Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride
PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets.LEVOCETIRIZINE dihydrochloride tablets for oral useInitial U.S. Approval: 1995RECENT MAJOR CHANGESWarnings and Precautions, Urinary Retention (5.2) 09/2012INDICATIONS AND USAGELevocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets are a histamine H1-receptor antagonist indicated for: The treatment of the uncomplicated skin manifestations of chronic idiopathic urticaria (1.3) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Adults and children 12 years of age and older: 5 mg once daily in the evening (2.1) Children 6 to 11 years of age: 2.5 mg once daily in the evening (2.2) Children 6 months to 5 years of age: 1.25 mg once daily in the evening (2.3) Renal Impairment Adjust the dose in patients 12 years of age and older with decreased renal function (2.4, 12.3) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Immediate release breakable (scored) tablets, 5 mg (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS Patients with a known hypersensitivity to levocetirizine or any of the ingredients of levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets or to cetirizine (4) Patients with end-stage renal disease at less than 10 mL/min creatinine clearance or patients undergoing hemodialysis (4) Children 6 months to 11 years of age with renal impairment (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Avoid engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness such as driving or operating machinery when taking levocetirizine (5.1). Avoid concurrent use of alcohol or other central nervous system depressants with levocetirizine (5.1). Use with caution in patients with predisposing factors of urinary retention (e.g. spinal cord lesion, prostatic hyperplasia). Discontinue levocetirizine if urinary retention occurs (5.2). Side EffectsThe most common adverse reactions (rate ≥ 2% and > placebo) were somnolence, nasopharyngitis, fatigue, dry mouth, and pharyngitis in subjects 12 years of age and older, and pyrexia, somnolence, cough, and epistaxis in children 6 to 12 years of age (6.1). In subjects 1 to 5 years of age, the most common adverse reactions (rate ≥ 2% and > placebo) were pyrexia, diarrhea, vomiting, and otitis media. In subjects 6 to 11 months of age, the most common adverse reactions (rate ≥ 3% and > placebo) were diarrhea and constipation. (6.1). To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact TEVA USA, PHARMACOVIGILANCE at 1-866-832-8537 or drug.safety@tevapharm.com; or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch .USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Renal Impairment Because levocetirizine is substantially excreted by the kidneys, the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function (8.6 and 12.3). Pediatric Use Do not exceed the recommended dose of 2.5 mg and 1.25 mg once daily in children 6 to 11 years and 6 months to 5 years of age, respectively. Systemic exposure with these doses in respective pediatric age groups is comparable to that from a 5 mg once daily dose in adults (12.3).
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 LEVOCETIRIZINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 LEVOCETIRIZINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 LEVOCETIRIZINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 LEVOCETIRIZINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 LEVOCETIRIZINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.3 Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria
Levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets are indicated for the treatment of the uncomplicated skin manifestations of chronic idiopathic urticaria in adults and children 6 months of age and older.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Levocetirizine is available as 5 mg breakable (scored) tablets, allowing for the administration of 2.5 mg, if needed. Levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets can be taken without regard to food consumption.
2.1 Adults and Children 12 Years of Age and Older
The recommended dose of levocetirizine is 5 mg (1 tablet) once daily in the evening. Some patients may be adequately controlled by 2.5 mg (½ tablet) once daily in the evening.
2.2 Children 6 to 11 Years of Age
The recommended dose of levocetirizine is 2.5 mg (½ tablet) once daily in the evening. The 2.5 mg dose should not be exceeded because the systemic exposure with 5 mg is approximately twice that of adults [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )].
2.3 Children 6 Months to 5 Years of Age
The recommended initial dose of levocetirizine is 1.25 mg once daily in the evening. The 1.25 mg once daily dose should not be exceeded based on comparable exposure to adults receiving 5 mg [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.4 Dose Adjustment for Renal and Hepatic Impairment
In adults and children 12 years of age and older with:
- Mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CLCR] = 50 to 80 mL/min): a dose of 2.5 mg once daily is recommended;
- Moderate renal impairment (CLCR = 30 to 50 mL/min): a dose of 2.5 mg once every other day is recommended;
- Severe renal impairment (CLCR = 10 to 30 mL/min): a dose of 2.5 mg twice weekly (administered once every 3 to 4 days) is recommended;
- End-stage renal disease patients (CLCR < 10 mL/min) and patients undergoing hemodialysis should not receive levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets.
