Fluoxetine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use fluoxetine safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for fluoxetine capsules. Fluoxetine Capsules, USP for Oral Use Initial U.S. Approval: 1987 RECENT MAJOR CHANGES(5.10)BOXED WARNING WARNING: SUICIDALITY AND ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults taking antidepressants for Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders (5.1). When using fluoxetine and olanzapine in combination, also refer to Boxed Warning section of the package insert for Symbyax. INDICATIONS AND USAGE Acute and maintenance treatment of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) in adult and pediatric patients aged 8 to 18 years (1.1) Acute and maintenance treatment of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) in adult and pediatric patients aged 7 to 17 years (1.2) Acute and maintenance treatment of Bulimia Nervosa in adult patients (1.3) Acute treatment of Panic Disorder, with or without agoraphobia, in adult patients (1.4) Fluoxetine capsules and olanzapine in combination for: Acute treatment of Depressive Episodes Associated with Bipolar I Disorder in adults (1.5) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Indication Adult Pediatric MDD (2.1) 20 mg/day in am (initial dose) 10 to 20 mg/day (initial dose) OCD (2.2) 20 mg/day in am (initial dose) 10 mg/day (initial dose) Bulimia Nervosa (2.3) 60 mg/day in am - Panic Disorder (2.4) 10 mg/day (initial dose) - Depressive Episodes Associated with Bipolar I Disorder (2.5) Oral in combination with olanzapine: 5 mg of oral olanzapine and 20 mg of fluoxetine once daily (initial dose) - Consider tapering the dose of fluoxetine for pregnant women during the third trimester (2.7) A lower or less frequent dosage should be used in patients with hepatic impairment, the elderly, and for patients with concurrent disease or on multiple concomitant medications (2.7) Fluoxetine capsules and olanzapine in combination: Dosage adjustments, if indicated, should be made with the individual components according to efficacy and tolerability (2.5) Fluoxetine monotherapy is not indicated for the treatment of Depressive Episodes associated with Bipolar I Disorder (2.5) Safety of the coadministration of doses above 18 mg olanzapine with 75 mg fluoxetine has not been evaluated (2.5) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Capsules: 10 mg, 20 mg, and 40 mg (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS Do not use with an MAOI or within 14 days of discontinuing an MAOI due to risk of drug interaction. At least 5 weeks should be allowed after stopping fluoxetine capsules before treatment with an MAOI (4, 7.1) Do not use with pimozide due to risk of drug interaction or QTc prolongation (4, 7.9) Do not use with thioridazine due to QTc interval prolongation or potential for elevated thioridazine plasma levels. Do not use thioridazine within 5 weeks of discontinuing fluoxetine capsules (4, 7.9) When using fluoxetine capsules and olanzapine in combination, also refer to the Contraindications section of the package insert for Symbyax (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk: Monitor for clinical worsening and suicidal thinking and behavior (5.1) Serotonin Syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)-like Reactions: Have been reported with fluoxetine. Discontinue fluoxetine and initiate supportive treatment (5.2) Allergic Reactions and Rash: Discontinue upon appearance of rash or allergic phenomena (5.3) Activation of Mania/Hypomania: Screen for Bipolar Disorder and monitor for mania/hypomania (5.4) Seizures: Use cautiously in patients with a history of seizures or with conditions that potentially lower the seizure threshold (5.5) Altered Appetite and Weight: Significant weight loss has occurred (5.6) Abnormal Bleeding: May increase the risk of bleeding. Use with NSAIDs, aspirin, warfarin, or drugs that affect coagulation may potentiate the risk of gastrointestinal or other bleeding (5.7) Hyponatremia: Has been reported with fluoxetine in association with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) (5.8) Anxiety and Insomnia: May occur (5.9) Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment: Has potential to impair judgment, thinking, and motor skills. Use caution when operating machinery (5.11) Long Half-Life: Changes in dose will not be fully reflected in plasma for several weeks (5.12) Fluoxetine and Olanzapine in Combination: When using fluoxetine and olanzapine in combination, also refer to the Warnings and Precautions section of the package insert for Symbyax (5.14) Side Effects6.1To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Med-Health Pharma, LLC at 1-877-896-6654 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch DRUG INTERACTIONS Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI): Fluoxetine is contraindicated for use with MAOI’s, or within 14 days of discontinuing an MAOI due to risk of drug interaction. At least 5 weeks should be allowed after stopping fluoxetine before starting treatment with an MAOI (4, 7.1) Pimozide: Fluoxetine is contraindicated for use with pimozide due to risk of drug interaction