Gabapentin
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- GABAPENTIN DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- PHARMACOKINETICS
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- GABAPENTIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- LABORATORY TESTS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- GERIATRIC USE
- GABAPENTIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
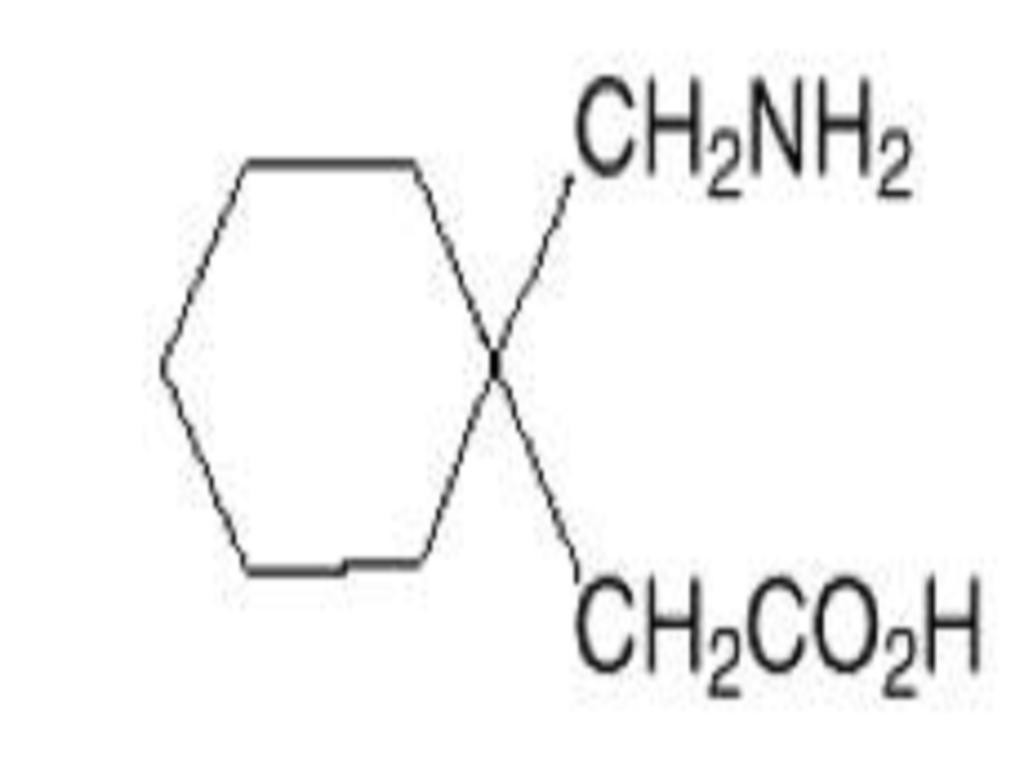
GABAPENTIN DESCRIPTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
PHARMACOKINETICS
Special Populations:Patients With Renal Insufficiency
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Table 6
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric UseDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
StudyStudyGabapentinPatients ReceivingPatients ReceivingDuration(mg/day)aGabapentinPlaceboTarget DoseTotal