No dose adjustment is needed in patients with solely hepatic impairment. In patients with both hepatic impairment and renal impairment, adjustment of the dose is recommended.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets are white to off-white, film-coated, oval-shaped, scored tablets and contain 5 mg levocetirizine dihydrochloride. One side of the tablet is scored in half and debossed with the number "9" on one side of the score and "3" on the other. The other side of the tablet is debossed with the number "7701."
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
The use of levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets is contraindicated in:
4.1 Patients With Known Hypersensitivity
Patients with known hypersensitivity to levocetirizine or any of the ingredients of levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets, or to cetirizine. Observed reactions range from urticaria to anaphylaxis [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.2 )].
4.2 Patients With End-Stage Renal Disease
Patients with end-stage renal disease (CLCR < 10 mL/min) and patients undergoing hemodialysis.
4.3 Pediatric Patients With Impaired Renal Function
Children 6 months to 11 years of age with impaired renal function.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Somnolence
In clinical trials the occurrence of somnolence, fatigue, and asthenia has been reported in some patients under therapy with levocetirizine. Patients should be cautioned against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness, and motor coordination such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle after ingestion of levocetirizine. Concurrent use of levocetirizine with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur.
5.2 Urinary Retention
Urinary retention has been reported postmarketing with levocetirizine. Levocetirizine should be used with caution in patients with predisposing factors of urinary retention (e.g. spinal cord lesion, prostatic hyperplasia) as levocetirizine may increase the risk of urinary retention. Discontinue levocetirizine if urinary retention occurs.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Use of levocetirizine has been associated with somnolence, fatigue, asthenia, and urinary retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5 )].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
The safety data described below reflect exposure to levocetirizine in 12 controlled clinical trials of 1 week to 6 months duration.
The short-term (exposure up to 6 weeks) safety data for adults and adolescents are based upon eight clinical trials in which 1896 patients (825 males and 1071 females aged 12 years and older) were treated with levocetirizine 2.5, 5, or 10 mg once daily in the evening.
The short-term safety data from pediatric patients are based upon two clinical trials in which 243 children (162 males and 81 females 6 to 12 years of age) were treated with levocetirizine 5 mg once daily for 4 to 6 weeks, one clinical trial in which 114 children (65 males and 49 females 1 to 5 years of age) were treated with levocetirizine 1.25 mg twice daily for 2 weeks, and one clinical trial in which 45 children (28 males and 17 females 6 to 11 months of age) were treated with levocetirizine 1.25 mg once daily for 2 weeks.
The long-term (exposure of 4 or 6 months) safety data in adults and adolescents are based upon two clinical trials in which 428 patients (190 males and 238 females) were exposed to treatment with levocetirizine 5 mg once daily. Long term safety data are also available from an 18 month trial in 255 levocetirizine-treated subjects 12 to 24 months of age.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trial of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adults and Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older
In studies up to 6 weeks in duration, the mean age of the adult and adolescent patients was 32 years, 44% of the patients were men and 56% were women, and the large majority (more than 90%) was Caucasian.
In these trials 43% and 42% of the subjects in the levocetirizine 2.5 mg and 5 mg groups, respectively, had at least one adverse event compared to 43% in the placebo group.
In placebo-controlled trials of 1 to 6 weeks in duration, the most common adverse reactions were somnolence, nasopharyngitis, fatigue, dry mouth, and pharyngitis, and most were mild to moderate in intensity. Somnolence with levocetirizine showed dose ordering between tested doses of 2.5, 5 and 10 mg and was the most common adverse reaction leading to discontinuation (0.5%).