or QTc prolongation (4, 7.9) Thioridazine: Fluoxetine is contraindicated for use with thioridazine due to QTc interval prolongation or potential for elevated thioridazine plasma levels. Do not use thioridazine within 5 weeks of discontinuing fluoxetine (4, 7.9) Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6: Fluoxetine is a potent inhibitor of CYP2D6 enzyme pathway (7.9) Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs): Monitor TCA levels during coadministration with fluoxetine or when fluoxetine has been recently discontinued (7.9) CNS Acting Drugs: Caution should be used when taken in combination with other centrally acting drugs (7.2) Benzodiazepines: Diazepam - increased t½, alprazolam – further psychomotor performance decrement due to increased levels (7.9) Antipsycotics: Potential for elevation of haloperidol and clozapine levels (7.9) Anticonvulsants: Potential for elevated phenytoin and carbamazepine levels and clinical anticonvulsant toxicity (7.9) Serotonergic Drugs: Potential for Serotonin Syndrome (5.2, 7.3) Triptans: There have been rare postmarketing reports of Serotonin Syndrome with use of an SSRI and a triptan (5.2, 7.4) Tryptophan: Concomitant use with tryptophan is not recommended (5.2, 7.5) Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g., NSAIDs, Aspirin, Warfarin): May potentiate the risk of bleeding (7.6) Drugs Tightly Bound to Plasma Proteins: May cause a shift in plasma concentrations (7.8, 7.9) Olanzapine: When used in combination with fluoxetine, also refer to the Drug Interactions section of the package insert for Symbyax (7.9) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: Fluoxetine should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risks to the fetus (8.1) Nursing Mothers: Breast feeding is not recommended (8.3) Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness of fluoxetine and olanzapine in combination have not been established in patients less than 18 years of age (8.4) Hepatic Impairment: Lower or less frequent dosing may be appropriate in patients with cirrhosis (8.6)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING: SUICIDALITY AND ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS
- 1 FLUOXETINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 FLUOXETINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 FLUOXETINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 5.1 Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
- 5.2 Serotonin Syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)-like Reactions
- 5.3 Allergic Reactions and Rash
- 5.4 Screening Patients for Bipolar Disorder and Monitoring for Mania/Hypomania
- 5.5 Seizures
- 5.6 Altered Appetite and Weight
- 5.7 Abnormal Bleeding
- 5.8 Hyponatremia
- 5.9 Anxiety and Insomnia
- 5.10 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
- 5.11 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
- 5.12 Long Elimination Half-Life
- 5.13 Discontinuation of Treatment
- 5.14 Fluoxetine and Olanzapine in Combination
- 6 FLUOXETINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 7.1 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI)
- 7.2 CNS Acting Drugs
- 7.3 Serotonergic Drugs
- 7.4 Triptans
- 7.5 Tryptophan
- 7.6 Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g., NSAIDs, Aspirin, Warfarin)
- 7.7 Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
- 7.8 Potential for Other Drugs to affect Fluoxetine
- 7.9 Potential for Fluoxetine to affect Other Drugs
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 FLUOXETINE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- 17.1 General Information
- 17.2 Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
- 17.3 Serotonin Syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)-like Reactions
- 17.4 Allergic Reactions and Rash
- 17.5 Abnormal Bleeding
- 17.6 Hyponatremia
- 17.7 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
- 17.8 Use of Concomitant Medications
- 17.9 Discontinuation of Treatment
- 17.10 Use in Specific Populations
- Medication Guide
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mg
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 40 mg
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: SUICIDALITY AND ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS
Antidepressants increased the risk compared to placebo of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Anyone considering the use of fluoxetine or any other antidepressant in a child, adolescent, or young adult must balance this risk with the clinical need. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction in risk with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older. Depression and certain other psychiatric disorders are themselves associated with increases in the risk of suicide. Patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Families and caregivers should be advised of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber. Fluoxetine is approved for use in pediatric patients with MDD and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ].
When using fluoxetine and olanzapine in combination, also refer to Boxed Warning section of the package insert for Symbyax.
