Glycopyrrolate
General Injectables & Vaccines, Inc
Glycopyrrolate 0.2 mg/mL Injection, USP 5 mL Multi Dose Vial
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Glycopyrrolate Indications and Usage
- Contraindications
- Warnings
- Precautions
- Side Effects
- Overdosage
- Dosage and Administration
- How Supplied
- Sample Outer Label
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Description
Glycopyrrolate Injection, USP is a synthetic anticholinergic agent. Each 1 mL contains:
Glycopyrrolate, USP 0.2 mg
Water for Injection, USP q.s.
Benzyl Alcohol, NF 0.9% (preservative)
pH adjusted, when necessary, with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide
For intramuscular (IM) or Intravenous (IV) administration.
Glycopyrrolate is a quaternary ammonium salt with the following chemical name:
3[(cyclopentylhydroxyphenylacetyl)oxy]-1, 1-dimethyl pyrrolidinium bromide. The molecular formula is C19H28BrNO3 and the molecular weight is 398.33.
Its stuctural formula is as follows:
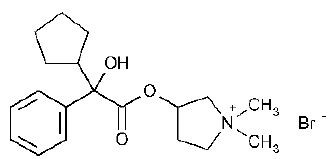
Glycopyrrolate occurs as a whilte, odorless crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and alcohol, and practically insoluble in chloroform and ether. Unlike atropine, glycopyrrolate is completely ionized at physiological pH values. Glycopyrrolate injection is a clear, colorless, sterile liquid; pH 2.0-3.0. The partition coefficient of clycopyrrolate in a n-octanol/water system is 0.304 (log10P=-1.52) at ambient room temperature (24o C).
Clinical Pharmacology
Glycopyrrolate, like other anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) agents, inhibits the action of acetylcholine on structures innervated by postganglionic cholinergic nerves and on smooth muscles that respond to acetylcholine but lack cholinergic innervation. These peripheral cholinergic receptors are present in the autonomic effector cells of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, the sinoatrial node, the atrioventricular node, exocrine glands and, to a limited degree, in the autonomic ganglia. Thus it diminishes the volume and free acidity of gastric secretions and controls excessive pharyngeal, tracheal, and bronchial secretions.
Glycopyrrolate antagonizes muscarinic symptoms (e.g., bronchorrhea, bronchspasm, bradycardia, and intestinal hypermotility) induced by cholinergic drugs such as the anticholinesterases.
The highly polar quaternary ammonium group of glycopyrrolate limits its passage across lipid membranes, such as the blood-brain barrier, in contrast to atropine sulfate and scopolamine hydrobromide, which are highly non-polar tertiary amines which penetrate lipid barriers easily.
With intravenous injection, the onset of action is generally evident within on minute. Following intramuscular administration, the onset of action is noted in 15 to 30 minutes, with peak effects occurring within approximately 30 to 45 minutes. The vagal blocking effects persist for 2 to 3 hours and the antisialogogue effects persist up to 7 hours, periods longer than for atropine.
Pharmacokinetics
As following pharmacokinetic information and conclusions were obtained from published studies that used nonspecific assay methods.
DISTRIBUTION
The mean volume of distribution of glycopyrrolate was estimated to be 0.42±0.22 L/kg.
METABOLISM
The in vivo metabolism of glycopyrrolate in humans has not been studied.
EXCRETION
The mean clearance and mean T1/2 values were reported to be 0.54±0.14 L/kg/hr and 0.83±0.13hr, respectively post IV administration. After IV administration of a 0.2 mg radiolabeld glycopyrrolate, 85% of dose recovered was recovered in urine 48 hours postdose and some of the radioactivity was also recovered in bile. After IM administration of glycopyrrolate to adults, the mean T1/2 vaule is reported to be between 0.55 to 1.25 hours. Over 80% of IM dose administered was recovered in urine and the bile as unchanged drug and half the IM dose is excreted within 3 hrs. The following table summarizes the mean and standard deviation of pharmacokinetic parameters from a study.
| Group |
t1/2 (hr) |
Vss (L/kg) |
CL (L/kg/hr) |
Tmax (min) |
Cmax (ug/L) |
AUC (ug/L*hr) |
| (6 ug/kg IV) |
0.83±0.27 | 0.42±0.22 | 0.54±0.14 | - |
- |
8.64±1.49* |
| (8 ug/kg IM) |
- |
- |
- |
27.48±6.12 | 3.47±1.48 | 6.64±2.33* |
Gender
Renal Impairment
Hepatic Impairment
Pediatrics
1/2
Glycopyrrolate Indications and Usage
In Anesthesia
Glycopyrrolate Injection is indicated for use as a preoperative antimuscarinic to reduce salivary, tracheobronchial, and pharyngeal secretions; to reduce the volume and free acidity of gastric secretions; and to block cardiac vagal inhibitory reflexes during induction of anesthesia and intubations. When indicated, Glycopyrrolate Injection may be used intraoperatively to conteract surgically or drug-induced or vagal reflexes associated arrhythmias. Glycopyrrolate protects against the peripheral muscarinic effects (e.g., bradycardia and excessive secretions) of cholinergic agents such as neostigmine and pyridostigmine given to reverse the neuromuscular blockade due to non-depolarizing muscle relaxants.
In Peptic Ulcer
For use in adults as adjunctive therapy for the treatment of peptic ulcer when rapid anticholinergic effect is desired or when oral medication is not tolerated.
