Homatropine
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Homatropine Hydrobromide ophthalmic solution is a sterile solution for ophthalmic administration in drop form, having the following composition:
Plastic squeeze bottle
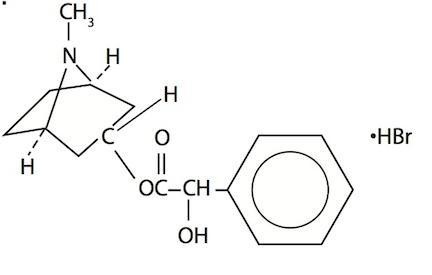
Homatropine Hydrobromide 20-50 mg/mL (cycloplegic-mydriatic) in a buffered aqueous solution containing boric acid, potassium chloride, edetate disodium and water for injection, preserved with benzalkonium chloride. The chemical name is 1αH, 3αH-Tropan-3α-o1mandelate (ester) hydrobromide. It has the following chemical structure:
Boric Acid, Potassium Chloride, Edetate Disodium, and Water for Injection USP.
Preservative: Benzalkonium Chloride USP 0.01% v/v
Homatropine Hydrobromide causes wide dilation of the pupil and paralysis of accommodation. Dilation is more rapid than with atropine but cycloplegia is not as pronounced and does not last as long.
Homatropine Hydrobromide is indicated for treatment of iritis and iridocyclitis, for relief of ciliary spasm, and also as an aid in refraction. It is frequently employed as a cycloplegic and mydriatic in preoperative and postoperative conditions.
Contraindicated in the presence of an anatomically narrow angle or in individuals with primary glaucoma and in individuals hypersensitive to one or more of the components of this preparation including the belladonna alkaloid group.
In infants and pediatric patients use with extreme caution. Excessive use in pediatric patients or certain individuals with a history of susceptibility to belladonna alkaloids may produce systemic symptoms of homatropine poisoning (see overdosage section).
Caution should be exercised when driving with dilated pupils or when engaging in hazardous activities. Parents of children should be cautious not to get the drug into the child’s mouth and to wash both the child’s and their hands after use of the drug.
If eye pain occurs from use of this medication, the patient should be advised to discontinue use and see prescribing physician immediately as this may indicate undiagnosed glaucoma. Use cautiously in elderly or hypertensive patients.
To avoid excessive systemic absorption, the lacrimal sac should be compressed by digital pressure for one minute after instillation.
Not for internal use. To prevent contaminating the dropper tip and solution, care should be taken not to touch the eyelids or surrounding area with the dropper tip of the bottle.
There have been no long-term studies using homatropine in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential.
Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been done with homatropine. It is also not known whether homatropine can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Homatropine should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Since homatropine is absorbed systemically and since it is detectable in very small amounts in human milk, and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from homatropine, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Homatropine should not be used during the first three months of life due to a possible association between the cycloplegia produced and the development of the amblyopia.
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Prolonged use may produce local irritation characterized by follicular conjunctivitis, vascular congestion, edema, exudate, and eczematoid dermatitis. Systemic homatropine toxicity is manifested by flushing and dryness of the skin (a rash may be present in children), dryness of the mouth, anhidrosis, blurred vision, photophobia, loss of neuromuscular coordination (ataxic gait), a rapid and irregular pulse, fever, abdominal and bladder distention, dysarthric quality of speech, and mental aberration (hallucinosis) with recovery frequently followed by retrograde amnesia.
When signs and symptoms of homatropine toxicity develop (see adverse reactions section), physostigmine should be administered parenterally (for dosage refer to Goodman & Gilman or other pharmacology reference). In infants and pediatric patients, the body surface must be kept moist.
Usual dosage is one or two drops of the 2% or 5% solution in the eye(s) two or three times a day, modified at discretion of physician.
For refraction: One or two drops of the 2% solution every 10-15 minutes for 5 doses or one or two drops of the 5% solution repeated in 15 minutes, modified at discretion of the physician.
KEEP THIS AND ALL DRUGS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
DO NOT USE IF IMPRINTED SEAL ON CAP IS TORN, BROKEN, OR MISSING.
5% solution: 5 mL plastic dropper tip squeeze bottle.
KEEP BOTTLE TIGHTLY CLOSED WHEN NOT IN USE. PROTECT FROM LIGHT.
STORE AT CONTROLLED ROOM TEMPERATURE 15°-30°C (59°-86°F).
Manufactured for: HUB Pharmaceuticals, LLC
Rancho Cucamonga, CA 91730

Image for Box
HomatropineHomatropine Hydrobromide SOLUTION/ DROPS
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||