Maxidex
Maxidex® 0.1%(dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension)Sterile
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- MAXIDEX DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- MAXIDEX INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- MAXIDEX CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- MAXIDEX ADVERSE REACTIONS
- MAXIDEX DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
MAXIDEX DESCRIPTION
MAXIDEX® 0.1% (dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension) is an adrenocortical steroid prepared as a sterile topical ophthalmic suspension. The active ingredient is represented by the chemical structure:
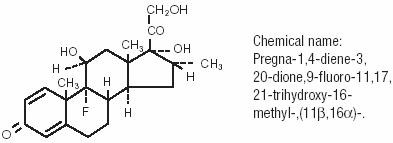
Each mL contains
Active: dexamethasone 0.1%. Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%. Vehicle: hypromellose 0.5%. Inactives: sodium chloride, dibasic sodium phosphate, polysorbate 80, edetate disodium, citric acid and/or sodium hydroxide (to adjust pH), purified water.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Dexamethasone suppresses the inflammatory response to a variety of agents and it probably delays or slows healing.
MAXIDEX INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Steroid responsive inflammatory conditions of the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva, cornea, and anterior segment of the globe such as allergic conjunctivitis, acne rosacea, superficial punctuate keratitis, herpes zoster keratitis, iritis, cyclitis, selected infective conjunctivitides when the inherent hazard of steroid use is accepted to obtain an advisable diminution in edema and inflammation; corneal injury from chemical, radiation, or thermal burns, or penetration of foreign bodies.
MAXIDEX CONTRAINDICATIONS
Contraindicated in epithelial herpes simplex (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, varicella, and most other viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva; tuberculosis of the eye; fungal disease of ocular structures; and in those persons who have shown hypersensitivity to any component of this preparation.
WARNINGS
Prolonged use may result in ocular hypertension and/or glaucoma, with damage to the optic nerve, defects in visual acuity and fields of vision, and posterior subcapsular cataract formation. Prolonged use may suppress the host response and thus increase the hazard of secondary ocular infections. In those diseases causing thinning of the cornea or sclera, perforations have been known to occur with the use of topical corticosteroids. In acute purulent conditions of the eye, corticosteroids may mask infection or enhance existing infection. If these products are used for 10 days or longer, intraocular pressure should be routinely monitored even though it may be difficult in children and uncooperative patients.
Employment of corticosteroid medication in the treatment of herpes simplex other than epithelial herpes simplex keratitis, in which it is contraindicated, requires great caution; periodic slit-lamp microscopy is essential.
PRECAUTIONS
General
FOR TOPICAL OPHTHALMIC USE ONLY. The possibility of persistent fungal infections of the cornea should be considered after prolonged corticosteroid dosing.
Information for Patients
Do not touch dropper tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the contents. The preservative in MAXIDEX® (dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension), benzalkonium chloride, may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. MAXIDEX® (dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension) should not be administered while wearing soft contact lenses.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential or the effect on fertility of MAXIDEX® dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Dexamethasone has been shown to be teratogenic in mice and rabbits following topical ophthalmic application in multiples of the therapeutic dose.
In the mouse, corticosteroids produce fetal resorptions and a specific abnormality, cleft palate. In the rabbit, corticosteroids have produced fetal resorptions and multiple abnormalities involving the head, ears, limbs, palate, etc.
There are no adequate or well-controlled studies in pregnant women. MAXIDEX® (dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension) should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the mother justifies the potential risk to the embryo or fetus. Infants born of mothers who have received substantial doses of corticosteroids during pregnancy should be observed carefully for signs of hypoadrenalism.
Nursing Mothers
Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. It is not known whether topical administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when MAXIDEX® (dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension) is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients.
MAXIDEX ADVERSE REACTIONS
Glaucoma with optic nerve damage, visual acuity and field defects; cataract formation; secondary ocular infection following suppression of host response; and perforation of the globe may occur.
MAXIDEX DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING. One or two drops topically in the conjunctival sac(s). In severe disease, drops may be used hourly, being tapered to discontinuation as the inflammation subsides. In mild disease, drops may be used up to four to six times daily.
HOW SUPPLIED
MAXIDEX® (dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension) in plastic DROP-TAINER® dispensers:
5 mL NDC 0998-0615-05
15 mL NDC 0998-0615-15
STORAGE
Store upright at 8°-27°C (46°-80°F).
Rx Only
© 2003 Alcon, Inc.

ALCON LABORATORIES, INC.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134 USA
Printed in USA
340907-0803
Maxidexdexamethasone SUSPENSION/ DROPS
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||