Flector
Flector® Patch (diclofenac epolamine topical patch) 1.3%
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- Cardiovascular Risk
- FLECTOR DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- FLECTOR INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- FLECTOR CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- FLECTOR ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- FLECTOR DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- What are Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
- Who should not take a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)?
- What are the possible side effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
- Get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Stop your NSAID medicine and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Flector Other information about Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Principal Display Panel
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION

Cardiovascular Risk
Gastrointestinal Risk
1 Throughout this package insert, the term NSAID refers to a non-aspirin non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
FLECTOR DESCRIPTION
Flector® Patch (10 cm x 14 cm) is comprised of an adhesive material containing 1.3% diclofenac epolamine which is applied to a non-woven polyester felt backing and covered with a polypropylene film release liner. The release liner is removed prior to topical application to the skin.
Diclofenac epolamine is a non-opioid analgesic chemically designated as 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl) amino]benzeneacetic acid, (2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl) ethanol salt, with a molecular formula of C20H24Cl2N2O3 (molecular weight 411.3), an n-octanol/water partition coefficient of 8 at pH 8.5, and the following structure:

Each adhesive patch contains 180 mg of diclofenac epolamine (13 mg per gram adhesive) in an aqueous base. It also contains the following inactive ingredients: 1,3-butylene glycol, dihydroxyaluminum aminoacetate, disodium edetate, D-sorbitol, fragrance (Dalin PH), gelatin, kaolin, methylparaben, polysorbate 80, povidone, propylene glycol, propylparaben, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, sodium polyacrylate, tartaric acid, titanium dioxide, and purified water.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacodynamics
Flector® Patch applied to intact skin provides local analgesia by releasing diclofenac epolamine from the patch into the skin. Diclofenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). In pharmacologic studies, diclofenac has shown anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activity. As with other NSAIDs, its mode of action is not known; its ability to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, however, may be involved in its anti-inflammatory activity, as well as contribute to its efficacy in relieving pain associated with inflammation.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following a single application of the Flector Patch on the upper inner arm, peak plasma concentrations of diclofenac (range 0.7 – 6 ng/mL) were noted between 10 – 20 hours of application. Plasma concentrations of diclofenac in the range of 1.3 – 8.8 ng/mL were noted after five days with twice-a-day Flector Patch application.
Systemic exposure (AUC) and maximum plasma concentrations of diclofenac, after repeated dosing for four days with Flector® Patch, were lower (<1%) than after a single oral 50 mg diclofenac sodium tablet.
The pharmacokinetics of Flector® Patch has been tested in healthy volunteers at rest or undergoing moderate exercise (cycling 20 min/h for 12 h at a mean HR of 100.3 bpm). No clinically relevant differences in systemic absorption were observed, with peak plasma concentrations in the range of 2.2 – 8.1 ng/m while resting, and 2.7 – 7.2 ng/mL during exercise.
Distribution
Diclofenac has a very high affinity (>99%) for human serum albumin.
Metabolism and Excretion
The plasma elimination half-life of diclofenac after application of Flector Patch is approximately 12 hours. Diclofenac is eliminated through metabolism and subsequent urinary and biliary excretion of the glucuronide and the sulfate conjugates of the metabolites.
CLINICAL STUDIES
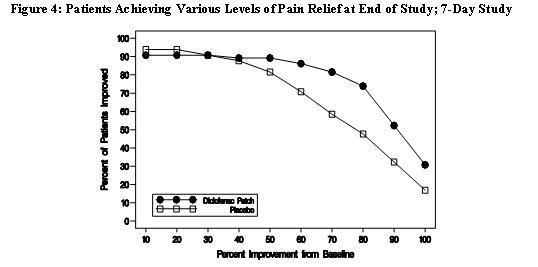
Efficacy of Flector® Patch was demonstrated in two of four studies of patients with minor sprains, strains, and contusions. Patients were randomly assigned to treatment with the Flector® Patch, or a placebo patch identical to the Flector® Patch minus the active ingredient. In the first of these two studies, patients with ankle sprains were treated once daily for a week. In the second study, patients with sprains, strains and contusions were treated twice daily for up to two weeks. Pain was assessed over the period of treatment. Patients treated with the Flector® Patch experienced a greater reduction in pain as compared to patients randomized to placebo patch as evidenced by the responder curves presented below.



FLECTOR INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of Flector® Patch and other treatment options before deciding to use Flector® Patch. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS ).
