Ibuprofen
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- BOXED WARNING
- IBUPROFEN DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- IBUPROFEN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- IBUPROFEN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- IBUPROFEN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- IBUPROFEN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- SPL Medguide
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
BOXED WARNING
Cardiovascular Risk
· NSAIDs may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk (see WARNINGS ).
· Ibuprofen tablets are contraindicated for treatment of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS ).
Gastrointestinal Risk
· NSAIDS cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events (see WARNINGS ).
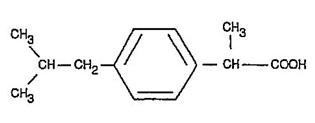
IBUPROFEN DESCRIPTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Ibuprofen tablets contain ibuprofen which possesses analgesic and antipyretic activities. Its mode of action, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood, but may be related to prostaglandin synthetase inhibition.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
IBUPROFEN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
WARNINGS
IBUPROFEN CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS , Anaphylactoid Reactions PRECAUTIONS , Preexisting Asthma
WARNINGS
WARNINGS
Cardiovascular Effects
WARNINGS, Gastrointestinal Effects-Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Gastrointestinal Effects-Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation
Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding
Renal Effects
Advanced Renal Disease
Anaphylactoid Reactions
CONTRAINDICATIONS PRECAUTIONS, Preexisting Asthma
Skin Reactions
Pregnancy
PRECAUTIONS
General Precautions
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed of the following information before initiating therapy with an NSAID and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy. Patients should also be encouraged to read the NSAID Medication Guide that accompanies each prescription dispensed.
- Ibuprofen tablets like other NSAIDs, may cause serious CV side effects, such as MI or stroke, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious CV events can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of chest pain , shortness of breath, weakness, slurring of speech, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Effects ).
- Ibuprofen tablets, like other NSAIDs, can cause GI discomfort and, rarely, serious GI side effects, such as ulcers and bleeding, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms including epigastric pain, dyspepsia , melena , and hematemesis . Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS, Gastrointestinal Effects- Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding and Perforation ).
- Ibuprofen tablets, like other NSAIDs, can cause serious skin side effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, SJS and TEN, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious skin reactions may occur without warning, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of skin rash and blisters, fever, or other signs hypersensitivity such as itching, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms. Patients should be advised to stop the drug immediately if they develop any type of rash and contact their physicians as soon as possible.
- Patients should promptly report signs or symptoms of unexplained weight gain or edema to their physicians.
- Patients should be informed of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness and "flu-like" symptoms). If these occur, patients should be instructed to stop therapy and seek immediate medical therapy.
- Patients should be informed of the signs of an anaphylactoid reaction (e.g. difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). If these occur, patients should be instructed to seek immediate emergency help (see WARNINGS ).
- In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, ibuprofen tablets should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
Laboratory Tests
Because serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, physicians should monitor for signs or symptoms of GI bleeding. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs should have their CBC and chemistry profile checked periodically. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver or renal disease develop, systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash etc.), or abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, ibuprofen tablets should be discontinued.
Drug Interactions
ACE-inhibitors
Reports suggest that NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE-inhibitors. This interaction should be given consideration in patients taking NSAIDs concomitantly with ACE-inhibitors.
Aspirin
When ibuprofen tablets are administered with aspirin, its protein binding is reduced, although the clearance of free ibuprofen tablets is not altered. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known; however, as with other NSAIDs, concomitant administration of ibuprofen and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential for increased adverse effects.
Diuretics
Clinical studies, as well as post marketing observations, have shown that ibuprofen tablets can reduce the natriuretic effect-of furosemide and thiazides in some patients. This response has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. During concomitant therapy with NSAIDs, the patient should be observed closely for signs of renal failure (see WARNINGS , Renal Effects ), as well as to assure diuretic efficacy.
Lithium
Ibuprofen produced an elevation of plasma lithium levels and a reduction in renal lithium clearance in a study of eleven normal volunteers. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15%and the renal clearance of lithium was decreased by 19%during this period of concomitant drug administration. This effect has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis by ibuprofen. Thus, when ibuprofen and lithium are administered concurrently, subjects should be observed carefully for signs of lithium toxicity. (Read circulars for lithium preparation before use of such concurrent therapy.)
