fomepizole
Fomepizole Injection
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- FOMEPIZOLE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- FOMEPIZOLE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- FOMEPIZOLE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- PRECAUTIONS
- FOMEPIZOLE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- FOMEPIZOLE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Rx only
Sterile
Caution: Must be diluted prior to use.
FOMEPIZOLE DESCRIPTION
462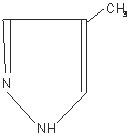
It is a clear to yellow liquid at room temperature. Its melting point is 25°C (77°F) and it may present in a solid form at room temperature. Fomepizole is soluble in water and very soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, and chloroform. Each vial contains 1.5 mL (1 g/mL) of fomepizole.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action : Fomepizole is a competitive inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase. Alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde. Alcohol dehydrogenase also catalyzes the initial steps in the metabolism of ethylene glycol and methanol to their toxic metabolites.
Ethylene glycol, the main component of most antifreezes and coolants, is metabolized to glycoaldehyde, which undergoes subsequent sequential oxidations to yield glycolate, glyoxylate, and oxalate. Glycolate and oxalate are the metabolic byproducts primarily responsible for the metabolic acidosis and renal damage seen in ethylene glycol toxicosis. The lethal dose of ethylene glycol in humans is approximately 1.4 mL/kg.
Methanol, the main component of windshield wiper fluid, is slowly metabolized via alcohol dehydrogenase to formaldehyde with subsequent oxidation via formaldehyde dehydrogenase to yield formic acid. Formic acid is primarily responsible for the metabolic acidosis and visual disturbances (e.g., decreased visual acuity and potential blindness) associated with methanol poisoning. A lethal dose of methanol in humans is approximately 1 to 2 mL/kg.
Fomepizole has been shown in vitro to block alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme activity in dog, monkey, and human liver. The concentration of fomepizole at which alcohol dehydrogenase is inhibited by 50% in vitro is approximately 0.1 µmol/L.
Several studies have demonstrated that fomepizole plasma concentrations of approximately 10 µmol/L (0.82 mg/L) in monkeys are sufficient to inhibit methanol metabolism to formate, which is also mediated by alcohol dehydrogenase. Based on these results, concentrations of fomepizole in humans in the range of 100 to 300 µmol/L (8.6 to 24.6 mg/L) have been targeted to assure adequate plasma concentrations for the effective inhibition of alcohol dehydrogenase.
In healthy volunteers, oral doses of fomepizole (10 to 20 mg/kg) significantly reduced the rate of elimination of moderate doses of ethanol, which is also metabolized through the action of alcohol dehydrogenase (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Pharmacokinetics : The plasma half-life of fomepizole varies with dose, even in patients with normal renal function, and has not been calculated.
Distribution :Metabolism : In healthy volunteers, only 1 to 3.5% of the administered dose of fomepizole (7 to 20 mg/kg oral and IV) was excreted unchanged in the urine, indicating that metabolism is the major route of elimination. In humans, the primary metabolite of fomepizole is 4-carboxypyrazole (approximately 80 to 85% of administered dose), which is excreted in the urine. Other metabolites of fomepizole observed in the urine are 4-hydroxymethylpyrazole and the N-glucuronide conjugates of 4-carboxypyrazole and 4-hydroxymethylpyrazole.
Excretion : The elimination of fomepizole is best characterized by Michaelis-Menten kinetics after acute doses, with saturable elimination occurring at therapeutic blood concentrations [100 to 300 µmol/L, 8.2 to 24.6 mg/L].
With multiple doses, fomepizole rapidly induces its own metabolism via the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, which produces a significant increase in the elimination rate after about 30 to 40 hours. After enzyme induction, elimination follows first-order kinetics.
Special Populations :
Geriatric :Pediatric :
Gender : Fomepizole has not been studied sufficiently to determine whether the pharmacokinetics differ between the genders.
Renal Insufficiency : The metabolites of fomepizole are excreted renally. Definitive pharmacokinetic studies have not been done to assess pharmacokinetics in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Insufficiency :Clinical Studies:DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
FOMEPIZOLE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Fomepizole is indicated as an antidote for ethylene glycol (such as antifreeze) or methanol poisoning, or for use in suspected ethylene glycol or methanol ingestion, either alone or in combination with hemodialysis (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION)
FOMEPIZOLE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Fomepizole should not be administered to patients with a documented serious hypersensitivity reaction to fomepizole or other pyrazoles.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Fomepizole should not be given undiluted or by bolus injection. Venous irritation and phlebosclerosis were noted in two of six normal volunteers given bolus injections (over 5 minutes) of fomepizole at a concentration of 25 mg/mL.