Flector® Patch is indicated for the topical treatment of acute pain due to minor strains, sprains, and contusions.
FLECTOR CONTRAINDICATIONS
Flector® Patch is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to diclofenac.
Flector® Patch should not be given to patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients (see WARNINGS - Anaphylactoid Reactions , and PRECAUTIONS - Preexisting Asthma ).
Flector® Patch is contraindicated for the treatment of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS ).
Flector® Patch should not be applied to non-intact or damaged skin resulting from any etiology e.g. exudative dermatitis, eczema, infected lesion, burns or wounds.
WARNINGS
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. All NSAIDs, both COX-2 selective and nonselective, may have a similar risk. Patients with known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease may be at greater risk. To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the signs and/or symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID does increase the risk of serious GI events (see GI WARNINGS ).
Two large, controlled, clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10-14 days following CABG surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke (see CONTRAINDICATIONS ).
Hypertension
NSAIDs, including Flector® Patch, can lead to onset of new hypertension or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking thiazides or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. NSAIDs, including Flector® Patch, should be used with caution in patients with hypertension. Blood pressure (BP) should be monitored closely during the initiation of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
Congestive Heart Failure and Edema
Fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients taking NSAIDs. Flector® Patch should be used with caution in patients with fluid retention or heart failure.
Gastrointestinal Effects- Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including Flector® Patch, can cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients, who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy, is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occur in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3-6 months, and in about 2-4% of patients treated for one year. These trends continue with longer duration of use, increasing the likelihood of developing a serious GI event at some time during the course of therapy. However, even short-term therapy is not without risk.
NSAIDs should be prescribed with extreme caution in those with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding who use NSAIDs have a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing a GI bleed compared to patients with neither of these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk for GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, older age, and poor general health status. Most spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in elderly or debilitated patients and therefore, special care should be taken in treating this population.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse GI event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible duration. Patients and physicians should remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during NSAID therapy and promptly initiate additional evaluation and treatment if a serious GI adverse event is suspected. This should include discontinuation of the NSAID until a serious GI adverse event is ruled out. For high risk patients, alternate therapies that do not involve NSAIDs should be considered.
Renal Effects
Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury. Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors, and the elderly. Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment state.
Advanced Renal Disease
No information is available from controlled clinical studies regarding the use of Flector® Patch in patients with advanced renal disease. Therefore, treatment with Flector® Patch is not recommended in these patients with advanced renal disease. If Flector® Patch therapy is initiated, close monitoring of the patient's renal function is advisable.
Anaphylactoid Reactions
As with other NSAIDs, anaphylactoid reactions may occur in patients without known prior exposure to Flector® Patch. Flector® Patch should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad. This symptom complex typically occurs in asthmatic patients who experience rhinitis with or without nasal polyps, or who exhibit severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS - Preexisting Asthma ). Emergency help should be sought in cases where an anaphylactoid reaction occurs.
Skin Reactions
NSAIDs, including Flector® Patch, can cause serious skin adverse events such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Patients should be informed about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations and use of the drug should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Pregnancy
In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, Flector® Patch should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Flector® Patch cannot be expected to substitute for corticosteroids or to treat corticosteroid insufficiency. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to disease exacerbation. Patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should have their therapy tapered slowly if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids.
The pharmacological activity of Flector® Patch in reducing inflammation may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, painful conditions.
Hepatic Effects
Borderline elevations of one or more liver tests may occur in up to 15% of patients taking NSAIDs including Flector® Patch. These laboratory abnormalities may progress, may remain unchanged, or may be transient with continuing therapy. Notable elevations of ALT or AST (approximately three or more times the upper limit of normal) have been reported in approximately 1% of patients in clinical trials with NSAIDs. In addition, rare cases of severe hepatic reactions, including jaundice and fatal fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis and hepatic failure, some of them with fatal outcomes have been reported.
A patient with symptoms and/or signs suggesting liver dysfunction, or in whom an abnormal liver test has occurred, should be evaluated for evidence of the development of a more severe hepatic reaction while on therapy with Flector® Patch. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), Flector® Patch should be discontinued.
Hematological Effects
Anemia is sometimes seen in patients receiving NSAIDs. This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including Flector® Patch, should have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs or symptoms of anemia.
NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown to prolong bleeding time in some patients. Unlike aspirin, their effect on platelet function is quantitatively less, of shorter duration, and reversible. Patients receiving Flector® Patch who may be adversely affected by alterations in platelet function, such as those with coagulation disorders or patients receiving anticoagulants, should be carefully monitored.
