Lupron Depot
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Lupron Depot safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Lupron Depot. Lupron Depot (leuprolide acetate for depot suspension) Initial U.S. Approval: 1995RECENT MAJOR CHANGESWarnings and Precautions , Convulsions (5.5) 7/2013INDICATIONS AND USAGELUPRON DEPOT is a gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist indicated for: palliative treatment of advanced prostatic cancer (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONLUPRON DEPOT must be administered under the supervision of a physician. Due to different release characteristics, the dosage strengths are not additive and must be selected based upon the desired dosing schedule. (2) LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3–month administration, given as a single intramuscular injection every 12 weeks (2.1) LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4–month administration, given as a single intramuscular injection every 16 weeks (2.2) LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6–month administration, given as a single intramuscular injection every 24 weeks (2.3) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS22.5 mg, 30 mg, and 45 mg injections in a kit with prefilled dual chamber syringe (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to GnRH, GnRH agonist or any of the excipients in LUPRON DEPOT (4.1) Pregnancy (4.2, 8.1) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Increased serum testosterone (~ 50% above baseline) during first week of treatment; monitor serum testosterone and PSA (5.1, 5.6) Isolated cases of transient worsening of symptoms, or additional signs and symptoms of prostate cancer during the first few weeks of treatment. (5.1) A small number of patients may experience a temporary increase in bone pain which can be managed symptomatically. (5.1) Isolated cases of ureteral obstruction and spinal cord compression have been reported with GnRH agonists, which may contribute to paralysis with or without fatal complications. (5.1) Hyperglycemia and Diabetes: Hyperglycemia and an increased risk of developing diabetes have been reported in men receiving GnRH analogs. Monitor blood glucose level and manage according to current clinical practice. (5.2) Cardiovascular Diseases: Increased risk of myocardial infarction, sudden cardiac death and stroke has been reported in association with use of GnRH analogs in men. Monitor for cardiovascular disease and manage according to current clinical practice. (5.3) Long-term androgen deprivation therapy prolongs the QT interval. Consider risks and benefits. (5.4) Convulsions have been observed in patients with or without a history of predisposing factors. Manage convulsions according to the current clinical practice. (5.5) Side Effects LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3–month administration: The most common related adverse reactions (>10%) were general pain, injection site reaction, hot flashes/sweats, GI disorders, joint disorders, testicular atrophy, urinary disorders. (6.1) LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4–month administration: The most common adverse reactions (>10%) were asthenia, flu syndrome, general pain, headache, injection site reaction, hot flashes/sweats, GI disorders, edema, skin reaction, urinary disorders. (6.2) LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6–month administration: The most common adverse reactions (>10%) were hot flush, injection site pain, upper respiratory infection, and fatigue. (6.3) In postmarketing experience, mood swings, depression, rare reports of suicidal ideation and attempt, rare reports of pituitary apoplexy, and rare reports of serious drug-induced liver injury have been reported (6.4). To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AbbVie Inc.at 1-800-633-9110 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatchDRUG INTERACTIONS No interactions with LUPRON DEPOT are expected. (7) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pediatric: These LUPRON DEPOT formulations are not indicated for use in children. See the LUPRON DEPOT PED® package insert for the use of leuprolide acetate in children with central precocious puberty. Geriatric: This label reflects clinical trials for LUPRON DEPOT in prostate cancer in which the majority of the subjects studied were at least 65 years of age.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 LUPRON DEPOT INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 LUPRON DEPOT DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 LUPRON DEPOT CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 LUPRON DEPOT ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 LUPRON DEPOT DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 15 REFERENCES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3–month administration, 30 mg for 4–month administration, and 45 mg for 6–month administration (leuprolide acetate) are indicated in the palliative treatment of advanced prostatic cancer.
LUPRON DEPOT is a gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
LUPRON DEPOT must be administered under the supervision of a physician.
| Dosage | 22.5 mg for 3-Month Administration | 30 mg for 4-Month Administration | 45 mg for 6-Month Administration |
| Recommended dose | 1 injection every 12 weeks | 1 injection every 16 weeks | 1 injection every 24 weeks |
2.1 LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-Month Administration
The recommended dose of LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-month administration is one injection every 12 weeks. Due to different release characteristics, a fractional dose, or a combination of doses of this depot formulation is not equivalent to the same dose of the monthly formulation and should not be given.
Incorporated in a depot formulation, the lyophilized microspheres are to be reconstituted and administered every 12 weeks as a single intramuscular injection.
For optimal performance of the prefilled dual chamber syringe (PDS), read and follow the instructions in Section 2.4.
2.2 LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-Month Administration
The recommended dose of LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-month administration is one injection every 16 weeks. Due to different release characteristics, a fractional dose, or a combination of doses of this depot formulation is not equivalent to the same dose of the monthly formulation and should not be given.
Incorporated in a depot formulation, the lyophilized microspheres are to be reconstituted and administered every 16 weeks as a single intramuscular injection.
For optimal performance of the prefilled dual chamber syringe (PDS), read and follow the instructions in Section 2.4.
2.3 LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-Month Administration
The recommended dose of LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-month administration is one injection every 24 weeks. Due to different release characteristics, a fractional dose, or a combination of doses of this depot formulation is not equivalent to the same dose of the monthly formulation and should not be given.
Incorporated in a depot formulation, the lyophilized microspheres are to be reconstituted and administered every 24 weeks as a single intramuscular injection.
For optimal performance of the prefilled dual chamber syringe (PDS), read and follow the instructions in Section 2.4.
2.4 Administration of Injection
- The lyophilized microspheres are to be reconstituted and administered as a single intramuscular injection.
- Since LUPRON DEPOT does not contain a preservative, the suspension should be injected immediately or discarded if not used within two hours.
- As with other drugs administered by injection, the injection site should be varied periodically.
