Lamivudine and Zidovudine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use lamivudine and zidovudine safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for lamivudine and zidovudine tablets USP. Lamivudine and Zidovudine Tablets USPInitial U.S. Approval: 1997 RECENT MAJOR CHANGES(5.8)BOXED WARNINGWARNING: RISK OF HEMATOLOGIC TOXICITY, MYOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS, EXACERBATIONS OF HEPATITIS B See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. Hematologic toxicity including neutropenia and anemia have been associated with the use of zidovudine, one of the components of lamivudine and zidovudine. (5.1) Symptomatic myopathy associated with prolonged use of zidovudine. (5.2) Lactic acidosis and hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogues including zidovudine. Suspend treatment if clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity occur. (5.3) Severe, acute exacerbations of hepatitis B have been reported in patients who are co-infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) and have discontinued lamivudine, a component of lamivudine and zidovudine. Monitor hepatic function closely in these patients and, if appropriate, initiate anti-hepatitis B treatment. (5.4) INDICATIONS AND USAGE(1)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Adults and Adolescents weighing ≥30 kg: 1 tablet twice daily. (2.1) Pediatrics: Dosage should be based on body weight not to exceed adult doses. (2.2) Lamivudine and Zidovudine tablets, a fixed-dose product, should not be prescribed for pediatric patients weighing less than 30 kg or patients requiring dosage adjustment, such as those with renal or hepatic impairment, or patients experiencing dose-limiting adverse reactions. (2.3) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS(3)CONTRAINDICATIONS(4)WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS See boxed warning for information about the following: Hematologic toxicity, symptomatic myopathy, lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly, and severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B. (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4) Lamivudine and Zidovudine should not be administered with other lamivudine- or zidovudine-containing products or emtricitabine-containing products. (5.5) Hepatic decompensation, some fatal, has occurred in HIV-1/HCV co-infected patients receiving combination antiretroviral therapy and interferon alfa with/without ribavirin. Discontinue lamivudine and zidovudine as medically appropriate and consider dose reduction or discontinuation of interferon alfa, ribavirin, or both. (5.6) Exacerbation of anemia has been reported in HIV-1/HCV co-infected patients receiving ribavirin and zidovudine. Coadministration of ribavirin and zidovudine is not advised. (5.6) Pancreatitis: Use with caution in pediatric patients with a history of pancreatitis or other significant risk factors for pancreatitis. Discontinue treatment as clinically appropriate. (5.7) Immune reconstitution syndrome (5.8) and redistribution/accumulation of body fat (5.9) have been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy. Side Effects Most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 15%) in adult and pediatric HIV-1 clinical studies of combination lamivudine and zidovudine were headache, nausea, malaise and fatigue, nasal signs and symptoms, diarrhea, and cough. (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-850-2876 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS Concomitant use with the following drugs should be avoided: Stavudine (7.1), zalcitabine (7.1), doxorubicin. (7.2) Bone marrow suppressive/cytotoxic agents: May increase the hematologic toxicity of zidovudine. (7.3) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: Physicians are encouraged to register patients in the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry by calling 1-800-258-4263. (8.1) Nursing Mothers: HIV-1 infected mothers in the United States should not breastfeed to avoid potential postnatal transmission of HIV-1. (8.3)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING: HEMATOLOGIC TOXICITY, MYOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS, EXACERBATIONS OF HEPATITIS B
- 1 LAMIVUDINE AND ZIDOVUDINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 LAMIVUDINE AND ZIDOVUDINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 LAMIVUDINE AND ZIDOVUDINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 5.1 Hemotologic Toxicity/Bone Marrow Suppression
- 5.2 Myopathy
- 5.3 Lactic Acidosis/Hepatomegaly With Steatosis
- 5.4 Patients With HIV-1 and Hepatitis B Virus Co-infection
- 5.5 Use With Other, Lamivudine-, Zidovudine-, and/or Emtricitabine-Containing Products
- 5.6 Use With Interferon- and Ribavirin-Based Regimens
- 5.7 Pancreatitis
- 5.8 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