Preexisting Asthma
Patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma. The use of aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma has been associated with severe bronchospasm which can be fatal. Since cross reactivity, including bronchospasm, between aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, Flector® Patch should not be administered to patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity and should be used with caution in patients with preexisting asthma.
Eye Exposure
Contact of Flector® Patch with eyes and mucosa, although not studied, should be avoided. If eye contact occurs, immediately wash out the eye with water or saline. Consult a physician if irritation persists for more than an hour.
Accidental Exposure in Children
Even a used Flector® Patch contains a large amount of diclofenac epolamine (as much as 170 mg). The potential therefore exists for a small child or pet to suffer serious adverse effects from chewing or ingesting a new or used Flector® Patch. It is important for patients to store and dispose of Flector® Patch out of the reach of children and pets.
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed of the following information before initiating therapy with an NSAID and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy. Patients should also be encouraged to read the NSAID Medication Guide that accompanies each prescription dispensed.
Laboratory Tests
Because serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, physicians should monitor for signs or symptoms of GI bleeding. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, should have their CBC and a chemistry profile checked periodically. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver or renal disease develop, systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.) or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, Flector® Patch should be discontinued.
Drug Interactions
ACE-inhibitors
Reports suggest that NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE-inhibitors. This interaction should be given consideration in patients taking NSAIDs concomitantly with ACE-inhibitors.
Aspirin
When Flector® Patch is administered with aspirin, the binding of diclofenac to protein is reduced, although the clearance of free diclofenac is not altered. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known; however, as with other NSAIDs, concomitant administration of diclofenac and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential of increased adverse effects.
Diuretics
Clinical studies, as well as post marketing observations, have shown that Flector® Patch may reduce the natriuretic effect-of furosemide and thiazides in some patients. This response has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. During concomitant therapy with NSAIDs, the patient should be observed closely for signs of renal failure (see WARNINGS, Renal Effects ), as well as to assure diuretic efficacy.
Lithium
NSAIDs have produced an elevation of plasma lithium levels and a reduction in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15% and the renal clearance was decreased by approximately 20%. These effects have been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis by the NSAID. Thus, when NSAIDs and lithium are administered concurrently, subjects should be observed carefully for signs of lithium toxicity.
Methotrexate
NSAIDs have been reported to competitively inhibit methotrexate accumulation in rabbit kidney slices. This may indicate that they could enhance the toxicity of methotrexate. Caution should be used when NSAIDs are administered concomitantly with methotrexate.
Warfarin
The effects of warfarin and NSAIDs on GI bleeding are synergistic, such that users of both drugs together have a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of either diclofenac epolamine or Flector Patch.
Mutagenesis
Diclofenac epolamine is not mutagenic in Salmonella Typhimurium strains, nor does it induce an increase in metabolic aberrations in cultured human lymphocytes, or the frequency of micronucleated cells in the bone marrow micronucleus test performed in rats.
Impairment of Fertility
Male and female Sprague Dawley rats were administered 1, 3, or 6 mg/kg/day diclofenac epolamine via oral gavage (males treated for 60 days prior to conception and during mating period, females treated for 14 days prior to mating through day 19 of gestation). Diclofenac epolamine treatment with 6 mg/kg/day resulted in increased early resorptions and postimplantation losses; however, no effects on the mating and fertility indices were found. The 6 mg/kg/day dose corresponds to 3-times the maximum recommended daily exposure in humans based on a body surface area comparison.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects Pregnancy Category C.
Pregnant Sprague Dawley rats were administered 1, 3, or 6 mg/kg diclofenac epolamine via oral gavage daily from gestation days 6-15. Maternal toxicity, embryotoxicity, and increased incidence of skeletal anomalies were noted with 6 mg/kg/day diclofenac epolamine, which corresponds to 3-times the maximum recommended daily exposure in humans based on a body surface area comparison. Pregnant New Zealand White rabbits were administered 1, 3, or 6 mg/kg diclofenac epolamine vial oral gavage daily from gestation days 6-18. No maternal toxicity was noted; however, embryotoxicity was evident at 6 mg/kg/day group which corresponds to 6.5-times the maximum recommended daily exposure in humans based on a body surface area comparison.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Flector Patch should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Because of the known effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of ductus arteriosus), use during pregnancy (particularly late pregnancy) should be avoided.