- The LUPRON DEPOT powder should be visually inspected and the syringe should NOT BE USED if clumping or caking is evident. A thin layer of powder on the wall of the syringe is considered normal prior to mixing with the diluent. The diluent should appear clear.
- To prepare for injection, screw the white plunger into the end stopper until the stopper begins to turn.
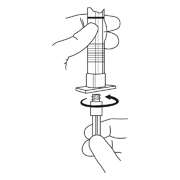
- Hold the syringe UPRIGHT. Release the diluent by SLOWLY PUSHING (6 to 8 seconds) the plunger until the first stopper is at the blue line in the middle of the barrel.
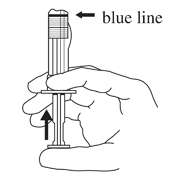
- Keep the syringe UPRIGHT. Gently mix the microspheres (powder) thoroughly to form a uniform suspension. The suspension will appear milky. If the powder adheres to the stopper or caking/clumping is present, tap the syringe with your finger to disperse. DO NOT USE if any of the powder has not gone into suspension.
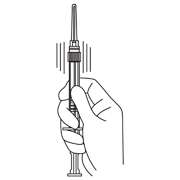
- Hold the syringe UPRIGHT. With the opposite hand pull the needle cap upward without twisting.
- Keep the syringe UPRIGHT. Advance the plunger to expel the air from the syringe.
- After cleaning the injection site with an alcohol swab, insert the needle completely at a 90 degree angle.
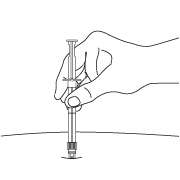
NOTE: Aspirated blood would be visible just below the luer lock connection if a blood vessel is accidentally penetrated. If present, blood can be seen through the transparent LuproLoc® safety device. If blood is present remove the needle immediately. Do not inject the medication
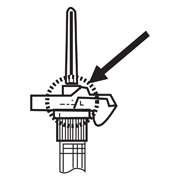
- Inject the entire contents of the syringe intramuscularly at the time of reconstitution. The suspension settles very quickly following reconstitution; therefore, LUPRON DEPOT should be mixed and used immediately.
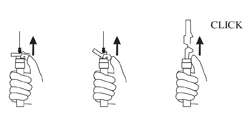
AFTER INJECTION
- Withdraw the needle. Immediately activate the LuproLoc® safety device by pushing the arrow forward with the thumb or finger, as illustrated, until the device is fully extended and a CLICK is heard or felt.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
- Please see the handling information in the Reference Section 15.0.
- Dispose of the syringe according to local regulations/procedures.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-month administration, 30 mg for 4-month administration, and 45 mg for 6-month administration are each supplied as a kit with prefilled dual chamber syringe.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity
LUPRON DEPOT is contraindicated in individuals with known hypersensitivity to GnRH agonists or any of the excipients in LUPRON DEPOT. Reports of anaphylactic reactions to GnRH agonists have been reported in the medical literature.
4.2 Pregnancy
LUPRON DEPOT may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Expected hormonal changes that occur with LUPRON DEPOT treatment increase the risk for pregnancy loss and fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. LUPRON DEPOT is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Tumor Flare
Initially, LUPRON DEPOT, like other GnRH agonists, causes increases in serum levels of testosterone to approximately 50% above baseline during the first weeks of treatment. Isolated cases of ureteral obstruction and spinal cord compression have been observed, which may contribute to paralysis with or without fatal complications. Transient worsening of symptoms may develop. A small number of patients may experience a temporary increase in bone pain, which can be managed symptomatically.
Patients with metastatic vertebral lesions and/or with urinary tract obstruction should be closely observed during the first few weeks of therapy.
5.2 Hyperglycemia and Diabetes
Hyperglycemia and an increased risk of developing diabetes have been reported in men receiving GnRH agonists. Hyperglycemia may represent development of diabetes mellitus or worsening of glycemic control in patients with diabetes. Monitor blood glucose and/or glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) periodically in patients receiving a GnRH agonist and manage with current practice for treatment of hyperglycemia or diabetes.
5.3 Cardiovascular Diseases
Increased risk of developing myocardial infarction, sudden cardiac death and stroke has been reported in association with use of GnRH agonists in men. The risk appears low based on the reported odds ratios, and should be evaluated carefully along with cardiovascular risk factors when determining a treatment for patients with prostate cancer. Patients receiving a GnRH agonist should be monitored for symptoms and signs suggestive of development of cardiovascular disease and be managed according to current clinical practice.
5.4 Effect on QT/QTc Interval
Long-term androgen deprivation therapy prolongs the QT interval. Physicians should consider whether the benefits of androgen deprivation therapy outweigh the potential risks in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, electrolyte abnormalities, or congestive heart failure and in patients taking class IA (e.g., quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic medications.
5.5 Convulsions
Postmarketing reports of convulsions have been observed in patients on leuprolide acetate therapy. These included patients with a history of seizures, epilepsy, cerebrovascular disorders, central nervous system anomalies or tumors, and in patients on concomitant medications that have been associated with convulsions such as bupropion and SSRIs. Convulsions have also been reported in patients in the absence of any of the conditions mentioned above. Patients receiving a GnRH agonist who experience convulsion should be managed according to current clinical practice.
