KYPROLIS
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use KYPROLIS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KYPROLIS. Initial U.S. Approval: [2012]INDICATIONS AND USAGEKYPROLIS is a proteasome inhibitor indicated for the treatment of patients with multiple myeloma who have received at least two prior therapies including bortezomib and an immunomodulatory agent and have demonstrated disease progression on or within 60 days of completion of the last therapy. Approval is based on response rate. Clinical benefit, such as improvement in survival or symptoms, has not been verified. (1, 14)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Administer intravenously over 2 to 10 minutes, on two consecutive days each week for three weeks (Days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15, and 16), followed by a 12-day rest period (Days 17 to 28). (2.1) Recommended Cycle 1 dose is 20 mg/m2/day and if tolerated increase Cycle 2 dose and subsequent cycles doses to 27 mg/m2/day. (2.1) Hydrate patients prior to and following administration. (2.2) Pre-medicate with dexamethasone prior to all Cycle 1 doses, during the first cycle of dose escalation, and if infusion reaction symptoms develop or reappear. (2.3) Modify dosing based on toxicity. (2.4) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSSingle-use vial: 60 mg sterile lyophilized powder (3)CONTRAINDICATIONSNone (4)WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Cardiac Adverse Reactions including heart failure and ischemia: Monitor for cardiac complications. Treat promptly and withhold KYPROLIS. (2.4, 5.1) Pulmonary Hypertension: Withhold dosing if suspected. (2.4, 5.2) Pulmonary Complications: Monitor for and manage dyspnea immediately; interrupt KYPROLIS until symptoms have resolved or returned to baseline. (2.4, 5.3) Infusion Reactions: Pre-medicate with dexamethasone to prevent. (2.3) Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms develop. (5.4) Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS): Hydrate patients to prevent. (2.2) Monitor for TLS and treat promptly. (5.5) Thrombocytopenia: Monitor platelet counts; reduce or interrupt dosing as clinically indicated. (2.4, 5.6) Hepatic Toxicity and Hepatic Failure: Monitor liver enzymes and withhold dosing if suspected. (2.4, 5.7) Embryo-fetal Toxicity: KYPROLIS can cause fetal harm. Females of reproductive potential should avoid becoming pregnant while being treated. (5.8, 8.1) Side EffectsMost commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 30%) are fatigue, anemia, nausea, thrombocytopenia, dyspnea, diarrhea, and pyrexia. (6) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Onyx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-877-669-9121 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Patients on dialysis: Administer KYPROLIS after the dialysis procedure. (8.6)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 KYPROLIS INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 KYPROLIS DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 KYPROLIS CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 KYPROLIS ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 KYPROLIS DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Carton Label
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
KYPROLIS is indicated for the treatment of patients with multiple myeloma who have received at least two prior therapies including bortezomib and an immunomodulatory agent and have demonstrated disease progression on or within 60 days of completion of the last therapy. Approval is based on response rate [see Clinical Studies ( 14.1 )]. Clinical benefit, such as improvement in survival or symptoms, has not been verified.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Guidelines
KYPROLIS is administered intravenously over 2 to 10 minutes, on two consecutive days, each week for three weeks (Days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15, and 16), followed by a 12-day rest period (Days 17 to 28). Each 28-day period is considered one treatment cycle (Table 1).
In Cycle 1, KYPROLIS is administered at a dose of 20 mg/m2. If tolerated in Cycle 1, the dose should be escalated to 27 mg/m2 beginning in Cycle 2 and continued at 27 mg/m2 in subsequent cycles. Treatment may be continued until disease progression or until unacceptable toxicity occurs [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.4 )].
The dose is calculated using the patient’s actual body surface area at baseline. Patients with a body surface area greater than 2.2 m2 should receive a dose based upon a body surface are of 2.2 m2. Dose adjustments do not need to be made for weight changes of less than or equal to 20%.