Table 1 lists adverse reactions that were reported in greater than or equal to 2% of subjects aged 12 years and older exposed to levocetirizine 2.5 mg or 5 mg in eight placebo-controlled clinical trials and that were more common with levocetirizine than placebo.
| Adverse Reactions |
Levocetirizine 2.5 mg (n = 421) |
Levocetirizine 5 mg (n = 1070) |
Placebo (n = 912) |
| Somnolence | 22 (5%) | 61 (6%) | 16 (2%) |
| Nasopharyngitis | 25 (6%) | 40 (4%) | 28 (3%) |
| Fatigue | 5 (1%) | 46 (4%) | 20 (2%) |
| Dry Mouth | 12 (3%) | 26 (2%) | 11 (1%) |
| Pharyngitis | 10 (2%) | 12 (1%) | 9 (1%) |
Additional adverse reactions of medical significance observed at a higher incidence than in placebo in adults and adolescents aged 12 years and older exposed to levocetirizine are syncope (0.2%) and weight increased (0.5%).
Pediatric Patients 6 to 12 Years of Age
A total of 243 pediatric patients 6 to 12 years of age received levocetirizine 5 mg once daily in two short-term placebo controlled double-blind trials. The mean age of the patients was 9.8 years, 79 (32%) were 6 to 8 years of age, and 50% were Caucasian. Table 2 lists adverse reactions that were reported in greater than or equal to 2% of subjects aged 6 to 12 years exposed to levocetirizine 5 mg in placebo-controlled clinical trials and that were more common with levocetirizine than placebo.
| Adverse Reactions |
Levocetirizine 5 mg (n = 243) |
Placebo (n = 240) |
| Pyrexia | 10 (4%) | 5 (2%) |
| Cough | 8 (3%) | 2 (< 1%) |
| Somnolence | 7 (3%) | 1 (< 1%) |
| Epistaxis | 6 (2%) | 1 (< 1%) |
Pediatric Patients 1 to 5 Years of Age
A total of 114 pediatric patients 1 to 5 years of age received levocetirizine 1.25 mg twice daily in a two week placebo-controlled double-blind safety trial. The mean age of the patients was 3.8 years, 32% were 1 to 2 years of age, 71% were Caucasian and 18% were Black. Table 3 lists adverse reactions that were reported in greater than or equal to 2% of subjects aged 1 to 5 years exposed to levocetirizine 1.25 mg twice daily in the placebo-controlled safety trial and that were more common with levocetirizine than placebo.
| Adverse Reactions |
Levocetirizine 1.25 mg Twice Daily (n = 114) |
Placebo (n = 59) |
| Pyrexia | 5 (4%) | 1 (2%) |
| Diarrhea | 4 (4%) | 2 (3%) |
| Vomiting | 4 (4%) | 2 (3%) |
| Otitis Media | 3 (3%) | 0 (0%) |
Pediatric Patients 6 to 11 Months of Age
A total of 45 pediatric patients 6 to 11 months of age received levocetirizine 1.25 mg once daily in a two week placebo-controlled double-blind safety trial. The mean age of the patients was 9 months, 51% were Caucasian and 31% were Black. Adverse reactions that were reported in more than 1 subject (i.e. greater than or equal to 3% of subjects) aged 6 to 11 months exposed to levoceterizine 1.25 mg once daily in the placebo-controlled safety trial and that were more common with levoceterizine than placebo included diarrhea and constipation which were reported in 6 (13%) and 1 (4%) and 3 (7%) and 1 (4%) children in the levocetirizine and placebo-treated groups, respectively.
Long-Term Clinical Trials Experience
In two controlled clinical trials, 428 patients (190 males and 238 females) aged 12 years and older were treated with levocetirizine 5 mg once daily for 4 or 6 months. The patient characteristics and the safety profile were similar to that seen in the short-term studies. Ten (2.3%) patients treated with levocetirizine discontinued because of somnolence, fatigue or asthenia compared to 2 (< 1%) in the placebo group.
There are no long term clinical trials in children below 12 years of age with chronic idiopathic urticaria.