- 5.9 Fat Redistribution
- 6 LAMIVUDINE AND ZIDOVUDINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 LAMIVUDINE AND ZIDOVUDINE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 150 mg/300 mg (60 Tablet Bottle)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: HEMATOLOGIC TOXICITY, MYOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS, EXACERBATIONS OF HEPATITIS B
Hematologic Toxicity: Zidovudine, one of the 2 active ingredients in lamivudine and zidovudine tablets, has been associated with hematologic toxicity including neutropenia and anemia, particularly in patients with advanced HIV-1 disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Myopathy: Prolonged use of zidovudine has been associated with symptomatic myopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Lactic Acidosis and Severe Hepatomegaly: Lactic acidosis and hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogues alone or in combination, including lamivudine, zidovudine, and other antiretrovirals. Suspend treatment if clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Exacerbations of Hepatitis B: Severe, acute exacerbations of hepatitis B have been reported in patients who are co-infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and HIV-1 and have discontinued lamivudine, which is one component of lamivudine and zidovudine. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who discontinue lamivudine and zidovudine and are co-infected with HIV-1 and HBV. If appropriate, initiation of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adults and Adolescents Weighing ≥30 kg
2.2 Pediatric Patients
®®
2.3 Patients Requiring Dosage Adjustment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Lamivudine and Zidovudine Tablets,
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hemotologic Toxicity/Bone Marrow Suppression
3[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.2 Myopathy
5.3 Lactic Acidosis/Hepatomegaly With Steatosis
5.4 Patients With HIV-1 and Hepatitis B Virus Co-infection
Posttreatment Exacerbations of Hepatitis:
Important Differences Among Lamivudine-Containinq Products:®
Emergence of Lamivudine-Resistant HBV:
5.5 Use With Other, Lamivudine-, Zidovudine-, and/or Emtricitabine-Containing Products
®®®®®®®TM
5.6 Use With Interferon- and Ribavirin-Based Regimens
In vitro[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)],
5.7 Pancreatitis
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.8 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Mycobacterium avium Pneumocystis jirovecii
disorders
5.9 Fat Redistribution
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hematologic toxicity, including neutropenia and anemia [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
- Symptomatic myopathy [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Lactic acidosis and hepatomegaly with steatosis [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Acute exacerbations of hepatitis B [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Hepatic decompensation in patients co-infected with HIV-1 and hepatitis C [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ].
- Exacerbation of anemia in HIV-1/HCV co-infected patients receiving ribavirin and zidovudine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Lamivudine Plus Zidovudine Administered As Separate Formulations:
| Adverse Reaction | EPIVIR plus RETROVIR (n = 251) |
|---|---|
|
Body as a whole
|
|
| Headache |
35% |
| Malaise & fatigue |
27% |
| Fever or chills |
10% |
|
Digestive
|
|
| Nausea |
33% |
| Diarrhea |
18% |
| Nausea & vomiting |
13% |
| Anorexia and/or decreased appetite |
10% |
| Abdominal pain |
9% |
| Abdominal cramps |
6% |
| Dyspepsia |
5% |
|
Nervous system
|
|
| Neuropathy |
12% |
| Insomnia & other sleep disorders |
11% |
| Dizziness |
10% |
| Depressive disorders |
9% |
|
Respiratory
|
|
| Nasal signs & symptoms |
20% |
| Cough |
18% |
|
Skin
|
|
| Skin rashes |
9% |
|
Musculoskeletal
|
|
| Musculoskeletal pain |
12% |
| Myalgia |
8% |
| Arthralgia |
5% |
| Test (Abnormal Level) |
EPIVIR plus RETROVIR % (n) |
|---|---|
| ULN = Upper limit of normal. ANC = Absolute neutrophil count. n = Number of patients assessed. * Frequencies of these laboratory abnormalities were higher in patients with mild laboratory abnormalities at baseline. |
|
| Neutropenia (ANC<750/mm3) |
7.2% (237) |
| Anemia (Hgb<8 g/dL) |
2.9% (241) |
| Thrombocytopenia (platelets<50,000/mm3) |
0.4% (240) |
| ALT (>5 x ULN) |
3.7% (241) |
| AST (>5 x ULN) |
1.7% (241) |
| Bilirubin (>2.5x ULN) |
0.8% (241) |
| Amylase (>2 x ULN) |
4.2% (72) |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Body as a Whole:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Cardiovascular:
Endocrine and Metabolic:
Gastrointestinal:
General:
Hemic and Lymphatic:
Hepatic and Pancreatic:[see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.3), (5.4) , (5.7)].
