Jeanatope
Jeanatope
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Rx Only
JEANATOPE DESCRIPTION
Jeanatope 1-125 (Iodinated 1-125 Albumin Injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic,
aqueous solution for intravenous use. Each milliliter provides approximately 10
mg protein (normal human serum albumin), 1.6 mg sodium phosphate, 16 mg
sodium biphosphate, not more than 0.4 mg guanidine hydrochloride, sodium
chloride for isotonicity, and 9 mg benzyl alcohol as a preservative. The
stabilizer aceryltryptophanate and sodium caprylate have a concentration of less
than 0.0089M. The pH has been adjusted to 7.2-7.8 with sodium hydroxide or
hydrochloric acid.
Jeanotope I-125 was prepared from the blood that was non-reactive when tested
for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and HIV antibody.
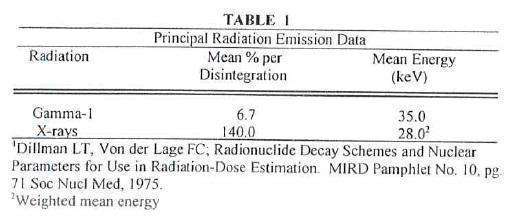
Iodine 125 decays by electron capture with a physical half-life of 60.14 days.1
Photons that are useful for detection and imaging studies are listed in Table 1.
External Radiation
The specific gamma ray constant for I-125 is 1.5 R/millicurie-hour at 1 cm. The
first half-value thickness of Pb for I-125 is .002 mm. A range of values for the
relative attenuation of the radiation emitted by this radionuclide that results from
interposition of various thicknesses of Pb is shown in Table 2. For example,
the use of .02 min of Pb will decrease the external radiation exposure by a factor of
1,000.