Laboratory Test Abnormalities
Elevations of blood bilirubin and transaminases were reported in < 1% of patients in the clinical trials. The elevations were transient and did not lead to discontinuation in any patient.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
In addition to the adverse reactions reported during clinical trials and listed above, adverse events have also been identified during post-approval use of levocetirizine. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Adverse events of hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis, increased appetite, angioedema, fixed drug eruption, pruritus, rash and urticaria, convulsion, paraesthesia, dizziness, tremor, dysgeusia, vertigo, aggression and agitation, hallucinations, depression, insomnia, suicidal ideation, visual disturbances, blurred vision, palpitations, tachycardia, dyspnea, nausea, vomiting, hepatitis, dysuria, urinary retention, myalgia, and edema have been reported.
Besides these events reported under treatment with levocetirizine, other potentially severe adverse events have been reported from the postmarketing experience with cetirizine. Since levocetirizine is the principal pharmacologically active component of cetirizine, one should take into account the fact that the following adverse events could also potentially occur under treatment with levocetirizine: orofacial dyskinesia, severe hypotension, cholestasis, glomerulonephritis, and stillbirth.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
In vitro data indicate that levocetirizine is unlikely to produce pharmacokinetic interactions through inhibition or induction of liver drug-metabolizing enzymes. No in vivo drug-drug interaction studies have been performed with levocetirizine. Drug interaction studies have been performed with racemic cetirizine.
7.1 Antipyrine, Azithromycin, Cimetidine, Erythromycin, Ketoconazole, Theophylline, and Pseudoephedrine
Pharmacokinetic interaction studies performed with racemic cetirizine demonstrated that cetirizine did not interact with antipyrine, pseudoephedrine, erythromycin, azithromycin, ketoconazole, and cimetidine. There was a small decrease (~ 16%) in the clearance of cetirizine caused by a 400 mg dose of theophylline. It is possible that higher theophylline doses could have a greater effect.
7.2 Ritonavir
Ritonavir increased the plasma AUC of cetirizine by about 42% accompanied by an increase in half-life (53%) and a decrease in clearance (29%) of cetirizine. The disposition of ritonavir was not altered by concomitant cetirizine administration.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
In rats and rabbits, levocetirizine was not teratogenic at oral doses approximately 320 and 390, respectively, times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis.
Pregnancy category B
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, levocetirizine should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
No peri- and post-natal animal studies have been conducted with levocetirizine. In mice, cetirizine caused retarded pup weight gain during lactation at an oral dose in dams that was approximately 40 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis. Studies in beagle dogs indicated that approximately 3% of the dose of cetirizine was excreted in milk. Cetirizine has been reported to be excreted in human breast milk. Because levocetirizine is also expected to be excreted in human milk, use of levocetirizine in nursing mothers is not recommended.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The recommended dose of levocetirizine for the treatment of the uncomplicated skin manifestations of chronic idiopathic urticaria in patients 6 months to 17 years of age is based on extrapolation of efficacy from adults 18 years of age and older [see Clinical Studies ( 14 )].
The recommended dose of levocetirizine in patients 6 months to 11 years of age for the treatment of the symptoms of chronic idiopathic urticaria is based on cross-study comparisons of the systemic exposure of levocetirizine in adults and pediatric patients and on the safety profile of levocetirizine in both adult and pediatric patients at doses equal to or higher than the recommended dose for patients 6 months to 11 years of age.
The safety of levocetirizine 5 mg once daily was evaluated in 243 pediatric patients 6 to 12 years of age in two placebo-controlled clinical trials lasting 4 and 6 weeks. The safety of levocetirizine 1.25 mg twice daily was evaluated in one 2 week clinical trial in 114 pediatric patients 1 to 5 years of age and the safety of levocetirizine 1.25 mg once daily was evaluated in one 2 week clinical trial in 45 pediatric patients 6 to 11 months of age [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.1 )].
The effectiveness of levocetirizine 1.25 mg once daily (6 months to 5 years of age) and 2.5 mg once daily (6 to 11 years of age) for the treatment of the symptoms of chronic idiopathic urticaria is supported by the extrapolation of demonstrated efficacy of levocetirizine 5 mg once daily in patients 12 years of age and older based on the pharmacokinetic comparison between adults and children.