Hypersensitivity:
Musculoskeletal:
Nervous:
Respiratory:
Skin:
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.1 Antiretroviral Agents
Lamivudine: Zalcitabine:
Zidovudine: Stavudine: in vitro
Nucleoside Analogues Affecting DNA Replication: in vitro
7.2 Doxorubicin
Zidovudine:in vitro
7.3 Hematologic/Bone Marrow Suppressive/Cytotoxic Agents
Zidovudine:
7.4 Interferon- and Ribavirin-Based Regimens
Lamivudine:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.5 Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX)
Lamivudine:
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Fetal Risk Summary:
Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry:
Clinical Considerations:[see Clinical Studies (14.2) ].
Data:Human Data: Lamivudine:
Zidovudine: [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Animal Data: Lamivudine: [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)].
Zidovudine: [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)].
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
Lamivudine and Zidovudine:
Lamivudine:
Zidovudine:OD
11 DESCRIPTION
Lamivudine and Zidovudine:
Lamivudine:81133
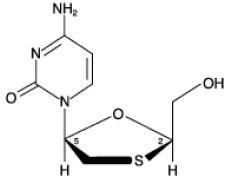
Zidovudine:101354
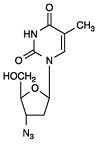
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics in Adults:Lamivudine and Zidovudine:
Lamivudine:
Zidovudine:
| Parameter | Lamivudine | Zidovudine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Data presented as mean ± standard deviation except where noted. † Median [range]. ‡ Children. § Adults. ║ Approximate range. |
||||
| Oral bioavailability (%) |
86 ± 16 |
N=12 |
64 ± 10 |
n = 5 |
| Apparent volume of distribution (L/kg) |
1.3 ± 0.4 |
N = 20 |
1.6 ± 0.6 |
n = 8 |
| Plasma protein binding (%) |
<36 |
<38 |
||
| CSF:plasma ratio†
|
0.12 [0.04 to 0.47] |
n = 38‡
|
0.6 [0.04 to 2.62] |
N = 39§
|
| Systemic clearance (L/hr/kg) |
0.33 ± 0.06 |
N = 20 |
1.6 ± 0.6 |
n = 6 |
| Renal clearance (L/hr/kg) |
0.22 ± 0.06 |
N = 20 |
0.34 ± 0.05 |
n = 9 |
| Elimination half-life (hr)║
|
5 to 7 |
0.5 to 3 |
||
Effect of Food on Absorption of Lamivudine and Zidovudine:
Special Populations:
Pregnancy: See Use in Specific Populations (8.1).
Lamivudine and Zidovudine:
Zidovudine:
Nursing Mothers: See Use in Specific Populations (8.3).
Pediatric Patients:
Geriatric Patients:
Gender:∞∞
Race:Lamivudine:
Zidovudine:
Drug Interactions:See Drug Interactions (7).
Lamivudine Plus Zidovudine:
| Note: ROUTINE DOSE MODIFICATION OF LAMIVUDINE AND ZIDOVUDINE IS NOT WARRANTED WITH COADMINISTRATION OF THE FOLLOWING DRUGS. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drugs That May Alter Lamivudine Blood Concentrations | |||||
| Coadministered Drug and Dose |
Lamivudine Dose |
n | Lamivudine Concentrations |
Concentration of Coadministered Drug |
|
| AUC | Variability | ||||
| ↑ = Increase; ↓= Decrease; ↔ = no significant change; AUC = area under the concentration versus time curve; CI = confidence interval. * This table is not all inclusive. † Estimated range of percent difference. |
|||||
| Nelfinavir 750 mg q 8 hr x 7 to 10 days |
single 150 mg |
11 |
↑AUC 10% |
95% CI: l% to 20% |
↔ |
| Trimethoprim 160 mg/Sulfamethoxazole 800 mg daily x 5 days |
single 300 mg |
14 |
↑AUC 43% |
90% CI: 32% to 55% |
↔ |
|
Drugs That May Alter Zidovudine Blood Concentrations
|
|||||
|
Coadministered Drug and Dose |
Zidovudine Dose |
n
|
Zidovudine Concentrations |
Concentration of
Coadministered Drug |
|
|
AUC
|
Variability
|
||||
| Atovaquone 750 mg q l2 hr with food |
200 mg q 8 hr |
14 |
↑AUC 31% |
Range 23% to 78%† |
↔ |
|
Clarithromycin 500 mg daily |
100 mg q 4 hr x 7 days |
4 |
↓AUC 12% |
Range ↓34% to ↑14% |
Not Reported |