5.6 Laboratory Tests
Response to LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-month administration, 30 mg for 4-month administration, and 45 mg for 6-month administration should be monitored by measuring serum levels of testosterone. In the majority of patients, testosterone levels increased above baseline, declining thereafter to castrate levels (< 50 ng/dL) within four weeks. [see Clinical Studies (14) and Adverse Reactions (6)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-Month Administration
Clinical Trials
In two clinical trials of LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-month administration, the following adverse reactions were reported to have a possible or probable relationship to drug as ascribed by the treating physician in 5% or more of the patients receiving the drug. Often, causality is difficult to assess in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Reactions considered not drug-related are excluded.
| LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-Month Administration | ||
| Body System/Reaction | N=94 | (%) |
| Body As A Whole | ||
| Asthenia | 7 | (7.4) |
| General Pain | 25 | (26.6) |
| Headache | 6 | (6.4) |
| Injection Site Reaction | 13 | (13.8) |
| Cardiovascular System | ||
| Hot flashes/Sweats | 55 | (58.5) |
| Digestive System | ||
| GI Disorders | 15 | (16.0) |
| Musculoskeletal System | ||
| Joint Disorders | 11 | (11.7) |
| Central/Peripheral Nervous System | ||
| Dizziness/Vertigo | 6 | (6.4) |
| Insomnia/Sleep Disorders | 8 | (8.5) |
| Neuromuscular Disorders | 9 | (9.6) |
| Respiratory System | ||
| Respiratory Disorders | 6 | (6.4) |
| Skin and Appendages | ||
| Skin Reaction | 8 | (8.5) |
| Urogenital System | ||
| Testicular Atrophy | 19 | (20.2) |
| Urinary Disorders | 14 | (14.9) |
In these same studies, the following adverse reactions were reported in less than 5% of the patients on LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-month administration.
Body As A Whole - Enlarged abdomen, Fever
Cardiovascular System - Arrhythmia, Bradycardia, Heart failure, Hypertension, Hypotension, Varicose vein
Digestive System - Anorexia, Duodenal ulcer, Increased appetite, Thirst/dry mouth
Hemic and Lymphatic System - Anemia, Lymphedema
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders - Dehydration, Edema
Central/Peripheral Nervous System - Anxiety, Delusions, Depression, Hypesthesia, Libido decreased*, Nervousness, Paresthesia
Respiratory System - Epistaxis, Pharyngitis, Pleural effusion, Pneumonia
Special Senses - Abnormal vision, Amblyopia, Dry eyes, Tinnitus
Urogenital System - Gynecomastia, Impotence*, Penis disorders, Testis disorders.
* Physiologic effect of decreased testosterone.
Laboratory
Abnormalities of certain parameters were observed, but are difficult to assess in this population. The following were recorded in ≥5% of patients: Increased BUN, Hyperglycemia, Hyperlipidemia (total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, triglycerides), Hyperphosphatemia, Abnormal liver function tests, Increased PT, Increased PTT. Additional laboratory abnormalities reported were: Decreased platelets, Decreased potassium and Increased WBC.
6.2 LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-Month Administration
Clinical Trials
The 4-month formulation of LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg was utilized in clinical trials that studied the drug in 49 nonorchiectomized prostate cancer patients for 32 weeks or longer and in 24 orchiectomized prostate cancer patients for 20 weeks.
In the above described clinical trials, the following adverse reactions were reported in ≥ 5% of the patients during the treatment period regardless of causality.
| LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-Month Administration | ||||
| Body System/Events | Nonorchiectomized | Orchiectomized | ||
| Study 013 | Study 012 | |||
| N=49 | (%) | N=24 | (%) | |
| Body As a Whole | ||||
| Asthenia | 6 | (12.2) | 1 | (4.2) |
| Flu Syndrome | 6 | (12.2) | 0 | (0.0) |
| General Pain | 16 | (32.7) | 1 | (4.2) |
| Headache | 5 | (10.2) | 1 | (4.2) |
| Injection Site Reaction | 4 | (8.2) | 9 | (37.5) |
| Cardiovascular System | ||||
| Hot flashes/Sweats | 23 | (46.9) | 2 | (8.3) |
| Digestive System | ||||
| GI Disorders | 5 | (10.2) | 3 | (12.5) |
| Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders | ||||
| Dehydration | 4 | (8.2) | 0 | (0.0) |
| Edema | 4 | (8.2) | 5 | (20.8) |
| Musculoskeletal System | ||||
| Joint Disorder | 8 | (16.3) | 1 | (4.2) |
| Myalgia | 4 | (8.2) | 0 | (0.0) |
| Nervous System | ||||
| Dizziness/Vertigo | 3 | (6.1) | 2 | (8.3) |
| Neuromuscular Disorders | 3 | (6.1) | 1 | (4.2) |
| Paresthesia | 4 | (8.2) | 1 | (4.2) |
| Respiratory System | ||||
| Respiratory Disorder | 4 | (8.2) | 1 | (4.2) |
| Skin and Appendages | ||||
| Skin Reaction | 6 | (12.2) | 0 | (0.0) |
| Urogenital System | ||||
| Urinary Disorders | 5 | (10.2) | 4 | (16.7) |
In these same studies, the following adverse reactions were reported in less than 5% of the patients on LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-month administration.
Body As a Whole - Abscess, Accidental injury, Allergic reaction, Cyst, Fever, Generalized edema, Hernia, Neck pain, Neoplasm
Cardiovascular System - Atrial fibrillation, Deep thrombophlebitis, Hypertension
Digestive System - Anorexia, Eructation, Gastrointestinal hemorrhage, Gingivitis, Gum hemorrhage, Hepatomegaly, Increased appetite, Intestinal obstruction, Periodontal abscess
Hemic and Lymphatic System - Lymphadenopathy
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders - Healing abnormal, Hypoxia, Weight loss
Musculoskeletal System - Leg cramps, Pathological fracture, Ptosis
Nervous System - Abnormal thinking, Amnesia, Confusion, Convulsion, Dementia, Depression, Insomnia/sleep disorders, Libido decreased*, Neuropathy, Paralysis
Respiratory System - Asthma, Bronchitis, Hiccup, Lung disorder, Sinusitis, Voice alteration
Skin and Appendages - Herpes zoster, Melanosis
Urogenital System - Bladder carcinoma, Epididymitis, Impotence*, Prostate disorder, Testicular atrophy*, Urinary incontinence, Urinary tract infection.
* Physiologic effect of decreased testosterone.