|
KYPROLIS (20 mg/m2): |
Cycle 1 | |||||||||
| Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | |||||||
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Days 3-7 |
Day 8 |
Day 9 |
Days 10-14 |
Day 15 |
Day 16 |
Days 17-21 |
Days 22-28 |
|
| 20 | 20 | No Dosing | 20 | 20 | No Dosing | 20 | 20 | No Dosing | No Dosing | |
|
KYPROLIS (27 mg/m2): |
Cycles 2 and Beyond |
|||||||||
| Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | |||||||
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Days 3-7 |
Day 8 |
Day 9 |
Days 10-14 |
Day 15 |
Day 16 |
Days 17-21 |
Days 22-28 |
|
| 27 | 27 | No Dosing | 27 | 27 | No Dosing | 27 | 27 | No Dosing | No Dosing | |
2.2 Hydration and Fluid Monitoring
Hydrate patients to reduce the risk of renal toxicity and of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) with KYPROLIS treatment [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5 )]. Maintain adequate fluid volume status throughout treatment and monitor blood chemistries closely. Prior to each dose in Cycle 1, give 250 mL to 500 mL of intravenous normal saline or other appropriate intravenous fluid. Give an additional 250 mL to 500 mL of intravenous fluids as needed following KYPROLIS administration. Continue intravenous hydration, as needed, in subsequent cycles. Also monitor patients during this period for fluid overload [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )].
2.3 Dexamethasone Premedication
Pre-medicate with dexamethasone 4 mg orally or intravenously prior to all doses of KYPROLIS during Cycle 1 and prior to all KYPROLIS doses during the first cycle of dose escalation to 27 mg/m2 to reduce the incidence and severity of infusion reactions [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4 )]. Reinstate dexamethasone premedication (4 mg orally or intravenously) if these symptoms develop or reappear during subsequent cycles.
2.4 Dose Modifications Based on Toxicities
Recommended actions and dose modifications are presented in Table 2.
| Hematologic Toxicity | Recommended Action |
|
|
| Non-Hematologic Toxicity | Recommended Action |
|
Cardiac Toxicity Grade 3 or 4, new onset or worsening of:
|
|
|
Pulmonary Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] |
|
|
Pulmonary Complications
|
|
|
Hepatic Toxicity
|
|
|
Renal Toxicity
|
|
|
Peripheral Neuropathy
|
|
|
Other
|
|
2.5 Administration Precautions
The quantity of KYPROLIS contained in one single-use vial (60 mg carfilzomib) may exceed the required dose. Caution should be used in calculating the quantity delivered to prevent overdosing.
Do not mix KYPROLIS with or administer as an infusion with other medicinal products.
The intravenous administration line should be flushed with normal saline or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP immediately before and after KYPROLIS administration. KYPROLIS should not be administered as a bolus. KYPROLIS should be administered over 2 to 10 minutes.
2.6 Reconstitution and Preparation for Intravenous Administration
KYPROLIS vials contain no antimicrobial preservatives and are intended only for single use. Unopened vials of KYPROLIS are stable until the date indicated on the package when stored in the original package at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). The reconstituted solution contains carfilzomib at a concentration of 2 mg/mL. Read the complete preparation instructions prior to reconstitution.
Reconstitution/Preparation Steps:
- Remove vial from refrigerator just prior to use.
- Aseptically reconstitute each vial by slowly injecting 29 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP, directing the solution onto the INSIDE WALL OF THE VIAL to minimize foaming.
- Gently swirl and/or invert the vial slowly for about 1 minute, or until complete dissolution of any cake or powder occurs. DO NOT SHAKE to avoid foam generation. If foaming occurs, allow solution to rest in vial for about 2 to 5 minutes, until foaming subsides.
- After reconstitution, KYPROLIS is ready for intravenous administration. The reconstituted product should be a clear, colorless solution. If any discoloration or particulate matter is observed, do not use the reconstituted product.
- When administering in an intravenous bag, withdraw the calculated dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] from the vial and dilute into 50 mL 5% Dextrose Injection, USP intravenous bag.
- Immediately discard the vial containing the unused portion.
The stabilities of reconstituted KYPROLIS under various temperature and container conditions are shown in Table 3.
| Storage Conditions of Reconstituted KYPROLIS |
Stability |
||
| Vial | Syringe |
IV Bag (D5W |
|
| Refrigerated (2°C to 8°C; 36°F to 46°F) | 24 hours | 24 hours | 24 hours |
| Room Temperature (15°C to 30°C; 59°F to 86°F) | 4 hours | 4 hours | 4 hours |
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
KYPROLIS single-use vial contains 60 mg of carfilzomib as a sterile, white to off-white lyophilized cake or powder.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiac Arrest, Congestive Heart Failure, Myocardial Ischemia
Death due to cardiac arrest has occurred within a day of KYPROLIS administration. New onset or worsening of pre-existing congestive heart failure with decreased left ventricular function or myocardial ischemia have occurred following administration of KYPROLIS. Cardiac failure events (e.g., cardiac failure congestive, pulmonary edema, ejection fraction decreased) were reported in 7% of patients. Monitor for cardiac complications and manage promptly. Withhold KYPROLIS for Grade 3 or 4 cardiac events until recovery and consider whether to restart KYPROLIS based on a benefit/risk assessment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. Patients with New York Heart Association Class III and IV heart failure, myocardial infarction in the preceding 6 months, and conduction abnormalities uncontrolled by medications were not eligible for the clinical trials. These patients may be at greater risk for cardiac complications.