Cross-study comparisons indicate that administration of a 5 mg dose of levocetirizine to 6 to 12 year old pediatric patients resulted in about 2 fold the systemic exposure (AUC) observed when 5 mg of levocetirizine was administered to healthy adults. Therefore, in children 6 to 11 years of age the recommended dose of 2.5 mg once daily should not be exceeded. In a population pharmacokinetics study the administration of 1.25 mg once daily in children 6 months to 5 years of age resulted in systemic exposure comparable to 5 mg once daily in adults. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2); Clinical Studies (14); and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of levocetirizine for each approved indication did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently than younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Levocetirizine is known to be substantially excreted by the kidneys and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Dosage and Administration ( 2 ) and Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
As levocetirizine is mainly excreted unchanged by the kidneys, it is unlikely that the clearance of levocetirizine is significantly decreased in patients with solely hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage has been reported with levocetirizine.
Symptoms of overdose may include drowsiness in adults and initially agitation and restlessness, followed by drowsiness in children. There is no known specific antidote to levocetirizine. Should overdose occur, symptomatic or supportive treatment is recommended. Levocetirizine is not effectively removed by dialysis, and dialysis will be ineffective unless a dialyzable agent has been concomitantly ingested.
The acute maximal non-lethal oral dose of levocetirizine was 240 mg/kg in mice (approximately 190 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults, approximately 230 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 to 11 years of age, and approximately 180 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 months to 5 years of age on a mg/m2 basis). In rats the maximal non-lethal oral dose was 240 mg/kg (approximately 390 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults, approximately 460 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 to 11 years of age, and approximately 370 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 months to 5 years of age on a mg/m2 basis).
11 DESCRIPTION
Levocetirizine dihydrochloride, the active component of levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets, is an orally active H1-receptor antagonist. The chemical name is R-(+)-2-[2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl) phenyl methyl] piperazin-1-yl] ethoxy] acetic acid dihydrochloride. Levocetirizine dihydrochloride is the R enantiomer of cetirizine hydrochloride, a racemic compound with antihistaminic properties. The chemical structure is shown below:
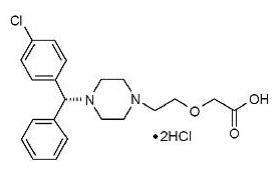
C21H25ClN2O3•2HCl M.W. 461.8
Levocetirizine dihydrochloride is a white, or almost white powder and is freely soluble in water, practically insoluble in acetone and in methylene chloride. Levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets, 5 mg are formulated as immediate-release white to off-white, film-coated, oval-shaped, scored tablets for oral administration. One side of the tablet is scored in half and debossed with the number "9" on one side of the score and "3" on the other. The other side of the tablet is debossed with the number "7701." Inactive ingredients are: colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Levocetirizine, the active enantiomer of cetirizine, is an anti-histamine; its principal effects are mediated via selective inhibition of H1 receptors. The antihistaminic activity of levocetirizine has been documented in a variety of animal and human models. In vitro binding studies revealed that levocetirizine has an affinity for the human H1-receptor 2 fold higher than that of cetirizine (Ki = 3 nmol/L vs. 6 nmol/L, respectively). The clinical relevance of this finding is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Studies in adult healthy subjects showed that levocetirizine at doses of 2.5 mg and 5 mg inhibited the skin wheal and flare caused by the intradermal injection of histamine. In contrast, dextrocetirizine exhibited no clear change in the inhibition of the wheal and flare reaction. Levocetirizine at a dose of 5 mg inhibited the wheal and flare caused by intradermal injection of histamine in 14 pediatric subjects (aged 6 to 11 years) and the activity persisted for at least 24 hours. The clinical relevance of histamine wheal skin testing is unknown.
A QT/QTc study using a single dose of 30 mg of levocetirizine did not demonstrate an effect on the QTc interval. While a single dose of levocetirizine had no effect, the effects of levocetirizine may not be at steady state following single dose. The effect of levocetirizine on the QTc interval following multiple dose administration is unknown. Levocetirizine is not expected to have QT/QTc effects because of the results of QTc studies with cetirizine and the long postmarketing history of cetirizine without reports of QT prolongation.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Levocetirizine exhibited linear pharmacokinetics over the therapeutic dose range in adult healthy subjects.