| Fluconazole 400 mg daily |
200 mg q 8 hr |
12 |
↑AUC 74% |
95% CI: 54% to 98% |
Not Reported |
| Methadone 30 to 90 mg daily |
200 mg q 4 hr |
9 |
↑AUC 43% |
Range 16% to 64%† |
↔ |
| Nelfinavir 750 mg q 8 hr x 7 to 10 days |
single 200 mg |
11 |
↓AUC 35% |
Range 28% to 41% |
↔ |
| Probenecid 500 mg q 6 hr x 2 days |
2 mg/kg q 8 hr x 3 days |
3 |
↑AUC 106% |
Range 100% to 170%† |
Not Assessed |
| Rifampin 600 mg daily x 14 days |
200 mg q 8 hr x 14 days |
8 |
↓AUC 47% |
90% CI: 41% to 53% |
Not Assessed |
| Ritonavir 300 mg q 6 hr x 4 days |
200 mg q 8 hr x 4 days |
9 |
↓ AUC 25% |
95% CI: 15% to 34% |
↔ |
| Valproic acid 250 mg or 500 mg q 8 hr x 4 days |
100 mg q 8 hr x 4 days |
6 |
↑AUC 80% |
Range 64% to l30%† |
Not Assessed |
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action: Lamivudine:
Zidovudine:
Antiviral ActivityLamivudine Plus Zidovudine:
Lamivudine: 505050
Zidovudine: 50905050
Resistance: Lamivudine Plus Zidovudine Administered As Separate Formulations:
Lamivudine:
Zidovudine:
Cross-Resistance:
Lamivudine Plus Zidovudine:
Lamivudine:
Zidovudine:
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity: Lamivudine:
Zidovudine:
Mutagenicity: Lamivudine: +/-in vitro
Zidovudine: +/-in vitro
Impairment of Fertility: Lamivudine:
Zidovudine:
13.2 Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology Studies
Lamivudine:
Zidovudine:in vitro
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
14.1 Adults
Lamivudine Plus Zidovudine:3
| Endpoint | Current Therapy (n = 460) |
EPIVIR plus Current Therapy (n = 896) |
EPIVIR Plus a NNRTI* plus Current Therapy (n = 460) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
* An investigational non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor not approved in the United States. |
|||
| HIV-1 progression or death |
90 (19.6%) |
86 (9.6%) |
41 (8.9%) |
| Death |
27 (5.9%) |
23 (2.6%) |
14 (3%) |
14.2 Prevention of Maternal-Fetal HIV-1 Transmission
33
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Lamivudine and Zidovudine Tablets USP,
Store at
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Advice for the Patient
Neutropenia and Anemia[see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Myopathy:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Lactic Acidosis/Hepatomegaly:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
HIV‑1/HBV Co‑Infection:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Use With Other Lamivudine-, Zidovudine-, and/or Emtricitabine‑Containing Products:™ [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
HIV‑1/HCV Co‑Infection:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Drug Interactions:[see Drug Interactions (7.3)]
Redistribution/Accumulation of Body Fat:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
Information About HIV-1 Infection:
- Do not share needles or other injection equipment.
- Do not share personal items that can have blood or body fluids on them, like toothbrushes and razor blades.
- Do not have any kind of sex without protection. Always practice safe sex by using a latex or polyurethane condom or other barrier method to lower the chance of sexual contact with semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
- Do not breastfeed. Lamivudine and zidovudine are excreted in human breast milk. Mothers with HIV-1 should not breastfeed because HIV-1 can be passed to the baby in the breast milk.
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 150 mg/300 mg (60 Tablet Bottle)
NDC 65862-597-60
Lamivudine and Zidovudine Tablets USP
150 mg/300 mg
Rx only 60 Tablets
AUROBINDO

Lamivudine and ZidovudineLamivudine and Zidovudine TABLET, FILM COATED
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!