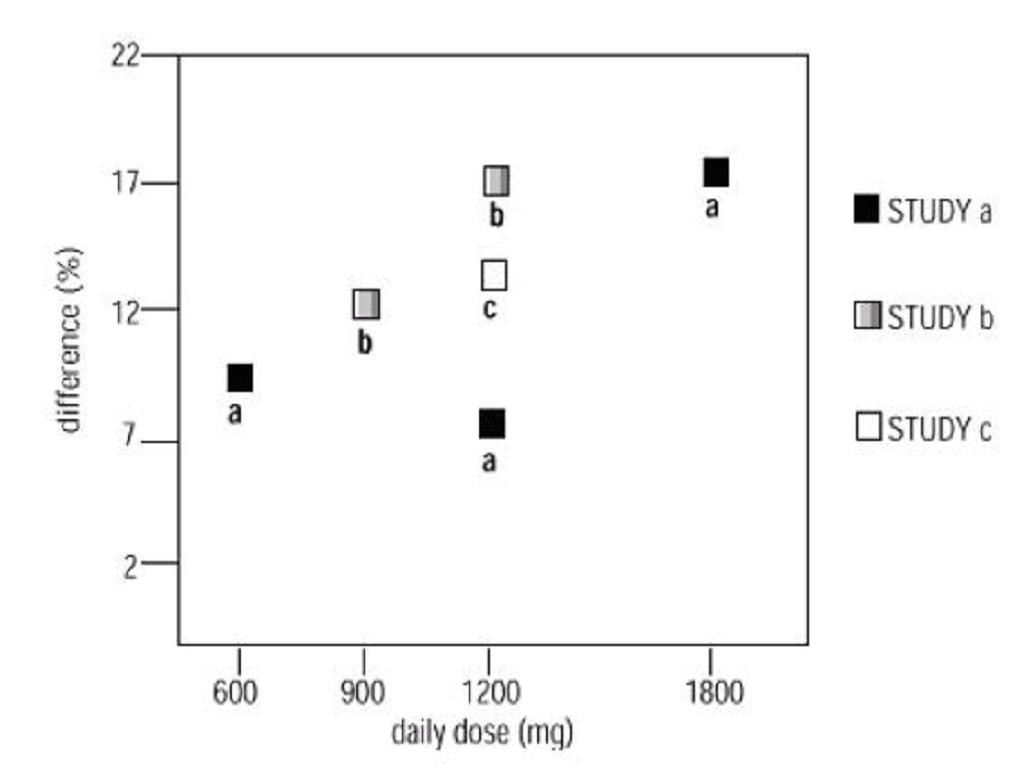
INDICATIONS & USAGE
GABAPENTIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
PRECAUTIONS: Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
PRECAUTIONS
Drug Interactions
PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy
LABORATORY TESTS
DRUG INTERACTIONS
PRECAUTIONS
DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
PREGNANCY
NURSING MOTHERS
PEDIATRIC USE
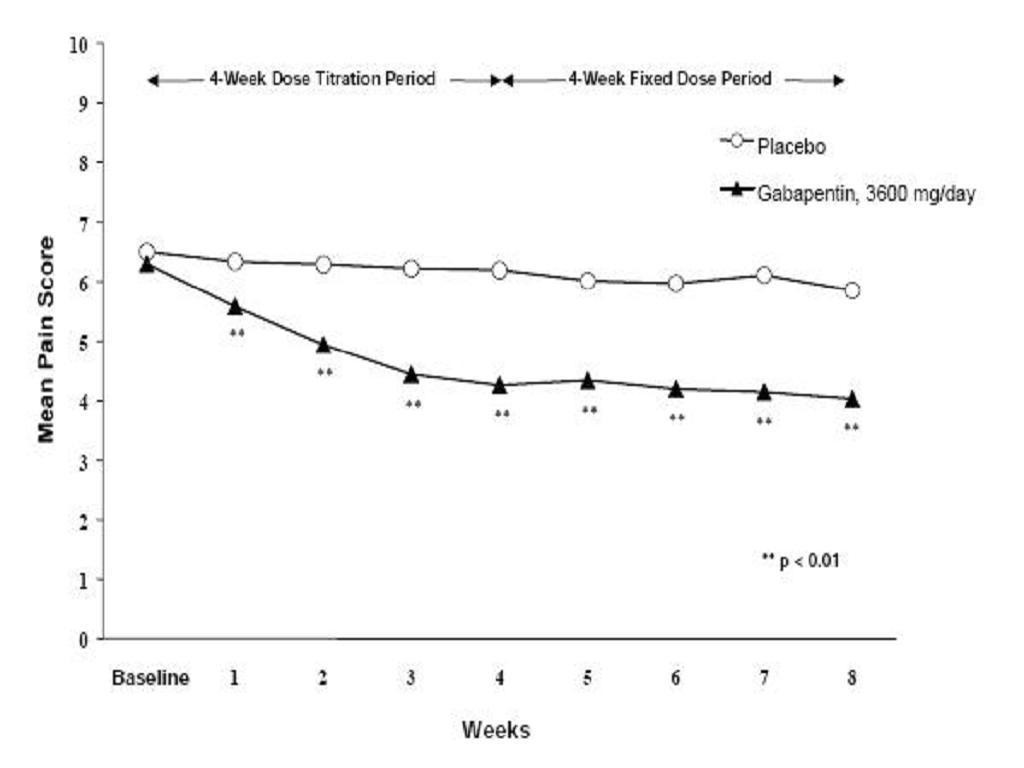
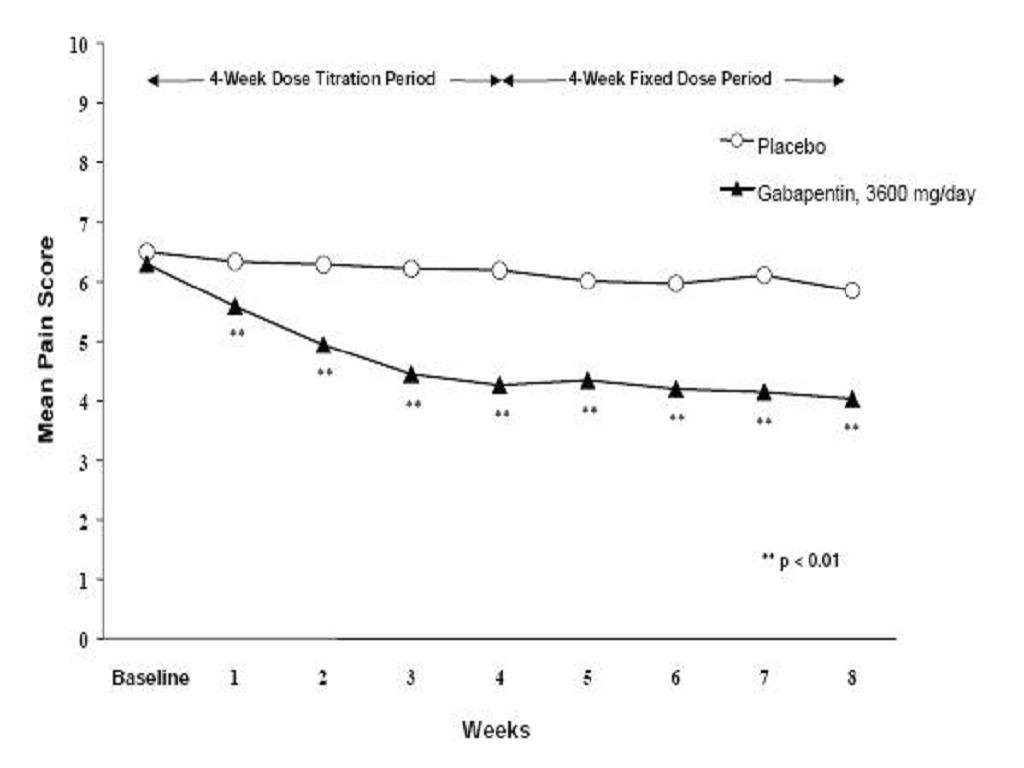
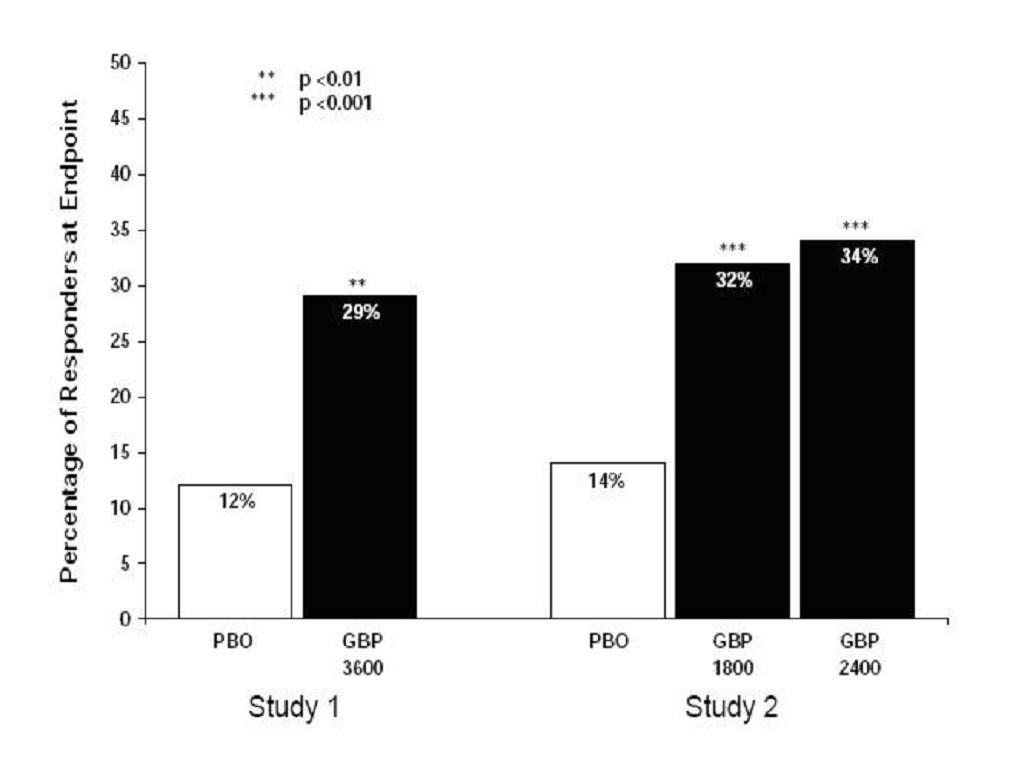
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies
GERIATRIC USE
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYADVERSE REACTIONSDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
GABAPENTIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