- Absorption
Levocetirizine is rapidly and extensively absorbed following oral administration. In adults, peak plasma concentrations are achieved 0.9 hour after administration of the oral tablet. The accumulation ratio following daily oral administration is 1.12 with steady state achieved after 2 days. Peak concentrations are typically 270 ng/mL and 308 ng/mL following a single and a repeated 5 mg once daily dose, respectively. Food had no effect on the extent of exposure (AUC) of the levocetirizine tablet, but Tmax was delayed by about 1.25 hours and Cmax was decreased by about 36% after administration with a high fat meal; therefore, levocetirizine can be administered with or without food.
A dose of 5 mg (10 mL) of levocetirizine dihydrochloride oral solution is bioequivalent to a 5 mg dose of levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets. Following oral administration of a 5 mg dose of levocetirizine dihydrochloride oral solution to healthy adult subjects, the mean peak plasma concentrations were achieved approximately 0.5 hour post-dose.
- Distribution
The mean plasma protein binding of levocetirizine in vitro ranged from 91 to 92%, independent of concentration in the range of 90 to 5000 ng/mL, which includes the therapeutic plasma levels observed. Following oral dosing, the average apparent volume of distribution is approximately 0.4 L/kg, representative of distribution in total body water.
- Metabolism
The extent of metabolism of levocetirizine in humans is less than 14% of the dose and therefore differences resulting from genetic polymorphism or concomitant intake of hepatic drug metabolizing enzyme inhibitors are expected to be negligible. Metabolic pathways include aromatic oxidation, N- and O-dealkylation, and taurine conjugation. Dealkylation pathways are primarily mediated by CYP 3A4 while aromatic oxidation involves multiple and/or unidentified CYP isoforms.
- Elimination
The plasma half-life in adult healthy subjects was about 8 to 9 hours after administration of oral tablets, and the mean oral total body clearance for levocetirizine was approximately 0.63 mL/kg/min. The major route of excretion of levocetirizine and its metabolites is via urine, accounting for a mean of 85.4% of the dose. Excretion via feces accounts for only 12.9% of the dose. Levocetirizine is excreted both by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion. Renal clearance of levocetirizine correlates with that of creatinine clearance. In patients with renal impairment the clearance of levocetirizine is reduced [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
- Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro data on metabolite interaction indicate that levocetirizine is unlikely to produce, or be subject to metabolic interactions. Levocetirizine at concentrations well above Cmax level achieved within the therapeutic dose ranges is not an inhibitor of CYP isoenzymes 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2A1, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A4, and is not an inducer of UGT1A or CYP isoenzymes 1A2, 2C9 and 3A4.
No formal in vivo drug interaction studies have been performed with levocetirizine. Studies have been performed with the racemic cetirizine [see Drug Interactions ( 7 )].
- Pediatric Patients
Data from a pediatric pharmacokinetic study with oral administration of a single dose of 5 mg levocetirizine in 14 children age 6 to 11 years with body weight ranging between 20 and 40 kg show that Cmax and AUC values are about 2 fold greater than that reported in healthy adult subjects in a cross-study comparison. The mean Cmax was 450 ng/mL, occurring at a mean time of 1.2 hours, weight-normalized, total body clearance was 30% greater, and the elimination half-life 24% shorter in this pediatric population than in adults.
Dedicated pharmacokinetic studies have not been conducted in pediatric patients younger than 6 years of age. A retrospective population pharmacokinetic analysis was conducted in 324 subjects (181 children 1 to 5 years of age, 18 children 6 to 11 years of age, and 124 adults 18 to 55 years of age) who received single or multiple doses of levocetirizine ranging from 1.25 mg to 30 mg. Data generated from this analysis indicated that administration of 1.25 mg once daily to children 6 months to 5 years of age results in plasma concentrations similar to those of adults receiving 5 mg once daily.
- Geriatric Patients
Limited pharmacokinetic data are available in elderly subjects. Following once daily repeat oral administration of 30 mg levocetirizine for 6 days in 9 elderly subjects (65 to 74 years of age), the total body clearance was approximately 33% lower compared to that in younger adults. The disposition of racemic cetirizine has been shown to be dependent on renal function rather than on age. This finding would also be applicable for levocetirizine, as levocetirizine and cetirizine are both predominantly excreted in urine. Therefore, the levocetirizine dose should be adjusted in accordance with renal function in elderly patients [see Dosage and Administration ( 2 )].