Male rats were orally administered diclofenac epolamine (1, 3, 6 mg/kg) for 60 days prior to mating and throughout the mating period, and females were given the same doses 14 days prior to mating and through mating, gestation, and lactation. Embryotoxicity was observed at 6 mg/kg diclofenac epolamine (3-times the maximum recommended daily exposure in humans based on a body surface area comparison), and was manifested as an increase in early resorptions, post-implantation losses, and a decrease in live fetuses. The number of live born and total born were also reduced as was F1 postnatal survival, but the physical and behavioral development of surviving F1 pups in all groups was the same as the deionized water control, nor was reproductive performance adversely affected despite a slight treatment-related reduction in body weight.
Labor and Delivery
In rat studies with NSAIDs, as with other drugs known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, an increased incidence of dystocia, delayed parturition, and decreased pup survival occurred. The effects of Flector® Patch on labor and delivery in pregnant women are unknown.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human-milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Flector® Patch, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Flector® Patch did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
Diclofenac, as with any NSAID, is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to Flector® Patch may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken when using Flector® Patch in the elderly, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
FLECTOR ADVERSE REACTIONS
In controlled trials during the premarketing development of Flector® Patch, approximately 600 patients with minor sprains, strains, and contusions have been treated with Flector® Patch for up to two weeks.
Adverse Events Leading to Discontinuation of Treatment
In the controlled trials, 3% of patients in both the Flector® Patch and placebo patch groups discontinued treatment due to an adverse event. The most common adverse events leading to discontinuation were application site reactions, occurring in 2% of both the Flector® Patch and placebo patch groups. Application site reactions leading to dropout included pruritus, dermatitis, and burning.
Common Adverse Events
Localized Reactions
Overall, the most common adverse events associated with Flector® Patch treatment were skin reactions at the site of treatment.
Table 1 lists all adverse events, regardless of causality, occurring in ≥ 1% of patients in controlled trials of Flector® Patch. A majority of patients treated with Flector® Patch had adverse events with a maximum intensity of “mild” or “moderate.”
| Diclofenac N=572 | Placebo N=564 | |||
| N | Percent | N | Percent | |
| 1 The table lists adverse events occurring in placebo-treated patients because the placebo-patch was comprised of the same ingredients as Flector® Patch except for diclofenac. Adverse events in the placebo group may therefore reflect effects of the non-active ingredients. | ||||
| 2 Includes: application site dryness, irritation, erythema, atrophy, discoloration, hyperhidriosis, and vesicles. | ||||
| 3 Includes: gastritis, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, upper abdominal pain, and dry mouth. | ||||
| 4 Includes: hypoaesthesia, dizziness, and hyperkinesias. | ||||
| Application Site Conditions | 64 | 11 | 70 | 12 |
| Pruritus | 31 | 5 | 44 | 8 |
| Dermatitis | 9 | 2 | 3 | < 1 |
| Burning | 2 | <1 | 8 | 1 |
| Other2 | 22 | 4 | 15 | 3 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | 49 | 9 | 33 | 6 |
| Nausea | 17 | 3 | 11 | 2 |
| Dysgeusia | 10 | 2 | 3 | < 1 |
| Dyspepsia | 7 | 1 | 8 | 1 |
| Other3 | 15 | 3 | 11 | 2 |
| Nervous System Disorders | 13 | 2 | 18 | 3 |
| Headache | 7 | 1 | 10 | 2 |
| Paresthesia | 6 | 1 | 8 | 1 |
| Somnolence | 4 | 1 | 6 | 1 |
| Other4 | 4 | 1 | 3 | < 1 |
Foreign labeling describes that dermal allergic reactions may occur with Flector® Patch treatment. Additionally, the treated area may become irritated or develop itching, erythema, edema, vesicles, or abnormal sensation.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Controlled Substance Class
Flector® Patch is not a controlled substance.
Physical and Psychological Dependence
Diclofenac, the active ingredient in Flector® Patch, is an NSAID that does not lead to physical or psychological dependence.
OVERDOSAGE
There is limited experience with overdose of Flector® Patch. In clinical studies, the maximum single dose administered was one Flector® Patch containing 180 mg of diclofenac epolamine. There were no serious adverse events.
Should systemic side effects occur due to incorrect use or accidental overdose of this product, the general measures recommended for intoxication with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be taken.
FLECTOR DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of Flector® Patch and other treatment options before deciding to use Flector® Patch. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS ).
