Haloperidol
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- BOXED WARNING
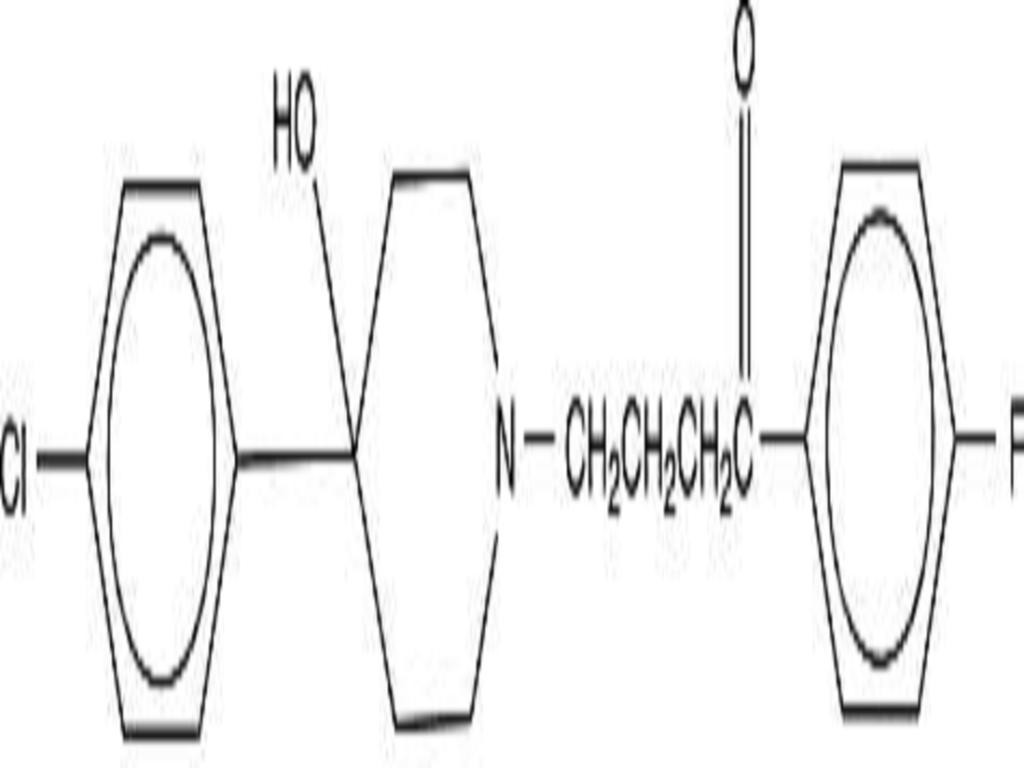
- HALOPERIDOL DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- HALOPERIDOL CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- GERIATRIC USE
- HALOPERIDOL ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
BOXED WARNING
Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related PsychosisElderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Analyses of seventeen placebo-controlled trials (modal duration of 10 weeks), largely in patients taking atypical antipsychotic drugs, revealed a risk of death in drug-treated patients of between 1.6 to 1.7 times the risk of death in placebo-treated patients. Over the course of a typical 10-week controlled trial, the rate of death in drug-treated patients was about 4.5%, compared to a rate of about 2.6% in the placebo group. Although the causes of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure, sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia) in nature. Observational studies suggest that, similar to atypical antipsychotic drugs, treatment with conventional antipsychotic drugs may increase mortality. The extent to which the findings of increased mortality in observational studies may be attributed to the antipsychotic drug as opposed to some characteristic(s) of the patients is not clear. Haloperidol is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis (seeWARNINGS).
HALOPERIDOL DESCRIPTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
INDICATIONS & USAGE
HALOPERIDOL CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related PsychosisElderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Haloperidol is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis (seeBOXED WARNING).
Cardiovascular Effects
Tardive Dyskinesia
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
Usage in Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Nonteratogenic Effects
Combined Use of Haloperidol and Lithium
General
PRECAUTIONS
PEDIATRIC USE
GERIATRIC USE
WARNINGS: Tardive DyskinesiaDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONLeukopenia, Neutropenia and Agranulocytosis
HALOPERIDOL ADVERSE REACTIONS
Cardiovascular EffectsWARNINGSPRECAUTIONS
CNS Effects
Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS)
Dystonia
Class Effect
Withdrawal Emergent Neurological Signs
Tardive Dyskinesia
Tardive Dystonia
Other CNS Effects
Body as a Whole:WARNINGS
Hematologic Effects:
Liver Effects:
Dermatologic Reactions:
Endocrine Disorders:
Gastrointestinal Effects
Autonomic Reactions:
Respiratory Effects:
Special Senses:
Post-marketing Events
OVERDOSAGE
ManifestationsADVERSE REACTIONS
Treatment
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Oral Administration
Inital Dosage Range
Adults
Children
Severely disturbed psychotic children may require higher doses. In severely disturbed, non-psychotic children or in hyperactive children with accompanying conduct disorders, who have failed to respond to psychotherapy or medications other than antipsychotics, it should be noted that since these behaviors may be short lived, short term administration of haloperidol may suffice. There is no evidence establishing a maximum effective dosage. There is little evidence that behavior improvement is further enhanced in dosages beyond 6 mg per day.
Maintenance Dosage
Switchover Procedure
HOW SUPPLIED
STORAGE AND HANDLING
Store at 20to 25(68to 77[See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]Protect from light.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

HaloperidolHaloperidol TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!