Laboratory
Abnormalities of certain parameters were observed, but their relationship to drug treatment is difficult to assess in this population. The following were recorded in ≥ 5% of patients: Decreased bicarbonate, Decreased hemoglobin/hematocrit/RBC, Hyperlipidemia (total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, triglycerides), Decreased HDL-cholesterol, Eosinophilia, Increased glucose, Increased liver function tests (ALT, AST, GGTP, LDH), Increased phosphorus. Additional laboratory abnormalities were reported: Increased BUN and PT, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopenia, Uricaciduria.
6.3 LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-Month Administration
Clinical Trials
One open label, multicenter study was conducted with LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-month administration in 151 prostate cancer patients. Patients were treated for 48 weeks, with 139/151 receiving two injections 24 weeks apart.
In the above described clinical trial, the following adverse events were reported in ≥ 5% of the patients during the treatment period. The Table 4 includes all adverse events reported in ≥ 5% of patients as well as the incidences of these adverse events that were considered, by the treating physician, to have a definite or possible relationship to LUPRON.
| LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-Month Administration | ||||
| Treatment Emergent | Treatment Related | |||
| Adverse Event | N = 151 | (%) | N = 151 | (%) |
| Hot Flush/Flushing | 89 | 58.9 | 88 | 58.3 |
| Injection Site Pain/Discomfort | 29 | 19.2 | 16 | 10.6 |
| Upper Respiratory Tract Infection/Influenza-like Illness1 | 32 | 21.2 | 0 | 0 |
| Fatigue/Lethargy | 20 | 13.2 | 18 | 11.9 |
| Constipation | 15 | 9.9 | 5 | 3.3 |
| Arthralgia | 14 | 9.3 | 2 | 1.3 |
| Insomnia/Sleep Disorder | 13 | 8.6 | 5 | 3.3 |
| Headache/Sinus Headache | 12 | 7.9 | 3 | 2.0 |
| Musculoskeletal Pain/ Myalgia | 12 | 7.9 | 3 | 2.0 |
| Second Primary Neoplasm2 | 11 | 7.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Cough | 10 | 6.6 | 2 | 1.3 |
| Hematuria/Hemorrhagic Cystitis | 10 | 6.6 | 0 | 0 |
| Hypertension/BP Increased | 10 | 6.6 | 3 | 2.0 |
| Rash | 9 | 6.0 | 3 | 2.0 |
| Dysuria | 9 | 6.0 | 1 | 0.7 |
| Urinary Tract Infection/Cystitis | 9 | 6.0 | 0 | 0 |
| Anemia/Hemoglobin Decreased | 10 | 6.6 | 2 | 1.3 |
| Back Pain | 8 | 5.3 | 0 | 0 |
| COPD | 8 | 5.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Dizziness | 8 | 5.3 | 3 | 2.0 |
| Dyspnea/Dyspnea on Exertion | 8 | 5.3 | 2 | 1.3 |
| Nocturia | 8 | 5.3 | 2 | 1.3 |
| Peripheral/Pitting Edema | 8 | 5.3 | 2 | 1.3 |
| Coronary Artery Disease/Angina | 8 | 5.3 | 1 | 0.7 |
1Includes influenza, nasal congestion, nasopharyngitis, rhinorrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, and viral upper respiratory tract infection
2Includes basal cell carcinoma, bladder transitional cell carcinoma, lung neoplasm, malignant melanoma, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and squamous cell carcinoma
The following adverse events led to discontinuation; fatigue, hot flush, second primary neoplasm, asthenia, coronary artery disease, constipation, hyperkalemia, and sleep disorder. Serious adverse events in ≥ 2% of patients, regardless of causality, included chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, coronary artery disease/angina, cerebrovascular accident/transient ischemic attack, pneumonia, and second primary neoplasms.
Laboratory
At baseline, 13.9% of patients had a CTCAE v4.0 grade 1 or 2 decreased hemoglobin. During the study, 42.4% of subjects had grade 1 decreased hemoglobin (10 - <12-5 g/dL), 2.0% had grade 2 ( 8 - <10 g/dL) and 1.3% of subjects had grade 3 or 4 (<8 g/dL). Likewise, 28.5% of patients had a grade 1 or 2 increased cholesterol at baseline while 55.0% had grade 1 increased cholesterol (>199- 300 mg/dL), 3.3% had a grade 2 increase (>300-400 mg/dL), and 0.7% of subjects had grade 3 (>400 mg/dL) during the study.
6.4 Postmarketing
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of LUPRON DEPOT. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
During postmarketing surveillance, which includes other dosage forms and other patient populations, the following adverse reactions were reported.
Like other drugs in this class, mood swings, including depression, have been reported. There have been very rare reports of suicidal ideation and attempt. Many, but not all, of these patients had a history of depression or other psychiatric illness. Patients should be counseled on the possibility of development or worsening of depression during treatment with LUPRON.
Symptoms consistent with an anaphylactoid or asthmatic process have been rarely (incidence rate of about 0.002%) reported. Rash, urticaria, and photosensitivity reactions have also been reported.
Changes in Bone Density - Decreased bone density has been reported in the medical literature in men who have had orchiectomy or who have been treated with a GnRH agonist analog. In a clinical trial, 25 men with prostate cancer, 12 of whom had been treated previously with leuprolide acetate for at least six months, underwent bone density studies as a result of pain. The leuprolide-treated group had lower bone density scores than the nontreated control group. It can be anticipated that long periods of medical castration in men will have effects on bone density.
Pituitary apoplexy - During post-marketing surveillance, rare cases of pituitary apoplexy (a clinical syndrome secondary to infarction of the pituitary gland) have been reported after the administration of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists. In a majority of these cases, a pituitary adenoma was diagnosed, with a majority of pituitary apoplexy cases occurring within 2 weeks of the first dose, and some within the first hour. In these cases, pituitary apoplexy has presented as sudden headache, vomiting, visual changes, ophthalmoplegia, altered mental status, and sometimes cardiovascular collapse. Immediate medical attention has been required.