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Major Depressive Disorder
[see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
[see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]
1.2 Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
[see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
[see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
1.3 Bulimia Nervosa
[see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]
1.4 Panic Disorder
[see Clinical Studies (14.4) ]
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
1.5 Fluoxetine Capsules and Olanzapine in Combination: Depressive Episodes Associated with Bipolar I Disorder
When using fluoxetine capsules and olanzapine in combination, also refer to the Clinical Studies section of the package insert for Symbyax®
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Major Depressive Disorder
Initial Treatment
Adult
Pediatric (children and adolescents) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]
All patients
Maintenance/Continuation/Extended Treatment
Daily Dosing [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]
Switching Patients to a Tricyclic Antidepressant (TCA) [see Drug Interactions (7.9) ]
Switching Patients to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]
2.2 Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Initial Treatment
Adult [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]
Pediatric (children and adolescents) [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]
Maintenance/Continuation Treatment
2.3 Bulimia Nervosa
Initial Treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]
Maintenance/Continuation Treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]
2.4 Panic Disorder
Initial Treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.4)]
Maintenance/Continuation Treatment
2.5 Fluoxetine Capsules and Olanzapine in Combination: Depressive Episodes Associated with Bipolar I Disorder
When using fluoxetine capsules and olanzapine in combination, also refer to the Clinical Studies section of the package insert for Symbyax
| For Symbyax (mg/day) | Use in Combination | |
|---|---|---|
| Olanzapine (mg/day) |
Fluoxetine (mg/day) |
|
|
1 Symbyax (olanzapine/fluoxetine hydrochloride) is a fixed-dose combination of fluoxetine and olanzapine. |
||
| 3 mg olanzapine/25 mg fluoxetine |
2.5 |
20 |
| 6 mg olanzapine/25 mg fluoxetine |
5 |
20 |
| 12 mg olanzapine/25 mg fluoxetine |
10+2.5 |
20 |
| 6 mg olanzapine/50 mg fluoxetine |
5 |
40+10 |
| 12 mg olanzapine/50 mg fluoxetine |
10+2.5 |
40+10 |
2.7 Dosing in Specific Populations
Treatment of pregnant Women During the Third Trimester [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Geriatric [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Hepatic Impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Concomitant Illness [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Fluoxetine Capsules and Olanzapine in Combination [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14) and Drug Interactions (7.9)]
2.8 Discontinuation of Treatment
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
When using fluoxetine capsules and olanzapine in combination, also refer to the Contraindications section of the package insert for Symbyax.
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]
- Pimozide [see Drug Interactions (7.9)]
- Thioridazine [see Drug Interactions (7.9)]
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
When using Fluoxetine and olanzapine in combination, also refer to the Warnings and Precautions section of the package insert for Symbyax.
5.1 Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
| Age Range | Drug-Placebo Difference in Number of Cases of Suicidality per 1000 Patients Treated |
|---|---|
| Increases Compared to Placebo |
|
| <18 |
14 additional cases |
| 18-24 |
5 additional cases |
| Decreases Compared to Placebo |
|
| 25-64 |
1 fewer case |
| ≥65 |
6 fewer cases |
All patients being treated with antidepressants for any indication should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, and unusual changes in behavior, especially during the initial few months of a course of drug therapy, or at times of dose changes, either increases or decreases.
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
Families and caregivers of patients being treated with antidepressants for Major Depressive Disorder or other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric, should be alerted about the need to monitor patients for the emergence of agitation, irritability, unusual changes in behavior, and the other symptoms described above, as well as the emergence of suicidality, and to report such symptoms immediately to health care providers. Such monitoring should include daily observation by families and caregivers.
