Gabapentin
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- GABAPENTIN DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- PHARMACOKINETICS
- CLINICAL STUDIES
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- GABAPENTIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- LABORATORY TESTS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- GERIATRIC USE
- GABAPENTIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- SPL MEDGUIDE
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
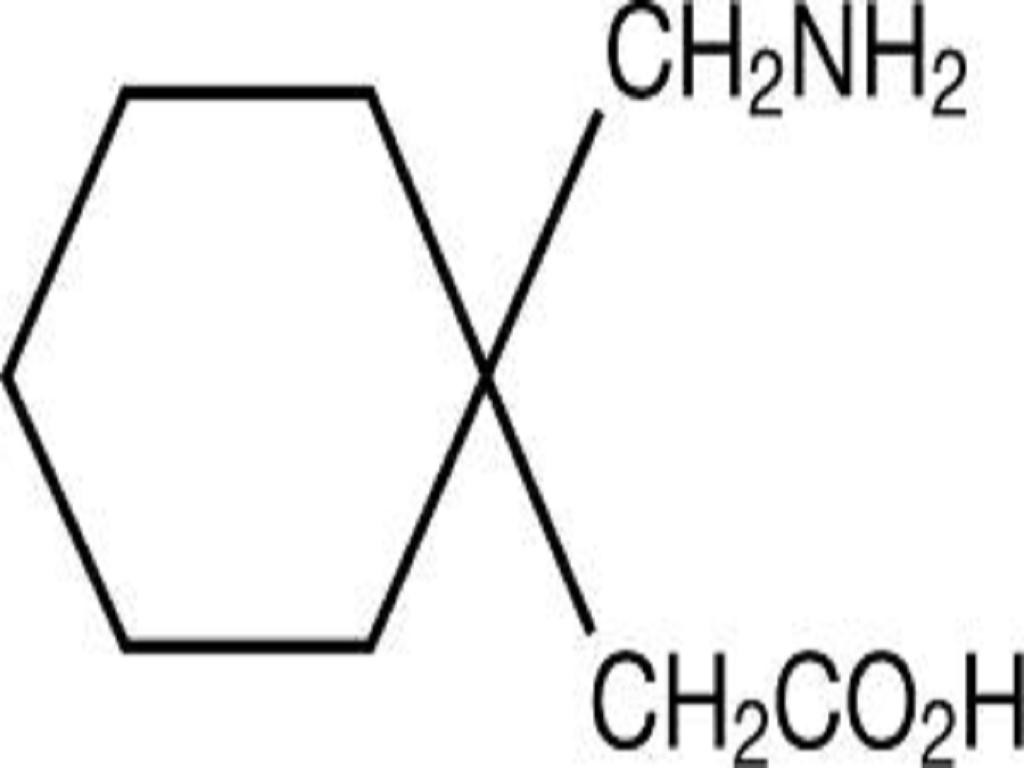
GABAPENTIN DESCRIPTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of ActionPHARMACOKINETICS
Pharmacokinetics and Drug MetabolismSpecial Populations: Adult Patients With Renal Insufficiency
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Table 6
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric UseDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
CLINICAL STUDIES
Postherpetic Neuralgia: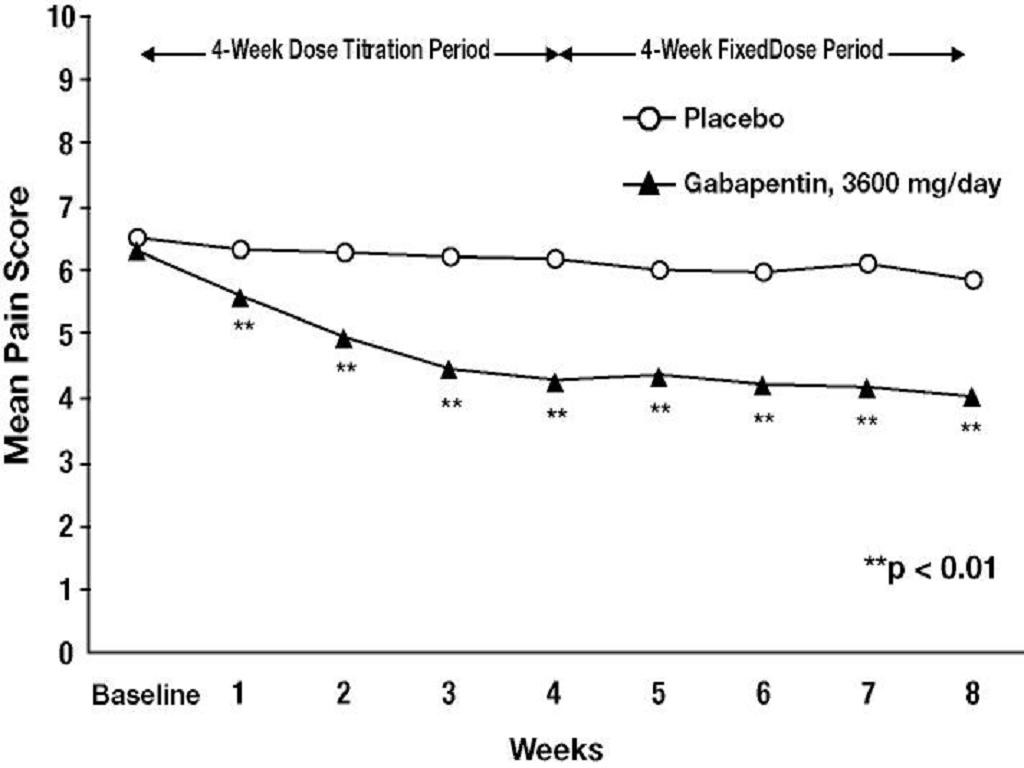
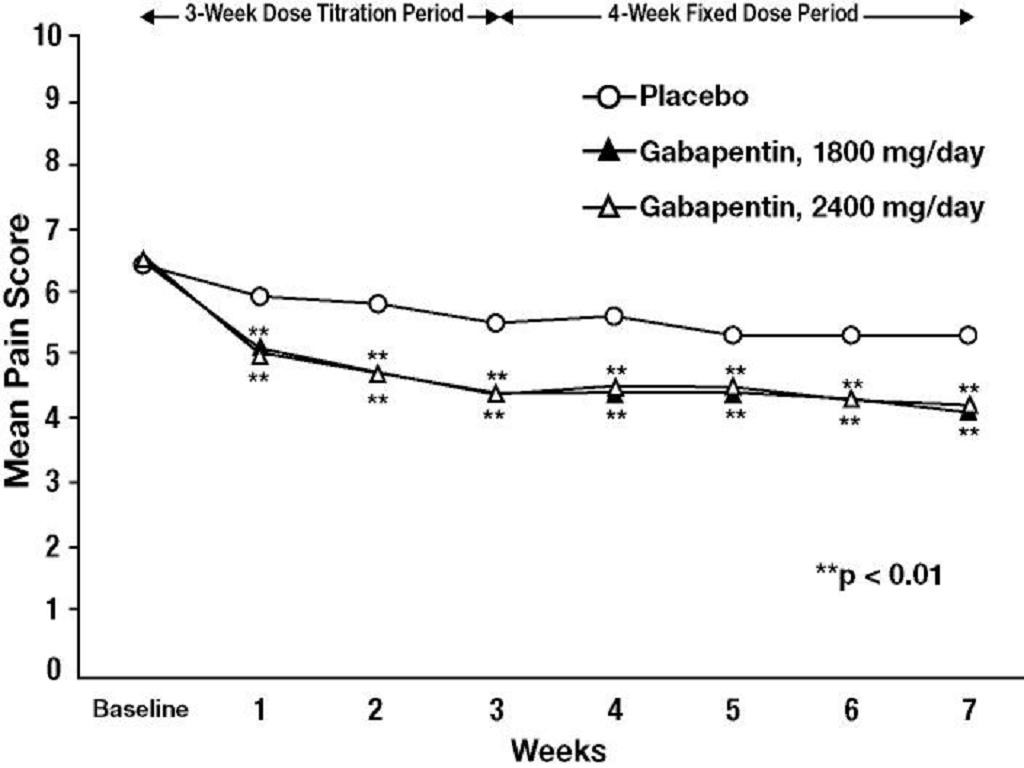
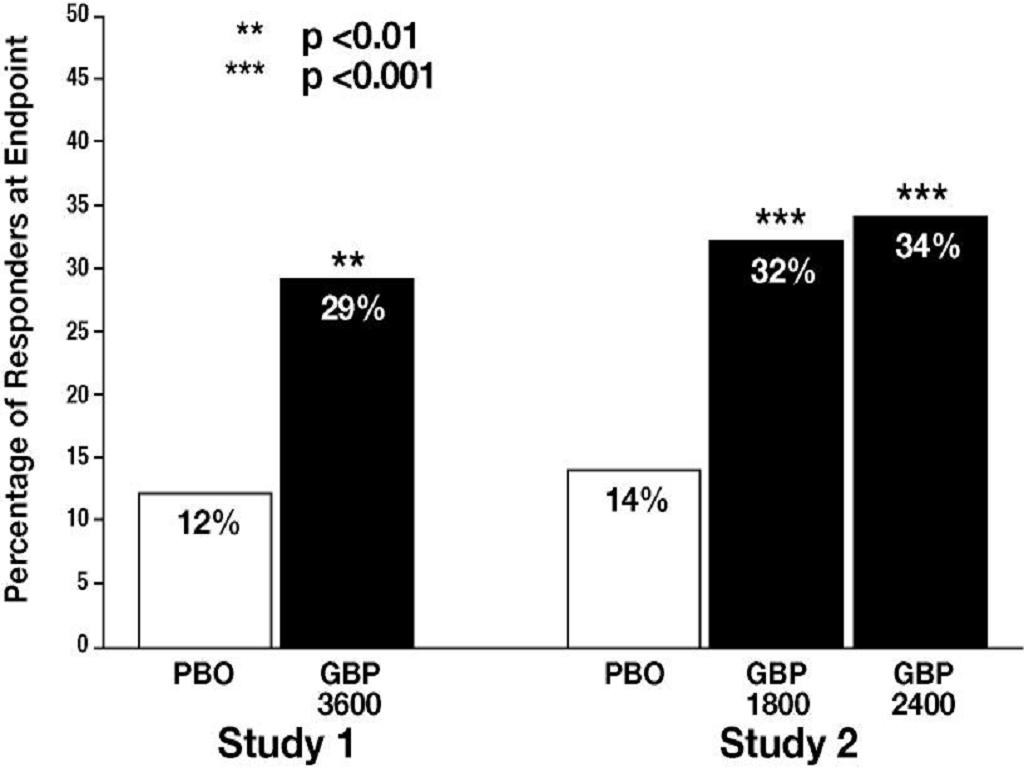
Epilepsy:
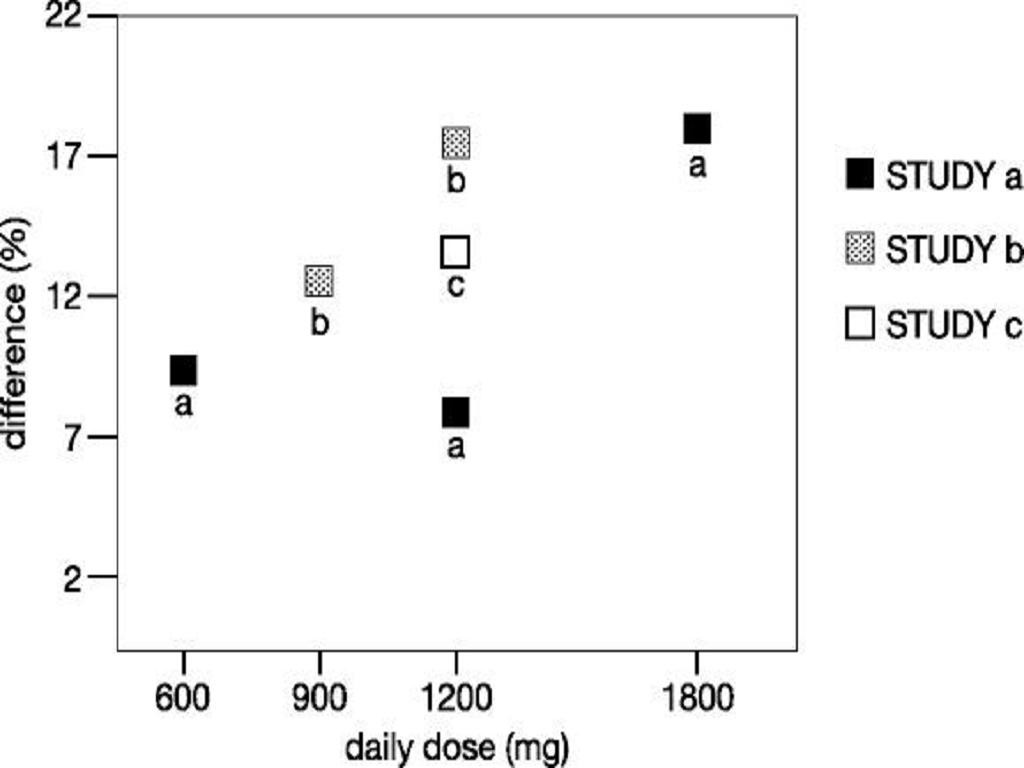
INDICATIONS & USAGE
Postherpetic NeuralgiaEpilepsy
GABAPENTIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
Suicidal Behavior and IdeationNeuropsychiatric Adverse EventsPediatric Patients 3 to 12 years of age
Withdrawal Precipitated Seizure, Status Epilepticus
Tumorigenic Potential
PRECAUTIONS: Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Sudden and Unexplained Death in Patients With Epilepsy