5.2 Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) was reported in 2% of patients treated with KYPROLIS and was Grade 3 or greater in less than 1% of patients. Evaluate with cardiac imaging and/or other tests as indicated. Withhold KYPROLIS for pulmonary hypertension until resolved or returned to baseline and consider whether to restart KYPROLIS based on a benefit/risk assessment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.3 Pulmonary Complications
Dyspnea was reported in 35% of patients enrolled in clinical trials. Grade 3 dyspnea occurred in 5%; no Grade 4 events, and 1 death (Grade 5) was reported. Monitor and manage dyspnea immediately; interrupt KYPROLIS until symptoms have resolved or returned to baseline [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.4 Infusion Reactions
Infusion reactions were characterized by a spectrum of systemic symptoms including fever, chills, arthralgia, myalgia, facial flushing, facial edema, vomiting, weakness, shortness of breath, hypotension, syncope, chest tightness, or angina. These reactions can occur immediately following or up to 24 hours after administration of KYPROLIS. Administer dexamethasone prior to KYPROLIS to reduce the incidence and severity of reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Inform patients of the risk and symptoms and to contact physician if symptoms of an infusion reaction occur [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.5 Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) occurred following KYPROLIS administration in < 1% of patients. Patients with multiple myeloma and a high tumor burden should be considered to be at greater risk for TLS. Prior to receiving KYPROLIS, ensure that patients are well hydrated [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Monitor for evidence of TLS during treatment, and manage promptly. Interrupt KYPROLIS until TLS is resolved [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.6 Thrombocytopenia
KYPROLIS causes thrombocytopenia with platelet nadirs occurring around Day 8 of each 28-day cycle and recovery to baseline by the start of the next 28-day cycle. In patients with multiple myeloma, 36% of patients experienced thrombocytopenia, including Grade 4 in 10%. Thrombocytopenia following KYPROLIS administration resulted in a dose reduction in 1% of patients and discontinuation of treatment with KYPROLIS in < 1% of patients. Monitor platelet counts frequently during treatment with KYPROLIS. Reduce or interrupt dose as clinically indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.7 Hepatic Toxicity and Hepatic Failure
Cases of hepatic failure, including fatal cases, have been reported (< 1%). KYPROLIS can cause elevations of serum transaminases and bilirubin. Withhold KYPROLIS in patients experiencing Grade 3 or greater elevations of transaminases, bilirubin, or other liver abnormalities until resolved or returned to baseline. After resolution, consider if restarting KYPROLIS is appropriate. Monitor liver enzymes frequently [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.8 Embryo-fetal Toxicity
KYPROLIS can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman based on its mechanism of action and findings in animals. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women using KYPROLIS. Carfilzomib caused embryo-fetal toxicity in pregnant rabbits at doses that were lower than in patients receiving the recommended dose.
Females of reproductive potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant while being treated with KYPROLIS. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Cardiac Arrest, Congestive Heart Failure, Myocardial Ischemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Pulmonary Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Pulmonary Complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Infusion Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Thrombocytopenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hepatic Toxicity and Hepatic Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
The most common adverse reactions (incidence of 30% or greater) to KYPROLIS observed in clinical trials of patients with multiple myeloma were fatigue, anemia, nausea, thrombocytopenia, dyspnea, diarrhea, and pyrexia.
6.1 Clinical Trials Safety Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug, and may not reflect the rates observed in medical practice.
A total of 526 patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma received KYPROLIS as monotherapy or with pre-dose dexamethasone. Patients received a median of four treatment cycles with a median cumulative KYPROLIS dose of 993.4 mg.