5.2 Serotonin Syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)-like Reactions
[see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]
[see Drug Interactions (7.4)]
[see Drug Interactions (7.3) ]
5.3 Allergic Reactions and Rash
5.4 Screening Patients for Bipolar Disorder and Monitoring for Mania/Hypomania
[see Warnings and Precautions section of the package insert for Symbyax]
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
5.5 Seizures
5.6 Altered Appetite and Weight
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ]
5.7 Abnormal Bleeding
[see Drug Interactions (7.6)]
5.8 Hyponatremia
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]
5.9 Anxiety and Insomnia
[see Table 5]
5.10 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
Cardiovascular
Glycemic Control
Acute Narrow-Angle Glaucoma has
5.11 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
5.12 Long Elimination Half-Life
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
5.13 Discontinuation of Treatment
5.14 Fluoxetine and Olanzapine in Combination
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
When using fluoxetine and olanzapine in combination, also refer to the Adverse Reactions section of the package insert for Symbyax.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Incidence in Major Depressive Disorder, OCD, bulimia, and Panic Disorder placebo-controlled clinical trials (excluding data from extensions of trials)
| Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major Depressive Disorder |
OCD | Bulimia | Panic Disorder | |||||
|
1 Incidence less than 1%. 2 Includes U.S. data for Major Depressive Disorder, OCD, Bulimia, and Panic Disorder clinical trials, plus non-U.S. data for Panic Disorder clinical trials. 3 Denominator used was for males only (N=690 fluoxetine Major Depressive Disorder; N=410 placebo Major Depressive Disorder; N=116 fluoxetine OCD; N=43 placebo OCD; N=14 fluoxetine bulimia; N=1 placebo bulimia; N=162 fluoxetine panic; N=121 placebo panic). |
||||||||
|
Body System/
Adverse Reaction
|
Fluoxetine
(N=1728) |
Placebo
(N=975) |
Fluoxetine
(N=266) |
Placebo
(N=89) |
Fluoxetine
(N=450) |
Placebo
(N=267) |
Fluoxetine
(N=425) |
Placebo
(N=342) |
|
Body as a Whole
|
||||||||
| Asthenia |
9 |
5 |
15 |
11 |
21 |
9 |
7 |
7 |
| Flu syndrome |
3 |
4 |
10 |
7 |
8 |
3 |
5 |
5 |
|
Cardiovascular
System
|
||||||||
| Vasodilatation |
3 |
2 |
5 |
-- |
2 |
1 |
1 |
-- |
|
Digestive System
|
||||||||
| Nausea |
21 |
9 |
26 |
13 |
29 |
11 |
12 |
7 |
| Diarrhea |
12 |
8 |
18 |
13 |
8 |
6 |
9 |
4 |
| Anorexia |
11 |
2 |
17 |
10 |
8 |
4 |
4 |
1 |
| Dry mouth |
10 |
7 |
12 |
3 |
9 |
6 |
4 |
4 |
| Dyspepsia |
7 |
5 |
10 |
4 |
10 |
6 |
6 |
2 |
|
Nervous System
|
||||||||
| Insomnia |
16 |
9 |
28 |
22 |
33 |
13 |
10 |
7 |
| Anxiety |
12 |
7 |
14 |
7 |
15 |
9 |
6 |
2 |
| Nervousness |
14 |
9 |
14 |
15 |
11 |
5 |
8 |
6 |
| Somnolence |
13 |
6 |
17 |
7 |
13 |
5 |
5 |
2 |
| Tremor |
10 |
3 |
9 |
1 |
13 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
| Libido decreased |
3 |
-- |
11 |
2 |
5 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
| Abnormal dreams |
1 |
1 |
5 |
2 |
5 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
|
Respiratory System
|
||||||||
| Pharyngitis |
3 |
3 |
11 |
9 |
10 |
5 |
3 |
3 |
| Sinusitis |
1 |
4 |
5 |
2 |
6 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
| Yawn |
-- |
-- |
7 |
-- |
11 |
-- |
1 |
-- |
|
Skin and Appendages
|
||||||||
| Sweating |
8 |
3 |
7 |
-- |
8 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
| Rash |
4 |
3 |
6 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
2 |
2 |
|
Urogenital System
|
||||||||
| Impotence3
|
2 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
7 |
-- |
1 |
-- |
| Abnormal ejaculation3
|
-- |
-- |
7 |
-- |
7 |
-- |
2 |
1 |
| Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | ||
|---|---|---|
| Major Depressive Disorder, OCD, Bulimia, and Panic Disorder Combined |
||
|
1 Incidence less than 1%. 2 Includes U.S. data for Major Depressive Disorder, OCD, bulimia, and Panic Disorder clinical trials, plus non-U.S. data for Panic Disorder clinical trials. |
||
|
Body System/Adverse Reaction
|
Fluoxetine
(N=2869) |
Placebo
(N=1673) |
|
Body as a Whole
|
||
| Headache |
21 |
19 |
| Asthenia |
11 |
6 |
| Flu syndrome |