Methotrexate
NSAIDs have been reported to competitively inhibit methotrexate accumulation in rabbit kidney slices. This may indicate that they could enhance the toxicity of methotrexate. Caution should be used when NSAIDs are administered concomitantly with methotrexate.
Warfarin-type anticoagulants
Several short-term controlled studies failed to show that ibuprofen tablets significantly affected prothrombin times or a variety of other clotting factors when administered to individuals on coumarin-type anticoagulants. However, because bleeding has been reported when ibuprofen tablets and other NSAIDs have been administered to patients on coumarin-type anticoagulants, the physician should be cautious when administering ibuprofen tablets to patients on anticoagulants. The effects of warfarin and NSAIDs on GI bleeding are synergistic, such that the users of both drugs together have a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone.
H-2 Antagonists
In studies with human volunteers, co-administration of cimetidine or ranitidine with ibuprofen had no substantive effect on ibuprofen serum concentrations.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Nonteratogenic Effects
Labor And Delivery
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human-milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from ibuprofen tablets, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ibuprofen tablets in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
As with any NSAIDs, caution should be exercised in treating the elderly (65 years and older).
Hepatic effects
Hematological effects
Preexisting asthma
Ophthalmological effects
Aseptic meningitis
IBUPROFEN ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequent type of adverse reaction occurring with ibuprofen tablets is gastrointestinal . In controlled clinical trials the percentage of patients reporting one or more gastrointestinal complaints ranged from 4%to 16%.
In controlled studies when ibuprofen tablets were compared to aspirin and indomethacin in equally effective doses, the overall incidence of gastrointestinal complaints was about half that seen in either the aspirin- or indomethacin-treated patients.
Adverse reactions observed during controlled clinical trials at an incidence greater than 1%are listed in the table. Those reactions listed in Column one encompass observations in approximately 3,000 patients. More than 500 of these patients were treated for periods of at least 54 weeks.
Still other reactions occurring less frequently than 1 in 100 were reported in controlled clinical trials and from marketing experience. These reactions have been divided into two categories: Column two of the table lists reactions with therapy with ibuprofen tablets where the probability of a causal relationship exists: for the reactions in Column three, a causal relationship with ibuprofen tablets has not been established.
Reported side effects were higher at doses of 3200 mg/day than at doses of 2400 mg or less per day in clinical trials of patients with rheumatoid arthritis . The increases in incidence were slight and still within the ranges reported in the table.
| Incidence Greater than 1%(but less than 3%) probable casual Relationship |
Precise Incidence Unknown (but less than 1%) probable Casual Relationship* | Precise Incidence Unknown (but less than 1%) Casual Relationship Unknown* |
|
GASTROINTESTINAL Nausea†, epigastric paint†, heartburn, diarrhea, abdominal distress, nausea and vomiting, indigestion, constipation, abdominal cramps or Pain, fullness of GI tract (bloating and flatulence) |
Gastric or duodenal ulcer with bleeding and/or perforation, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, melena, gastritis, hepatitis, jaundice, abnormal liver function tests; pancreatis |
|
|
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Dizziness†, headache, nervousness |
Depression, insomnia, confusion, emotional liability, somnolence, aseptic meningitis with fever and coma (see PRECAUTIONS ) |
Paresthesias, hallucinations, dream abnormalities, pseudo-tumor cerebri |
|
DERMATOLOGIC Rash† (including maculopapular type), pruritis |
Vesiculobullous eruptions, urticaria, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, alopecia |
Toxic epidermal necrolysis, photoallergic skin reactions |
|
SPECIAL SENSES Tinnitus |
Hearing loss, amblyopia (blurred and/or diminished vision, scotomata and/or changes in color vision) (see PRECAUTIONS ) |
Conjuctivitis, diplopia, optic neuritis, cataracts |
|
HEMATOLOGIC |
Neutropenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia (sometimes Coombs positive), thrombocytopenia with or without purpura, eosinophilia, decreases in hemoglobin and hematocrit (see PRECAUTIONS ) |
Bleeding episodes (eg epistaxis, menorrhagia) |
|
METABOLIC/ENDOCRINE Decreased appetite |
|
Gynecomastia, hypoglycemic reaction, acidosis |
|
CARDIOVASCULAR Edema, fluid retention (generally responds promptly to drug discontinuation) (see PRECAUTIONS ) |
Congestive heart failure in patients with marginal cardiac function elevated blood pressure, palpitations |
Arrhythmias (sinus tachycardia, sinus bradycardia) |
|
ALLERGIC |
Syndrome of abdominal pain, fever, chills, nausea and vomiting; anaphylaxis; bronchospasm (see CONTRADICATIONS ) |
Serum sickness, lupuserythematosus syndrome, Henoch-Schonlein vasculitis, angioedema |
|
RENAL |
Acute renal failure see PRECAUTIONS ), decreased creatinine clearance, polyuria, azotemia, cystitis, Hematuria |
Renal papillary necrosis |
|
MISCELLANEOUS |
Dry eyes and mouth, gingival ulcer, rhinitis |
|
*Reactions are classified under "Probable Causal Relationship (PCR)" if there has been one positive rechallenge or if three or more cases occur which might be causally related. Reactions are classified under "Causal Relationship Unknown" if seven or more events have been reported but the criteria for PCR have not been met.
†Reactions occurring in 3%to 9%of patients treated with ibuprofen tablets. (Those reactions occurring in less than 3%of the patients are unmarked).
OVERDOSAGE
Approximately 1½ hours after the reported ingestion of from 7 to 10 ibuprofen tablets (400 mg), a 19-month old child weighing 12 kg was seen in the hospital emergency room, apneic and cyanotic , responding only to painful stimuli. This type of stimulus, however, was sufficient to induce respiration . Oxygen and parenteral fluids were given; a greenish-yellow fluid was aspirated from the stomach with no evidence to indicate the presence of ibuprofen . Two hours after ingestion the child's condition seemed stable; she still responded only to painful stimuli and continued to have periods of apnea lasting from 5 to 10 seconds. She was admitted to intensive care and sodium bicarbonate was administered as well as infusions of dextrose and normal saline. By four hours post-ingestion she could be aroused easily, sit by herself and respond to spoken commands. Blood level of ibuprofen was 102.9 µg/mL approximately 8½ hours after accidental ingestion. At 12 hours she appeared to be completely recovered.
In two other reported cases where children (each weighing approximately 10 kg) accidentally, acutely ingested approximately 120 mg/kg, there were no signs of acute intoxication or late sequelae . Blood level in one child 90 minutes after ingestion was 700 µg/mL — about 10 times the peak levels seen in absorption-excretion studies.
A 19-year old male who had taken 8,000 mg of ibuprofen over a period of a few hours complained of dizziness , and nystagmus was noted. After hospitalization, parenteral hydration and three days bed rest, he recovered with no reported sequelae.
In cases of acute overdosage, the stomach should be emptied by vomiting or lavage, though little drug will likely be recovered if more than an hour has elapsed since ingestion. Because the drug is acidic and is excreted in the urine, it is theoretically beneficial to administer alkali and induce diuresis . In addition to supportive measures, the use of oral activated charcoal may help to reduce the absorption and reabsorption of ibuprofen tablets.
IBUPROFEN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
WARNINGS
Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, including flare-ups of chronic disease
Suggested Dosage:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
In chronic conditions
Mild to moderate pain:
Dysmenorrhea
HOW SUPPLIED
Ibuprofen tablets are available in the following strengths:
400 mg (white to off white, round, biconvex, film coated tablets debossed with ‘121’ on one side and plain on other side)
Bottles of 30 (NDC 25000-121-03)
Bottles of 500 (NDC 25000-121-12)
600 mg (white to off white, capsule shaped, biconvex, film coated tablets debossed with ‘122’ on one side and plain on other side)
Bottles of 30 (NDC 25000-122-03)
Bottles of 500 (NDC 25000-122-12)
800 mg (white to off white, capsule shaped, biconvex, film coated tablets debossed with ‘123’ on one side and plain on other side)
Bottles of 30 (NDC 25000-123-03)
Bottles of 500 (NDC 25000-123-12)
Store at controlled room temperature 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP].