Deaths due to all causes within 30 days of the last dose of KYPROLIS occurred in 37/526 (7%) of patients. Deaths not attributed to disease progression were cardiac in 5 patients (acute coronary syndrome, cardiac arrest, cardiac disorder), end-organ failure in 4 patients (multi-organ failure, hepatic failure, renal failure), infection in 4 patients (sepsis, pneumonia, respiratory tract bacterial infection), dyspnea and intracranial hemorrhage in 1 patient each, and 1 patient found dead of unknown causes.
Serious adverse reactions were reported in 45% patients. The most common serious adverse reactions were pneumonia (10%), acute renal failure (4%), pyrexia (3%), and congestive heart failure (3%). Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of KYPROLIS occurred in 15% of patients and included congestive heart failure (2%), cardiac arrest, dyspnea, increased blood creatinine, and acute renal failure (1% each).
Adverse reactions occurring at a rate of 10% or greater are presented in Table 4.
| Patients (N = 526) [n (%)] |
|||
| Event | All Grades  |
Grade 3 Events |
Grade 4 Events |
| Fatigue | 292 (55.5) | 38 (7.2) | 2 (0.4) |
| Anemia | 246 (46.8) | 111 (21.1) | 7 (1.3) |
| Nausea | 236 (44.9) | 7 (1.3) | 0 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 191 (36.3) | 69 (13.1) | 54 (10.3) |
| Dyspnea | 182 (34.6) | 25 (4.8) | 1 (0.2) |
| Diarrhea | 172 (32.7) | 4 (0.8) | 1 (0.2) |
| Pyrexia | 160 (30.4) | 7 (1.3) | 2 (0.4) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 149 (28.3) | 17 (3.2) | 0 |
| Headache | 145 (27.6) | 7 (1.3) | 0 |
| Cough | 137 (26.0) | 1 (0.2) | 0 |
| Blood creatinine increased | 127 (24.1) | 13 (2.5) | 1 (0.2) |
| Lymphopenia | 126 (24.0) | 84 (16.0) | 11 (2.1) |
| Edema peripheral | 126 (24.0) | 3 (0.6) | 0 |
| Vomiting | 117 (22.2) | 5 (1.0) | 0 |
| Constipation | 110 (20.9) | 1 (0.2) | 0 |
| Neutropenia | 109 (20.7) | 50 (9.5) | 4 (0.8) |
| Back pain | 106 (20.2) | 15 (2.9) | 0 |
| Insomnia | 94 (17.9) | 0 | 0 |
| Chills | 84 (16.0) | 1 (0.2) | 0 |
| Arthralgia | 83 (15.8) | 7 (1.3) | 0 |
| Muscle spasms | 76 (14.4) | 2 (0.4) | 0 |
| Hypertension | 75 (14.3) | 15 (2.9) | 2 (0.4) |
| Asthenia | 73 (13.9) | 12 (2.3) | 1 (0.2) |
| Hypokalemia | 72 (13.7) | 14 (2.7) | 3 (0.6) |
| Hypomagnesemia | 71 (13.5) | 2 (0.4) | 0 |
| Leukopenia | 71 (13.5) | 27 (5.1) | 1 (0.2) |
| Pain in extremity | 70 (13.3) | 7 (1.3) | 0 |
| Pneumonia | 67 (12.7) | 52 (9.9) | 3 (0.6) |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 66 (12.5) | 15 (2.9) | 1 (0.2) |
| Dizziness | 66 (12.5) | 5 (1.0) | 1 (0.2) |
| Hypoesthesia | 64 (12.2) | 3 (0.6) | 0 |
| Anorexia | 63 (12.0) | 1 (0.2) | 0 |
| Pain | 63 (12.0) | 12 (2.3) | 1 (0.2) |
| Hyperglycemia | 62 (11.8) | 16 (3.0) | 3 (0.6) |
| Chest wall pain | 60 (11.4) | 3 (0.6) | 0 |
| Hypercalcemia | 58 (11.0) | 13 (2.5) | 8 (1.5) |
| Hypophosphatemia | 55 (10.5) | 24 (4.6) | 3 (0.6) |
| Hyponatremia | 54 (10.3) | 31 (5.9) | 3 (0.6) |
Renal Events
The most common renal adverse reactions were increase in blood creatinine (24%) and renal failure (9%), which were mostly Grade 1 or Grade 2 in severity. Grade 3 renal adverse reactions occurred in 6% of patients and Grade 4 events occurred in 1%. Discontinuations due to increased blood creatinine and acute renal failure were 1% each. In one patient, death occurred with concurrent sepsis and worsening renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy (including all events of peripheral sensory neuropathy and peripheral motor neuropathy) occurred in 14% of patients enrolled in clinical trials. Grade 3 peripheral neuropathy occurred in 1% of patients. Serious peripheral neuropathy events occurred in < 1% of patients, which resulted in dose reduction in < 1% and treatment discontinuation in < 1%. Withhold or discontinue treatment as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Herpes Virus Infection