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to glycopyrrolate or any of its inactive ingredients.
In addition, in the management of peptic ulcer patients, because of the longer duration of therapy, Glycopyrrolate Injection may be contraindicated in patients with the following concurrent conditions: glaucoma; obstructive uropathy (for example, bladder neck obstruction due to prostatic hypertrophy); obstructive disease of the gastrointestinal tract (as in achalasia, pyloroduodenal stenosis, etc.); paralytic ileus, intestinal atony of the elderly or debilitated patient; unstable cardiovascular status in acute hemorrhage; severe ulcerative colitis; toxic megacolon complicating ulcerative colitis; myasthenia gravis.
Warnings
This drug should be used with great caution, if at all, in patients with glaucoma. Exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol has been associated with toxicity (hypotension, metabolic acidosis), particularly in neonates, and an increased incidence of kernicterus, particularly in small preterm infants. There have been rare reports of deaths, primarily in preterm infants, associated with exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol. The amount of benzyl alcohol from medications is usually considered negligible compared to that received in flush solutions containing benzyl alcohol. Administration of high dosages of medications containing this preservative must take into account the total amount of benzyl alcohol administered. The amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. If the patient requires more than the recommended dosages or other medications containing this preservative, the practitioner must consider the daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from these combined sources. (see PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use)
Glycopyrrolate Injection may produce drowsiness or blurred vision. The patient should be cautioned regarding activities requiring mental alertness such as operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or performing hazardous work while taking this drug. In addition, in the presence of fever, high environmental temperature and/or during physical exercise, heart prostration can occur with use of anticholinergic agents including glycopyrrolate (due to decreased sweating), particularly in children and the elderly. Diarrhea may be an early symptom of incomplete intestinal obstruction, especially in patients with ileostomy or colostomy. In this instance treatment with Glycopyrrolate Injection would be inappropriate and possibly harmful.
Precautions
GeneralInformation for the Patient
Drug Interactions
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Pregnancy
2 2
Nursing Mothers
Pediatric Use
Geriatric Use
Side Effects
Overdosage
To combat peripheral anticholinergic effects, a quaternary ammonium anticholinesterase such as neostigmine methylsufate (which does not cross the blood-brain barrier) may be given intravenously in increments of 0.25 mg in adults. This dosage may be repeated every five to ten minutes until anticholinergic overactivity is reversed or up to a maximum of 2.5 mg. Proportionately smaller doses should be used in pediatric patients. Indication of repetitive doses of neostigmine should be based on close monitoring of the decrease in heart rate and the return of bowel sounds.
If CNS symptoms (e.g., excitement, restlessness, convulsions, psychotic behavior) occur, physostigmine (which does cross the blood-brain barrier) may be used. Physostigmine 0.5 to 2 mg should be slowly administered intravenously and repeated as necessary up to a total of 5 mg in adults. Proportionately smaller doses should be used in pediatric patients. To combat hypotension, administer IV fluids and/or pressor agents along with supportive care.
Fever should be treated symptomatically.
Following overdosage, a curare-like action may occur, i.e., neuromuscular blockade leading to muscular weakness and possible paralysis. In the event of a curare-like effect on respiratory muscles, artificial respiration should be instituted and maintained until effective respiratory action returns.
Dosage and Administration
NOTE: CONTAINS BENZYL ALCOHOL (see PRECAUTIONS)
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
Glycopyrrolate Injection may be administered intramuscularly, or intravenously, without dilution, in the following indications.
Adults
PREANESTHETIC MEDICATION
The recommended dose of Glycopyrrolate Injection is 0.004 mg/kg by intramuscular injection, given 30 to 60 minutes prior to the anticipated time of induction of anesthesia or at the time the preanesthetic narcotic and/or sedative are administered.
INTRAOPERATIVE MEDICATION
Glycopyrrolate Injection may be used during surgery to counteract drug-induced or bagal reflexes and their associated arrhythmias (e.g., bradycardia). It should be administered intravenously as single doses of 0.1 mg and repeated, as needed, at intervals of 2 to 3 minutes. The usual attempts should be made to determine the etiology of the arrhythmia, and the surgical or anesthetic manipulation necessary to correct parasympathetic imbalance should be performed.
REVERSAL OF NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKADE
The recommended dose of Glycopyrrolate Injection is 0.2 mg for each 1.0 mg of neostigmine or 5.0 mg of pyridostigmine. In order to minimize the appearance of cardiac side effects, the drugs may be administered simultaneously by intravenous injection and may be mixed in the same syringe.
Pediatric Patients
Diluent Compatibilities
Diluent Incompatibilities
Admixture Compatibilities
Admixture Incompatibilities
How Supplied
Glycopyrrolate Injection, USP, 0.2 mg/mL, is available in:
1 mL single dose vials packaged in 25s (NDC 10019-016-81)
2 mL single dose vials packaged in 25s (NDC 10019-016-17)
5 mL multiple dose vials packaged in 25s (NDC 10019-016-54)
20 mL multiple dose vials in 10s (NDC 10019-016-02
Store at controlled room temperature, between 20o C and 25o C (68o F and 77o F)
Baxter is a registered trademark of Baxter International Inc.
Manufactured by
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Deerfield, IL 60015 USA
For product Inquiry 1 800 ANA drugs (1-800-262-3784)
Revised October 2006
MLT-00078/5.0
Sample Outer Label

GlycopyrrolateGlycopyrrolate INJECTION, POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||