PRECAUTIONS
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
Drug Interactions
PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy
LABORATORY TESTS
DRUG INTERACTIONS
PRECAUTIONS
DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
PREGNANCY
NURSING MOTHERS
PEDIATRIC USE
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Studies
GERIATRIC USE
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYADVERSE REACTIONSDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
GABAPENTIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
Postherpetic NeuralgiaIncidence in Controlled Clinical Trials
Epilepsy:
WARNINGS, Neuropsychiatric Adverse Events
Incidence in Controlled Clinical Trials:
Other Adverse Events Observed During All Clinical Trials:
Clinical Trials in Pediatric Patients With Epilepsy:
Postmarketing and Other Experience
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
OVERDOSAGE
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Postherpetic Neuralgia
Epilepsy
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pediatrics
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage in Elderly
HOW SUPPLIED
SPL MEDGUIDE
-
● thoughts about suicide or dying
-
● attempts to commit suicide
-
● new or worse depression
-
● new or worse anxiety
-
● feeling agitated or restless
-
● panic attacks
-
● trouble sleeping (insomnia)
-
● new or worse irritability
-
● acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
-
● acting on dangerous impulses
-
● an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
-
● other unusual changes in behavior or mood
-
● Pay attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings.
-
● Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled.
-
● Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause serious problems. Stopping a seizure medicine suddenly in a patient who has epilepsy can cause seizures that will not stop (status epilepticus).
-
● Pain from damaged nerves (postherpetic pain) that follows healing of shingles (a painful rash that comes after a herpes zoster infection) in adults.
-
● Partial seizures when taken together with other medicines in adults and children 3 years of age and older.
-
● have or have had kidney problems or are on hemodialysis
-
● have or have had depression, mood problems, or suicidal thoughts or behavior
-
● are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if gabapentin can harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant while taking gabapentin. You and your healthcare provider will decide if you should take gabapentin while you are pregnant.
-
● If you become pregnant while taking gabapentin, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. You can enroll in this registry by calling 1-888-233-2334.
-
● are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. Gabapentin can pass into breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide how you will feed your baby while you take gabapentin.
-
● Take gabapentin exactly as prescribed. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much gabapentin to take.
-
● Do not change your dose of gabapentin without talking to your healthcare provider. If you break a tablet in half the unused half of the tablet should be taken at your next scheduled dose. Half tablets not used within several days of breaking should be thrown away.
-
● Gabapentin can be taken with or without food. If you take an antacid containing aluminum and magnesium, such as MaaloxMylantaGelusilGavisconor Di-Gelyou should wait at least 2 hours before taking your next dose of gabapentin.
-
● If you take too much gabapentin, call your healthcare provider or your local Poison Control Center right away.
-
● Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy or dizzy while taking gabapentin without first talking with your healthcare provider. Taking gabapentin with alcohol or drugs that cause sleepiness or dizziness may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse.
-
● Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how gabapentin affects you. Gabapentin can slow your thinking and motor skills.
-
● SeeWhat is the most important information I should know about gabapentin?
-
● The most common side effects of gabapentin include:
-
● Store gabapentin tablets between 59to 86(15to 30
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

GabapentinGabapentin TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!