Irbesartan and Hydrochlorothiazide
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets, USP. Irbesartan and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USPInitial U.S. Approval: 1997RECENT MAJOR CHANGES(5.9)(5.1)(5.6)BOXED WARNINGWARNING: FETAL TOXICITY See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. When pregnancy is detected, discontinue irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide as soon as possible. (5.1) Drugs that act directly on the renin-angiotensin system can cause injury and death to the developing fetus. (5.1) INDICATIONS AND USAGE In patients not adequately controlled with monotherapy. (1) As initial therapy in patients likely to need multiple drugs to achieve their blood pressure goals. (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONGeneral Considerations Maximum effects within 2 to 4 weeks after dose change. (2.1) Renal Impairment: Not recommended for patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING: FETAL TOXICITY
- 1 IRBESARTAN AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 IRBESARTAN AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 IRBESARTAN AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 IRBESARTAN AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 IRBESARTAN AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 150 mg/12.5 mg (30 Tablet Bottle)
- PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 mg/12.5 mg (30 Tablet Bottle)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: FETAL TOXICITY
- When pregnancy is detected, discontinue irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide as soon as possible. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1).]
- Drugs that act directly on the renin-angiotensin system can cause injury and death to the developing fetus. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1).]
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
[see Clinical Studies (14.2)]




2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Considerations
[see Adverse Reactions (6)]
Renal impairment.
Hepatic impairment.
2.2 Add-On Therapy
In patients not controlled on monotherapy with irbesartan or hydrochlorothiazide, the recommended doses of irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets, in order of increasing mean effect, are (irbesartan-hydrochlorothiazide) 150 mg/12.5 mg, 300 mg/12.5 mg, and 300 mg/25 mg. The largest incremental effect will likely be in the transition from monotherapy to 150 mg/12.5 mg [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
2.3 Replacement Therapy
Irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets may be substituted for the titrated components.
2.4 Initial Therapy
[see Clinical Studies (14.2)][see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets are contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to any component of this product.
- Because of the hydrochlorothiazide component, this product is contraindicated in patients with anuria or hypersensitivity to other sulfonamide-derived drugs.
- Do not co-administer aliskiren with irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets in patients with diabetes [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Fetal Toxicity
Pregnancy Category D
Use of drugs that act on the renin-angiotensin system during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy reduces fetal renal function and increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death. Resulting oligohydramnios can be associated with fetal lung hypoplasia and skeletal
deformations. Potential neonatal adverse effects include skull hypoplasia, anuria, hypotension, renal failure, and death. When pregnancy is detected, discontinue irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide as soon as possible [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Thiazides cross the placenta, and use of thiazides during pregnancy is associated with a risk of fetal or neonatal jaundice, thrombocytopenia, and possibly other adverse reactions that have occurred in adults.
5.2 Hypotension in Volume- or Salt-Depleted Patients
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reaction
Hydrochlorothiazide
5.4 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Hydrochlorothiazide
5.5 Lithium Interaction
Hydrochlorothiazide
[see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.6 Electrolyte and Metabolic Imbalances
Irbesartan-Hydrochlorothiazide
In double-blind clinical trials of various doses of irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide, the incidence of hypertensive patients who developed hypokalemia (serum potassium <3.5 mEq/L) was 7.5% versus 6% for placebo; the incidence of hyperkalemia (serum potassium >5.7 mEq/L) was <1% versus 1.7% for placebo. No patient discontinued due to increases or decreases in serum potassium. On average, the combination of irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide had no effect on serum potassium. Higher doses of irbesartan ameliorated the hypokalemic response to hydrochlorothiazide.
Based on experience with the use of other drugs that affect the renin-angiotensin system, concomitant use of potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, or salt substitutes containing potassium may lead to increases in serum potassium. Concurrent therapy with hydrochlorothiazide may reduce the frequency of this effect.
Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide can cause hypokalemia and hyponatremia. Hypomagnesemia can result in hypokalemia which appears difficult to treat despite potassium repletion. Drugs that inhibit the renin-angiotensin system can cause hyperkalemia. Monitor serum electrolytes periodically.
Hyperuricemia may occur or frank gout may be precipitated in certain patients receiving thiazide therapy.
Hydrochlorothiazide may alter glucose tolerance and raise serum levels of cholesterol and triglycerides.
5.7 Hepatic Impairment
Hydrochlorothiazide
5.8 Impaired Renal Function
[see Drug Interactions (7)]
5.9 Acute Myopia and Secondary Angle-Closure Glaucoma
Sulfonamide or sulfonamide derivative drugs, such as hydrochlorothiazide, can cause an idiosyncratic reaction, resulting in transient myopia and acute angle-closure glaucoma. Cases of acute angle-closure glaucoma have been reported with hydrochlorothiazide. Symptoms include acute onset of decreased visual acuity or ocular pain and typically occur within hours to weeks of drug initiation. Untreated acute angle-closure glaucoma can lead to permanent vision loss. The primary treatment is to discontinue drug intake as rapidly as possible. Prompt medical or surgical treatments may need to be considered if the intraocular pressure remains uncontrolled. Risk factors for developing acute angle-closure glaucoma may include a history of sulfonamide or penicillin allergy.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Irbesartan-Hydrochlorothiazide
| Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide (n=898) (%) |
Placebo (n=236) (%) |
Irbesartan (n=400) (%) |
Hydrochlorothiazide (n=380) (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Body as a Whole
|
||||
| Chest Pain |
2 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
| Fatigue |
6 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
| Influenza |
3 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
|
Cardiovascular
|
||||
| Edema |
3 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
| Tachycardia |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
Gastrointestinal
|
||||
| Abdominal Pain |
2 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
| Dyspepsia/heartburn |
2 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
| Nausea/vomiting |
3 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
|
Immunology
|
||||
| Allergy |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
Musculoskeletal
|
||||
| Musculoskeletal Pain |
6 |
5 |
6 |
10 |
|
Nervous System
|
||||
| Dizziness |
8 |
4 |
6 |
5 |
| Dizziness Orthostatic |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
Renal/Genitourinary
|
||||
| Abnormality Urination |
2 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
Irbesartan
Body as a Whole:
Cardiovascular:
Dermatologic:
Endocrine/Metabolic/Electrolyte Imbalances:
Gastrointestinal:
Musculoskeletal/Connective Tissue:
Nervous System:
Renal/Genitourinary:
Respiratory:
Special Senses:
Hydrochlorothiazide
Body as a Whole:
Digestive:
Hematologic:
Hypersensitivity:
Metabolic:
Musculoskeletal:
Nervous System/Psychiatric:
Renal:
Skin:
Special Senses:
Initial Therapy
hydrochlorothiazide
[see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
6.3 Laboratory Abnormalities
Creatinine, Blood Urea Nitrogen:
Liver Function Tests:
Serum Electrolytes: [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.6)].
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Irbesartan
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents Including Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors (COX-2 Inhibitors)
Dual Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS)
Hydrochlorothiazide
Alcohol, Barbiturates, or Narcotics:
Antidiabetic Drugs (oral agents and insulin):
Other Antihypertensive Drugs:
Cholestyramine and Colestipol Resins:
Corticosteroids, ACTH:
Pressor Amines (e.g., Norepinephrine):
Skeletal Muscle Relaxants, Nondepolarizing (e.g., Tubocurarine):
Lithium: [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs:
Carbamazepine
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D
in utero[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
[see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)]
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
Neonates with a history of in utero exposure to irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide:
8.5 Geriatric Use
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Irbesartan
Physicians’ Desk Reference
2
Hydrochlorothiazide
50
11 DESCRIPTION
1
poH25286