- Gender
Pharmacokinetic results for 77 patients (40 men, 37 women) were evaluated for potential effect of gender. The half-life was slightly shorter in women (7.08 ± 1.72 hr) than in men (8.62 ± 1.84 hr); however, the body weight-adjusted oral clearance in women (0.67 ± 0.16 mL/min/kg) appears to be comparable to that in men (0.59 ± 0.12 mL/min/kg). The same daily doses and dosing intervals are applicable for men and women with normal renal function.
- Race
The effect of race on levocetirizine has not been studied. As levocetirizine is primarily renally excreted, and there are no important racial differences in creatinine clearance, pharmacokinetic characteristics of levocetirizine are not expected to be different across races. No race-related differences in the kinetics of racemic cetirizine have been observed.
- Renal Impairment
Levocetirizine exposure (AUC) exhibited 1.8, 3.2, 4.3, and 5.7 fold increase in mild, moderate, severe, renal impaired, and end-stage renal disease patients, respectively, compared to healthy subjects. The corresponding increases of half-life estimates were 1.4, 2, 2.9, and 4 fold, respectively.
The total body clearance of levocetirizine after oral dosing was correlated to the creatinine clearance and was progressively reduced based on severity of renal impairment. Therefore, it is recommended to adjust the dose and dosing intervals of levocetirizine based on creatinine clearance in patients with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment. In end-stage renal disease patients (CLCR < 10 mL/min) levocetirizine is contraindicated. The amount of levocetirizine removed during a standard 4 hour hemodialysis procedure was < 10%.
The dosage of levocetirizine should be reduced in patients with mild renal impairment. Both the dosage and frequency of administration should be reduced in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.4 )].
- Hepatic Impairment
Levocetirizine has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment. The non-renal clearance (indicative of hepatic contribution) was found to constitute about 28% of the total body clearance in healthy adult subjects after oral administration.
As levocetirizine is mainly excreted unchanged by the kidney, it is unlikely that the clearance of levocetirizine is significantly decreased in patients with solely hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration ( 2 )].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity studies have been performed with levocetirizine. However, evaluation of cetirizine carcinogenicity studies are relevant for determination of the carcinogenic potential of levocetirizine. In a 2 year carcinogenicity study, in rats, cetirizine was not carcinogenic at dietary doses up to 20 mg/kg (approximately 15 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults, approximately 10 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 to 11 years of age and approximately 15 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 months to 5 years of age on a mg/m2 basis). In a 2 year carcinogenicity study in mice, cetirizine caused an increased incidence of benign hepatic tumors in males at a dietary dose of 16 mg/kg (approximately 6 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults, approximately 4 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 to 11 years of age, and approximately 6 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 months to 5 years of age on a mg/m2 basis). No increased incidence of benign tumors was observed at a dietary dose of 4 mg/kg (approximately 2 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults, equivalent to the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 to 11 years of age and approximately 2 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in children 6 months to 5 years of age on a mg/m2 basis). The clinical significance of these findings during long-term use of levocetirizine is not known.
Levocetirizine was not mutagenic in the Ames test, and not clastogenic in the human lymphocyte assay, the mouse lymphoma assay, and the in vivo micronucleus test in mice.
In a fertility and general reproductive performance study in mice, cetirizine did not impair fertility at an oral dose of 64 mg/kg (approximately 25 times the recommended daily oral dose in adults on a mg/m² basis).
13.2 Animal Toxicology
Reproductive Toxicology Studies
In rats and rabbits, levocetirizine was not teratogenic at oral doses up to 200 and 120 mg/kg, respectively, (approximately 320 and 390, respectively, times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis).