Localized reactions including induration and abscess have been reported at the site of injection.
Symptoms consistent with fibromyalgia (e.g., joint and muscle pain, headaches, sleep disorders, gastrointestinal distress, and shortness of breath) have been reported individually and collectively.
Cardiovascular System – Hypotension, Myocardial infarction, Pulmonary embolism
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorder – Interstitial lung disease
Hepato-biliary disorder: Serious drug-induced liver injury
Hemic and Lymphatic System - Decreased WBC
Central/Peripheral Nervous System - Convulsion, Peripheral neuropathy, Spinal fracture/paralysis
Endocrine System – Diabetes
Musculoskeletal System - Tenosynovitis-like symptoms
Urogenital System - Prostate pain
See other LUPRON DEPOT and LUPRON Injection package inserts for other reactions reported in women and pediatric populations.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No pharmacokinetic-based drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted with LUPRON DEPOT. However, because leuprolide acetate is a peptide that is primarily degraded by peptidase and not by Cytochrome P-450 enzymes as noted in specific studies, and the drug is only about 46% bound to plasma proteins, drug interactions would not be expected to occur.
See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) .
7.1 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Administration of LUPRON DEPOT in therapeutic doses results in suppression of the pituitary-gonadal system. Normal function is usually restored within three months after treatment is discontinued. Due to the suppression of the pituitary-gonadal system by LUPRON DEPOT, diagnostic tests of pituitary gonadotropic and gonadal functions conducted during treatment and up to three months after discontinuation of LUPRON DEPOT may be affected.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category X [see Contraindications (4.2)].
LUPRON DEPOT is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant while receiving the drug. Expected hormonal changes that occur with LUPRON DEPOT treatment increase the risk for pregnancy loss and fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Major fetal abnormalities were observed in rabbits after a single administration of the monthly formulation of LUPRON DEPOT on day 6 of pregnancy at doses of 0.00024, 0.0024, and 0.024 mg/kg (approximately 1/1600 to 1/16 the human dose based on body surface area using an estimated daily dose in animals and humans). Since a depot formulation was utilized in the study, a sustained exposure to leuprolide was expected throughout the period of organogenesis and to the end of gestation. Similar studies in rats did not demonstrate an increase in fetal malformations, however, there was increased fetal mortality and decreased fetal weights with the two higher doses of the monthly formulation of LUPRON DEPOT in rabbits and with the highest dose (0.024 mg/kg) in rats.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
LUPRON DEPOT is not indicated for women [see Indications and Usage (1) ]. It is not known whether leuprolide is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from LUPRON DEPOT, a decision should be made to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
See LUPRON DEPOT-PED® (leuprolide acetate for depot suspension) labeling for the safety and effectiveness in children with central precocious puberty.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the clinical trials for LUPRON DEPOT in prostate cancer, the majority (approximately 80%) of the subjects studied were at least 65 years of age. Therefore, the labeling reflects the pharmacokinetics, efficacy and safety of LUPRON DEPOT in this population.
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no experience of overdosage in clinical trials. In rats, a single subcutaneous dose of 100 mg/kg (approximately 4,000 times the estimated daily human dose based on body surface area), resulted in dyspnea, decreased activity, and excessive scratching. In early clinical trials with daily subcutaneous leuprolide acetate, doses as high as 20 mg/day for up to two years caused no adverse effects differing from those observed with the 1 mg/day dose.
11 DESCRIPTION
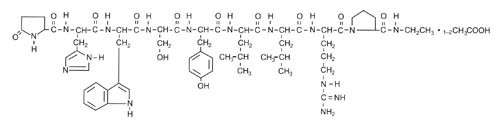
Leuprolide acetate is a synthetic nonapeptide analog of naturally occurring gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). The analog possesses greater potency than the natural hormone. The chemical name is 5-oxo-L-prolyl-L-histidyl-L-tryptophyl-L-seryl-L-tyrosyl-D-leucyl-L-leucyl-L-arginyl-N-ethyl-L-prolinamide acetate (salt) with the following structural formula:
LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-month administration is available in a prefilled dual-chamber syringe containing sterile lyophilized microspheres which, when mixed with diluent, become a suspension intended as an intramuscular injection to be given ONCE EVERY 12 WEEKS.
The front chamber of LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-month administration prefilled dual-chamber syringe contains leuprolide acetate (22.5 mg), polylactic acid (198.6 mg) and D-mannitol (38.9 mg). The second chamber of diluent contains carboxymethylcellulose sodium (7.5 mg), D-mannitol (75.0 mg), polysorbate 80 (1.5 mg), water for injection, USP, and glacial acetic acid, USP to control pH.
LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-month administration is available in a prefilled dual-chamber syringe containing sterile lyophilized microspheres which, when mixed with diluent, become a suspension intended as an intramuscular injection to be given ONCE EVERY 16 WEEKS.
The front chamber of LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-month administration prefilled dual-chamber syringe contains leuprolide acetate (30 mg), polylactic acid (264.8 mg) and D-mannitol (51.9 mg). The second chamber of diluent contains carboxymethylcellulose sodium (7.5 mg), D-mannitol (75.0 mg), polysorbate 80 (1.5 mg), water for injection, USP, and glacial acetic acid, USP to control pH.
LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-month administration is available in a prefilled dual-chamber syringe containing sterile lyophilized microspheres which, when mixed with diluent, become a suspension intended as an intramuscular injection to be given ONCE EVERY 24 WEEKS.
The front chamber of LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-month administration prefilled dual-chamber syringe contains leuprolide acetate (45 mg), polylactic acid (169.9 mg), D-mannitol (39.7 mg), and stearic acid (10.1 mg). The second chamber of diluent contains carboxymethylcellulose sodium (7.5 mg), D-mannitol (75.0 mg), polysorbate 80 (1.5 mg), water for injection, USP, and glacial acetic acid, USP to control pH.