H78342
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Irbesartan
12
11 2
1
Hydrochlorothiazide
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Irbesartan
Hydrochlorothiazide
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Irbesartan
Hydrochlorothiazide
Metabolism and Elimination
Irbesartan
14
14
In vitro
Hydrochlorothiazide
Distribution
Irbesartan
1
Hydrochlorothiazide
Pediatric
Gender
Geriatric
max
Race
max
Renal Insufficiency
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hepatic Insufficiency
Drug-Drug Interactions
In vitro in vitro
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Irbesartan-Hydrochlorothiazide
in vitroin vitro–in vivo–
Irbesartan
0-24 hours
in vitroin vitro–in vivo–
0-24 hours
Hydrochlorothiazide
in vitroSalmonella typhimuriumin vivoDrosophila in vitroAspergillus nidulans
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Reproductive Toxicology Studies
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Irbesartan Monotherapy
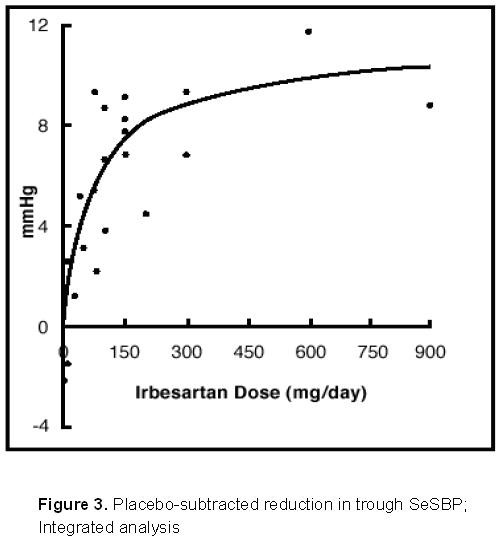

14.2 Irbesartan-Hydrochlorothiazide
Initial Therapy
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Irbesartan and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets USP, 150 mg/12.5 mg
Irbesartan and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets USP, 300 mg/12.5 mg
16.2 Storage
Store at
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Pregnancy
Female patients of childbearing age should be told about the consequences of exposure to irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide during pregnancy. Discuss treatment options with women planning to become pregnant. Patients should be asked to report pregnancies to their physician as soon as possible.
17.2 Symptomatic Hypotension
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 150 mg/12.5 mg (30 Tablet Bottle)
NDC 65862-629-30
Irbesartan and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP
150 mg/12.5 mg
Rx only 30 Tablets
AUROBINDO

PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 mg/12.5 mg (30 Tablet Bottle)
NDC 65862-630-30
Irbesartan and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP
300 mg/12.5 mg
Rx only 30 Tablets
AUROBINDO

Irbesartan and HydrochlorothiazideIrbesartan and Hydrochlorothiazide TABLET, FILM COATED
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Irbesartan and HydrochlorothiazideIrbesartan and Hydrochlorothiazide TABLET, FILM COATED
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||