Herpes zoster reactivation was reported in 2% of patients. Consider antiviral prophylaxis for patients who have a history of herpes zoster infection.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Carfilzomib is primarily metabolized via peptidase and epoxide hydrolase activities, and as a result, the pharmacokinetic profile of carfilzomib is unlikely to be affected by concomitant administration of cytochrome P450 inhibitors and inducers. Carfilzomib is not expected to influence exposure of other drugs [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Females of reproductive potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant while being treated with KYPROLIS. Based on its mechanism of action and findings in animals, KYPROLIS can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Carfilzomib caused embryo-fetal toxicity in pregnant rabbits at doses that were lower than in patients receiving the recommended dose. If KYPROLIS is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Carfilzomib was administered intravenously to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis at doses of 0.5, 1, and 2 mg/kg/day in rats and 0.2, 0.4, and 0.8 mg/kg/day in rabbits. Carfilzomib was not teratogenic at any dose tested. In rabbits, there was an increase in pre-implantation loss at ≥ 0.4 mg/kg/day and an increase in early resorptions and post-implantation loss and a decrease in fetal weight at the maternally toxic dose of 0.8 mg/kg/day. The doses of 0.4 and 0.8 mg/kg/day in rabbits are approximately 20% and 40%, respectively, of the recommended dose in humans of 27 mg/m2 based on body surface area.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether KYPROLIS is excreted in human milk. Since many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from KYPROLIS, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of KYPROLIS in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In studies of KYPROLIS there were no clinically significant differences observed in safety and efficacy between patients less than 65 years of age and patients 65 years of age and older.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics and safety of KYPROLIS were evaluated in a Phase 2 trial in patients with normal renal function and those with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment and patients on chronic dialysis. On average, patients were treated for 5.5 cycles using KYPROLIS doses of 15 mg/m2 on Cycle 1, 20 mg/m2 on Cycle 2, and 27 mg/m2 on Cycles 3 and beyond. The pharmacokinetics and safety of KYPROLIS were not influenced by the degree of baseline renal impairment, including the patients on dialysis. Since dialysis clearance of KYPROLIS concentrations has not been studied, the drug should be administered after the dialysis procedure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
The safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics of KYPROLIS have not been evaluated in patients with baseline hepatic impairment. Patients with the following laboratory values were excluded from the KYPROLIS clinical trials: ALT/AST ≥ 3 × upper limit of normal (ULN) and bilirubin ≥ 2 × ULN [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.8 Cardiac Impairment
Patients with New York Heart Association Class III and IV heart failure were not eligible for the clinical trials. Safety in this population has not been evaluated.
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no known specific antidote for KYPROLIS overdosage. In the event of an overdosage, monitor the patient and provide appropriate supportive care.
11 DESCRIPTION
KYPROLIS (carfilzomib) for Injection is an antineoplastic agent available for intravenous use only. KYPROLIS is a sterile, white to off-white lyophilized powder and is available as a single-use vial. Each vial of KYPROLIS contains 60 mg of carfilzomib, 3000 mg sulfobutylether beta-cyclodextrin, 57.7 mg citric acid, and sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment (target pH 3.5).
