Maxidex
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- MAXIDEX DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDCIATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAININDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- MAXIDEX ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DOSAGE AND ADMINSTRATION
- HOW TO APPLY MAXIDEX OINTMENT
- HOW SUPPLIED
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
MAXIDEX DESCRIPTION
MAXIDEX®(Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate) is an adrenocortical steroid prepared as a sterile ophthalmic ointment. The active ingredient is represented by the chemical structure:
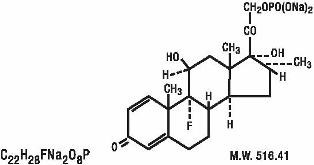
Established name:
Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate
Chemical name:
Pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione,9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-16-methyl-21-(phosphonoxy)-, disodium salt, (11β,16α)-.
Each gram contains: Active: Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate equivalent to Dexamethasone Phosphate 0.5 mg (0.05%) Inactive: Mineral Oil.
White Petrolatum. DM-00
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Dexamethasone sodium phosphate suppresses the inflammatory response to a variety of agents and it probably delays or slows healing. No generally accepted explanation of these steroid properties has been advanced.
INDCIATIONS AND USAGE
Steroid responsive inflammatory conditions of the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva, cornea, and anterior segment of the globe. These include allergic conjunctivitis, acne rosacea, superficial punctate keratits, herpes zoster keratitis, iritis, cyclitis, selected infective conjunctivities when the inherent hazard of steroid use is accepted to obtain an advisable diminution in edema and inflammation; corneal injury from chemical or thermal burns, or penetration of foreign bodies.
CONTRAININDICATIONS
Contraindicated in epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis); fungal diseases of ocular structures; acute infectious stages of vaccinia, varicella and many other viral disease of the cornea and conjunctiva; mycobacterial infection of the eye and in those persons who have shown hypersensitivity to any component of this preparation.
WARNINGS
Prolonged use may result in ocular hypertension and/or glaucoma, with damage to the optic nerve, defects in visual acuity and fields of vision, and posterior subcapsular cataract formation. Prolonged use may suppress the host response an thus increase the hazard of secondary ocular infections. In those diseases causing thinning of the cornea or sclera, perforations have been known to occur with the use of topical corticosteroids. In acute purulent conditions of the eye, corticosteroids may mask infection or enhance existing infection. If these products are used for 10 days or longer, intraocular pressure should be routinely monitored even though it may be difficult in children and uncooperative patients. Employment of corticosteroid medication in the treatment of herpes simplex other than epithelial herpes simplex keratitis, in which it is contraindicated, requires great caution; periodic slit-lamp microscopy is essential.
PRECAUTIONS
General
The possibility of persistent fungal infections of the cornea should be considered after prolonged corticosteroid dosing.
Information for Patients
Do not touch tube tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the contents.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential or the effect on fertility of MAXIDEX® Ointment.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. Dexamethasone has been shown to be teratogenic in mice and rabbits following topical ophthalmic application in multiples of the therapeutic dose.
In the mouse, corticosteroids produce fetal resorptions and a specific abnormality, cleft palate. In the rabbit, corticosteroids have produced fetal resorptions and multiple abnormalities involving the head, ears, limbs, palate, etc.
There are no adequate or well-controlled studies in pregnant women. MAXIDEX Ointment should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the mother justifies the potential risk to the embryo or fetus. Infants born of mothers who have received substantial doses of corticosteroids during pregnancy should be observed carefully for signs of hypoadrenalism.
Nursing Mothers
Topically applied steroids are absorbed systemically. Therefore, because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from dexamethasone sodium phosphate, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in children have not been established.
MAXIDEX ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions have been reported: glaucoma with optic nerve damage, visual acuity and field defects, posterior subcapsular cataract formation, secondary ocular infections from pathogens including herpes simplex, and perforation of the globe. Rarely, filtering blebs have been reported when topical steroids have been used following cataract surgery. Rarely, stinging or burning may occur.
DOSAGE AND ADMINSTRATION
The duration of treatment will vary with the type of lesion and may extend from a few days to several weeks, according to therapeutic response. Relapses, more common in chronic active lesions than in self-limited conditions, usually respond to treatment. Apply a one-half to one inch ribbon of ointment into the conjunctival sac(s) up to four times daily. When a favorable response is observed, dosage may be reduced gradually to once a day application for several days. MAXIDEX Ointment may be used in conjunction with MAXIDEX suspension.
HOW TO APPLY MAXIDEX OINTMENT
- Tilt your head back.
- Place a finger on your cheek just under your eye and gently pull down until a “V” pocket is formed between your eyeball and your lower lid.
- Place a small amount (about ½ inch) of MAXIDEX in the “V” pocket. Do not let the tip of the tube touch your eye.
- Look downward before closing your eye.
HOW SUPPLIED
In 3.5g ophthalmic tubes.
NDC 0065-0616-35
STORAGE
Store at 8° - 27°C (46° to 80°F).
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law prohibits dispensing without prescription.
ALCON®
Ophthalmic
Alcon Laboratories, Inc.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134
Maxidexdexamethasone sodium phosphate OINTMENT
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||