Body System Preferred TermGabapentin CapsulesPlaceboPreferred TermN = 336N = 227%%Body as a WholeAsthenia5.74.8Infection5.13.5Headache3.33.1Accidental injury3.31.3Abdominal pain2.72.6Digestive SystemDiarrhea5.73.1Dry mouth4.81.3Constipation3.91.8Nausea3.93.1Vomiting3.31.8Flatulence2.11.8Metabolic and Nutritional DisordersPeripheral edema8.32.2Weight gain1.80.0Hyperglycemia1.20.4Nervous SystemDizziness28.07.5Somnolence21.45.3Ataxia3.30.0Thinking Abnormal2.70.0Abnormal gait1.50.0Incoordination1.50.0Amnesia1.20.9Hypesthesia1.20.9Respiratory SystemPharyngitis1.20.4Skin and AppendagesRash1.20.9Special SensesAmblyopiaa2.70.9Conjunctivitis1.20.0Diplopia1.20.0Otitis media1.20.0aReported as blurred vision
Other events in more than 1% of patients but equally or more frequent in the placebo group included pain, tremor, neuralgia, back pain, dyspepsia, dyspnea, and flu syndrome.
There were no clinically important differences between men and women in the types and incidence of adverse events. Because there were few patients whose race was reported as other than white, there are insufficient data to support a statement regarding the distribution of adverse events by race.
Epilepsy
The most commonly observed adverse events associated with the use of Gabapentin Capsules in combination with other antiepileptic drugs in patients >12 years of age, not seen at an equivalent frequency among placebo-treated patients, were somnolence, dizziness, ataxia, fatigue, and nystagmus. The most commonly observed adverse events reported with the use of Gabapentin Capsules in combination with other antiepileptic drugs in pediatric patients 3 to 12 years of age, not seen at an equal frequency among placebo-treated patients, were viral infection, fever, nausea and/or vomiting, somnolence, and hostility (seeWARNINGS, Neuropsychiatric Adverse Events).