5 |
4 |
| Fever |
2 |
1 |
|
Cardiovascular System
|
||
| Vasodilatation |
2 |
1 |
|
Digestive System
|
||
| Nausea |
22 |
9 |
| Diarrhea |
11 |
7 |
| Anorexia |
10 |
3 |
| Dry mouth |
9 |
6 |
| Dyspepsia |
8 |
4 |
| Constipation |
5 |
4 |
| Flatulence |
3 |
2 |
| Vomiting |
3 |
2 |
|
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders
|
||
| Weight loss |
2 |
1 |
|
Nervous System
|
||
| Insomnia |
19 |
10 |
| Nervousness |
13 |
8 |
| Anxiety |
12 |
6 |
| Somnolence |
12 |
5 |
| Dizziness |
9 |
6 |
| Tremor |
9 |
2 |
| Libido decreased |
4 |
1 |
| Thinking abnormal |
2 |
1 |
|
Respiratory System
|
||
| Yawn |
3 |
-- |
|
Skin and Appendages
|
||
| Sweating |
7 |
3 |
| Rash |
4 |
3 |
| Pruritus |
3 |
2 |
|
Special Senses
|
||
| Abnormal vision |
2 |
1 |
|
1 Includes U.S. Major Depressive Disorder, OCD, bulimia, and Panic Disorder clinical trials, plus non-U.S. Panic Disorder clinical trials. |
||||
|
Major Depressive Disorder, OCD, Bulimia, and Panic Disorder Combined
(N=1533) |
Major Depressive Disorder
(N=392) |
OCD
(N=266) |
Bulimia
(N=450) |
Panic Disorder
(N=425) |
| Anxiety (1%)
|
--
|
Anxiety (2%)
|
--
|
Anxiety (2%)
|
| --
|
--
|
--
|
Insomnia (2%)
|
--
|
| --
|
Nervousness (1%)
|
--
|
--
|
Nervousness (1%)
|
| --
|
--
|
Rash (1%)
|
--
|
--
|
Other adverse reactions in pediatric patients (children and adolescents)
Male and female sexual dysfunction with SSRIs
6.2 Other Reactions
Body as a Whole Frequent: Infrequent: Rare:
Cardiovascular System Frequent: Infrequent: 1
Digestive System Infrequent: Rare:
Hemic and Lymphatic System Infrequent: Rare:
Nervous System Frequent: Infrequent: 11Rare:
Respiratory System Rare:
Skin and Appendages Infrequent: Rare:
Special Senses Frequent: Infrequent:
Urogenital System — Frequent: Infrequent: 2
1
2
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
1111111
1
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI)
[see Contraindications (4)][see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
7.2 CNS Acting Drugs
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
7.3 Serotonergic Drugs
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)][see Drug Interactions (7.4), (7.5)]
7.4 Triptans
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.3)]
7.5 Tryptophan
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.3)]
7.6 Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g., NSAIDs, Aspirin, Warfarin)
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
7.7 Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
7.8 Potential for Other Drugs to affect Fluoxetine
Drugs Tightly Bound to Plasma Proteins —[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
7.9 Potential for Fluoxetine to affect Other Drugs
Pimozide —cc[see Contraindications (4)]
Thioridazine —[see Contraindications (4)]
max
c
Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6 — [see Contraindications (4)]
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) — [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
Benzodiazapines — [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
Antipsychotics — [see Contraindications (4)]
Anticonvulsants —
Lithium —
Drugs Tightly Bound to Plasma Proteins — [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
Drugs Metabolized by CYP3A4 — in vivo
in vitro
Olanzapine —
When using fluoxetine and olanzapine and in combination, also refer to the Drug Interactions section of the package insert for Symbyax.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
When using fluoxetine and olanzapine in combination, also refer to the Use in Specific Populations section of the package insert for Symbyax.
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Treatment of Pregnant Women during the First Trimester
Treatment of Pregnant Women during the Third Trimester
Clinical Considerations
[see Dosage and Administration (2.7)]
Animal Data2222
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
[see Clinical Studies (14.1)]
[see Clinical Studies (14.2) ]
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
[see Box Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
2
2
8.5 Geriatric Use
[see Clinical Studies (14.1)][see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)][see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)].