Rxonly
Manufactured for:
Marksans Pharma Inc.
Lake Grove, NY 11755, USA
Manufactured by:
Marksans Pharma Ltd.
Verna, Goa-403 722, India
Iss. 07/08
SPL Medguide
Medication Guide for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
(See the end of this Medication Guide for a list of prescription NSAID medicines)
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines may increase the chance of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death.This chance increases:
- with longer use of NSAID medicines
- in people who have heart disease
NSAID medicines should never be used right before or after a heart surgery called a "coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)."
NSAID medicines can cause ulcers and bleeding in the stomach and intestines at any time during treatment. Ulcers and bleeding:
- can happen without warning symptoms
- may cause death
The chance of a person getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
- taking medicines called "corticosteroids" and "anticoagulants"
- longer use
- smoking
- drinking alcohol
- older age
- having poor health
NSAID medicines should only be used:
- exactly as prescribed
- at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
- for the shortest time needed
What are Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as:
- different types of arthritis
- menstrual cramps and other types of short-term pain
Who should not take a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)?
Do not take an NSAID medicine:
- if you had an asthma attack, hives, or other allergic reaction with aspirin or any other NSAID medicine
- for pain right before or after heart bypass surgery
Tell your healthcare provider:
- about all of your medical conditions
- about all of the medicines you take. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Keep a list of your medicines to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist.
- if you are pregnant. NSAID medicines should not be used by pregnant women late in their pregnancy.
- if you are breastfeeding. Talk to your doctor.
What are the possible side effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
|
Serious side effects include:
|
Other side effects include:
|
Get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- chest pain
- weakness in one part or side of your body
- slurred speech
- swelling of the face or throat
Stop your NSAID medicine and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- nausea
- more tired or weaker than usual
- itching
- your skin or eyes look yellow
- stomach pain
- flu-like symptoms
- vomit blood
- there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and sticky like tar
- unusual weight gain
- skin rash or blisters with fever
- swelling of the arms and legs, hands and feet
These are not all the side effects with NSAID medicines. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information about NSAID medicines.
Other information about Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Aspirin is an NSAID medicine but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain, stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
- Some of these NSAID medicines are sold in lower doses without a prescription (over-the-counter). Talk to your healthcare provider before using over-the-counter NSAIDs for more than 10 days.
NSAID medicines that need a prescription
|
Generic Name |
Tradename |
|
Celecoxib |
Celebrex |
|
Diclofenac |
Cataflam, Volataren, Arthrotec (combined with misoprostol) |
|
Diflunisal |
Dolobid |
|
Etodolac |
Lodine, Lodine XL |
|
Fenoprofen |
Nalfon, Nalfon 200 |
|
Flurbiprofen |
Ansaid |
|
Ibuprofen |
Motrin, Tab-Profen, Vicoprofen* (combined with hydrocodone), combunox (combined with oxycodone) |
|
Indomethacin |
Indocin, Indocin SR, Indo-Lemmon, Indomethagan |
|
Ketoprofen |
Oruvail |
|
Ketorolac |
Toradol |
|
Mefenamic Acid |
Ponstel |
|
Meloxicam |
Mobic |
|
Nabumetone |
Relafen |
|
Naproxen |
Naprosyn, Anaprox, Anaprox DS, EC-Naproxyn, Naprelan, Naprapac (copackaged with lansoprazole) |
|
Oxaprozin |
Daypro |
|
Piroxicam |
Feldene |
|
Sulindac |
Clinoril |
|
Tolmetin |
Tolectin, Tolectin DS, Tolectin 600 |
*Vicoprofen contains the same dose of ibuprofen as over-the-counter (OTC) NSAIDs, and is usually used for less than 10 days to treat pain. The OTC NSAID label warns that long term continuous use may increase the risk of heart attack or stroke.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for:
Marksans Pharma Inc.
Lake Grove, NY 11755, USA
Manufactured by:
Marksans Pharma Ltd.
Verna, Goa-403 722, India
Iss. 07/08
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

IbuprofenIbuprofen TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
IbuprofenIbuprofen TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
IbuprofenIbuprofen TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||