Glofil-125
Glofil-125
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Rx Only
GLOFIL-125 DESCRIPTION
General
GLOFIL-125 (Sodium Iothalamate I-125 Injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic aqueous
injection containing approximately 1 mg sodium iothalamate per mL, and 0.9 percent
benzyl alcohol as a preservative. The radioactive concentration of the material is
250-300 µCi/mL as of the calibration date. Sodium bicarbonate and hydrochloric
acid are present for pH adjustment.
Iodine-125 decays by electron capture with a physical half-life of 60.14 days.
Photons that are useful for detection are listed in Table 1.
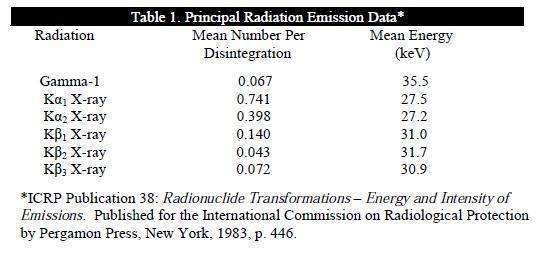
The specific gamma ray constant for I-125 is 1.43 R/mCi-hr at 1 cm. The first
half value thickness of lead (Pb) for I-125 is 0.017 mm. A range of values for the
relative attenuation of the radiation emitted by this radionuclide resulting from
interposition of various thicknesses of Pb is shown in Table 2. For example, the use
of 0.28 mm of Pb will decrease the external radiation exposure by a factor of
10,000.

To correct for physical decay of this radionuclide, the fractions that remain at
selected time intervals after the date of calibration are shown in Table 3.

The renal clearance of sodium iothalamate in man closely approximates that of
inulin. The compound is cleared by glomerular filtration without tubular secretion
or reabsorption. Following infusion administration of I-125 iothalamate, the
effective half-life is about 0.07 days.
GLOFIL-125 (Sodium Iothalamate I-125 Injection) is indicated for evaluation of glomerular filtration in the diagnosis or monitoring of patients with renal disease.
GLOFIL-125 should not be administered via a central venous line.
None known
General
As in the use of any radioactive material, care should be taken to minimize radiation
exposure to the patient, consistent with proper patient management, and to insure
minimum radiation exposure to occupational workers.
Radiopharmaceuticals should be used only by physicians who are qualified by
training and experience in the safe use and handling of radionuclides.
Rapid or bolus-like injections should be avoided.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term animal studies have been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential,
mutagenic potential, or whether this drug affects fertility in males or females.
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with GLOFIL-125. It is also
not known whether GLOFIL-125 can cause fetal harm when administered to a
pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. GLOFIL-125 should be given
to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Radioiodine is excreted in human milk during lactation. It is not known whether
GLOFIL-125 is excreted in human milk. Therefore, formula feedings should be
substituted for breast feedings.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in children have not been established.
None Reported
The suggested dose range employed in the average patient (70 kg) is as follows:
Continuous intravenous infusion: 20 to 100 μCi (0.74-3.7 megabecquerels)
(Sigman, et al (1) method).
Single intravenous injection: 10 to 30 µCi (0.37-1.11 megabecquerels)
(Cohen, et al (2) method).
The patient dose should be measured by a suitable radioactivity calibration system
immediately prior to administration.
Technique
Continuous intravenous infusion
Sigman1 method
I. Preparation:
1. Adequate diuresis (a urine flow exceeding 3 mL/min.) is established, preferably
by an oral water load of 1,500 mL two hours prior to the beginning of the
clearance study.
2. It is not necessary to withhold breakfast or admit the patient the night before.
II. Procedure:
1. After the establishment of adequate diuresis, a number 14 or 16 French Foley
catheter is aseptically inserted into the bladder.
2. An intravenous infusion of Lactated Ringers (Hartmanns) solution is started
in each arm, one to maintain a site for injection of the GLOFIL-125, the other
to serve as a site for serial withdrawal of blood. A two-way stopcock connects
the needle and intravenous tubing of each arm.
3. The dose is equally divided into (1) an intravenous priming dose to be injected
as is and (2) a sustaining dose to be diluted in 30 to 60 mL of isotonic sodium
chloride, depending on how many collection periods are anticipated.
4. The priming dose is slowly injected into one arm. This is immediately followed
by infusion of the sustaining solution through the same site, usually at the rate of
0.5 mL/min., by means of an automatic pump. During this infusion, the Lactated
Ringers solution in the same arm is discontinued, and 40 to 45 minutes are
allowed for equilibration in order to reach a state of constant plasma
concentration of radioactivity.
5. After attaining equilibrium, consecutive 15 minute collection periods
are started. From the arm opposite the injection site, 5 mL of blood (allowing
duplicate plasma counting volumes) is drawn six minutes prior to the
midpoint of each collection period, placed in heparinized tubes, mixed, and
centrifuged. The blood samples may be obtained through the two-way
stopcock after discarding the first 30 mL aspirated into the syringe. This
30 mL contains the contents of the tubing, including infusion fluid, and must
be cleared in order to obtain an undiluted blood sample. If desired, this step
may be eliminated and blood samples obtained by direct venipuncture.
6. During each collection period, total urine must be accurately collected and
the volume accurately measured. Three such consecutive collection periods
are sufficient for most clinical studies.
III. Clearance Calculations:
1. Aliquots (1 mL each) of plasma and urine from each collection period are
counted in a standard gamma-ray scintillation well detector.
2. All counts are corrected for background activity.
3. Glomerular filtration rate is calculated by the formula C=UV/P, in which:
C = glomerular filtration rate in mL/min
U= urinary concentration of radioactivity in net counts/min/mL
V= urinary flow rate in mL/min
P = plasma concentration of radioactivity in net counts/min/mL
4. Average glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is calculated from the rates for the
individual collection periods. GFR can be expressed in terms of body
weight (mL/min/kg) or body surface area (mL/min/m2).
5. Unilateral glomerular filtration rates can be determined by the same technique
by utilizing ureteral catheterization.
Single intravenous injection
Cohen2 method:
The method of Cohen, et al2 requires little preparation, few and small blood samples,
no bladder catheterization, and no constant intravenous infusion. It is simple to
perform, rapid, and utilizes equipment which is readily available in most modern
laboratories.
I. Preparation:
1. Lugol's solution, 3 drops orally, three times a day, is administered for one or
two days prior to the test.
No diet or water restriction is necessary.
2. Oral water load is begun one hour before starting the test. Start with 20 mL/kg
and force any clear liquids (unless contraindicated) until the test is complete.
II. Procedure: Record actual times for the collection of the blood and urine samples.
1. Empty the bladder and label the urine Urine control.
2. Inject 10-30 µCi GLOFIL-125 intravenously; wait 30 to 60 minutes.
3. Collect the entire urine and label Urine discard.
4. Draw 4 to 5 mL of blood into a heparinized syringe. Label Plasma #1.
5. After another 30 to 60 minutes, collect the entire urine and label Urine #1.
6. Immediately draw another blood specimen. Label Plasma #2.
7. After final 30 to 60 minute wait, collect the urine. Label Urine #2.
8. Draw the last blood specimen immediately. Label Plasma #3.
III. Clearance Calculations:
1. Radioactivity of one mL aliquots of both urine and plasma are determined
using a well-scintillation detector with a single channel pulse-height analyzer.
Sufficiently reproducible counts are usually obtained with time settings of 2
minutes for urine samples and 20 minutes for the plasma samples. Calculations
of the clearance rates are made by using the formula:(1)
C = C = UV/P + 1.73/SA where
C = glomerular filtration rate in mL/min/1.73 m2
U = urine radioactivity in counts/min/mL
V = urine flow rate in mL/min
P= mean plasma radioactivity in counts/min/mL
SA= body surface area in m2
Radiation Dosimetry
The estimated absorbed radiation doses to an average (70 kg) patient from an
intravenous dose of 100 µCi (3.7 megabecquerels) of GLOFIL-125 are shown in
Table 4. Calculations assume that there is 1% free iodide in the preparation and that
the thyroid uptake of the iodine is 25%.