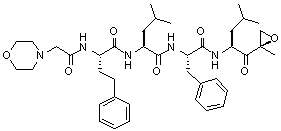
Carfilzomib is a modified tetrapeptidyl epoxide, isolated as the crystalline free base. The chemical name for carfilzomib is (2S)-N-((S)-1-((S)-4-methyl-1-((R)-2-methyloxiran-2-yl)-1-oxopentan-2-ylcarbamoyl)-2-phenylethyl)-2-((S)-2-(2-morpholinoacetamido)-4-phenylbutanamido)-4-methylpentanamide. Carfilzomib has the following structure:
Carfilzomib is a crystalline substance with a molecular weight of 719.9. The molecular formula is C40H57N5O7. Carfilzomib is practically insoluble in water, and very slightly soluble in acidic conditions.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Carfilzomib is a tetrapeptide epoxyketone proteasome inhibitor that irreversibly binds to the N-terminal threonine-containing active sites of the 20S proteasome, the proteolytic core particle within the 26S proteasome. Carfilzomib had antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities in vitro in solid and hematologic tumor cells. In animals, carfilzomib inhibited proteasome activity in blood and tissue and delayed tumor growth in models of multiple myeloma, hematologic, and solid tumors.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Intravenous carfilzomib administration resulted in suppression of proteasome chymotrypsin-like activity when measured in blood 1 hour after the first dose. On Day 1 of Cycle 1, proteasome inhibition in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) ranged from 79% to 89% at 15 mg/m2, and from 82% to 83% at 20 mg/m2. In addition, carfilzomib administration resulted in inhibition of the LMP2 and MECL1 subunits of the immunoproteasome ranging from 26% to 32% and 41% to 49%, respectively, at 20 mg/m2. Proteasome inhibition was maintained for ≥ 48 hours following the first dose of carfilzomib for each week of dosing.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: The Cmax and AUC following a single intravenous dose of 27 mg/m2 was 4232 ng/mL and 379 ng•hr/mL, respectively. Following repeated doses of carfilzomib at 15 and 20 mg/m2, systemic exposure (AUC) and half-life were similar on Days 1 and 15 or 16 of Cycle 1, suggesting there was no systemic carfilzomib accumulation. At doses between 20 and 36 mg/m2, there was a dose-dependent increase in exposure.
Distribution: The mean steady-state volume of distribution of a 20 mg/m2 dose of carfilzomib was 28 L. When tested in vitro, the binding of carfilzomib to human plasma proteins averaged 97% over the concentration range of 0.4 to 4 micromolar.
Metabolism: Carfilzomib was rapidly and extensively metabolized. The predominant metabolites measured in human plasma and urine, and generated in vitro by human hepatocytes, were peptide fragments and the diol of carfilzomib, suggesting that peptidase cleavage and epoxide hydrolysis were the principal pathways of metabolism. Cytochrome P450-mediated mechanisms played a minor role in overall carfilzomib metabolism. The metabolites have no known biologic activity.
Elimination: Following intravenous administration of doses ≥ 15 mg/m2, carfilzomib was rapidly cleared from the systemic circulation with a half-life of ≤ 1 hour on Day 1 of Cycle 1. The systemic clearance ranged from 151 to 263 L/hour, and exceeded hepatic blood flow, suggesting that carfilzomib was largely cleared extrahepatically. The pathways of carfilzomib elimination have not been characterized in humans.
Age: Analysis of population pharmacokinetics data after the first dose of Cycle 1 (Day 1) in 154 patients who had received an IV dose of 20 mg/m2 showed no clinically significant difference in exposure between patients < 65 years and ≥ 65 years of age.
Gender: Mean dose-normalized AUC and Cmax values were comparable between male and female patients in the population pharmacokinetics study.
Hepatic Impairment: No pharmacokinetic studies were performed with KYPROLIS in patients with hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Renal Impairment: A pharmacokinetic study was conducted in which 43 multiple myeloma patients who had various degrees of renal impairment and who were classified according to their creatinine clearances (CLcr) into the following groups: normal function (CLcr > 80 mL/min, n = 8), mild impairment (CLcr 50–80 mL/min, n = 12), moderate impairment (CLcr 30–49 mL/min, n = 8), severe impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min, n = 7), and chronic dialysis (n = 8). KYPROLIS was administered intravenously over 2 to 10 minutes, on two consecutive days, weekly for three weeks (Days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15, and 16), followed by a 12-day rest period every 28 days. Patients received an initial dose of 15 mg/m2, which could be escalated to 20 mg/m2 starting in Cycle 2 if 15 mg/m2 was well tolerated in Cycle 1. In this study, renal function status had no effect on the clearance or exposure of carfilzomib following a single or repeat-dose administration [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Cytochrome P450: In an in vitro study using human liver microsomes, carfilzomib showed modest direct and time-dependent inhibitory effect on human cytochrome CYP3A4/5. In vitro studies indicated that carfilzomib did not induce human CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 in cultured fresh human hepatocytes. Cytochrome P450-mediated mechanisms play a minor role in the overall metabolism of carfilzomib. A clinical trial of 17 patients using oral midazolam as a CYP3A probe demonstrated that the pharmacokinetics of midazolam were unaffected by concomitant carfilzomib administration. KYPROLIS is not expected to inhibit CYP3A4/5 activities and/or affect the exposure to CYP3A4/5 substrates.