During the manufacture of LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-month administration, 30 mg for 4-month administration, and 45 mg for 6-month administration, acetic acid is lost, leaving the peptide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Leuprolide acetate, a GnRH agonist, acts as an inhibitor of gonadotropin secretion. Animal studies indicate that following an initial stimulation, continuous administration of leuprolide acetate results in suppression of ovarian and testicular steroidogenesis. This effect was reversible upon discontinuation of drug therapy.
Administration of leuprolide acetate has resulted in inhibition of the growth of certain hormone dependent tumors (prostatic tumors in Noble and Dunning male rats and DMBA-induced mammary tumors in female rats) as well as atrophy of the reproductive organs.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In humans, administration of leuprolide acetate results in an initial increase in circulating levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), leading to a transient increase in levels of the gonadal steroids (testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in males, and estrone and estradiol in premenopausal females). However, continuous administration of leuprolide acetate results in decreased levels of LH and FSH. In males, testosterone is reduced to castrate levels. In premenopausal females, estrogens are reduced to postmenopausal levels. These decreases occur within two to four weeks after initiation of treatment, and castrate levels of testosterone in prostatic cancer patients have been demonstrated for more than five years.
Leuprolide acetate is not active when given orally.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-Month Administration
Following a single injection of LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-month administration in patients, mean peak plasma leuprolide concentration of 48.9 ng/mL was observed at 4 hours and then declined to 0.67 ng/mL at 12 weeks. Leuprolide appeared to be released at a constant rate following the onset of steady-state levels during the third week after dosing, providing steady plasma concentrations through the 12-week dosing interval. However, intact leuprolide and an inactive major metabolite could not be distinguished by the assay which was employed in the study. Detectable levels of leuprolide were present at all measurement points in all patients. The initial burst, followed by the rapid decline to a steady-state level, was similar to the release pattern seen with the monthly formulation.
LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-Month Administration
Following a single injection of LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-month administration in sixteen orchiectomized prostate cancer patients, mean plasma leuprolide concentration of 59.3 ng/mL was observed at 4 hours and the mean concentration then declined to 0.30 ng/mL at 16 weeks. The mean plasma concentration of leuprolide from weeks 3.5 to 16 was 0.44 ± 0.20 ng/mL (range: 0.20-1.06). Leuprolide appeared to be released at a constant rate following the onset of steady-state levels during the fourth week after dosing, providing steady plasma concentrations throughout the 16-week dosing interval. However, intact leuprolide and an inactive major metabolite could not be distinguished by the assay which was employed in the study. The initial burst, followed by the rapid decline to a steady-state level, was similar to the release pattern seen with the other depot formulations.
LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-Month Administration
Following a single injection of LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-month administration in 26 prostate cancer patients, mean peak plasma leuprolide concentration of 6.7 ng/mL was observed at 2 hours and the mean concentration then declined to 0.07 ng/mL at 24 weeks. Leuprolide appeared to be released continuously following the onset of steady-state levels during the third week after dosing providing steady plasma concentrations through the 24-week dosing interval. The initial burst, followed by the rapid decline to a steady-state level, was similar to the release pattern seen with the other depot formulations. In this study, mean leuprolide plasma concentration-time profiles were similar after the first and second dose.
Distribution
The mean steady-state volume of distribution of leuprolide following intravenous bolus administration to healthy male volunteers was 27 L. In vitro binding to human plasma proteins ranged from 43% to 49%.
Metabolism
In healthy male volunteers, a 1 mg bolus of leuprolide administered intravenously revealed that the mean systemic clearance was 7.6 L/h, with a terminal elimination half-life of approximately 3 hours based on a two compartment model.
In rats and dogs, administration of 14C-labeled leuprolide was shown to be metabolized to smaller inactive peptides, a pentapeptide (Metabolite I), tripeptides (Metabolites II and III) and a dipeptide (Metabolite IV). These fragments may be further catabolized.
The major metabolite (M-I) plasma concentrations measured in 5 prostate cancer patients reached maximum concentration 2 to 6 hours after dosing and were approximately 6% of the peak parent drug concentration. One week after dosing, mean plasma M-I concentrations were approximately 20% of mean leuprolide concentrations.
Excretion
Following administration of LUPRON DEPOT 3.75 mg to 3 patients, less than 5% of the dose was recovered as parent and M-I metabolite in the urine.
Special Populations
The pharmacokinetics of the drug in hepatically and renally impaired patients have not been determined.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Two-year carcinogenicity studies were conducted in rats and mice. In rats, a dose-related increase of benign pituitary hyperplasia and benign pituitary adenomas was noted at 24 months when the drug was administered subcutaneously at daily doses (0.6 to 4 mg/kg). There was a significant but not dose-related increase of pancreatic islet-cell adenomas in females and of testicular interstitial cell adenomas in males (highest incidence in the low dose group). In mice, no pituitary abnormalities were observed at a dose as high as 60 mg/kg for two years. Patients have been treated with leuprolide acetate for up to three years with doses as high as 10 mg/day and for two years with doses as high as 20 mg/day without demonstrable pituitary abnormalities.
Genotoxicity studies were conducted with leuprolide acetate using bacterial and mammalian systems. These studies provided no evidence of mutagenic effects or chromosomal aberrations.
Leuprolide may reduce male and female fertility. Administration of leuprolide acetate to male and female rats at dose of 0.024, 0.24, and 2.4 mg/kg as monthly depot formulation for up to 3 months (approximately as low as 1/30 of the human dose based on body surface area using an estimated daily dose in animals and humans) caused atrophy of the reproductive organs, and suppression of reproductive function. These changes were reversible upon cessation of treatment. Clinical and pharmacologic studies in adults (≥ 18 years) with leuprolide acetate and similar analogs have shown reversibility of fertility suppression when the drug is discontinued after continuous administration for periods of up to 24 weeks.