Minor allergic reactions (mild rash, eosinophilia) have been reported in a few patients receiving fomepizole (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). Therefore, patients should be monitored for signs of allergic reactions.
Laboratory Tests
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONDrug Interactions
Oral doses of fomepizole (10 to 20 mg/kg), via alcohol dehydrogenase inhibition, significantly reduced the rate of elimination of ethanol (by approximately 40%) given to healthy volunteers in moderate doses. Similarly, ethanol decreased the rate of elimination of fomepizole (by approximately 50%) by the same mechanism.
Reciprocal interactions may occur with concomitant use of fomepizole and drugs that increase or inhibit the cytochrome P450 system (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine, cimetidine, ketoconazole), though this has not been studied.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
There have been no long-term studies performed in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential.
There was a positive Ames test result in the Escherichia coli tester strain WP2uvrA and the Salmonella typhimurium tester strain TA102 in the absence of metabolic activation. There was no evidence of a clastogenic effect in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
In rats, fomepizole (110 mg/kg) administered orally for 40 to 42 days resulted in decreased testicular mass (approximately 8% reduction). This dose is approximately 0.6 times the human maximum daily exposure based on surface area (mg/m2). This reduction was similar for rats treated with either ethanol or fomepizole alone. When fomepizole was given in combination with ethanol, the decrease in testicular mass was significantly greater (approximately 30% reduction) compared to those rats treated exclusively with fomepizole or ethanol.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C : Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with fomepizole. It is also not known whether fomepizole can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women or can affect reproduction capacity. Fomepizole should be given to pregnant women only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
FOMEPIZOLE ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequent adverse events reported as drug-related or unknown relationship to study drug in the 78 patients and 63 normal volunteers who received fomepizole injection were headache (14%), nausea (11%), and dizziness, increased drowsiness, and bad taste/metallic taste (6% each). All other adverse events in this population were reported in approximately 3% or fewer of those receiving fomepizole and were as follows:
Body as a Whole : Abdominal pain, fever, multiorgan system failure, pain during fomepizole injection, inflammation at injection site, lumbalgia/backache, hangover.
Cardiovascular : Sinus bradycardia/bradycardia, phlebosclerosis, tachycardia, phlebitis, shock, hypotension.
Gastrointestinal : Vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, heartburn, decreased appetite, transient transaminitis.
Hemic/Lymphatic : Eosinophilia/hypereosinophilia, lymphangitis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, anemia.
Nervous : Lightheadedness, seizure, agitation, feeling drunk, facial flush, vertigo, nystagmus, anxiety, "felt strange", decreased environmental awareness.
Respiratory : Hiccups, pharyngitis.
Skin/Appendages : Application site reaction, rash.
Special Senses : Abnormal smell, speech/visual disturbances, transient blurred vision, roar in ear.
Urogenital : Anuria
OVERDOSAGE
Nausea, dizziness, and vertigo were noted in healthy volunteers receiving 50 and 100 mg/kg doses of fomepizole (at plasma concentrations of 290 to 520 µmol/L, 23.8 to 42.6 mg/L). These doses are 3 to 6 times the recommended dose. This dose-dependent CNS effect was short-lived in most subjects and lasted up to 30 hours in one subject.
Fomepizole is dialyzable, and hemodialysis may be useful in treating cases of overdosage.
FOMEPIZOLE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Treatment Guidelines : If ethylene glycol or methanol poisoning is left untreated, the natural progression of the poisoning leads to accumulation of toxic metabolites, including glycolic and oxalic acids (ethylene glycol intoxication) and formic acid (methanol intoxication). These metabolites can induce metabolic acidosis, nausea/vomiting, seizures, stupor, coma, calcium oxaluria, acute tubular necrosis, blindness, and death. The diagnosis of these poisonings may be difficult because ethylene glycol and methanol concentrations diminish in the blood as they are metabolized to their respective metabolites. Hence, both ethylene glycol and methanol concentrations and acid base balance, as determined by serum electrolyte (anion gap) and/or arterial blood gas analysis, should be frequently monitored and used to guide treatment.
