Fluphenazine Hydrochloride
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- BOXED WARNING
- FLUPHENAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- FLUPHENAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- FLUPHENAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
BOXED WARNING
WARNINGIncreased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Analyses of seventeen placebo-controlled trials (modal duration of 10 weeks), largely in patients taking atypical antipsychotic drugs, revealed a risk of death in drug-treated patients of between 1.6 to 1.7 times the risk of death in placebo-treated patients. Over the course of a typical 10-week controlled trial, the rate of death in drug-treated patients was about 4.5%, compared to a rate of about 2.6% in the placebo group. Although the causes of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure, sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia) in nature. Observational studies suggest that, similar to atypical antipsychotic drugs, treatment with conventional antipsychotic drugs may increase mortality. The extent to which the findings of increased mortality in observational studies may be attributed to the antipsychotic drug as opposed to some characteristic(s) of the patients is not clear. Fluphenazine hydrochloride is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis (seeWARNINGS).
FLUPHENAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
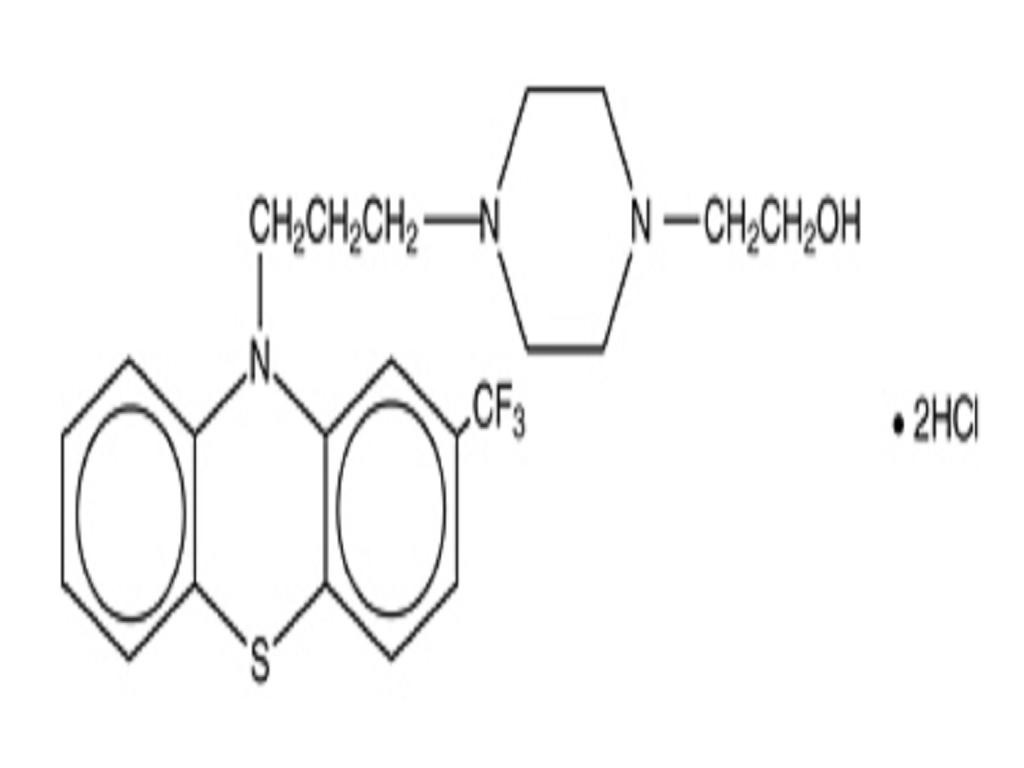
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
INDICATIONS & USAGE
FLUPHENAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related PsychosisBOXED WARNING
Tardive Dyskinesia
PRECAUTIONS: Information for PatientsADVERSE REACTIONS: Tardive Dyskinesia
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
Usage in Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Nonteratogenic Effects
PRECAUTIONS
GeneralINFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
Abrupt Withdrawal
Leukopenia, Neutropenia and Agranulocytosis
FLUPHENAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Central Nervous SystemExtrapyramidal Symptoms
Dystonia
Class Effect
Tardive Dyskinesia
WARNINGS
Other CNS Effects
WARNINGS: Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Drowsiness or lethargy, if they occur, may necessitate a reduction in dosage; the induction of a catatonic-like state has been known to occur with dosages of fluphenazine far in excess of the recommended amounts. As with other phenothiazine compounds, reactivation or aggravation of psychotic processes may be encountered.
Phenothiazine derivatives have been known to cause, in some patients, restlessness, excitement, or bizarre dreams.
Autonomic Nervous System
Hypertension and fluctuations in blood pressure have been reported with fluphenazine hydrochloride.
Hypotension has rarely presented a problem with fluphenazine. However, patients with pheochromocytoma, cerebral vascular or renal insufficiency, or a severe cardiac reserve deficiency such as mitral insufficiency appear to be particularly prone to hypotensive reactions with phenothiazine compounds, and should therefore be observed closely when the drug is administered. If severe hypotension should occur, supportive measures including the use of intravenous vasopressor drugs should be instituted immediately. Norepinephrine bitartrate injection is the most suitable drug for this purpose; epinephrine should not be used since phenothiazine derivatives have been found to reverse its action, resulting in a further lowering of blood pressure.
Autonomic reactions including nausea and loss of appetite, salivation, polyuria, perspiration, dry mouth, headache, and constipation may occur. Autonomic effects can usually be controlled by reducing or temporarily discontinuing dosage.
In some patients, phenothiazine derivatives have caused blurred vision, glaucoma, bladder paralysis, fecal impaction, paralytic ileus, tachycardia, or nasal congestion.
Metabolic and Endocrine
Weight change, peripheral edema, abnormal lactation, gynecomastia, menstrual irregularities, false results on pregnancy tests, impotency in men and increased libido in women have all been known to occur in some patients on phenothiazine therapy.
Allergic Reactions
Skin disorders such as itching, erythema, urticaria, seborrhea, photosensitivity, eczema and even exfoliative dermatitis have been reported with phenothiazine derivatives. The possibility of anaphylactoid reactions occurring in some patients should be borne in mind.
Hematologic
Routine blood counts are advisable during therapy since blood dyscrasias including leukopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenic or nonthrombocytopenic purpura, eosinophilia, and pancytopenia have been observed with phenothiazine derivatives. Furthermore, if any soreness of the mouth, gums, or throat, or any symptoms of upper respiratory infection occur and confirmatory leukocyte count indicates cellular depression, therapy should be discontinued and other appropriate measures instituted immediately.
Hepatic
Others
Although this is not a general feature of fluphenazine, potentiation of central nervous system depressants (opiates, analgesics, antihistamines, barbiturates, alcohol) may occur.
The following adverse reactions have also occurred with phenothiazine derivatives: systemic lupus erythematosus-like syndrome, hypotension severe enough to cause fatal cardiac arrest, altered electrocardiographic and electroencephalographic tracings, altered cerebrospinal fluid proteins, cerebral edema, asthma, laryngeal edema, and angioneurotic edema; with long-term useskin pigmentation, and lenticular and corneal opacities.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
HOW SUPPLIED
STORAGE AND HANDLING
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

Fluphenazine HydrochlorideFluphenazine Hydrochloride TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!