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.3 Dependence
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Human Experience
10.2 Animal Experience
[see Overdosage (10.3)]
10.3 Management of Overdose
[see Drug Interactions (7.9)]
Physicians’ Desk Reference (PDR)
11 DESCRIPTION
®p17183
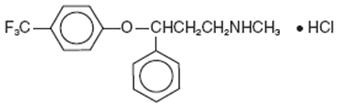
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
1in vitro
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Systemic Bioavailability
Protein Binding in vitro1
Enantiomers RSS
Metabolism SRSR
Variability in Metabolism SSSR
[see Drug Interactions (7.9)]
Accumulation and Slow Elimination [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
12.4 Specific Populations
Liver Disease [see Dosage and Administration (2.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]
Renal Disease
Geriatric Pharmacokinetics
Pediatric Pharmacokinetics (children and adolescents)
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity 2
Mutagenicity in vivo
Impairment of Fertility 2[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
When using fluoxetine and olanzapine in combination, also refer to the Clinical Studies section of the package insert for Symbyax.
14.1 Major Depressive Disorder
Daily Dosing
Adult — .
Pediatric (children and adolescents) —
14.2 Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Adult
| Fluoxetine | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome Classification |
Placebo |
20 mg |
40 mg |
60 mg |
| Worse |
8% |
0% |
0% |
0% |
| No change |
64% |
41% |
33% |
29% |
| Minimally improved |
17% |
23% |
28% |
24% |
| Much improved |
8% |
28% |
27% |
28% |
| Very much improved |
3% |
8% |
12% |
19% |
Pediatric (children and adolescents)
14.3 Bulimia Nervosa
14.4 Panic Disorder
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Fluoxetine Capsules USP, 10 mg*
Fluoxetine Capsules USP, 20 mg*
Fluoxetine Capsules USP, 40 mg*
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See the FDA-approved Medication Guide.
17.1 General Information
When using fluoxetine and olanzapine in combination, also refer to the Medication Guide for Symbyax.
17.2 Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
[see Box Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
17.3 Serotonin Syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)-like Reactions
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.3)].
17.4 Allergic Reactions and Rash
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
17.5 Abnormal Bleeding
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Drug Interactions (7.6)].
17.6 Hyponatremia
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
17.7 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
17.8 Use of Concomitant Medications
17.9 Discontinuation of Treatment
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
17.10 Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ]
Nursing Mothers [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]
Pediatric Use [see Box Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ][see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
®®
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
Repackaged By:
Med-Health Pharma, LLC
North Las Vegas, NV 89032
SP-60030 Rev03
Medication Guide
Fluoxetine Capsules, USP
What is the most important information I should know about fluoxetine capsules?
1. Suicidal thoughts or actions:
- Fluoxetine capsules and other antidepressant medicines may increase suicidal thoughts or actions in some children, teenagers, or young adults within the first few months of treatment or when the dose is changed.
- Depression or other serious mental illnesses are the most important causes of suicidal thoughts or actions.
- Watch for these changes and call your healthcare provider right away if you notice:
- New or sudden changes in mood, behavior, actions, thoughts, or feelings, especially if severe.
- Pay particular attention to such changes when fluoxetine capsules is started or when the dose is changed.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms, or call 911 if an emergency, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- attempts to commit suicide
- acting on dangerous impulses
- acting aggressive or violent
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety or panic attacks
- feeling agitated, restless, angry or irritable
- trouble sleeping
- an increase in activity or talking more than what is normal for you
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms, or call 911 if an emergency. Fluoxetine capsules may be associated with these serious side effects:
2. Serotonin Syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome-like reactions. This condition can be life-threatening and may include:
- agitation, hallucinations, coma or other changes in mental status
- coordination problems or muscle twitching (overactive reflexes)
- racing heartbeat, high or low blood pressure
- sweating or fever
- nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- muscle rigidity
3.Severe allergic reactions:
- trouble breathing
- swelling of the face, tongue, eyes or mouth
- rash, itchy welts (hives) or blisters, alone or with fever or joint pain
4. Abnormal bleeding: ®®
5. Seizures or convulsions
6. Manic episodes:
- greatly increased energy
- severe trouble sleeping
- racing thoughts
- reckless behavior
- unusually grand ideas
- excessive happiness or irritability
- talking more or faster than usual
7. Changes in appetite or weight.
8. Low salt (sodium) levels in the blood.
- headache
- weakness or feeling unsteady
- confusion, problems concentrating or thinking or memory problems
Do not stop fluoxetine capsules without first talking to your healthcare provider.
- anxiety, irritability, high or low mood, feeling restless or changes in sleep habits
- headache, sweating, nausea, dizziness
- electric shock-like sensations, shaking, confusion
What are fluoxetine capsules?
