GENTAMICIN SULFATE
GENTAMICIN SULFATEOphthalmic Solution, USP 0.3%
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- GENTAMICIN SULFATE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- GENTAMICIN SULFATE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- GENTAMICIN SULFATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- GENTAMICIN SULFATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- GENTAMICIN SULFATE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- Principal Display Panel
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Sterile
GENTAMICIN SULFATE DESCRIPTION
GENTAMICIN SULFATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION, USP is a sterile, topical anti-infective agent for ophthalmic use. The active ingredient, gentamicin sulfate, is a water-soluble antibiotic of the aminoglycoside group.
Gentamicin is obtained from cultures of Micromonospora purpurea. It is a mixture of the sulfate salts of gentamicin C1, C2, and C1A. All three components appear to have similar antimicrobial activities. Gentamicin sulfate occurs as a white to buff powder and is soluble in water but insoluble in alcohol. The structural formula is as follows:
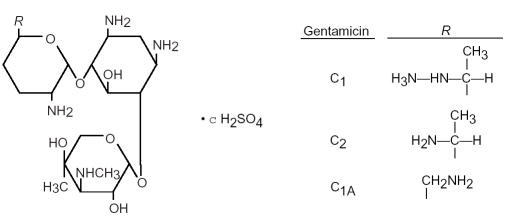
Each mL contains: Active: gentamicin sulfate equivalent to 3 mg (0.3%) gentamicin base. Preservative: benzalkonium chloride. Inactives: edetate disodium; polyvinyl alcohol 1.4%; purified water; sodium chloride; sodium phosphate, dibasic; and hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH. The solution is an aqueous, buffered solution with a shelf life pH range of 6.5 to 7.5.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Microbiology: Gentamicin sulfate is active in vitro against many strains of the following micro-organisms: Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterobacter aerogenes, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Serratia marcescens.
GENTAMICIN SULFATE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
GENTAMICIN SULFATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION, USP is indicated in the topical treatment of ocular bacterial infections including conjunctivitis, keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis, corneal ulcers, blepharitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, acute meibomianitis, and dacryocystitis, caused by susceptible strains of the following microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterobacter aerogenes, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Serratia marcescens.
GENTAMICIN SULFATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
GENTAMICIN SULFATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION, USP is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any of the components.
WARNINGS
NOT FOR INJECTION INTO THE EYE.
GENTAMICIN SULFATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION, USP is not for injection. It should never be injected subconjunctivally, nor should it be directly introduced into the anterior chamber of the eye.
PRECAUTIONS
General:
Prolonged use of topical antibiotics may give rise to overgrowth of nonsusceptible microorganisms, including fungi. Bacterial resistance to gentamicin may also develop. If purulent discharge, inflammation or pain becomes aggravated, the patient should discontinue use of the medication and consult a physician.
If irritation or hypersensitivity to any component of the drug develops, the patient should discontinue use of this preparation and appropriate therapy should be instituted.
Information for Patients:
To avoid contamination, do not touch tip of container to the eye, eyelid or any surface.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
There are no published carcinogenicity or impairment of fertility studies on gentamicin. Aminoglycoside antibiotics have been found to be non-mutagenic.
Pregnancy:
Pregnancy Category C: Gentamicin has been shown to depress body weights, kidney weights and median glomerular counts in newborn rats when administered systemically to pregnant rats in daily doses approximately 500 times the maximum recommended ophthalmic human dose. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Gentamicin should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Pediatric Use:
Safety and effectiveness in neonates have not been established.
GENTAMICIN SULFATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Bacterial and fungal corneal ulcers have developed during treatment with gentamicin ophthalmic preparations.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions are ocular burning and irritation upon drug instillation, non-specific conjunctivitis, conjunctival epithelial defects and conjunctival hyperemia. Other reactions which have occurred rarely are allergic reactions, thrombocytopenic purpura and hallucinations.
GENTAMICIN SULFATE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Instill one or two drops into the affected eye(s) every four hours. In severe infections, dosage may be increased to as much as two drops every hour.
HOW SUPPLIED
GENTAMICIN SULFATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION, USP 0.3% is supplied sterile in white opaque LDPE plastic bottles and tips with white high impact polystyrene (HIPS) caps as follows:
-
Note: Store at or below 25°C (77°F). Avoid exposure to excessive heat (40°C/104°F or above).
Rx only
Rev January 2003
© 2004 PACIFIC PHARMA
Irvine, CA 92612 U.S.A.
6622X
71759PY10P
Repackaged by:
Rebel Distributors Corp
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
Principal Display Panel
GENTAMICIN SULFATEgentamicin sulfate SOLUTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||