P-gp: Carfilzomib is a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrate and showed marginal inhibitory effects on P-gp in a Caco-2 monolayer system. Given that KYPROLIS is administrated intravenously and is extensively metabolized, the pharmacokinetic profile of KYPROLIS is unlikely to be affected by P-gp inhibitors or inducers.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with carfilzomib.
Carfilzomib was clastogenic in the in vitro chromosomal aberration test in peripheral blood lymphocytes. Carfilzomib was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) test and was not clastogenic in the in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Fertility studies with carfilzomib have not been conducted. No effects on reproductive tissues were noted during 28-day repeat-dose rat and monkey toxicity studies or in 6-month rat and 9-month monkey chronic toxicity studies.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Monkeys administered a single bolus intravenous dose of carfilzomib at 3 mg/kg (approximately 1.3 times recommended dose in humans of 27 mg/m2 based on body surface area) experienced hypotension, increased heart rate, and increased serum levels of troponin-T. The repeated bolus intravenous administration of carfilzomib at ≥ 2 mg/kg/dose in rats and 2 mg/kg/dose in monkeys using dosing schedules similar to those used clinically resulted in mortalities that were due to toxicities occurring in the cardiovascular (cardiac failure, cardiac fibrosis, pericardial fluid accumulation, cardiac hemorrhage/degeneration), gastrointestinal (necrosis/hemorrhage), renal (glomerulonephropathy, tubular necrosis, dysfunction), and pulmonary (hemorrhage/inflammation) systems. The dose of 2 mg/kg/dose in rats is approximately half the recommended dose in humans of 27 mg/m2 based on body surface area. The dose of 2 mg/kg/dose in monkeys is approximately equivalent to the recommended dose in humans based on body surface area.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Relapsed Multiple Myeloma
The safety and efficacy of KYPROLIS were evaluated in a single-arm, multicenter clinical trial. Two hundred and sixty-six patients with relapsed multiple myeloma who had received at least two prior therapies (including bortezomib and thalidomide and/or lenalidomide) were enrolled. Patients were enrolled in the trial whose disease had a less than or equal to 25% response to the most recent therapy or had disease progression during or within 60 days of the most recent therapy. Patients were excluded from the trial with total bilirubin levels ≥ 2 × upper limit of normal (ULN); creatinine clearance rates < 30 mL/min; New York Heart Association Class III to IV congestive heart failure; symptomatic cardiac ischemia; myocardial infarction within the last 6 months; peripheral neuropathy Grade 3 or 4, or peripheral neuropathy Grade 2 with pain; active infections requiring treatment; and pleural effusion.
KYPROLIS was administered intravenously over 2 to 10 minutes on two consecutive days each week for three weeks, followed by a 12-day rest period (28-day treatment cycle), until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or for a maximum of 12 cycles. Patients received 20 mg/m2 at each dose in Cycle 1, and 27 mg/m2 in subsequent cycles. To reduce the incidence and severity of fever, rigors, chills, dyspnea, myalgia, and arthralgia, dexamethasone 4 mg by mouth or by intravenous infusion was administered prior to all KYPROLIS doses during the first cycle and prior to all KYPROLIS doses during the first dose-escalation (27 mg/m2) cycle. Dexamethasone premedication (4 mg orally or intravenously) was reinstated if these symptoms reappeared during subsequent cycles.
Baseline patient and disease characteristics are summarized in Table 5.