Clinical and pharmacologic studies in adults (≥ 18 years) with leuprolide acetate and similar analogs have shown reversibility of fertility suppression when the drug is discontinued after continuous administration for periods of up to 24 weeks.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-Month Administration
In clinical studies, serum testosterone was suppressed to castrate within 30 days in 87 of 92 (95%) patients and within an additional two weeks in three patients. Two patients did not suppress for 15 and 28 weeks, respectively. Suppression was maintained in all of these patients with the exception of transient minimal testosterone elevations in one of them, and in another an increase in serum testosterone to above the castrate range was recorded during the 12 hour observation period after a subsequent injection. This represents stimulation of gonadotropin secretion.
Figure 1. LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-Month Administration Mean Serum Testosterone Concentrations
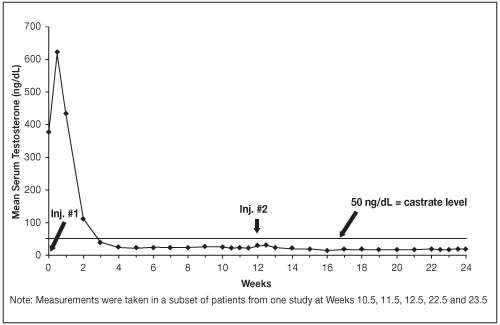
An 85% rate of "no progression" was achieved during the initial 24 weeks of treatment. A decrease from baseline in serum PSA of ≥90% was reported in 71% of the patients and a change to within the normal range (≤3.99 ng/mL) in 63% of the patients.
Periodic monitoring of serum testosterone and PSA levels is recommended, especially if the anticipated clinical or biochemical response to treatment has not been achieved. It should be noted that results of testosterone determinations are dependent on assay methodology. It is advisable to be aware of the type and precision of the assay methodology to make appropriate clinical and therapeutic decisions.
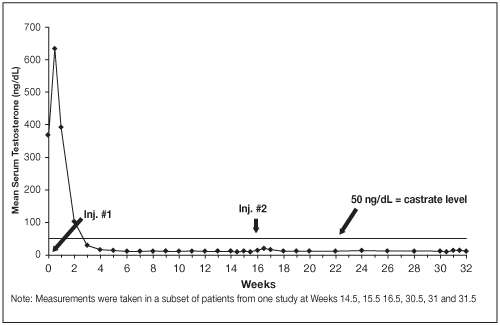
14.2 LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-Month Administration
In an open-label, noncomparative, multicenter clinical study of LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-month administration, 49 patients with stage D2 prostatic adenocarcinoma (with no prior treatment) were enrolled. The objectives were to determine whether a 30 mg depot formulation of leuprolide injected once every 16 weeks would reduce and maintain serum testosterone levels at castrate levels (≤ 50 ng/dL), and to assess the safety of the formulation. The study was divided into an initial 32-week treatment phase and a long-term treatment phase. Serum testosterone levels were determined biweekly or weekly during the first 32 weeks of treatment. Once the patient completed the initial 32-week treatment period, treatment continued at the investigator's discretion with serum testosterone levels being done every 4 months prior to the injection.
In the majority of patients, testosterone levels increased 50% or more above the baseline during the first week of treatment. Mean serum testosterone subsequently suppressed to castrate levels within 30 days of the first injection in 94% of patients and within 43 days in all 49 patients during the initial 32-week treatment period. The median dosing interval between injections was 112 days. One escape from suppression (two consecutive testosterone values greater than 50 ng/dL after castrate levels achieved) was noted at Week 16. In this patient, serum testosterone increased to above the castrate range following the second depot injection (Week 16) but returned to the castrate level by Week 18. No adverse reactions were associated with this rise in serum testosterone. A second patient had a rise in testosterone at Week 17, then returned to the castrate level by Week 18 and remained there through Week 32. In the long-term treatment phase two patients experienced testosterone elevations, both at Week 48. Testosterone for one patient returned to the castrate range at Week 52, and one patient discontinued the study at Week 48 due to disease progression.
Secondary efficacy endpoints evaluated in the study were the objective tumor response as assessed by clinical evaluations of tumor burden (complete response, partial response, objectively stable and progression) and evaluations of changes in prostatic involvement and prostate-specific antigen (PSA). These evaluations were performed at Weeks 16 and 32 of the treatment phase. The long-term treatment phase monitored PSA at each visit (every 16 weeks). The objective tumor response analysis showed "no progression" (i.e. complete or partial response, or stable disease) in 86% (37/43) of patients at Week 16, and in 77% (37/48) of patients at Week 32. Local disease improved or remained stable in all patients evaluated at Week 16 and/or 32. For patients with elevated baseline PSA, 50% (23/46) had a normal PSA (less than 4.0 ng/mL) at Week 16, and 51% (19/37) had a normal PSA at Week 32.
Periodic monitoring of serum testosterone and PSA levels is recommended, especially if the anticipated clinical or biochemical response to treatment has not been achieved. It should be noted that results of testosterone determinations are dependent on assay methodology. It is advisable to be aware of the type and precision of the assay methodology to make appropriate clinical and therapeutic decisions.
Using historical comparisons, the safety and efficacy of LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-month administration appear similar to the other LUPRON DEPOT formulations.
Figure 2. LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-Month Administration Mean Serum Testosterone Concentrations
14.3 LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-Month Administration
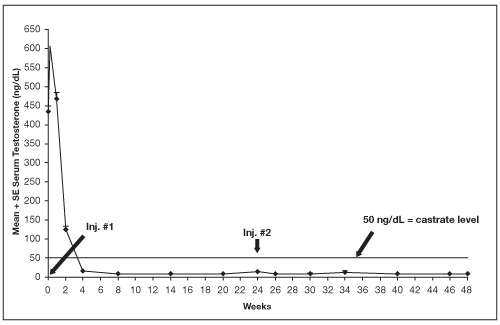
An open-label, non-comparative, multicenter clinical study of LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-month administration enrolled 151 patients with prostate cancer. The study drug was administered as two intramuscular injections of LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg at 24 week intervals (139/151 received 2 injections), and patients were followed for a total of 48 weeks.