Following intravenous injection, radioiodinated serum albumin is uniformly
distributed throughout the intravascular pool within 10 minutes; extravascular
distribution takes place more slowly. Labeled albumin also can be detected in
the lymph and in certain body tissues within 10 minutes after injection, but
maximum distribution of radioactivity throughout the extravascular space does
not occur until two to four days after administration. The time at which
extravascular activity is maximal has been designated as the "equilibrium time."
When this point has been reached, the radioactivity remaining in the
intravascular and extravascular spaces decreases slowly and exponentially in
parallel fashion.
The administered radioactivity is eliminated almost entirely in the urine, only
about 2 percent of the total dose ultimately appearing in the feces. The biologic
half-life of labeled albumin is dependent upon a number of factors, and
published studies have varied considerably in their reporting of this figure. It
has ranged, in the literature, from below 10 days to over 20 days. One important
factor affecting the biologic half-life is the initial rate of excretion, and this
depends in part on the quality of the labeled albumin. With Jeanatope 1-125 the
biologic half-life in normal individuals has been reported to be approximately 14
days.
Jeanotope I-125 is indicated for use in the determination of total blood and plasma volume.
At present there are no known contraindications to the use of this preparation.
Radiopharmaceuticals should not be administered to patients who are pregnant
or to nursing mothers unless the expected benefit to be gained outweighs
the potential hazards.
Since I-125 is excreted in human milk during lactation, formula-feedings
should be substituted for breast-feedings.
Ideally, examinations using radiopharmaceuticats, especially those elective in
nature, of a woman of childbearing capability should be performed during the
first few (approximately 10) days following the onset of menses.
A few instances of hyperpyrexia and aseptic (chemical) meningeal irritation
have been reported with the use of this product in cisternography. This material
is not approved for use in cisternography.
In the use of any radioactive material, care should be taken to insure minimum
radiation exposure to the patient and occupational workers consistent with
proper patient management.
Although the immunological properties of serum albumin are believed to be
virtually unaltered by the iodinated process, there is a theoretical possibility that
allergic reactions may occur in patients receiving additional doses a number of
weeks after an initial dose.
Radioiodinated serum albumin is administered intravenously. When a
procedure such as a blood volume determination is to be repeated, the total
dosage administered in any one week should not exceed 7.4 megabecquerels
(200 microcuries).
To minimise the uptake of radioactive iodine by the thyroid, prior
administration of Lugol's Solution (Strong Iodine Solution USP) may be used.
Ten drops of Lugol's Solution three times a daily, beginning at least 24 hours
before administration of Iodinated Serum Albumin I-125 and continuing for one
or two weeks thereafter, is a suitable dose.
Complete assay data for each vial are provided on the container.
Note: The expiration date given on the container pertains to the biologic
properties of the material and not to the radioactivity label, it is important to
make certain that the radioactivity in the dose at the time of administration is
sufficient for the intended use.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for
particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution
and container permit.
Jeanotope (Iodinated I-125 Albumin Injection) may be colorless to very pale
yellow. Solutions with excessive coloration should not be used.
The patient dose should be measured by a suitable radioactivity calibration
system immediately prior to administration.
Note: A shielded syringe should be used for withdrawing and injecting the
Iodinated I-125 Albumin.
Total Blood and Plasma Volumes
Dosage may range from .185 to 1.85 megabecquerels (5 to 50 microcuries).
Blood Volume Determination
A. Preparation of Reference Solution
Remove an aliquot of the contents of the vial to be used in the procedure
identical in volume to the dose to be administered to the patient. Prepare a
reference solution using normal saline as a diluent. The recommended dilution
is 1:4000 (Dilution Factor (DF) = 4000). Determine the radioactivity
concentration (net cpm/ml) of the reference solution. Care must be taken to
assure that the reference solution and the blood samples (Step B3) are assayed
using the same geometric configuration.
A. Administration of Dose
1. Inject the dose into a large vein in patient's arm. Measure the residual
radioactivity in the syringe and needle.
2. Destroy the syringe after injecting. Do not attempt to resterilize.
CAUTION: the syringe should be disposed of in accordance with the US
Nuclear Regulatory Commission or Agreement State regulations
pertaining to the disposal of radioactive waste.
3. At 5 and 15 minutes after injecting the dose, withdraw blood samples
from the patient's other arm with a sterile heparinized syringe.
B. Calculation of Blood Volume
1. Take a known aliquot from each blood sample and determine
radioconcentration in net cpm/mL.
2. Plot the 5- and 15-minute sample counts (net cpm/mL) on semilog graph
paper using the average count value of each sample and determine the
radioconcentration at injection time (zero time) by drawing a straight line
through the 15- and 5- minute points to zero time. The x ordinate iof the
graph is the sample withdrawal time and the logarithmic y ordinate is
radioconcentration in net cpm/mL.
3. Calculate the patient's blood volume (in mL) using the following formula:
Net cpm/mL reference solution × DF = blood volume (in mL)
Net cpm/mL patient's blood sample
Sample Blood Volume Calculations
Volume of blood sample aliquot = 1.0 mL
Volume of reference solution aliquot = 1.0 mL
Net counts at zero time = 2500
Net counts obtained from reference solution aliquot = 2725
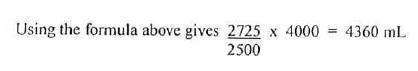
Serial Blood Volume Determinations
Jeanotope (Iodinated I-125 Albumin Injection) is administered in sufficiently
low dosage to permit repetitions as often as required by clinical circumstances.
It must be remembered that it is always necessary to correct for background
radioactivity remaining in the blood from former determinations. Therefore, for
each determination after the first one, a background blood sample must be taken
just before the iodinated I-125 Albumin is injected.
Background Blood Sample:
1. Prior to injecting Jeanotope I-125, withdraw background blood sample
from large vein in patient's arm with a sterile heparinized syringe.
2. Leaving needle in a patient's vein, detach syringe containing blood sample.
3. Withdraw Jeanotope I-125 from the vial and administer (see instructions
under Blood Volume Determination, Administration of Dose).
4. Determine radioconcentration in net cpm/mL of aliquots taken from
background and postinjection blood samples, and from the reference
solution.
The radioconcentration (net cpm/mL) per aliquot of the background blood
sample must be subtracted from the radioconcentration per aliquot of the blood
sample obtained after the injection of Iodinated I-125 Albumin. The formula
for calculating each blood volume determination after the first one thus
becomes:
Net cpm/mL reference solution × 400 = blood volume
Net cpm/mL Net cpm/mL (in mL)
postinjection minus background
blood sample blood sample
Plasma Volume Determination
The procedure is essentially the same as that for blood volume determination,
except that the blood sample drawn from the patient is centrifuged, the red blood
cells are removed, and net cpm/mL of the plasma is determined. The formula
for calculation of plasma volume, therefore is:
Net cpm/mL reference solution × 400 = plasma volume
Net cpm/mL patient's plasma sample (in mL)
Radiation Dosimetry
The estimated absorbed radiation doses to an average patient (70 kg) from an
intravenous injection of 1.85 megabecquerels (50 microcuries) of iodinated
I-125 Albumin USP are shown in Table 4.

For doses of 2.775, 5.55, 18.5 and 27.75 megabecquerels (75, 150, 500 and
750 microcuries), the estimated absorbed doses are 1.5, 3, 10 and 15 times the
number of rads given respectively.
Jeanotope (Iodinated I-125 Albumin Injection USP) is available in multiple dose
vials containing the following amounts of activity on the date of calibration: 3.7
megabequerels /10.0 ml (100 microcuries/10.0 ml), 18.5 megabequerels/0.5 ml
(500 microcuries/0.5 ml) and 37.0 megabequerels/1.0 ml (1.0 millicuries/1.0
ml). Complete assay data for each vial is provided on the container.
The maximum concentration of Iodinated I-125 Injection does not exceed
one millicurie per milliliter at time of calibration.
Store between 2°C - 8°C.
This radiopharmaceutical is licensed by the Texas Department of Health, Bureau of Radiation Control for distribution to persons licensed pursuant
to 41.26 (b) and Appendix 41-C, Group I and Group II, "Texas Regulations for Control of Radiation," or under equivalent licenses of the U.S.
Nuclear Regulatory Commission, an Agreement State, or a Licensing State.
Iso-Tex Diagnostics, Inc.
P.O. Box 909 . Friendswood, Texas 77549 . USA.
Phone: 281-482-1231 . Customer Service: 800-477-4839 . Fax: 281-482-1070

JeanatopeIodinated I-125 Albumin INJECTION, SOLUTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||