| Characteristic | Number of Patients (%) |
| Patient Characteristics | |
| Enrolled patients | 266 (100) |
| Median age, years (range) | 63.0 (37, 87) |
| Age group, < 65 / ≥ 65 (years) | 146 (54.9) / 120 (45.1) |
| Gender (male / female) | 155 (58.3) / 111 (41.7) |
| Race (White / Black / Asian / Other) | 190 (71.4) / 53 (19.9) / 6 (2.3) / 17 (6.4) |
| Disease Characteristics | |
| Number of Prior Regimens (median) | 5 |
| Prior Transplant | 198 (74.4) |
Refractory Status to Most Recent Therapy |
|
| Refractory: Progression during most recent therapy |
198 (74.4) |
| Refractory: Progression within 60 days after completion of most recent therapy |
38 (14.3) |
| Refractory: ≤ 25% response to treatment | 16 (6.0) |
| Relapsed: Progression after 60 days post treatment |
14 (5.3) |
| Years since diagnosis, median (range) | 5.35 (0.5, 22.3) |
| Plasma cell involvement (< 50% / ≥ 50% / unknown or missing) |
143 (53.8) / 106 (39.8) / 17 (6.4) |
| Cytogenetics or FISH analyses | |
| Normal/Favorable | 159 (59.8) |
| Poor Prognosis | 75 (28.2) |
| Unknown/Not tested | 32 (12.0) |
| Serum Beta-2 Microglobulin | |
| median (range) | 4.3 (0.4, 20.5) |
| Creatinine clearance < 30 (mL/min) | 6 (2.3) |
The median number of cycles started was four.
The primary endpoint was the overall response rate (ORR) as determined by Independent Review Committee assessment using International Myeloma Working Group criteria. The ORR (stringent complete response [sCR] + complete response [CR] + very good partial response [VGPR] + partial response [PR]) was 22.9% (95% CI: 18.0, 28.5) (N = 266) (see Table 6). The median duration of response (DOR) was 7.8 months (95% CI: 5.6, 9.2).
| Characteristic |
Study Patients n (%) |
| Number of patients (%) | 266 (100) |
Response category |
|
| Complete response | 1 (0.4) |
| Very good partial response | 13 (4.9) |
| Partial response | 47 (17.7) |
| Overall response | 61 (22.9) |
95% CI |
(18.0, 28.5) |
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
KYPROLIS (carfilzomib) for Injection is supplied as an individually cartoned single-use vial containing a dose of 60 mg of carfilzomib as a white to off-white lyophilized cake or powder.
- NDC 76075-101-01, 60 mg carfilzomib per vial
16.2 Storage and Handling
Unopened vials should be stored refrigerated (2°C to 8°C; 36°F to 46°F). Retain in original package to protect from light.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Discuss the following with patients prior to treatment with KYPROLIS:
Instruct patients to contact their physician if they develop any of the following symptoms: fever, chills, rigors, chest pain, cough, or swelling of the feet or legs.
Advise patients that KYPROLIS may cause fatigue, dizziness, fainting, and/or drop in blood pressure. Advise patients not to drive or operate machinery if they experience any of these symptoms.
Advise patients that they may experience shortness of breath (dyspnea) during treatment with KYPROLIS. This most commonly occurs within a day of dosing. Advise patients to contact their physicians if they experience shortness of breath.
Counsel patients to avoid dehydration, since patients receiving KYPROLIS therapy may experience vomiting and/or diarrhea. Instruct patients to seek medical advice if they experience symptoms of dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting spells.
Counsel females of reproductive potential to use effective contraceptive measures to prevent pregnancy during treatment with KYPROLIS. Advise the patient that if she becomes pregnant during treatment, to contact her physician immediately. Advise patients not to take KYPROLIS treatment while pregnant or breastfeeding. If a patient wishes to restart breastfeeding after treatment, advise her to discuss the appropriate timing with her physician.
Advise patients to discuss with their physician any medication they are currently taking prior to starting treatment with KYPROLIS, or prior to starting any new medication(s) during treatment with KYPROLIS.
Manufactured for:
Onyx Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
249 East Grand Avenue
South San Francisco, CA 94080
U.S. Patent Numbers: 7,232,818; 7,417,042; 7,491,704; 7,737,112
05-1088-00
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Carton Label

NDC 76075-101-01
Kyprolis™
(carfilzomib) for Injection
60 mg/vial
Single-Use Vial.
Discard unused portion.
For Intravenous Administration Only
Rx only
ONYX Pharmaceuticals™
Manufactured for:
Onyx Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
South San Francisco, CA 94080
LOT:
EXP.:
Each vial contains 60 mg carfilzomib,
3,000 mg sulfobutylether beta-cyclodextrin,
and 57.7 mg anhydrous citric acid. After
reconstitution with 29 mL of Sterile Water for
Injection, USP, the concentration of Kyprolis
is 2 mg/mL.
Recommended Dosage:
See Prescribing Information
Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C
(36°F to 46°F).
Store in carton to protect from light.
KYPROLIScarfilzomib INJECTION, POWDER, LYOPHILIZED, FOR SOLUTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||