The recommended dose of Flector® Patch is one (1) patch to the most painful area twice a day.
Flector® patch should not be applied to damaged or non-intact skin.
Flector® patch should not be worn when bathing or showering.
HANDLING AND DISPOSAL
Patients and caregivers should wash their hands after applying, handling or removing the patch. Eye contact should be avoided.
HOW SUPPLIED
The Flector® Patch is supplied in resealable envelopes, containing 1 patch (10 cm x 14 cm) (NDC 21695-707-01). It is also supplied in boxes of 30 patches (NDC 21695-707-30). Each individual patch is embossed with “Diclofenac Epolamine Patch 1.3%”.
Manufacturer: Teikoku Seiyaku Co., Ltd., Sanbonmatsu, Kagawa 769-2695, Japan
Distributor: Alpharma Pharmaceuticals LLC, One New England Avenue, Piscataway, NJ 08854 (Telephone: 1-877-452-3426)
Repackaged by: Rebel Distributors Corp, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
Medication Guide for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
(See the end of this Medication Guide for a list of prescription NSAID medicines.)
| What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)? | |
|
NSAID medicines may increase the chance of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death. This chance increases: ● with longer use of NSAID medicines ● in people who have heart disease |
|
| NSAID medicines should never be used right before or after a heart surgery called a “coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).” | |
|
NSAID medicines can cause ulcers and bleeding in the stomach and intestines at any time during treatment. Ulcers and bleeding:
● can happen without warning symptoms ● may cause death |
|
|
The chance of a person getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
● taking medicines called “corticosteroids” and “anticoagulants” ● longer use ● smoking ● drinking alcohol ● older age ● having poor health |
|
|
NSAID medicines should only be used:
● exactly as prescribed ● at the lowest dose possible for your treatment ● for the shortest time needed |
|
What are Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as:
Who should not take a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)?
Do not take an NSAID medicine:
Tell your healthcare provider:
What are the possible side effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
| Serious side effects include: | Other side effects include: |
| ● heart attack | ● stomach pain |
| ● stroke | ● constipation |
| ● high blood pressure | ● diarrhea |
| ● heart failure from body swelling (fluid retention) | ● gas |
| ● kidney problems including kidney failure | ● heartburn |
| ● bleeding and ulcers in the stomach and intestine | ● nausea |
| ● low red blood cells (anemia) | ● vomiting |
| ● life-threatening skin reactions | ● dizziness |
| ● life-threatening allergic reactions | |
| ● liver problems including liver failure | |
| ● asthma attacks in people who have asthma |
Get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
Stop your NSAID medicine and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
These are not all the side effects with NSAID medicines. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information about NSAID medicines.
Other information about Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAID medicines that need a prescription
| Generic Name | Tradename |
| Celecoxib | Celebrex |
| Diclofenac | Flector, Cataflam, Voltaren, Arthrotec (combined with misoprostol) |
| Diflunisal | Dolobid |
| Etodolac | Lodine, Lodine XL |
| Fenoprofen | Nalfon, Nalfon 200 |
| Flurbirofen | Ansaid |
| Ibuprofen | Motrin, Tab-Profen, Vicoprofen (combined with hydrocodone), Combunox (combined with oxycodone) |
| Indomethacin | Indocin, Indocin SR, Indo-Lemmon, Indomethagan |
| Ketoprofen | Oruvail |
| Ketorolac | Toradol |
| Mefenamic Acid | Ponstel |
| Meloxicam | Mobic |
| Nabumetone | Relafen |
| Naproxen | Naprosyn, Anaprox, Anaprox DS, EC-Naproxyn, Naprelan, Naprapac (copackaged with lansoprazole) |
| Oxaprozin | Daypro |
| Piroxicam | Feldene |
| Sulindac | Clinoril |
| Tolmetin | Tolectin, Tolectin DS, Tolectin 600 |
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by: Alpharma Pharmaceuticals LLC
One New England Avenue, Piscataway, NJ 08854 USA
(Telephone:1-888-840-8884) • www.FlectorPatch.com
Manufactured for: IBSA Institut Biochimique SA, CH-6903 Lugano, Switzerland
Manufactured by: Teikoku Seiyaku Co., Ltd., Sanbonmatsu, Kagawa 769-2695 Japan
Repackaged by: Rebel Distributors Corp, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
Principal Display Panel

FlectorDiclofenac epolamine PATCH
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||