Treatment consists of blocking the formation of toxic metabolites using inhibitors of alcohol dehydrogenase, such as fomepizole, and correction of metabolic abnormalities. In patients with high ethylene glycol or methanol concentrations (≥ 50 mg/dL), significant metabolic acidosis, or renal failure, hemodialysis should be considered to remove ethylene glycol or methanol and the respective toxic metabolites of these alcohols.
Treatment with fomepizole : Begin fomepizole treatment immediately upon suspicion of ethylene glycol or methanol ingestion based on patient history and/or anion gap metabolic acidosis, increased osmolar gap, visual disturbances, or oxalate crystals in the urine, OR a documented serum ethylene glycol or methanol concentration greater than 20 mg/dL.
Hemodialysis : Hemodialysis should be considered in addition to fomepizole in the case of renal failure, significant or worsening metabolic acidosis, or a measured ethylene glycol or methanol concentration of greater than or equal to 50 mg/dL. Patients should be dialyzed to correct metabolic abnormalities and to lower the ethylene glycol concentrations below 50 mg/dL.
Discontinuation of fomepizole Treatment : Treatment with fomepizole may be discontinued when ethylene glycol or methanol concentrations are undetectable or have been reduced below 20 mg/dL, and the patient is asymptomatic with normal pH.
Dosing of fomepizole : A loading dose of 15 mg/kg should be administered, followed by doses of 10 mg/kg every 12 hours for 4 doses, then 15 mg/kg every 12 hours thereafter until ethylene glycol or methanol concentrations are undetectable or have been reduced below 20 mg/dL, and the patient is asymptomatic with normal pH. All doses should be administered as a slow intravenous infusion over 30 minutes (see Administration).
Dosage with Renal Dialysis : Fomepizole Injection is dialyzable and the frequency of dosing should be increased to every 4 hours during hemodialysis.
| DOSE AT THE BEGINNING OF HEMODIALYSIS | |
|---|---|
If <6 hours since last fomepizole dose | If ≥ 6 hours since last fomepizole dose |
Do not administer dose | Administer next scheduled dose |
| DOSING DURING HEMODIALYSIS |
|---|
Dose every 4 hours |
| DOSING AT THE TIME HEMODIALYSIS IS COMPLETED | |
|---|---|
Time between last dose and the end of hemodialysis | |
<1 hour | Do not administer dose at the end of hemodialysis |
1-3 hours | Administer 1/2 of next scheduled dose |
>3 hours | Administer next scheduled dose |
| MAINTENANCE DOSING OFF HEMODIALYSIS |
|---|
Give next scheduled dose 12 hours from last dose administered |
Administration : Fomepizole solidifies at temperatures less than 25°C (77°F). If the fomepizole solution has become solid in the vial, the solution should be liquefied by running the vial under warm water or by holding in the hand. Solidification does not affect the efficacy, safety, or stability of fomepizole. Using sterile technique, the appropriate dose of fomepizole should be drawn from the vial with a syringe and injected into at least 100 mL of sterile 0.9% sodium chloride injection or dextrose 5% injection. Mix well. The entire contents of the resulting solution should be infused over 30 minutes. Fomepizole, like all parenteral products, should be inspected visually for particulate matter prior to administration.
Stability : Fomepizole diluted in 0.9% sodium chloride injection or dextrose 5% injection remains stable and sterile for at least 24 hours when stored refrigerated or at room temperature. Fomepizole does not contain preservatives. Therefore, maintain sterile conditions, and after dilution do not use beyond 24 hours.
Solutions showing haziness, particulate matter, precipitate, discoloration, or leakage should not be used.
HOW SUPPLIED
Fomepizole Injection is available as a sterile, preservative-free solution for intravenous use, in vials containing 1.5mL (1 g/mL) of fomepizole.
Fomepizole Injection is supplied in cartons of one single use vial (NDC 14593-123-01) or four individual cartons placed into one outer carton (NDC 14593-123-02).
Store at controlled room temperature, 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP].
Manufactured for:Navinta LLC,Manufactured By:
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd.(Sterile Products Division)
Date of Revision: 10/2008
Version 04
fomepizolefomepizole INJECTION, SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||