Approximately 7% of the 2074 patients >12 years of age and approximately 7% of the 449 pediatric patients 3 to 12 years of age who received Gabapentin Capsules in premarketing clinical trials discontinued treatment because of an adverse event. The adverse events most commonly associated with withdrawal in patients >12 years of age were somnolence (1.2%), ataxia (0.8%), fatigue (0.6%), nausea and/or vomiting (0.6%), and dizziness (0.6%). The adverse events most commonly associated with withdrawal in pediatric patients were emotional lability (1.6%), hostility (1.3%), and hyperkinesia (1.1%).
Incidence in Controlled Clinical Trials
Table 4 lists treatment-emergent signs and symptoms that occurred in at least 1% of Gabapentin Capsule-treated patients >12 years of age with epilepsy participating in placebo-controlled trials and were numerically more common in the Gabapentin Capsules group. In these studies, either Gabapentin Capsules or placebo was added to the patient's current antiepileptic drug therapy. Adverse events were usually mild to moderate in intensity.
The prescriber should be aware that these figures, obtained when Gabapentin Capsules was added to concurrent antiepileptic drug therapy, cannot be used to predict the frequency of adverse events in the course of usual medical practice where patient characteristics and other factors may differ from those prevailing during clinical studies. Similarly, the cited frequencies cannot be directly compared with figures obtained from other clinical investigations involving different treatments, uses, or investigators. An inspection of these frequencies, however, does provide the prescribing physician with one basis to estimate the relative contribution of drug and nondrug factors to the adverse event incidences in the population studied.
TABLE 4. Treatment-Emergent Adverse Event Incidence in Controlled Add-On Trials in >12 years of age (Events in at least 1% of Gabapentin Capsules patients and numerically more in the placebo group frequent than Patients.
Body System /Gabapentin CapsulesaPlaceboaAdverse EventN = 543N = 378%%Body as a WholeFatigue11.05.0Weight Increase2.91.6Back Pain1.80.5Peripheral Edema1.70.5CardiovascularVasodilatation1.10.3Digestive SystemDyspepsia2.20.5Mouth or Throat Dry1.70.5Constipation1.50.8Dental Abnormalities1.50.3Increased Appetite1.10.8Hematologic and Lymphatic SystemsLeukopenia1.10.5Musculoskeletal SystemMyalgia2.01.9Fracture1.10.8Nervous SystemSomnolence19.38.7Dizziness17.16.9Ataxia12.55.6Nystagmus8.34.0Tremor6.83.2Nervousness2.41.9Dysarthria2.40.5Amnesia2.20.0Depression1.81.1Thinking Abnormal1.71.3Twitching1.30.5Coordination Abnormal1.10.3Respiratory SystemRhinitis4.13.7Pharyngitis2.81.6Coughing1.81.3Skin and AppendagesAbrasion1.30.0Pruritus1.30.5Urogenital SystemImpotence1.51.1Special SensesDiplopia5.91.9Amblyopiab4.21.1Laboratory DeviationsWBC Decreased1.10.5a Plus background antoepileptic drug therapy
bAmblyopia was often describes as blured vision
Other events in more than 1% of patients >12 years of age but equally or more frequent in the placebo group included: headache, viral infection, fever, nausea and/or vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, convulsions, confusion, insomnia, emotional lability, rash, acne.
Among the treatment-emergent adverse events occurring at an incidence of at least 10% of Gabapentin Capsule-treated patients, somnolence and ataxia appeared to exhibit a positive dose-response relationship.
The overall incidence of adverse events and the types of adverse events seen were similar among men and women treated with Gabapentin Capsules. The incidence of adverse events increased slightly with increasing age in patients treated with either Gabapentin Capsules or placebo. Because only 3% of patients (28/921) in placebo-controlled studies were identified as nonwhite (black or other), there are insufficient data to support a statement regarding the distribution of adverse events by race.
