Felodipine
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- FELODIPINE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- FELODIPINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- FELODIPINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- PRECAUTIONS
- FELODIPINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- FELODIPINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 2.5 mg (100 Tablet Bottle)
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 2.5 mg Blister Carton (10 x 10 Unit-dose)
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 5 mg (100 Tablet Bottle)
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 10 mg (100 Tablet Bottle)
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 10 mg Blister Carton (10 x 10 Unit-dose)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
FELODIPINE DESCRIPTION
181924
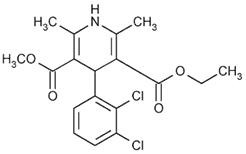
aluminium silicateFD&C blue #2
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
++
In vitro in vitro
Cardiovascular Effects
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
1/2
1/2 50
50 Cardiovascular Effects DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
14
max
Geriatric Use
Cardiovascular Effects
PRECAUTIONS
Renal/Endocrine Effects
Clinical Studies
| Dose | N | Systolic /Diastolic Mean Peak Response |
Mean Trough Response |
Trough/Peak Ratios (%s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
*
Placebo response subtracted ** Different number of patients available for peak and trough measurements |
||||
| Study 1 (8 weeks) |
||||
| 2.5 mg |
68 |
9.4/4.7 |
2.7/2.5 |
29/53 |
| 5 mg |
69 |
9.5/6.3 |
2.4/3.7 |
25/59 |
| 10 mg |
67 |
18/10.8 |
10/6 |
56/56 |
| Study 2 (4 weeks) |
||||
| 10 mg |
50 |
5.3/7.2 |
1.5/3.2 |
33/40
**
|
| 20 mg |
50 |
11.3/10.2 |
4.5/3.2 |
43/34
**
|
FELODIPINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Felodipine extended-release tablets, USP are indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure lowers the risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes including felodipine.
Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than 1 drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program’s Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC).
Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly.
Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal.
Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy.
Felodipine extended-release tablets, USP may be administered with other antihypertensive agents.
FELODIPINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
PRECAUTIONS
General
ADVERSE REACTIONS
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Information for Patients
Drug Interactions
Itraconazole
max
Erythromycin
max
Grapefruit Juice
max
Cimetidine
max
Beta-Blocking Agents
max
Digoxin
Anticonvulsants
Tacrolimus
Other Concomitant Therapy
Interaction with Food
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
**2 **2
**2
in vitro in vivo **2in vitro
**2
**
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
** 2
Nonteratogenic Effects
**2
2
**
Nursing Mothers
Pediatric Use
Geriatric Use
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Geriatric Use
FELODIPINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
| Body System Adverse Events |
Placebo N = 334 |
2.5 mg N = 255 |
5 mg N = 581 |
10 mg N = 408 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
* Patients in titration studies may have been exposed to more than one dose level of felodipine extended-release tablets. |
||||
|
Body as a Whole
|
||||
| Peripheral Edema
|
3.3 (0)
|
2 (0)
|
8.8 (2.2)
|
17.4 (2.5)
|
| Asthenia
|
3.3 (0)
|
3.9 (0)
|
3.3 (0)
|
2.2 (0)
|
| Warm Sensation
|
0 (0)
|
0 (0)
|
0.9 (0.2)
|
1.5 (0)
|
|
Cardiovascular
|
||||
| Palpitation |
2.4 (0) |
0.4 (0) |
1.4 (0.3) |
2.5 (0.5) |
|
Digestive
|
||||
| Nausea |
1.5 (0.9) |
1.2 (0) |
1.7 (0.3) |
1 (0.7) |
| Dyspepsia |
1.2 (0) |
3.9 (0) |
0.7 (0) |
0.5 (0) |
| Constipation |
0.9 (0) |
1.2 (0) |
0.3 (0) |
1.5 (0.2) |
|
Nervous
|
||||
| Headache |
10.2 (0.9) |
10.6 (0.4) |
11 (1.7) |
14.7 (2) |
| Dizziness |
2.7 (0.3) |
2.7 (0) |
3.6 (0.5) |
3.7 (0.5) |
| Paresthesia |
1.5 (0.3) |
1.6 (0) |
1.2 (0) |
1.2 (0.2) |
|
Respiratory
|
||||
| Upper Respiratory Infection |
1.8 (0) |
3.9 (0) |
1.9 (0) |
0.7 (0) |
| Cough |
0.3 (0) |
0.8 (0) |
1.2 (0) |
1.7 (0) |
| Rhinorrhea |
0 (0) |
1.6 (0) |
0.2 (0) |
0.2 (0) |
| Sneezing |
0 (0) |
1.6 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
Skin
|
||||
| Rash |
0.9 (0) |
2 (0) |
2 (0) |
2 (0) |
| Flushing |
0.9 (0.3) |
3.9 (0) |
5.3 (0.7) |
6.9 (1.2) |
Body as a Whole:
Cardiovascular: Myocardial infarction, hypotension, syncope, angina pectorisarrhythmia
Digestive:
Endocrine:
Hematologic: Anemia
Metabolic:
Musculoskeletal:
Nervous/Psychiatric:
Respiratory:
Skin: Angioedema, , leukocytoclastic vasculitis
Special Senses:
Urogenital:
Gingival Hyperplasia: PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patients.)
Clinical Laboratory Test Findings
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Renal/Endocrine Effects
OVERDOSAGE
Physicians' Desk Reference (PDR)
FELODIPINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Geriatric Use
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Patients with Impaired Liver Function
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
HOW SUPPLIED
Felodipine Extended-Release Tablets USP, 2.5 mg
Felodipine Extended-Release Tablets USP, 5 mg
Felodipine Extended-Release Tablets USP, 10 mg
Store at
Protect from light.
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 2.5 mg (100 Tablet Bottle)
NDC 65862-673-01
Felodipine Extended-Release
Tablets, USP
2.5 mg
Rx only 100 Tablets
AUROBINDO

PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 2.5 mg Blister Carton (10 x 10 Unit-dose)
NDC 65862-673-78
Felodipine Extended-Release
Tablets, USP 2.5 mg
Rx only 100 (10 x 10) Unit-dose Tablets
AUROBINDO

PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 5 mg (100 Tablet Bottle)
NDC 65862-674-01
Felodipine Extended-Release
Tablets, USP
5 mg
Rx only 100 Tablets
AUROBINDO

PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 10 mg (100 Tablet Bottle)
NDC 65862-675-01
Felodipine Extended-Release
Tablets, USP
10 mg
Rx only 100 Tablets
AUROBINDO

PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 10 mg Blister Carton (10 x 10 Unit-dose)
NDC 65862-675-78
Felodipine Extended-Release
Tablets, USP 10 mg
Rx only 100 (10 x 10) Unit-dose Tablets
AUROBINDO

FelodipineFelodipine TABLET, FILM COATED, EXTENDED RELEASE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FelodipineFelodipine TABLET, FILM COATED, EXTENDED RELEASE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FelodipineFelodipine TABLET, FILM COATED, EXTENDED RELEASE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||