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Bulimia Nervosa*
- Panic Disorder*
- Depressive episodes associated with Bipolar I Disorder, taken with olanzapine (Zyprexa)*
Who should not take fluoxetine capsules?
- are allergic to fluoxetine hydrochloride or any of the ingredients in fluoxetine capsules. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in fluoxetine capsules.
- take a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI). Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if you take an MAOI.
- Do not take an MAOI within 5 weeks of stopping fluoxetine capsules.
- Do not start fluoxetine capsules if you stopped taking an MAOI in the last 2 weeks.
People who take fluoxetine capsules close in time to an MAOI may have serious or even life-threatening side effects. Get medical help right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- high fever
- uncontrolled muscle spasms
- stiff muscles
- rapid changes in heart rate or blood pressure
- confusion
- loss of consciousness (pass out)
- take Mellaril® (thioridazine). Do not take Mellaril® within 5 weeks of stopping fluoxetine capsules because this can cause serious heart rhythm problems or sudden death.
- take the antipsychotic medicine pimozide (Orap®) because this can cause serious heart problems.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking fluoxetine capsules? Ask if you are not sure.
- Are taking certain drugs or treatments such as:
- Triptans used to treat migraine headache
- Medicines used to treat mood, anxiety, psychotic or thought disorders, including tricyclics, lithium, SSRIs, SNRIs, MAOI’s (including linezolid, an antibiotic), or antipsychotics
- Tramadol
- Over-the-counter supplements such as tryptophan or St. John’s Wort
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
- have liver problems
- have kidney problems
- have heart problems
- have or had seizures or convulsions
- have bipolar disorder or mania
- have low sodium levels in your blood
- have a history of a stroke
- have high blood pressure
- have or had bleeding problems
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if fluoxetine capsules will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of treating depression during pregnancy.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Some fluoxetine may pass into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby while taking fluoxetine capsules.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines that you take,
- Symbyax
- Sarafem
How should I take fluoxetine capsules?
- Take fluoxetine capsules exactly as prescribed. Your healthcare provider may need to change the dose of fluoxetine capsules until it is the right dose for you.
- Fluoxetine capsules may be taken with or without food.
- If you miss a dose of fluoxetine capsules, take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and take your next dose at the regular time. Do not take two doses of fluoxetine capsules at the same time.
- If you take too much fluoxetine call your healthcare provider or poison control center right away, or get emergency treatment.
What should I avoid while taking fluoxetine capsules?
What are the possible side effects of fluoxetine capsules?
- See “What is the most important information I should know about fluoxetine capsules?”
- Problems with blood sugar control. People who have diabetes and take fluoxetine capsules may have problems with low blood sugar while taking fluoxetine capsules. High blood sugar can happen when fluoxetine capsules are stopped. Your healthcare provider may need to change the dose of your diabetes medicines when you start or stop taking fluoxetine capsules.
- Feeling anxious or trouble sleeping
- unusual dreams
- sexual problems
- loss of appetite, diarrhea, indigestion, nausea or vomiting, weakness, or dry mouth
- flu symptoms
- feeling tired or fatigued
- change in sleep habits
- yawning
- sinus infection or sore throat
- tremor or shaking
- sweating
- feeling anxious or nervous
- hot flashes
- rash
- increased thirst
- abnormal increase in muscle movement or agitation
- nose bleed
- urinating more often
- heavy menstrual periods
- possible slowed growth rate and weight change. Your child’s height and weight should be monitored during treatment with fluoxetine capsules.
CALL YOUR DOCTOR FOR MEDICAL ADVICE ABOUT SIDE EFFECTS. YOU MAY REPORT SIDE EFFECTS TO THE FDA AT 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store fluoxetine capsules?
- Store fluoxetine capsules at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- Keep fluoxetine capsules away from light.
- Keep fluoxetine capsules bottle closed tightly.
Keep fluoxetine capsules and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about fluoxetine capsules
What are the ingredients in fluoxetine capsules?
Symbyax® and Sarafem® are registered trademarks of Eli Lilly and Company.
®
®
®
®
®
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
Repackaged By:
Med-Health Pharma, LLC
North Las Vegas, NV 89032
SP-60030 Rev03
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg

PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mg

PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 40 mg

FluoxetineFluoxetine Hydrochloride CAPSULE
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FluoxetineFluoxetine Hydrochloride CAPSULE
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FluoxetineFluoxetine Hydrochloride CAPSULE
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!