In mice, cetirizine caused retarded pup weight gain during lactation at an oral dose in dams of 96 mg/kg (approximately 40 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.2 Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria
Adult Patients 18 Years of Age and Older
The efficacy of levocetirizine for the treatment of the uncomplicated skin manifestations of chronic idiopathic urticaria was evaluated in two multi-center, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trials of 4 weeks duration in adult patients 18 to 85 years of age with chronic idiopathic urticaria. The two trials included one 4 week dose-ranging trial and one 4 week single-dose level efficacy trial. These trials included 423 patients (139 males and 284 females). Most patients (> 90%) were Caucasian and the mean age was 41. Of these patients, 146 received levocetirizine 5 mg once daily in the evening. Efficacy was assessed based on patient recording of pruritus severity on a severity score of 0 to 3 (0 = none to 3 = severe). The primary efficacy endpoint was the mean reflective pruritus severity score over the first week and over the entire treatment period. Additional efficacy variables were the instantaneous pruritus severity score, the number and size of wheals, and duration of pruritus.
The dose-ranging trial was conducted to evaluate the efficacy of levocetirizine 2.5, 5, and 10 mg once daily in the evening. In this trial, each of the three doses of levocetirizine demonstrated greater decrease in the reflective pruritus severity score than placebo and the difference was statistically significant for all three doses (see Table 6 ).
The single dose level trial evaluated the efficacy of levocetirizine 5 mg once daily in the evening compared to placebo in patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria over a 4 week treatment period. Levocetirizine 5 mg demonstrated a greater decrease from baseline in the reflective pruritus severity score than placebo and the difference from placebo was statistically significant.
Duration of pruritus, number and size of wheals, and instantaneous pruritus severity score also showed significant improvement over placebo. The significant improvement in the instantaneous pruritus severity score over placebo confirmed end of dosing interval efficacy (see Table 6 ).
| Treatment | N | Baseline | On Treatment Adjusted Mean | Difference from Placebo | ||
| Estimate | 95% CI | p-value | ||||
| Dose-Ranging Trial – Reflective Pruritus Severity Score | ||||||
| Levocetirizine 2.5 mg | 69 | 2.08 | 1.02 | 0.82 | (0.58, 1.06) | < 0.001 |
| Levocetirizine 5 mg | 62 | 2.07 | 0.92 | 0.91 | (0.66, 1.16) | < 0.001 |
| Levocetirizine 10 mg | 55 | 2.04 | 0.73 | 1.11 | (0.85, 1.37) | < 0.001 |
| Placebo | 60 | 2.25 | 1.84 | |||
| Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria Trial – Reflective Pruritus Severity Score | ||||||
| Levocetirizine 5 mg | 80 | 2.07 | 0.94 | 0.62 | (0.38, 0.86) | < 0.001 |
| Placebo | 82 | 2.06 | 1.56 | |||
Pediatric Patients
There are no clinical efficacy trials in pediatric patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.4 )].
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Levocetirizine dihydrochloride tablets are available as follows:
5 mg - white to off-white, film-coated, oval-shaped, scored tablets. One side of the tablet is scored in half and debossed with the number "9" on one side of the score and "3" on the other. The other side of the tablet debossed with the number "7701". They are available in bottles of 90.
Storage:
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure (as required).
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Somnolence
Caution patients against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness, and motor coordination such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle after ingestion of levocetirizine.
17.2 Concomitant Use of Alcohol and Other Central Nervous System Depressants
Instruct patients to avoid concurrent use of levocetirizine with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants because additional reduction in mental alertness may occur.
17.3 Dosing of Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride Tablets
Do not exceed the recommended daily dose in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older of 5 mg once daily in the evening. In children 6 to 11 years of age the recommended dose is 2.5 mg once daily in the evening. In children 6 months to 5 years of age, the recommended dose is 1.25 mg once daily in the evening. Advise patients to not ingest more than the recommended dose of levocetirizine because of the increased risk of somnolence at higher doses.
Manufactured In Israel By:
TEVA PHARMACEUTICAL IND. LTD.
Jerusalem, 91010, Israel
Manufactured For:
TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA
Sellersville, PA 18960
Rev. G 7/2013
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride Tablets 5 mg 90s Label Text
NDC 0093-7701-98
LEVOCETIRIZINE
DIHYDROCHLORIDE
Tablets
5 mg
Rx only
90 TABLETS
TEVA
Levocetirizine DihydrochlorideLevocetirizine Dihydrochloride TABLET, FILM COATED
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||