre-specified subpopulations: irinotecan refractory patients, and irinotecan and oxaliplatin failures. In patients receiving Erbitux plus irinotecan, the objective response rate was 23% (95% confidence interval 18%–29%), median duration of response was 5.7 months, and median time to progression was 4.1 months. In patients receiving Erbitux monotherapy, the objective response rate was 11% (95% confidence interval 6%–18%), median duration of response was 4.2 months, and median time to progression was 1.5 months. Similar response rates were observed in the pre-defined subsets in both the combination arm and monotherapy arm of the study.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Erbitux® (cetuximab) is supplied at a concentration of 2 mg/mL as a 100 mg/50 mL, single-use vial or as a 200 mg/100 mL, single-use vial as a sterile, injectable liquid containing no preservatives.
NDC 66733-948-23 100 mg/50 mL, single-use vial, individually packaged in a carton
NDC 66733-958-23 200 mg/100 mL, single-use vial, individually packaged in a carton
Store vials under refrigeration at 2° C to 8° C (36° F to 46° F). Do not freeze. Increased particulate formation may occur at temperatures at or below 0° C. This product contains no preservatives. Preparations of Erbitux in infusion containers are chemically and physically stable for up to 12 hours at 2° C to 8° C (36° F to 46° F) and up to 8 hours at controlled room temperature (20° C to 25° C; 68° F to 77° F). Discard any remaining solution in the infusion container after 8 hours at controlled room temperature or after 12 hours at 2° C to 8° C. Discard any unused portion of the vial.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients:
- To report signs and symptoms of infusion reactions such as fever, chills, or breathing problems.
- Of the potential risks of using Erbitux during pregnancy or nursing and of the need to use adequate contraception in both males and females during and for 6 months following the last dose of Erbitux therapy.
- That nursing is not recommended during, and for 2 months following the last dose of Erbitux therapy.
- To limit sun exposure (use sunscreen, wear hats) while receiving and for 2 months following the last dose of Erbitux.
—————————————————————————————————
Erbitux® is a registered trademark of ImClone LLC a wholly-owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly and Company.
Manufactured by ImClone LLC a wholly-owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly and Company, Branchburg, NJ 08876 USA
Distributed and marketed by Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Princeton, NJ 08543 USA
Co-marketed by Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN 46285 USA
Copyright © 2004–2013 ImClone LLC a wholly-owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly and Company, and Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. All rights reserved.
1236886B3
Rev August 2013
---------------------------------------------
REPRESENTATIVE PACKAGING
See HOW SUPPLIED section for a complete list of available packages of Erbitux.
NDC 66733-948-23
ERBITUX®
CETUXIMAB
Injection
For intravenous infusion
Rx only
100 mg/50 mL
(2 mg/mL)
DO NOT DILUTE
Bristol-Myers Squibb
Lilly

NDC 66733-958-23
ERBITUX®
CETUXIMAB
Injection
For intravenous infusion
Rx only
200 mg/100 mL
(2 mg/mL)
DO NOT DILUTE
Bristol-Myers Squibb
Lilly

ERBITUXcetuximab SOLUTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ERBITUXcetuximab SOLUTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||