Among 148 patients who had testosterone value at Week 4, serum testosterone was suppressed to castrate levels (< 50 ng/dL) from Week 4 through Week 48 in an estimated 93.4% (two-sided 95% CI: 89.2%, 97.6%) of patients. One patient failed to achieve testosterone suppression by Week 4, and eight patients had escapes from suppression (any testosterone value > 50 ng/dL after castrate levels were achieved). Mean testosterone levels increased to 608 ng/dL from a baseline of 435 ng/dL during the first week of treatment. By Week 4, the mean testosterone concentration had decreased to below castrate levels (16 ng/dL).
Periodic monitoring of serum testosterone levels is recommended, especially if the anticipated clinical or biochemical response to treatment has not been achieved. Testosterone determinations are dependent on assay methodology and it is advisable to be aware of the type and precision of the assay methodology to make appropriate clinical and therapeutic decisions.
Figure 3 below shows the mean testosterone concentration at various time points.
Figure 3. LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-Month Administration Serum Testosterone Concentrations (Mean + SE)
15 REFERENCES
1. NIOSH Alert: Preventing occupational exposures to antineoplastic and other hazardous drugs in healthcare settings. 2004. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 2004-165.
2. OSHA Technical Manual, TED 1-0.15A, Section VI: Chapter 2. Controlling Occupational Exposure to Hazardous Drugs. OSHA, 1999. http://www.osha.gov/dts/osta/otm/otm_vi/otm_vi_2.html
3. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. ASHP guidelines on handling hazardous drugs. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 2006; 63; 1172-1193.
4. Polovich, M., White, J.M., & Kelleher, L.O. (eds.) 2005. Chemotherapy and biotherapy guidelines and recommendations for practice (2nd Ed.) Pittsburgh, PA: Oncology Nursing Society.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Each LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-month administration (NDC 0074-3346-03), 30 mg for 4-month administration (NDC 0074-3683-03), 45 mg for 6-month administration (NDC 0074-3473-03) contains:
- one prefilled dual-chamber syringe containing needle with LuproLoc® safety device
- one plunger
- two alcohol swabs
- a complete prescribing information enclosure
The prefilled dual-chamber syringe contains sterile lyophilized microspheres of leuprolide acetate incorporated in a biodegradable lactic acid polymer.
When mixed with 1.5 mL of accompanying diluent, LUPRON DEPOT 22.5 mg for 3-month administration is administered as a single intramuscular injection EVERY 12 WEEKS.
When mixed with 1.5 mL of accompanying diluent, LUPRON DEPOT 30 mg for 4-month administration is administered as a single intramuscular injection EVERY 16 WEEKS.
When mixed with 1.5 mL of accompanying diluent, LUPRON DEPOT 45 mg for 6-month administration is administered as a single intramuscular injection EVERY 24 WEEKS.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15–30°C (59–86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed that:
- If they experience an allergic reaction to other drugs like LUPRON DEPOT, they should not use this drug.
- The most common side effects associated with LUPRON DEPOT are hot flashes, pain (especially joint pain and back pain), injection site pain and fatigue.
- LUPRON DEPOT may cause impotence.
- The increase in testosterone that occurs during the first weeks of therapy can cause an increase in urinary symptoms or pain.
- If they have metastatic cancer to the spine or urinary tract, they need close medical attention during the first weeks of therapy.
- They should notify their doctor if they develop new or worsened symptoms after beginning LUPRON DEPOT treatment.
Manufactured for
AbbVie Inc.
North Chicago, IL 60064
by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
Osaka, Japan 540-8645
03-A853 July, 2013
NDC 0074-3473-03
FOR ADULT USE
45 mg for 6-month administration
Single Dose Administration Kit with prefilled dual-chamber syringe.
LupronDepot®
(Leuprolide Acetate for Depot Suspension)
45 mg for 6-month administration
FOR INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTION
The front chamber contains: leuprolide acetate 45 mg
• polylactic acid 169.9 mg • D-mannitol 39.7 mg • stearic acid 10.1 mg
The second chamber contains: carboxymethylcellulose sodium 7.5 mg
• D-mannitol 75.0 mg • polysorbate 80 1.5 mg • water for injection, USP,
and glacial acetic acid, USP to control pH
Rx only

NDC 0074-3346-03
FOR ADULT USE
22.5 mg for 3-month administration
Single Dose Administration Kit with prefilled dual-chamber syringe
LupronDepot®
(Leuprolide Acetate for Depot Suspension)
22.5 mg for 3-month administration
FOR INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTION
The front chamber contains: leuprolide acetate 22.5 mg
• polylactic acid 198.6 mg • D-mannitol 38.9 mg
The second chamber contains: carboxymethylcellulose sodium 7.5 mg
• D-mannitol 75.0 mg • polysorbate 80 1.5 mg • water for injection, USP,
and glacial acetic acid, USP to control pH
Rx only

NDC 0074-3683-03
FOR ADULT USE
30 mg for 4-month administration
Single Dose Administration Kit with prefilled dual-chamber syringe.
LupronDepot®
(Leuprolide Acetate for Depot Suspension)
30 mg for 4-month administration
FOR INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTION
The front chamber contains: leuprolide acetate 30 mg
• polylactic acid 264.8 mg • D-mannitol 51.9 mg
The second chamber contains: carboxymethylcellulose sodium 7.5 mg
• D-mannitol 75.0 mg • polysorbate 80 1.5 mg • water for injection, USP,
and glacial acetic acid, USP to control pH
Rx only
Lupron Depotleuprolide acetate KIT
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lupron Depotleuprolide acetate KIT
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lupron Depotleuprolide acetate KIT
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||