Parental drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and
discoloration prior to administration,whenever solution and container permit.
HOW SUPPLIED
Identity
No. 1000, GLOFIL-125 is a clear, colorless, sterile, and nonpyrogenic solution available
as a 4 mL vial. It is supplied in a concentration of approximately 1 mg/mL sodium
iothalamate (range is 0.5–2.0 mg sodium iothalamate per mL), with a radioactivity
concentration of 250 to 300 μCi/mL at the time of calibration. Benzyl alcohol 0.9%, is
added as a preservative. Sodium bicarbonate and hydrochloric acid are added for pH
adjustment. The calibration and expiration dates are shown on the label.
Refrigerate the product upon receipt at 2°C to 8°C.
Table 3 provides the required factors for the determination of activity per mL post
calibration date for GLOFIL-125 sterile solution.
To determine the dose volume, locate the decay factor (fraction remaining) which
corresponds to the day that the dose is to be administered. The following equation is
then utilized to determine the dose volume:
activity of desired dose = dose
decay factor x amount of activity/mL on calibration day volume (mL)
(information on label)
1. Sigman EM, Elmwood CM, Reagan ME, Morris AM, Calanzaro A. The renal
clearance of 131 I labeled sodium iothalamate in man. Invest Urol 1965; 2:432.
2. Cohen ML, Smith FG Jr., Mindell RS, Vernier RL. A simple reliable method of
measuring glomerular filtration rate using single low dose sodium iothalamate 131I.
Pediatrics 1969; 43:407
ADDITIONAL REFERENCES
3. Maher FT, Nolan NG, Elveback LR. Comparisons of simultaneous clearances of
125I labeled sodium iothalamate (Glofil) and of Inulin. Mayo Clin Proc 1971; 46:
690-691.
4. Skov PE. Glomerular filtration rate in patients with severe and very severe renal
insufficiency. Acta Med Scand 1970; 187:419-428.
Manufactured by Iso-Tex Diagnostics, Inc.
Iso-Tex Diagnostics, Inc.
Friendswood, TX 77546
Phone: (877) 482-2035

Glofil-125Sodium Iothalamate I-125 injection INJECTION, SOLUTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||