Table 5 lists treatment-emergent signs and symptoms that occurred in at least 2% of Gabapentin Capsule-treated patients age 3 to 12 years of age with epilepsy participating in placebo-controlled trials and were numerically more common in the Gabapentin Capsules group. Adverse events were usually mild to moderate in intensity.
TABLE 5. TreatmentEmergent Adverse Event Incidence in Pediatric Patients Age 3 to 12 Years in a Controlled Add-On Trial (Events in at least 2% of Gabapentin Capsules patients and numerically more frequent than in the placebo group)
Body System/Gabapentin CapsulesaPlaceboaAdverse EventN = 119N = 128%%Body as a WholeViral Infection10.93.1Fever10.13.1Weight Increase3.40.8Fatigue3.41.6Digestive SystemNausea and / or Vomiting8.47.0Nervous SystemSomnolence8.44.7Hostility7.62.3Emotional Lability4.21.6Dizziness2.51.6Hyperkinesia2.50.8Respiratory SystemBronchitis3.40.8Respiratory Infection2.50.8a Plus background antiepileptic drug therapy
Other events in more than 2% of pediatric patients 3 to 12 years of age but equally or more frequent in the placebo group included: pharyngitis, upper respiratory infection, headache, rhinitis, convulsions, diarrhea, anorexia, coughing, and otitis media.
Other Adverse Events Observed During All Clinical Trials
Clinical Trials in Adults and Adolescents (Except Clinical Trials in Neuropathic Pain)
Gabapentin Capsules has been administered to 4717 patients >12 years of age during all adjunctive therapy clinical trials (except clinical trials in patients with neuropathic pain), only some of which were placebo-controlled. During these trials, all adverse events were recorded by the clinical investigators using terminology of their own choosing. To provide a meaningful estimate of the proportion of individuals having adverse events, similar types of events were grouped into a smaller number of standardized categories using modified COSTART dictionary terminology. These categories are used in the listing below. The frequencies presented represent the proportion of the 4717 patients >12 years of age exposed to Gabapentin Capsules who experienced an event of the type cited on at least one occasion while receiving Gabapentin Capsules. All reported events are included except those already listed in Table 4, those too general to be informative, and those not reasonably associated with the use of the drug.
Endocrine System: Rare: hyperthyroid, hypothyroid, goiter, hypoestrogen, ovarian failure, epididymitis, swollen testicle, cushingoid appearance.
Clinical trials in Pediatric Patients With Epilepsy
Adverse events occurring during epilepsy clinical trials in 449 pediatric patients 3 to 12 years of age treated with gabapentin that were not reported in adjunctive trials in adults are:
Body as a Whole: dehydration, infectious mononucleosis
Digestive System: hepatitis
Hemic and Lymphatic System: coagulation defect
Nervous System: aura disappeared, occipital neuralgia
Psychobiologic Function: sleepwalking
Respiratory System: pseudocroup, hoarseness
Clinical Trials in Adults With Neuropathic Pain of Various Etiologies
Safety information was obtained in 1173 patients during double-blind and open-label clinical trials including neuropathic pain conditions for which efficacy has not been demonstrated. Adverse events reported by investigators were grouped into standardized categories using modified COSTART IV terminology. Listed below are all reported events except those already listed in Table 3 and those not reasonably associated with the use of the drug.
Endocrine System: Infrequent: diabetes mellitus.
Postmarketing and Other Experience
In addition to the adverse experiences reported during clinical testing of Gabapentin Capsules, the following adverse experiences have been reported in patients receiving marketed Gabapentin Capsules. These adverse experiences have not been listed above and data are insufficient to support an estimate of their incidence or to establish causation. The listing is alphabetized: angioedema, blood glucose fluctuation, breast hypertrophy, erythema multiforme, elevated liver function tests, fever, hyponatremia, jaundice, movement disorder, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Adverse events following the abrupt discontinuation of gabapentin have also been reported. The most frequently reported events were anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain and sweating.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
OVERDOSAGE
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pediatrics
HOW SUPPLIED
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION


GabapentinGabapentin CAPSULE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!